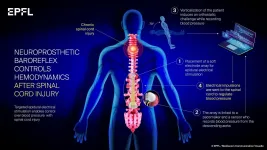
New treatment helps patients with a spinal cord injury
2021-01-28
An international team of scientists headed by Grégoire Courtine at EPFL and CHUV and Aaron Phillips at the University of Calgary has developed a treatment that can dramatically improve the lives of patients with a spinal cord injury.
VIDEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UGXnuHgDWFU
"A serious and underrecognized result of these injuries is unstable blood pressure, which can have devastating consequences that reduce quality of life and are life threatening. Unfortunately, there are no effective therapies for unstable blood pressure after spinal cord injury". said Dr. Aaron Phillips, co-lead author of the study (see affiliations below). ...
Frequent cannabis use by young people linked to decline in IQ
2021-01-28
Thursday, 28 January 2021: A study has found that adolescents who frequently use cannabis may experience a decline in Intelligence Quotient (IQ) over time. The findings of the research provide further insight into the harmful neurological and cognitive effects of frequent cannabis use on young people.
The paper, led by researchers at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is published in Psychological Medicine.
The results revealed that there were declines of approximately 2 IQ points over time in those who use cannabis frequently compared to those who didn't use cannabis. Further analysis suggested that this decline in IQ points was primarily related to reduction in verbal IQ.
The research involved systematic review and statistical analysis on seven longitudinal studies ...
Chinese spice helps unravel the mysteries of human touch
2021-01-28
New insight into how human brains detect and perceive different types of touch, such as fluttery vibrations and steady pressures, has been revealed by UCL scientists with the help of the ancient Chinese cooking ingredient, Szechuan pepper.
Humans have many different types of receptor cells in the skin that allow us to perceive different types of touch. For more than a century, scientists have puzzled over whether touch signals from each type of receptor are processed independently by the brain, or whether these different signals interact before reaching conscious perception.
For the study, published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, UCL researchers took a novel approach to this question by stimulating one type of touch receptor chemically, and another type mechanically. ...
Crowdfunding? Check weather forecast first!
2021-01-28
Investors' moods are affected by gloomy weather. New research from Copenhagen Business School recommends entrepreneurs looking for finance should be aware of the weather forecast at the time they want to launch their crowdfunding campaigns.
The researchers wanted to explore whether weather-induced moods can explain crowdfunders' contributions and focused on the role of investors' moods and emotions including day-to-day decisions on the crowdfunding platform Companisto.
"Financial investment plays a vital role in the success of an entrepreneurial venture ...
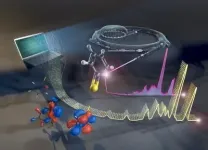
An efficient tool to link X-ray experiments and ab initio theory
2021-01-28
Molecules consisting of many atoms are complex structures. The outer electrons are distributed among the different orbitals, and their shape and occupation determine the chemical behaviour and reactivity of the molecule. The configuration of these orbitals can be analysed experimentally. Synchrotron sources such as BESSY II provide a method for this purpose: Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). However, to obtain information about the orbitals from experimental data, quantum chemical simulations are necessary. Typical computing times for larger molecules take weeks, even on high-performance computers.
Speeding up the evaluation
"Up to now, these calculations have mostly been carried out subsequent to the measurements", explains theoretical chemist Dr. Vinicius Vaz da Cruz, ...
New gene variant linked to stroke
2021-01-28
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden believe they have identified a gene variant that can cause cerebral small vessel disease and stroke. The study is published in Neurology Genetics.
"The patients we have studied are from the same extended family, and several of them have been diagnosed with cerebral small vessel disease and suffered strokes. After tissue examination and using genetic sequencing methods, we found that they were carriers of a new gene variant that could be connected to their diagnoses," says Andreea Ilinca, researcher at Lund University ...
Food export restrictions by a few countries could skyrocket global food crop prices
2021-01-28
Recent events such as the Covid-19 pandemic, locust infestations, drought and labour shortages have disrupted food supply chains, endangering food security in the process. A recent study published in Nature Food shows that trade restrictions and stockpiling of supplies by a few key countries could create global food price spikes and severe local food shortages during times of threat.
