Nasal spray that protects against COVID-19 is also effective against the common cold
2021-02-02
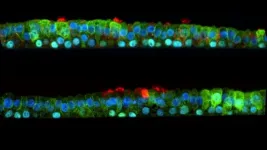
Research into a new drug which primes the immune system in the respiratory tract and is in development for COVID-19 shows it is also effective against rhinovirus. Rhinovirus is the most common respiratory virus, the main cause of the common cold and is responsible for exacerbations of chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In a study recently published in the European Respiratory Journal (LINK), the drug, known as INNA-X, is shown to be effective in a pre-clinical infection model and in human airway cells.
Treatment with INNA-X prior to infection with rhinovirus significantly reduced viral load and inhibited harmful inflammation.
University of Newcastle and Hunter Medical Research Institute (HMRI) researcher Associate Professor ...
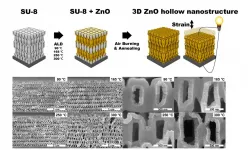
Highly deformable piezoelectric nanotruss for tactile electronics
2021-02-02
With the importance of non-contact environments growing due to COVID-19, tactile electronic devices using haptic technology are gaining traction as new mediums of communication.
Haptic technology is being applied in a wide array of fields such as robotics or interactive displays. haptic gloves are being used for augmented information communication technology. Efficient piezoelectric materials that can convert various mechanical stimuli into electrical signals and vice versa are a prerequisite for advancing high-performing haptic technology.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong confirmed the potential of tactile devices by developing ceramic piezoelectric materials that are three times more deformable. For the fabrication of highly deformable nanomaterials, the ...
Youth with autism see sharp decline in physical activity between ages 9-13
2021-02-02
A recent study from Oregon State University has found that to best help kids with autism maintain healthy rates of physical activity, interventions should be targeted during the ages of 9 to 13, as that's when kids show the biggest drop in active time.
The study is one of the first to look at this issue on a longitudinal scale. It relied on a dataset of families in Ireland spanning three in-depth interviews between 2007 and 2016. Kids in the survey had their first interview at age 9, the second at 13 and the third at 17 or 18.
The OSU study compared 88 children with autism to 88 children without autism over the nine-year survey period to gauge both how physical activity changed over time, and how much ...
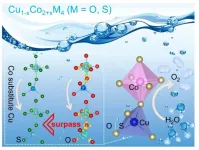
Non-metallic electronic regulation in CuCo oxy-/thio-spinel as OER electrocatalysts
2021-02-02
Oxygen evolution reaction (OER), as a vital half-reaction in some clean energy storage and conversion technologies including rechargeable metal-air batteries, regenerative fuel cells and electrochemical water splitting, has been of crucial importance for exploring highly efficient sustainable energy to substitute exhaustible fossil fuels. Among them, electrochemical water splitting can effectively produce clean and reproducible hydrogen fuels through renewable energy sources as power input like solar energy, etc. Unfortunately, the efficiency of water splitting is mainly impeded by the high anodic overpotential of OER, in which seeking efficient and stable electrocatalysts is highly desirable. It has been considered that spinel-structure materials can be meaningful alternative catalysts ...
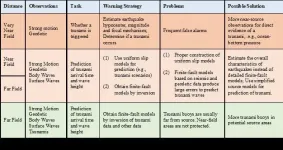
Tsunamis and tsunami warning: recent progress and future prospects
2021-02-02
Tsunamis are one of the most destructive disasters in the ocean. Large tsunamis are mostly generated by earthquakes, and they can propagate across the ocean without significantly losing energy. During the shoaling process in coastal areas, the wave amplitude increases dramatically, causing severe life loss and property damage. There have been frequent tsunamis since the 21st century, drawing the attention of many countries on the study of tsunami mechanism and warning. Tsunami records also play an essential role in deriving earthquake rupture models in subduction zones.
A recent paper entitled "Tsunamis and tsunami warning: recent progress and future prospects" by Dr. Chao An from Shanghai Jiao Tong University reviews the recent research progress of earthquake-generated ...
Study finds recommended ICU sedatives equally safe, effective
2021-02-02
Sedative medications used in intensive care are associated with increased delirium, which is in turn connected with higher medical costs and greater risk of death and ICU-related dementia.
