Wonder fungi
2021-02-01
Michelle O'Malley(link is external) has long been inspired by gut microbes. Since she began studying the herbivore digestive tract, the UC Santa Barbara chemical engineering professor has guided several students to their doctoral degrees, won early and mid-career awards (including a recognition from President Obama), attained tenure and advanced to the position of full professor. She even had three children along the way. A constant through it all: goat poop.
"This has been the longest single effort in my lab," said O'Malley, who with her research team way back in 2015 first embarked on an ambitious project to characterize gut microbes in large herbivores. The purpose? To understand how these animals manage, via their microbiomes, ...
Paving the way for effective field theories
2021-02-01
Over the past century, a wide variety of models have emerged to explain the complex behaviours which unfold within atomic nuclei at low energies. However, these theories bring up deep philosophical questions regarding their scientific value. Indeed, traditional epistemological tools have been rather elaborated to account for a unified and stabilised theory rather than to apprehend a plurality of models. Ideally, a theory is meant to be reductionist, unifying and fundamentalist. In view of the intrinsic limited precision of their prediction and of the difficulty in assessing a priori their range of applicability, as well as of their specific and disconnected character, traditional ...
Discovery could lead to self-propelled robots
2021-02-01
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- Army-funded researchers discovered how to make materials capable of self-propulsion, allowing materials to move without motors or hands.
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst discovered how to make materials that snap and reset themselves, only relying upon energy flow from their environment. This research, published in Nature Materials and funded by the U.S. Army, could enable future military robots to move from their own energy.
"This work is part of a larger multi-disciplinary effort that seeks to understand biological and engineered impulsive systems that will lay the foundations for scalable methods for generating forces for mechanical action and energy storing structures and materials," said Dr. Ralph ...
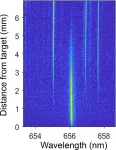
Optimized LIBS technique improves analysis of nuclear reactor materials
2021-02-01
WASHINGTON -- In a new study, investigators report an optimized approach to using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for analyzing hydrogen isotopes. Their new findings could enable improved rapid identification and measurement of hydrogen and other light isotopes that are important in nuclear reactor materials and other applications.
LIBS is promising for measuring hydrogen isotopes because it requires no sample preparation and data can be rapidly acquired with a relatively simple experimental setup. However, quantifying the concentration of hydrogen ...
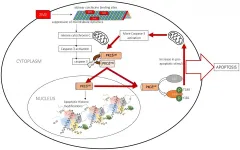
Oncotarget: The pro-apoptotic actions of 2-methoxyestradiol against ovarian cancer
2021-02-01
Oncotarget published "The pro-apoptotic actions of 2-methoxyestradiol against ovarian cancer involve catalytic activation of PKCδ signaling" which reported that the authors have previously shown that a flaxseed-supplemented diet decreases both the incidence and severity of ovarian cancer in laying hens, also induces CYP1A1 expression in liver.
Recently, they have shown that as a biologically derived active component of flax diet, 2MeOE2 induces apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells which is partially dependent on p38 MAPK.
The objective of this Oncotarget study was to elucidate the molecular mechanism of actions of 2MeOE2, a known microtubule disrupting agent, in inducing apoptosis in ovarian tumors.
The objective of this ...
A full-scale prototype for muon tomography
2021-02-01
Each year, billions of tons of goods are transported globally using cargo containers. Currently, there are concerns that this immense volume of traffic could be exploited to transport illicit nuclear materials, with little chance of detection. One promising approach to combating this issue is to measure how goods interact with charged particles named muons - which form naturally as cosmic rays interact with Earth's atmosphere. Studies worldwide have now explored how this technique, named 'muon tomography,' can be achieved through a variety of detection technologies and reconstruction algorithms. In this article of EPJ Plus, a team headed by Francesco Riggi at the University of Catania, Italy, build on these results to develop a full-scale muon tomograph ...
Holonyak lab team creates fast, cheap, accessible COVID-19 antibody test
2021-02-01
As the numbers of those infected with COVID-19 has continued to climb, the desperate need for a vaccine was apparent. Even now with the invention and administration of several COVID-19 vaccinations, the question remains: How effective are these vaccines? HMNTL students Congnyu Che, Weijing Wang, and Nantao Li, also members of the ECE Nanosensors Group, along with Postdoctoral Researcher Bin Zhao and Professor Brian Cunningham have recently been published in Talanta journal for the development of a cost efficient COVID-19 antibody test.
"Compared with other detection methods, our method is a simple, 15-minute sample-to-answer test," says Zhao, a postdoctoral research associate and IGB Fellow. "It costs less ...
Troubles paying rent or being forced to move linked to lower levels of sleep
2021-02-01
People who are unable to make their rent or mortgage payments sleep less than than their peers who don't have such problems, and those who are forced to move because of financial problems sleep even less, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
The study, which followed 1,046 people receiving welfare in California over several years, is the first to analyze the relationship between housing insecurity and sleep outcomes after controlling for sleep duration and sleep quality measured prior to experiences with housing insecurity.