'We quantified the potential effects of these co-occurring global and local shocks globally with their impacts on food security,' explains Aalto University Associate Professor Matti Kummu. The results of this research have critical ...
New concept for rocket thruster exploits the mechanism behind solar flares
2021-01-28
A new type of rocket thruster that could take humankind to Mars and beyond has been proposed by a physicist at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL).
The device would apply magnetic fields to cause particles of plasma, electrically charged gas also known as the fourth state of matter, to shoot out the back of a rocket and, because of the conservation of momentum, propel the craft forward. Current space-proven plasma thrusters use electric fields to propel the particles.
The new concept would accelerate the particles using magnetic reconnection, a process found throughout the universe, including the surface of the sun, in which magnetic ...
Machine-learning to predict the performance of organic solar cells
2021-01-28
Knowing how to predict the specific composition and cell design that would result in optimum performance is one of the greatest unresolved problems in materials science. This is, in part, due to the fact that the device performance depends on multiple factors.
Now, researchers from the Institute of Materials Science of Barcelona, specialized on materials for energy applications, have collaborated with researchers from the Universitat Rovira i Virgili specialized in Artificial Intelligence, to combine the experimental data points that they gather with artificial intelligence algorithms ...
Scientists 'farm' natural killer cells in novel cancer fighting approach
2021-01-28
Building on the promise of emerging therapies to deploy the body's "natural killer" immune cells to fight cancer, researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center and U-M College of Engineering have gone one step further.
They've developed what is believed to be the first systematic way to catch natural killer cells and get them to release cancer-killing packets called exosomes. These nano-scale exosomes are thousands of times smaller than natural killer cells -- or NK cells for short -- and thus better able to penetrate cancer cells' defenses.
A proof-of-concept study in blood samples from five patients with non-small cell lung cancer demonstrated that the approach was able to capture natural killer cells on a microfluidic ...
New AI-severity score COVID-19 integrating CT images published to Nature Communications
2021-01-28
Paris, France, January 27th 2021 -- COVID-19 vaccine distribution has begun across the globe, while many countries are still struggling with the rampant rise of infections. Owkin, a French-American startup pioneering AI and Federated Learning in medical research, has been focusing it's COVID-19 research efforts on aspects of the pandemic that still require much public health attention, despite the arrival of an effective vaccine.
Efforts to support frontline health systems as they devote their resources to the influx of COVID-19 related hospitalizations, ...
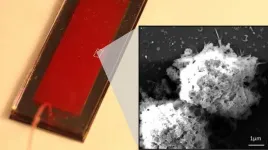
New catalyst moves seawater desalination, hydrogen production closer to commercialization
2021-01-28
Seawater makes up about 96% of all water on earth, making it a tempting resource to meet the world's growing need for clean drinking water and carbon-free energy. And scientists already have the technical ability to both desalinate seawater and split it to produce hydrogen, which is in demand as a source of clean energy.
But existing methods require multiple steps performed at high temperatures over a lengthy period of time in order to produce a catalyst with the needed efficiency. That requires substantial amounts of energy and drives up the cost.
Researchers from the University of Houston have reported an oxygen evolving catalyst that takes just minutes to grow at room temperature on commercially available nickel foam. ...
George Mason University expands testing and tracking behind faculty research
2021-01-28
Mason scientists employ a rapid-result, saliva-based test that significantly expands testing capacity, and an antibody test that can track vaccine response.
George Mason University announces it is introducing a rapid-result, saliva-based COVID-19 test that will greatly expand testing capabilities on its campuses this spring. The effort, led by Mason's faculty, is part of a comprehensive program to better track and control the virus on campus.
Mason scientists, who are pushing the boundaries of technologies that are keeping Mason's campuses safe, are ...