A study published today in the New England Journal of Medicine provides the most definitive evidence to date that, of the two drugs recommended for light sedation of patients receiving mechanical ventilation in the ICU, one is as effective and safe as the other.
Mechanical ventilation is a life-saving intervention often involving a breathing tube inserted in the patient's windpipe, typically entailing light sedation to quell the attendant discomfort, anxiety and psychological stress. Several studies have sought evidence of which ...
New evidence sheds light on treatment for patients with respiratory failure from COVID-19
2021-02-02
Boston, Mass. - COVID-19 has caused more than 2 million deaths worldwide since the World Health Organization declared it a pandemic in March 2020. Patients with severe COVID-19 frequently experience respiratory distress and require assistance breathing. For patients whose lungs are so injured that even a ventilator is unable to deliver enough oxygen, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) -- which does the work of the lungs by removing carbon dioxide and adding oxygen to blood outside the body -- may improve the odds of survival for certain patients with severe COVID-19.
A study by physician-researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) provides new evidence that critically ill patients with ...
Harvard researchers use machine learning models to study health impacts of walnuts
2021-02-02
FOLSOM, Calif., February 2, 2021 - Researchers, from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in collaboration with investigators from Rovira i Virgili University and the University of Navarra, Spain, used machine learning models, a subset of artificial intelligence, to identify more precisely the components in walnuts that may be responsible for potentially reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases - two of the leading causes of death in the U.S.
This study, supported by the California Walnut Commission and published in the Journal of Nutrition, used a novel machine learning model to identify 19 metabolites that were associated with walnut consumption. The body forms specific metabolites based on what food is consumed. The walnut ...
Study aims to break the chains of incarceration in African American males
2021-02-02
Over the last three decades, the United States prison population has exploded from 300,000 to more than 2 million. More than 1.1 million are African American men - the vast number of whom have returned within one to three years of their release. In fact, according to the World Prison Brief, America boasts the highest recidivism rate at more than 50 percent.
Although African American men are more likely to participate in re-entry programs, they continue to struggle with recidivism and reunification at higher rates. The common conception of assisting individuals impacted by incarceration is to provide practical needs such as housing, food and employment. Often, these services are insufficient when the core of their issues is related to psychological factors. ...
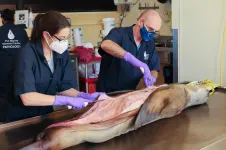
Significant cancer rates in California sea lions has major human health implications
2021-02-02
Scientists at The Marine Mammal Center - the world's largest marine mammal hospital - have found that viral-caused cancer in adult California sea lions is significantly increased by their exposure to toxins in the environment. The study is the result of over 20 years of research and examination of nearly 400 California sea lion patients by The Marine Mammal Center.
The Marine Mammal Center has been on the forefront of researching and understanding cancer in California sea lions and its connection to both ocean and human health. Since the cancer in sea lions was first discovered in 1979, between 18-23 percent of adult sea lions admitted to the Center's hospital have died of the fatal disease - the ...
Big name corporations more likely to commit fraud
2021-02-02
PULLMAN, Wash. - Fortune 500 firms with strong growth profiles are more susceptible to "cooking the books" than smaller, struggling companies, according to a recent study published in Justice Quarterly.
Researchers from Washington State University, Pennsylvania State University and Miami University examined the characteristics of more than 250 U.S. public corporations that were involved in financial securities fraud identified in Securities and Exchange Commission filings from 2005-2013. They were then compared to a control sample of firms that were not named in SEC fraud filings.
Clear trends emerged in the risk of fraud including corporations that were listed in the Fortune 500, traded on the New York Stock Exchange and had strong growth expectations. ...
Breast cancer-on-a-chip for testing immunotherapy drugs
2021-02-02
(LOS ANGELES) - There are many mechanisms by which the body responds to foreign invaders. One of these involves the T-cells of the immune system, which have a number of different proteins on their surface called "checkpoint proteins." These checkpoint proteins bind to proteins on the surface of other cells and can result in either stimulation or suppression of T-cell activity. Normally, surface proteins on foreign or invading cells will produce a stimulation of T-cell activity against these cells, while T-cell suppression is a built-in mechanism to prevent the immune system from attacking the body's own normal cells.