The study found that people who were unable to make a rent or mortgage payment slept on average 22 fewer minutes a night than their peers who were able to make their rent or mortgage payments.
People who were ...
Synthetic biology reinvents development
2021-02-01
Richard Feynman, one of the most respected physicists of the twentieth century, said "What I cannot create, I do not understand". Not surprisingly, many physicists and mathematicians have observed fundamental biological processes with the aim of precisely identifying the minimum ingredients that could generate them. One such example are the patterns of nature observed by Alan Turing. The brilliant English mathematician demonstrated in 1952 that it was possible to explain how a completely homogeneous tissue could be used to create a complex embryo, and he did so using one of the simplest, most elegant mathematical models ever written. One of the results of such models is that the symmetry shown by a cell or a tissue can "break" under a set of conditions. However, ...
Searching for dark matter through the fifth dimension
2021-02-01
Theoretical physicists of the PRISMA+ Cluster of Excellence at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz are working on a theory that goes beyond the Standard Model of particle physics and can answer questions where the Standard Model has to pass - for example, with respect to the hierarchies of the masses of elementary particles or the existence of dark matter. The central element of the theory is an extra dimension in spacetime. Until now, scientists have faced the problem that the predictions of their theory could not be tested experimentally. They have now overcome this problem in a publication in the current issue of the European Physical Journal C.
Already in the 1920s, in an attempt to unify the forces of gravity and electromagnetism, Theodor Kaluza and Oskar Klein speculated ...
Stem cell study illuminates the cause of a devastating inherited heart disorder
2021-02-01
PHILADELPHIA--Scientists in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have uncovered the molecular causes of a congenital form of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), an often-fatal heart disorder.
This inherited form of DCM -- which affects at least several thousand people in the United States at any one time and often causes sudden death or progressive heart failure -- is one of multiple congenital disorders known to be caused by inherited mutations in a gene called LMNA. The LMNA gene is active in most cell types, and researchers have ...
Public attitudes about COVID-19 in response to President Trump's social media posts
2021-02-01
What The Study Did: Researchers used near real-time social media data to capture the public's changing COVID-19-related attitudes when former President Trump was infected.
Authors: Sean D. Young, Ph.D., of the University of California, Irvine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0101)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
Stimulant-associated deaths in US
2021-02-01
What The Study Did: Researchers looked at changes in the rate of deaths associated with the use of illicit (such as cocaine) and medical stimulants in the United States from 2010 to 2017.
Authors: Joshua C. Black, Ph.D., of Rocky Mountain Poison & Drug Safety in Denver, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.7850)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
Concussions, repetitive head impacts among college football players
2021-02-01
What The Study Did: This report summarizes frequency and patterns of concussions and repetitive head impacts over the course of several seasons among college football players who wore sensors in their helmets.
Authors: Michael McCrea, Ph.D., of the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.5193)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
Human activity forces animals to move 70% further to survive
2021-02-01
For the first time, scientists have calculated the global impact of human activity on animal movement, revealing widespread impacts that threaten species survival and biodiversity.
While it has been shown that activities such as logging and urbanisation can have big impacts on wildlife, the study by scientists at the University of Sydney and Deakin University in Australia shows that episodic events such as hunting, military activity and recreation can trigger even bigger changes in animal behaviour.
"It is vital we understand the scale of impact that humans have on other animal species," said lead author Dr Tim Doherty, a wildlife ecologist at the University of Sydney. "The consequences of changed animal movement can be profound and lead to reduced ...
Physicists create tunable superconductivity in twisted graphene 'nanosandwich'
2021-02-01
When two sheets of graphene are stacked atop each other at just the right angle, the layered structure morphs into an unconventional superconductor, allowing electric currents to pass through without resistance or wasted energy.
This "magic-angle" transformation in bilayer graphene was observed for the first time in 2018 in the group of Pablo Jarillo-Herrero, the Cecil and Ida Green Professor of Physics at MIT. Since then, scientists have searched for other materials that can be similarly twisted into superconductivity, in the emerging field of "twistronics." For the most part, no other twisted material has exhibited superconductivity other than the original twisted bilayer ...
The first steps toward a quantum brain
2021-02-01
An intelligent material that learns by physically changing itself, similar to how the human brain works, could be the foundation of a completely new generation of computers. Radboud physicists working toward this so-called "quantum brain" have made an important step. They have demonstrated that they can pattern and interconnect a network of single atoms, and mimic the autonomous behaviour of neurons and synapses in a brain. They report their discovery in Nature Nanotechnology on 1 February.
Considering the growing global demand for computing capacity, more and more data centres are necessary, all of which leave an ever-expanding energy footprint. 'It is clear that ...
