Scientists establish multiple primate models of SARS-CoV-2 airborne infection
2021-02-04
Army scientists evaluated three nonhuman primate species as potential models of SARS-CoV-2 airborne infection, according to results published online this week in PLOS ONE. Their work demonstrates that any of these species may be useful for testing vaccines and therapies in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, which has resulted in over 104 million cases and more than 2 million deaths worldwide in the past year.
Given the global impact of COVID-19, experts are working rapidly to develop medical countermeasures, and testing in animal models is critically important to evaluate the efficacy of these products. Recent studies suggest that aerosol ...
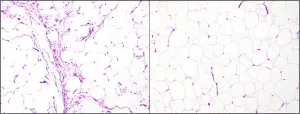
New test provides fast and accurate diagnosis of liposarcomas
2021-02-04
Philadelphia, February 4, 2021 - Researchers have leveraged the latest advances in RNA technology and machine learning methods to develop a gene panel test that allows for highly accurate diagnosis of the most common types of liposarcoma. It quickly and reliably distinguishes benign lipomas from liposarcomas and can be performed in laboratories at a lower cost than current "gold standard" tests. The new assay is described in The Journal of Molecular Diagnosis, published by Elsevier.
"Liposarcomas are a type of malignant cancer that is difficult to diagnose because, even under a microscope, it is hard to differentiate liposarcomas from benign tumors or other types ...
New study examines addiction medicine treatment in Vietnam
2021-02-04
An assessment published this week in the journal The Lancet HIV provides new insight about an initiative to integrate treatment of opioid use disorder along with HIV in Vietnam.
The study marks one of the first scientifically robust assessments of a new model of treating HIV in lower or middle income countries where injection drug use is a major cause of HIV infection. It also suggests the importance of building support for peer and community connections to tackle the opioid epidemic that continues to ravage the United States in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study was led by scientists and physicians at Hanoi Medical University and Oregon Health & Science University.
"Our study suggests that countries that ...
Imaging the first moments of a body plan emerging in the embryo
2021-02-04
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Egg cells start out as round blobs. After fertilization, they begin transforming into people, dogs, fish, or other animals by orienting head to tail, back to belly, and left to right. Exactly what sets these body orientation directions has been guessed at but not seen. Now researchers at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) have imaged the very beginning of this cellular rearrangement, and their findings help answer a fundamental question.
"The most interesting and mysterious part of developmental biology is the origin of the body axis in animals," said researcher Tomomi Tani. An MBL scientist in the Eugene Bell Center at the time of the research, Tani is now with Japan's National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology.
The work by Tani and ...
Mysterious organic scum boosts chemical reaction efficiency, may reduce chemical waste
2021-02-04
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Chemical manufacturers frequently use toxic solvents such as alcohols and benzene to make products like pharmaceuticals and plastics. Researchers are examining a previously overlooked and misunderstood phenomenon in the chemical reactions used to make these products. This discovery brings a new fundamental understanding of catalytic chemistry and a steppingstone to practical applications that could someday make chemical manufacturing less wasteful and more environmentally sound.
The study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researcher David Flaherty, University of Minnesota, Twin Cities researcher Matthew Neurock and Virginia Tech researcher Ayman Karim is published in the journal Science.
Combining ...
An optical coating like no other
2021-02-04
For more than a century, optical coatings have been used to better reflect certain wavelengths of light from lenses and other devices or, conversely, to better transmit certain wavelengths through them. For example, the coatings on tinted eyeglasses reflect, or "block out," harmful blue light and ultraviolet rays.
But until now, no optical coating had ever been developed that could simultaneously reflect and transmit the same wavelength, or color.
In a paper in Nature Nanotechnology, researchers at the University of Rochester and Case Western Reserve University describe a new class of optical coatings, so-called Fano Resonance Optical Coatings (FROCs), that can be used on filters to reflect and transmit colors of remarkable purity.
In addition, ...
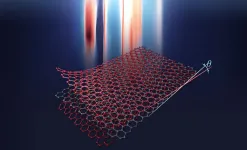
Comb-like etching regulated growth for large-area graphene nanoribbon arrays
2021-02-04
The rapid development of silicon-based transistors leads to its integration getting closer to the limit of Moore's law. Graphene is expected to become the next generation of mainstream chip materials due to its ultra-high carrier mobility. However, it is difficult to obtain a high on/off current ratio for intrinsic graphene-based transistor owing to the absence of bandgap. Graphene nanoribbons, which possess a tunable bandgap and unique optoelectrical properties, have attracted extensive attention and exploration.
