New combination therapy offers chance of healing hepatitis B
2021-02-04
The new therapeutic approach is based on shutting down the viral hepatitis B genome located in the nucleus of infected liver cells. Upon infection of the liver cell, the viral genome is transformed inside the nucleus into a closed circular DNA molecule. This deoxyribonucleic acid is a stable molecule known as covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) and serves as the template for the production of new viruses. The cccDNA represents the central reservoir of the hepatitis B viruses and enables their persistence in the liver. The virologist Prof. Dr. Maura Dandri and her team at the UKE managed to prevent the HBV-cccDNA from producing further viruses in the animal model.
The point of attack of their ...
'Stealthy' stem cells better for treating tendon injuries in horses
2021-02-04
Treating equine donor stem cells with a growth factor called TGF-β2 may allow them to avoid "tripping" the immune response in recipients, according to new research from North Carolina State University. The work could simplify the stem cell treatment process for ligament and tendon injuries in horses, and may also have implications for human stem cell therapies.
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy is a promising avenue for treating musculoskeletal injuries - particularly tendon and ligament injuries - in horses. Mesenchymal stem cells are adult stem cells found in bone marrow that act as repair directors, producing secretions that recruit paracrine, or healing, factors to the site of injury.
Just as blood cells have "types," ...
Stanford research could lead to injectable gels that release medicines over time
2021-02-04
Gels are formed by mixing polymers into fluids to create gooey substances useful for everything from holding hair in place to enabling contact lenses to float over the eye.
Researchers want to develop gels for healthcare applications by mixing in medicinal compounds, and giving patients injections so that the gel releases the active pharmaceutical ingredient over a period of months to avoid weekly or daily needle sticks.
But standing in the way is a problem that's as easily understandable as the difference between using hair gel on a beach versus in a ...
Exercise caution after working out in virtual reality
2021-02-04
Virtual 'exergaming' has become a popular way to exercise - especially among younger people - since the release of virtual reality (VR) fitness games on consoles such as Nintendo and Playstation.
But while VR is undoubtedly raising fitness games to a whole new level, researchers at the University of South Australia are cautioning players about the potential side effects of VR, particularly in the first hour after playing.
In a new study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, UniSA researchers investigated the consequences of playing one of the most popular VR exergames - Beat Saber* - finding that one in seven players still ...
Polymer-derived carbon as metal-free, "green" alternative to catalysts and nano carbons
2021-02-04
Catalysts are key materials in modern society, enabling selective conversion of raw materials into valuable products while reducing waste and saving energy. In case of industrially relevant oxidative dehydrogenation reactions, most known catalyst systems are based on transition metals such as Iron, Vanadium, Molybdenum or Silver. Due to intrinsic drawbacks associated with the use of transition metals, such as rare occurrence, environmentally harmful mining processes, and toxicity, the fact that pure carbon exhibits catalytic activity in this type of reaction and thus has high potential as a sustainable substitution material is of high interest.
To date, the development of carbon-based catalysts for oxidative dehydrogenation reactions may be divided into two ...
Fossil pigments shed new light on vertebrate evolution
2021-02-04
UCC palaeontologists have discovered new evidence that the fate of vertebrate animals over the last 400 million years has been shaped by microscopic melanin pigments.
This new twist in the story of animal evolution is based on cutting-edge analyses of melanin granules - melanosomes - in many different fossil and modern vertebrates, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals. Melanin and melanosomes have traditionally been linked to outermost body tissues such as skin, hair and feathers, with important roles in UV protection and stiffening of tissues. Analyses of where different animals store melanin in the body, however, show that different vertebrate groups concentrate melanin in different organs, revealing ...
Innovation from Vienna: Ultrasound in the treatment of brain diseases
2021-02-04
Ultrasound is not only used as an imaging technique but targeted pulses of ultrasound can be used as a highly accurate treatment for a range of brain diseases, for which there were previously only limited treatment options. Over the last few years, several revolutionary techniques of this kind have been developed, primarily in Toronto but also at MedUni Vienna. The Viennese technique improves brain functions by externally activating neurons that are still functional. Improvements can be expected in various neuropsychiatric brain diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, stroke, Multiple Sclerosis, and neuralgia. A review jointly written by ...