Tumor cells, ...
Child head injury guidelines created
2021-02-02
Australia's and New Zealand's first set of clinical guidelines for children's head injuries has been created by a network of specialists based at the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI).
The guidelines, developed by the Paediatric Research in Emergency Departments International Collaborative (PREDICT) and published in Emergency Medicine Australasia, will allow emergency department clinicians to best diagnose and treat children's head injuries while reducing unnecessary exposure to radiation from CT scans. They also address head injuries in children with underlying problems, such as a bleeding disorder.
Matthew ...
Bottoms are up at the HIV Research for Prevention Virtual Conference
2021-02-02
PITTSBURGH, 2 February, 2021 - Researchers seeking to develop on-demand and behaviorally congruent HIV prevention options for people who practice anal sex are reporting the results of three early phase clinical trials of rectal microbicides at this week's HIV Research for Prevention (HIV R4P) Virtual Conference. The Phase I studies, led by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded Microbicide Trials Network (MTN), found both of two gel-based products well-tolerated, with higher doses of the active drugs likely required to provide protection from HIV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The results are being presented ...
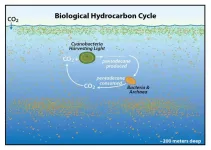
A surprising cycle
2021-02-02
Hydrocarbons and petroleum are almost synonymous in environmental science. After all, oil reserves account for nearly all the hydrocarbons we encounter. But the few hydrocarbons that trace their origin to biological sources may play a larger ecological role than scientists originally suspected.
A team of researchers at UC Santa Barbara and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution investigated this previously neglected area of oceanography for signs of an overlooked global cycle. They also tested how its existence might impact the ocean's response to oil spills.
"We demonstrated that there is a massive and rapid hydrocarbon cycle that occurs in the ocean, and that it is distinct from the ocean's capacity to respond to petroleum input," said Professor David Valentine(link ...
Delaying colonoscopy following abnormal stool test increases risk of colorectal cancer
2021-02-02
A new Veterans Affairs study finds that delays in undergoing colonoscopy following an abnormal stool test increase the risk of a colorectal cancer diagnosis and cancer-related death.
The results appeared online in the journal Gastroenterology in January 2021.
In a retrospective study of more than 200,000 Veterans, the researchers found that patients who received colonoscopy more than 13 months after an abnormal stool blood test were up to 1.3 times more likely to have colorectal cancer, compared with those who had colonoscopy up to three months after the stool test. Odds of an advanced stage of cancer at diagnosis were up to 1.7 times higher when colonoscopy was delayed beyond 16 months.
The findings also ...
The secrets of 3000 galaxies laid bare
2021-02-02
The complex mechanics determining how galaxies spin, grow, cluster and die have been revealed following the release of all the data gathered during a massive seven-year Australian-led astronomy research project.
The scientists observed 13 galaxies at a time, building to a total of 3068, using a custom-built instrument called the Sydney-AAO Multi-Object Integral-Field Spectrograph (SAMI), connected to the 4-metre Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT) at Siding Spring Observatory in New South Wales. The telescope is operated by the Australian National University.
Overseen by the ARC Centre of Excellence for All Sky Astrophysics ...
Gene mutations linked to worse outcomes from leukemia in Hispanic and Latino children
2021-02-02
A combination of genetic mutations may explain the higher incidence of and poorer outcomes from pediatric leukemia in Hispanic and Latino children, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers. They said a novel therapeutic drug combination - as well as testing for these mutations - may help address the disparity.
Hispanic and Latino children are between 1.2 and 1.75 times more likely to develop B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the most common childhood cancer, than non-Hispanic and Latino children. They also have a 40% higher death rate than their counterparts after correcting for socioeconomic factors. Dr. Sinisa Dovat, a researcher and pediatric ...
Survival tip: Start at normal weight and slowly add pounds
2021-02-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio - People who start adulthood with a body mass index (BMI) in the normal range and move later in life to being overweight - but never obese - tend to live the longest, a new study suggests.
Adults in this category lived longer than even those whose BMI stayed in the normal range throughout their life. Those who started adulthood as obese and continued to add weight had the highest mortality rate.