Astronomers detect extended dark matter halo around ancient dwarf galaxy
2021-02-01
The Milky Way is surrounded by dozens of dwarf galaxies that are thought to be relics of the very first galaxies in the universe. Among the most primitive of these galactic fossils is Tucana II -- an ultrafaint dwarf galaxy that is about 50 kiloparsecs, or 163,000 light years, from Earth.
Now MIT astrophysicists have detected stars at the edge of Tucana II, in a configuration that is surprisingly far from its center but nevertheless caught up in the tiny galaxy's gravitational pull. This is the first evidence that Tucana II hosts an extended dark matter halo ...
New realm of personalized medicine with brain stimulation
2021-02-01
Millions of patients suffering from neurological and mental disorders such as depression, addiction, and chronic pain are treatment-resistant. In fact, about 30% of all major depression patients do not respond at all to any medication or psychotherapy. Simply put, many traditional forms of treatment for these disorders may have reached their limit. Where do we go from here?
Research to be published in Nature Biomedical Engineering led by Maryam Shanechi, the Andrew and Erna Viterbi Early Career Chair in electrical and computer engineering at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering, ...
New study strengthens claims Richard III murdered 'the Princes in the Tower
2021-02-01
King Richard III's involvement in one of the most notorious and emotive mysteries in English history may be a step closer to being confirmed following a new study by Professor Tim Thornton of the University of Huddersfield.
Richard has long been held responsible of the murder of his nephews King Edward V and his brother, Richard, duke of York - dubbed 'the Princes in the Tower' - in a dispute about succession to the throne. The pair were held in the Tower of London, but disappeared from public view in 1483 with Richard taking the blame following his death two years later.
It has become of the most enduring unsolved mysteries of all, stoked by references in Shakespeare's play about the ...
Skoltech imaging resources used in international experiment with new photocatalysts
2021-02-01
Skoltech researchers helped their colleagues from Japan, Germany, the United States, and China study the crystal structure and optical properties of a new class of two-dimensional compounds, which can be used as effective visible-light-responsive photocatalysts for energy and chemical conversion. They used the Advanced Imaging Core Facility equipment for imaging and structural analysis. The paper was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
One potential use of photocatalysts, so-called water splitting can help substitute climate-warming fossil fuels with more environmentally friendly hydrogen. For this process to work on ...
A study reveals that the brain distributes sensory information highly efficiently
2021-02-01
It has sometimes been suggested that humans use a tiny fraction of their brains. But, is this statement true? The authors of a study published on 20 January in the journal Nature Communications answer this question using neural records of mice subjected to visual stimuli.
This paper demonstrates, in the visual system of mice, the presence of a type of coordination of neural activity called differential correlations. A study by Rubén Moreno-Bote, a researcher at the Center for Brain and Cognition (CBC) and Serra Hunter research professor with the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies ...
Backreaction observed for first time in water tank black hole simulation
2021-02-01
Scientists have revealed new insights into the behaviour of black holes with research that demonstrates how a phenomenon called backreaction can be simulated.
The team from the University of Nottingham have used their simulation of a black hole, involving a specially designed water tank, for this latest research published in Physical Review Letters. This study is the first to demonstrate that the evolution of black holes resulting from the fields surrounding them can be simulated in a laboratory experiment.
The researchers used a water tank simulator consisting of a draining vortex, like the one that forms when you pull the plug in the bath. This mimics a black hole since a wave which comes too ...
Researchers describe a molecular mechanism involved in the pathology's neurodegeneration
2021-02-01
Protein alteration in the family of lamins causes several diseases, known as laminopathies, such as progeria or precocious ageing. A study in which UB researchers have taken part states that alterations in the levels of one of these proteins, lamin B1, contribute to the degeneration of different brain neuronal populations in Huntington's disease. Caused by a mutation in the huntingtin gen, this pathology features involuntary movements, cognitive deficit and psychiatric disorders, and has no cure yet.
According to the study, published in the journal EMBO Molecular Medicine, these results open new therapeutic pathways for the treatment of this disease, since research shows pharmacological normalization of levels of lamin ...
How governments address COVID-19 misinformation--for better or for worse
2021-02-01
As COVID-19 spread across the world, so did conspiracy theories and false information about the virus. This proliferation of misinformation--labeled an "infodemic" by the World Health Organization (WHO)--makes it difficult to identify trustworthy sources and can threaten public health by undermining confidence in science, governments, and public health recommendations.
The consequences of misinformation can be tragic: hundreds died and thousands were poisoned in Iran after consuming toxic methanol alcohol, falsely believing it could cure COVID-19.
In a new article in the Journal of Public ...
[1] ... [2689]
[2690]
[2691]
[2692]
[2693]
[2694]
[2695]
[2696]
2697
[2698]
[2699]
[2700]
[2701]
[2702]
[2703]
[2704]
[2705]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.