Nowadays, the preparation of graphene nanoribbons is underdeveloped, and common strategies include the clip of carbon materials (graphene films, carbon nanotubes, or graphite) ...
Imaging technique provides link to innovative products
2021-02-04
When we think about the links to the future - the global transition to solar and wind energy, tactile virtual reality or synthetic neurons - there's no shortage of big ideas. It's the materials to execute the big ideas - the ability to manufacture the lithium-ion batteries, opto-electronics and hydrogen fuel cells - that stand between concept and reality.
Enter two-dimensional materials, the latest step in innovation. Consisting of a single layer of atoms, two-dimensional materials like graphene and phosphorene exhibit new properties with far-reaching potential. With a capability to be combined like Lego bricks, these materials ...
Using Artificial Intelligence to prevent harm caused by immunotherapy
2021-02-04
CLEVELAND--Researchers at Case Western Reserve University, using artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze simple tissue scans, say they have discovered biomarkers that could tell doctors which lung cancer patients might actually get worse from immunotherapy.
Until recently, researchers and oncologists had placed these lung cancer patients into two broad categories: those who would benefit from immunotherapy, and those who likely would not.
But a third category--patients called hyper-progressors who would actually be harmed by immunotherapy, including a shortened lifespan after treatment--has begun ...
Fecal transplant turns cancer immunotherapy non-responders into responders
2021-02-04
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 4, 2021 - Researchers at UPMC Hillman Cancer Center and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) demonstrate that changing the gut microbiome can transform patients with advanced melanoma who never responded to immunotherapy--which has a failure rate of 40% for this type of cancer--into patients who do.
The results of this proof-of-principle phase II clinical trial were published online today in Science. In this study, a team of researchers from UPMC Hillman administered fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) and anti-PD-1 immunotherapy to melanoma patients ...
Even in same desert location, species experience differences in exposure to climate warming
2021-02-04
Despite living in the same part of the Mojave Desert, and experiencing similar conditions, mammals and birds native to this region experienced fundamentally different exposures to climate warming over the last 100 years, a new study shows; small mammal communities there remained much more stable than birds, in the face of local climate change, it reports. The study presents an integrative approach to understanding the climate vulnerability of biodiversity in rapidly warming regions. Exposure to rising temperature extremes threatens species worldwide. It is expected to push many ever closer toward extinction. Thus, understanding ...
Human-generated noise pollution dominates the ocean's soundscape
2021-02-04
The soundscapes of the Anthropocene ocean are fundamentally different from those of pre-industrial times, becoming more and more a raucous cacophony as the noise from human activity has grown louder and more prevalent. In a Review, Carlos Duarte and colleagues show how the rapidly changing soundscape of modern oceans impacts marine life worldwide. According to the authors, mitigating these impacts is key to achieving a healthier ocean. From the plangent songs of cetaceans to grinding arctic sea ice, the world's oceans' natural chorus is performed by a vast ensemble of geological (geophony) and biological (biophony) sounds. However, for more than a century, ...
Special Issue: Human genome at 20
2021-02-04
In February 2001, the first drafts of the human genome were published. In this Special Issue of Science, "Human Genome at 20," an Editorial, a Policy Forum, a series of NextGen Voices Letters and a Perspective explore the complicated legacy of the Human Genome Project (HGP). "Millions of people today have access to their personal genomic information, with direct-to-consumer services and integration with other 'big-data' increasingly commoditizing what was rightly celebrated as a singular achievement in February 2001," writes Science Senior Editor Brad Wible.
An Editorial by Claire Frasier, director of the Institute for Genome Sciences at the University ...
Iodine oxoacids drive rapid aerosol formation in pristine atmospheric areas
2021-02-04
Iodine plays a bigger role than thought in rapid new particle formation (NPF) in relatively pristine regions of the atmosphere, such as along marine coasts, in the Arctic boundary layer or in the upper free troposphere, according to a new study. The authors say their measurements indicate that iodine oxoacid particle formation can compete with sulfuric acid - another vapor that can form new particles under atmospheric conditions - in pristine atmospheric regions. Tiny particles suspended high in the atmosphere - aerosols - play an essential role in Earth's climate system. Clouds require airborne particles, or cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), ...