NUI Galway demonstrate the promise of precision genomics in cancer treatment
2021-02-04
Researchers at NUI Galway have identified genomic signatures in women developing the most common type of breast cancer that can be associated with long-term survival. The NUI Galway team analysed the genomes of breast cancer patients to look for associations with survival rates using advanced statistical techniques.
Carried out by Lydia King during her studies in NUI Galway's MSc in Biomedical Genomics programme, the research has been published in the international journal PLOS ONE.
Early detection by national screening programmes and timely treatment for patients diagnosed with "luminal" types of breast cancer have resulted in excellent prognoses with survival rates of over 80% within five years of treatment. The challenge of long-term survival ...
Sweden ahead of Denmark in the public sector organic food race
2021-02-04
FOOD SCIENCE Sweden takes first, Denmark second and Norway lags at the bottom when it comes to how much organic food is served in canteens, kindergartens and other public sector workplaces across the three Nordic nations. This, according to the results of a new report by the University of Copenhagen. The report details plenty of potential for expanding the conversion to organic food service in the Danish public sector--a topic of discussion across the EU at the moment.
Plate with potatoes and beef
The governments of Denmark, Norway and Sweden are all keen on ramping up the amount of organic food ...
Father's early-life exposure to stress associated with child's brain development
2021-02-04
The FinnBrain research of the University of Turku has demonstrated for the first time that the stress the father has experienced in his childhood is connected to the development of the white matter tracts in the child's brain. Whether this connection is transmitted through epigenetic inheritance needs further research.
Evidence from multiple new animal studies demonstrates that the changes in gene function caused by environment can be inherited between generations through gametes. In particular, nutrition and stress have been proven to cause these types of changes. However, these do not alter the nucleic acid sequence of ...
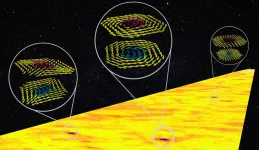
Researchers from NUS create 'whirling' nano-structures in anti-ferromagnets
2021-02-04
Today's digital world generates vast amounts of data every second. Hence, there is a need for memory chips that can store more data in less space, as well as the ability to read and write that data faster while using less energy.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS), working with collaborators from the University of Oxford, Diamond Light Source (the United Kingdom's national synchrotron science facility) and University of Wisconsin Madison, have now developed an ultra-thin material with unique properties that could eventually achieve some of these goals. Their ...
Book developed at Cincinnati Children's helps identify risks of reading difficulties
2021-02-04
A study published in the journal Pediatrics expands validation evidence for a new screening tool that directly engages preschool-age children during clinic visits to assess their early literacy skills. The tool, which is the first of its kind, has the potential to identify reading difficulties as early as possible, target interventions and empower families to help their child at home, according to researchers at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center.
The Reading House (TRH) is an assessment for ages 3-5 based on a specially designed children's book, which was developed by John Hutton, MD, and his team at Cincinnati Children's. Screening takes five minutes and gauges performance levels ...
Engineering immunity
2021-02-04
An inexpensive, long-lasting and easy-to-administer vaccine against malaria could be a game-changer for millions of people living in countries where the mosquito-borne disease is endemic.
Lucie Jelinkova, a graduate student in the laboratory of Bryce Chackerian, PhD, professor in The University of New Mexico Department of Molecular Genetics & Microbiology, has identified a method that could make that dream into reality.
In research recently published in the journal NPJ Vaccines, Jelinkova and colleagues at Johns Hopkins and Flinders University in Australia report ...
Solving a puzzle
2021-02-04
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) afflicts as many as two million people around the world, affecting multiple organs, including lungs, brain, skin and kidneys. In about 80 percent of cases, it causes cysts and benign tumors to form in the kidney, eventually resulting in kidney failure.