"The impact of weight gain on mortality is complex. It depends on both the timing and the magnitude of weight gain and where BMI started," said Hui Zheng, lead author of the study and associate ...
Biomedical basis of the Barker hypothesis uncovered
2021-02-02
According to the Barker hypothesis (Hales and Barker 1992) (also referred to as "small baby syndrome"), infants with too low body weight have an increased risk of suffering from cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, diabetes and chronic kidney diseases in adulthood. According to this hypothesis, fetal protective mechanisms enable adaptation to unfavorable intrauterine conditions (chronic oxygen or nutrient deficiency) and allow for fetal survival. At the same time, however, they lead to permanent structural and functional strains and changes into adulthood. The comprehensive study recently published in Nature Communications now clarifies central mechanisms of this phenomenon.
Fetuin-A plays a key role
Under the program of the Swiss National ...
Study shows aspirin before a diagnosis may lower colorectal cancer mortality
2021-02-02
ATLANTA - FEBRUARY 2, 2021 - A new study finds that long-term aspirin use before a diagnosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) may be associated with lower CRC-specific mortality. The report that appears in JNCI: The Journal of the National Cancer Institute, suggests that the findings for pre-diagnosis aspirin use might help reduce CRC mortality in the overall population by limiting metastatic spread of colorectal tumors before diagnosis. Preventing distant metastases leads to fewer deaths from colorectal cancer.
The study, led by Peter T. Campbell, PhD, of the American Cancer Society, used data from men and women enrolled in the American Cancer Society's Cancer Prevention Study-II (CPS-II) Nutrition Cohort who were cancer-free ...
Surgery to heal inflamed gut may create new target for disease
2021-02-02
A surgical procedure meant to counter ulcerative colitis, an immune disease affecting the colon, may trigger a second immune system attack, a new study shows.
The study results revolve around the immune system, the cells and proteins that destroy invading bacteria and viruses. Activating it brings about inflammation, responses like swelling and pain that result from cells homing in on the site of infection or injury. Autoimmune diseases like ulcerative colitis occur when this system mistakenly damages the body's own tissues.
Colon tissue damaged by the disease is routinely addressed with a "J-pouch" procedure wherein a pouch is surgically constructed from nearby, healthy ...
Test for early detection of heart problems reduces risk of heart damage from chemotherapy
2021-02-02
Toronto, ON - Results of a multi-centre, international, clinical trial co-led by Peter Munk Cardiac Centre (PMCC) cardiologist Dr. Dinesh Thavendiranathan point to the benefit of using a more sensitive test to detect heart function issues early, so cancer patients don't have to fight heart failure too.
Unfortunately, for 1 in 20 high-risk patients, treating cancer with certain therapies means the added potential of developing heart failure. The one-year results of the highly anticipated trial compared heart function at the end of anthracycline-based chemotherapy, a treatment that can successfully treat cancer but ...
Racial disparities: Young, Black adults had significantly worse heart transplant outcomes
2021-02-02
DALLAS, Feb. 2, 2021 — Young, Black adults are more than twice as likely to die in the first year after a heart transplant when compared to same-age, non-Black heart transplant recipients, according to new research published today in Circulation: Heart Failure, an American Heart Association journal.
Research has consistently shown that Black heart transplant recipients have a higher risk of death following heart transplantation compared to non-Black recipients. Black patients have higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease at younger ages, and therefore, they may need heart transplants at younger ...
Imaging identifies breast cancer patients unlikely to benefit from hormone therapy
2021-02-02
Hormone therapy commonly is given as a targeted treatment for women whose cancer cells carry receptors for estrogen. But the therapy only works for about half of all patients. Until now, there hasn't been a good way to reliably predict who will benefit and who will not.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown they can distinguish patients likely or unlikely to benefit from hormone therapy using an imaging test that measures the function of the estrogen receptors in their cancer cells. In a small phase 2 clinical trial, the researchers showed that the cancers of all patients with working estrogen receptors remained stable or improved on hormone therapy, and progressed in all women with nonfunctional ...
[1] ... [2690]
[2691]
[2692]
[2693]
[2694]
[2695]
[2696]
[2697]
2698
[2699]
[2700]
[2701]
[2702]
[2703]
[2704]
[2705]
[2706]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.