How a cancer drug carrier's structure can help selectively target cancer cells
2021-01-28
The main culprit in cancer is healthy cells that have gone rogue and acquire the ability to divide uncontrollably. These cells acquire growth advantages over normal cells and manipulate their environment by altering the cellular pathways involved in growth and metabolism. Over the past few decades, various altered pathways and proteins have been identified as targets for therapeutic interventions. However, what remains challenging is selectively targeting cancer cells and ensuring that the drug reaches the tumor in adequate amounts, without severely affecting normal cells. And in this regard, biocompatible delivery vehicles (which are non-toxic to normal cells) can be useful.
One such potential candidate is "porphyrins," a group of organic cyclic compounds that form the ...
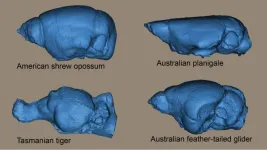
Squeeze it like toothpaste: The flexible brain of marsupial mammals
2021-01-28
Being stretchy and squeezable may be the key to finding space for the brain in mammals, including humans.
An international study, co-led by Flinders University's Vera Weisbecker, has revealed that marsupial mammals like possums, kangaroos, and wombats appear to have a lot of flexibility when it comes to accommodating their brains into their skulls.
"The brain is one of the heaviest parts of the head, particularly in smaller mammals. But it needs to be placed in a way that doesn't interfere with the many vital functions of the head, such as seeing, hearing, smelling and of course feeding," says Dr. Weisbecker.
"Stowing" a large brain ...
Improvements to holographic displays poised to enhance virtual and augmented reality
2021-01-28
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a new approach that improves the image quality and contrast for holographic displays. The new technology could help improve near-eye displays used for virtual and augmented reality applications.
"Augmented and virtual reality systems are poised to have a transformative impact on our society by providing a seamless interface between a user and the digital world," said research team member Jonghyun Kim from technology company NVIDIA and Stanford University. "Holographic displays could overcome some of the biggest ...
Press briefing highlights disparities among key groups
2021-01-28
(Singapore--January 28, 2021 11:00 p.m. SPT/10:00 a.m. EST)----Several leading international lung cancer researchers at a press briefing held by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer today, presented compelling new data revealing that factors of race, gender, sexual orientation and income continue to be significant barriers to those living with lung cancer. The press briefing is part of the IASLC's World Conference on Lung Cancer 2020 Singapore.
The press briefing is moderated by IASLC Communications Committee Chair Dr. Anne-Marie Baird, senior research fellow at Trinity College in ...
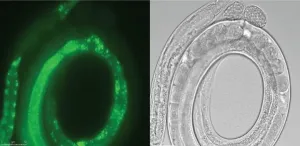
Rules of resistance against transgene silencing
2021-01-28
Clear rules for engineering transgenes that can be inserted and propagated over multiple generations of nematodes include ways to protect inserted genes from the organism's natural defenses against foreign DNA. Developed by KAUST researchers, the rules have implications for many research fields, including gene therapy development.
Scientists often study biological processes, such as normal and mutant gene functions, in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans because it has many genes and molecular pathways in common with humans. Specific gene functions can be investigated by injecting DNA into the worm's reproductive organs, where it links into what is known as an extra-chromosomal array. This array is eventually incorporated into the nucleus, where it is duplicated ...
Brain 3D genome study uncovers human-specific regulatory changes during development
2021-01-28
A team led by Prof. SU Bing from the Kunming Institute of Zoology (KIZ) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Prof. LI Cheng from Peking University, and Prof. ZHANG Shihua from the Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science of CAS has reported the highest resolution by far of the 3D genome of the primate brain, and demonstrated the molecular regulatory mechanisms of human brain evolution through cross-species multi-omics analysis and experimental validation. The study was published in Cell.
The unique pattern of human brain development stems from accumulated genetic changes during human evolution. Among the huge number of diverging genetic changes, only a small portion of the between-species ...
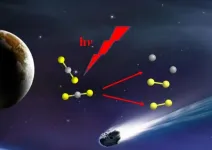
Dalian coherent light source reveals the origin of interstellar medium S2 fragments
2021-01-28
Studying the creation and evolution of sulfur-containing compounds in outer space is essential for understanding interstellar chemistry. CS2 is believed to be the most important molecule in comet nuclei, interstellar dust, or ice cores. CS and S2 are the photodissociation fragments of CS2.