It's known that the disease is triggered by genetic mutations, but how these mutations lead to the formation of kidney cysts has been poorly understood - until now.
Nephrologist Manoocher Soleimani, MD, a professor in The University of New Mexico Department of Internal Medicine, led a team that solved the puzzle and pointed the way toward potential ...
Story of COVID's mental health impact - a thread
2021-02-04
Twitter has long provided a short, sharp take on the community's fears, anxieties and experiences. Now, data scientists have analysed 94 million tweets from the first months of the pandemic to track COVID-19's effect on mental health in NSW.
The research team used machine learning to develop a model able to capture data indicating depression, stress, anxiety and suicidal thoughts among users of the social media platform.
The aim was to tap into popular technology to help public health experts identify changes in community levels of depression over time.
The World Health Organisation highlighted early in 2020 that the pandemic would likely have a negative impact on mental health, with the disease affecting many facets of life including work, health and relationships.
Researchers from ...
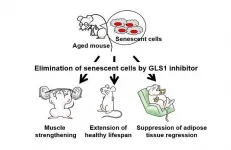
Senolysis by glutaminolysis inhibition ameliorates various age-associated disorders
2021-02-04
Senescent cells accumulate in organs during aging, promote tissue dysfunction, and cause numerous aging-related diseases like cancer. The cells arise through a process called "cellular senescence," a permanent cell cycle arrest resulting from multiple stresses.
A collaborative research group led by Professor Makoto Nakanishi of the Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo (IMSUT), and co-researchers has identified an inhibitor of the glutamate metabolic enzyme GLS1(*1) so that its administration selectively eliminates senescent cells in vivo. They confirmed that the GLS1 inhibitor eliminated senescent cells from various organs and tissues in aged mice, ameliorating age-associated tissue dysfunction and the symptoms of obese diabetes, arteriosclerosis, and ...
New discovery sheds light on human history of symbols
2021-02-04
While scientists and historians have long surmised that etchings on stones and bones have been used as a form of symbolism dating back as early as the Middle Paleolithic period (250,000-45,000 BCE), findings to support that theory are extremely rare.
A recent discovery by archeologists from the Hebrew University and the University of Haifa alongside a team from the Le Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique in France have uncovered evidence of what may be the earliest-known use of symbols. The symbols were found on a bone fragment in the Ramle region in central ...
Researchers explore link between 'Alzheimer's gene' and COVID-19
2021-02-04
A City of Hope-led research team found that the same gene that increases the risk for Alzheimer's disease, ApoE4, can increase the susceptibility to and severity of COVID-19.
"Our study provides a causal link between the Alzheimer's disease risk factor ApoE4 and COVID-19 and explains why some (e.g., ApoE4 carriers) but not all COVID-19 patients exhibit neurological manifestations" said Yanhong Shi, Ph.D., director of the Division of Stem Cell Biology at City of Hope and co-corresponding author of the new study. "Understanding how risk factors for neurodegenerative diseases ...
Liver cancer 'signature' in gut holds clues to cancer risk
2021-02-04
The distinctive gut microbiome profile of a person with liver cancer linked to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) could be the key to predicting someone's risk of developing the cancer, say researchers from the UNSW Microbiome Research Centre (MRC).
Their new study, published in Nature Communications recently, found the gut microbiome - the kingdom of microorganisms living in our digestive tracts - can modulate the immune response in liver cancer patients with NAFLD, in a way that promotes the cancer's survival.
While the research is still in its early stages, this finding could lead to more effective preventative and therapeutic treatments for people at risk of developing NAFLD-related liver ...
Stopping intestinal bacteria in their tracks
2021-02-04
The intestine harbors the largest number of immune cells in our body. Since the intestine is constantly exposed to various antigens like bacteria and food, appropriate induction of gut immune cells plays a pivotal role in gut homeostasis.