Forty years ago, the emission spectra of only CS and S2 species, and not those of CS2 species, were observed from several comets by the International Ultraviolet Explorer satellite. The photodissociation mechanism of CS2 molecules remains unclear, and S2 fragments have not been experimentally observed before.
Recently, a team led by Prof. YUAN Kaijun from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in cooperation with Prof. WANG Xing'an's group ...
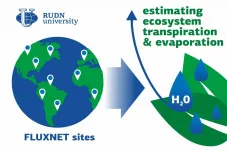
Ecologists conducted a novel study on vegetation transpiration from a global network of 251 sites
2021-01-28
An ecologist from RUDN University together with colleagues from 14 countries compared three methods for estimating ecosystem transpiration in a study. In the first ever research with such a comprehensive data-set, the team used land-atmosphere water vapor flux data of collected at 251 locations all over the planet, from Australia to Greenland. The outcome of the research help to understand the role of plants in the global water and carbon cycles in the current predicament of global warming. The results of the study were published in the December 2020 issue of the journal Global ...
Three mental health conditions contribute to violent offenses, WCU study finds
2021-01-28
Western Carolina University researchers find a disproportionate number of inmates with violent offenses suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder, panic disorder and alcohol use disorder, and published their findings in the Journal of Criminal Psychology.
Alexa Barrett, clinical psychology master's student at WCU, and Al Kopak, associate professor of criminology and criminal justice at WCU, discovered the combination of PTSD, PD and AUD significantly increased the likelihood of violent offenses while conducting research at three county detention centers in North Carolina.
Supported by a Summer Research Assistantship provided by the Graduate School, the purpose of this study was to detail ...
Micro-brewing goes more micro
2021-01-28
A PhD student and 'beer scientist' has inadvertently discovered a way to conduct extremely small-scale brewing experiments, potentially leading to better beer.
It came about when University of Queensland PhD candidate Edward Kerr hit a hurdle when he completed a beer brewing experiment for a paper.
"I was looking at barley protein changes during the mashing stage of beer brewing, when one of the paper's reviewers asked if the changes were caused by temperature or time spent mashing the barley," Mr Kerr said.
"It was a good question, but to find out I'd need to brew all over again, with an instrument that would hold at least 23 litres ...
Majority skeptical healthcare costs will fall anytime soon as Biden begins presidency
2021-01-28
WASHINGTON, D.C. and SAN DIEGO, CA -- In his inaugural address, President Joe Biden vowed that "help is on the way" to a nation grappling with a pandemic that has already claimed over 420,000 lives and counting. However, despite the promise of a better future, a new survey from West Health and Gallup finds Americans remain largely skeptical that issues as varied as managing the COVID-19 crisis, lowering healthcare costs, improving the economy, fixing immigration and addressing climate change, will improve anytime soon.
The findings from the monthly West Health-Gallup U.S. Healthcare Study are based on a ...
Blood discoveries advance efforts to grow organs, battle cancer
2021-01-28
Pioneering research into how our bodies manufacture the cells that make blood has moved us closer to regrowing tissues and organs. The findings also may let doctors grow the cells for transplantation into people to battle cancer, blood disorders and autoimmune diseases.
Researcher Karen K. Hirschi, PhD, of the Department of Cell Biology and the Robert M. Berne Cardiovascular Research Center at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, has developed a simple and efficient way to generate "hemogenic endothelial cells." These cells are the first step in the production line of blood cells, and Hirschi's new findings provide a blueprint for creating them outside the body.
"By studying how hemogenic endothelial cells develop normally, we gain insights needed ...
[1] ... [2685]
[2686]
[2687]
[2688]
[2689]
[2690]
[2691]
[2692]
2693
[2694]
[2695]
[2696]
[2697]
[2698]
[2699]
[2700]
[2701]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.