A POSTECH research team - led by Professor Seung-Woo Lee, Ph.D. candidate Sookjin Moon and research assistant professor Yunji Park of the Department of Life Sciences - has uncovered for the first the mechanism for regulating the differentiation of T cells (intraepithelial lymphocyte, IEL) via intestinal epithelial cells (IEC). These findings were recently published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine ...
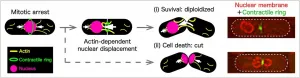
Researchers identify "rescue" mechanism that helps cells survive malfunctioning split
2021-02-04
Cells replicate their genetic material and divide into two identical clones, perpetuating life -- until they don't. Some cells pause -- or are intentionally made to pause -- in the process. When the cell resumes division after such a pause, a displaced nucleus -- an essential part of cell survival -- can become caught in the fissure, splitting violently and killing both cells. But that is not always the case; some mutant cells can recover by pushing their nucleus to safety. Researchers from Hiroshima University in Japan are starting to understand how in the first step toward potential cell death rescue applications.
The results were published on Jan. 22 in iScience, a Cell Press journal.
The researchers examined fission yeast, a common model organism ...
Cancer leading cause of death among people with diabetes
2021-02-04
This is the finding of an 18-year-study of over 300,000 people with diabetes in England, from scientists from Imperial College London and published in the journal The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Thursday Feb 4th is World Cancer Day.
The research, funded by the Wellcome Trust, reveals that between 2001-2018 heart disease and stroke were no longer the leading causes of death among people with diabetes, as they were 18 years ago.
Diabetes affects 4.7 million people in the UK, and is caused by the body being unable to regulate blood sugar levels. Around 90 per cent have type ...
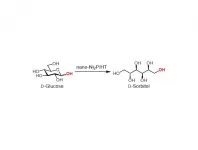
Nickel phosphide nanoparticle catalyst is the full package
2021-02-04
Osaka - Many different catalysts that promote the conversion of glucose to sorbitol have been studied; however, most offer certain properties while requiring compromises on others. Now, researchers from Osaka University have reported a hydrotalcite-supported nickel phosphide nanoparticle catalyst (nano-Ni2P/HT) that ticks all the boxes. Their findings are published in Green Chemistry.
Sorbitol is a versatile molecule that is widely used in the food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals industries. There is therefore a pressing need to produce sorbitol in a sustainable, low-cost, and green manner.
The nickel catalysts that are commonly used in the industrial hydrogenation of glucose to sorbitol are unstable in air and require hash reaction conditions. Rare metal alternatives--despite being ...
Battling bugs help solve mysteries of weapon evolution
2021-02-04
Remember the first rule of fight club? That's right: You don't talk about fight club. Luckily, the rules of Hollywood don't apply to science. In new published research, University of Arizona researchers report what they learned when they started their own "fight club" - an exclusive version where only insects qualify as members, with a mission to shed light on the evolution of weapons in the animal kingdom.
In many animal species, fighting is a common occurrence. Individuals may fight over food, shelter or territory, but especially common are fights between males over access to females for mating. Many of the most striking and unusual features of animals are associated with these mating-related fights, including the horns of beetles and the antlers of deer. What is less clear ...
New biomarker may predict which pancreatic cancer patients respond to CD40 immunotherapy
2021-02-04
PHILADELPHA--Inflammation in the blood could serve as a new biomarker to help identify patients with advanced pancreatic cancer who won't respond to the immune-stimulating drugs known as CD40 agonists, suggests a new study from researchers in the Abramson Cancer Center of the University of Pennsylvania published in JCI Insight
It is known that pancreatic cancer can cause systemic inflammation, which is readily detectable in the blood. The team found that patients with systemic inflammation had worse overall survival rates than patients without inflammation when treated with both a CD40 agonist and the chemotherapy gemcitabine.
The ...
[1] ... [2667]
[2668]
[2669]
[2670]
[2671]
[2672]
[2673]
[2674]
2675
[2676]
[2677]
[2678]
[2679]
[2680]
[2681]
[2682]
[2683]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.