Fecal microbiota transplants help patients with advanced melanoma respond to immunotherapy
2021-02-04
For patients with cancers that do not respond to immunotherapy drugs, adjusting the composition of microorganisms in the intestines--known as the gut microbiome--through the use of stool, or fecal, transplants may help some of these individuals respond to the immunotherapy drugs, a new study suggests. Researchers at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Center for Cancer Research, part of the National Institutes of Health, conducted the study in collaboration with investigators from UPMC Hillman Cancer Center at the University of Pittsburgh.
In the study, some patients with advanced melanoma who initially did not respond to treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor, a type of immunotherapy, did respond to the drug after receiving a transplant ...
Some sperms poison their competitors
2021-02-04
Competition among sperm cells is fierce - they all want to reach the egg cell first to fertilize it. A research team from Berlin now shows in mice that the ability of sperm to move progressively depends on the protein RAC1. Optimal amounts of active protein improve the competitiveness of individual sperm, whereas aberrant activity can cause male infertility.
It is literally a race for life when millions of sperm swim towards the egg cells to fertilize them. But does pure luck decide which sperm succeeds? As it turns out, there are differences in competitiveness between individual sperm. ...
In a desert seared by climate change, burrowers fare better than birds
2021-02-04
Berkeley -- In the arid Mojave Desert, small burrowing mammals like the cactus mouse, the kangaroo rat and the white-tailed antelope squirrel are weathering the hotter, drier conditions triggered by climate change much better than their winged counterparts, finds a new study published today in Science.
Over the past century, climate change has continuously nudged the Mojave's searing summer temperatures ever higher, and the blazing heat has taken its toll on the desert's birds. Researchers have documented a collapse in the region's bird populations, likely resulting ...
Human immune cells have natural alarm system against HIV
2021-02-04
Treatment for HIV has improved tremendously over the past 30 years; once a death sentence, the disease is now a manageable lifelong condition in many parts of the world. Life expectancy is about the same as that of individuals without HIV, though patients must adhere to a strict regimen of daily antiretroviral therapy, or the virus will come out of hiding and reactivate. Antiretroviral therapy prevents existing virus from replicating, but it can't eliminate the infection. Many ongoing clinical trials are investigating possible ways to clear HIV infection.
In a study published Feb. 4 in the journal Science, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a potential way to eradicate ...
Harvard scientists use trilayer graphene to observe more robust superconductivity
2021-02-04
In 2018, the physics world was set ablaze with the discovery that when an ultrathin layer of carbon, called graphene, is stacked and twisted to a "magic angle," that new double layered structure converts into a superconductor, allowing electricity to flow without resistance or energy waste. Now, in a literal twist, Harvard scientists have expanded on that superconducting system by adding a third layer and rotating it, opening the door for continued advancements in graphene-based superconductivity.
The work is described in a new paper in Science and can one day help lead toward superconductors that operate at higher or even close to room temperature. These superconductors are considered the holy grail of condensed matter physics ...
Food allergies are more common among Black children
2021-02-04
Black children have significantly higher rates of shellfish and fish allergies than White children, in addition to having higher odds of wheat allergy, suggesting that race may play an important role in how children are affected by food allergies, researchers at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, Rush University Medical Center and two other hospitals have found.
Results of the study were published in the February issue of the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
"Food allergy is a common condition in the U.S., and we know from our previous research that there are important differences between Black and White children with food allergy, but there is so much we need to know to be able to help our patients ...
Pharmacologist offers plan to solve disparities in designing medicine
2021-02-04
In a new perspective piece published in the Feb. 5 issue of Science, pharmacologist Namandje Bumpus, Ph.D. -- who recently became the first African American woman to head a Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine department, and is the only African American woman leading a pharmacology department in the country -- outlines the molecular origins for differences in how well certain drugs work among distinct populations. She also lays out a four-part plan to improve the equity of drug development.
"Human beings are more similar than we are different," says Bumpus. "Yet, the slightest variations in our genetic material ...
Studies use mathematics to analyze the semantics of dream reports during the pandemic
2021-02-04
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected people's behavior everywhere. Fear, apprehensiveness, sadness, anxiety, and other troublesome feelings have become part of the daily lives of many families since the first cases of the disease were officially recorded early last year.
These turbulent feelings are often expressed in dreams reflecting a heavier burden of mental suffering, fear of contamination, stress caused by social distancing, and lack of physical contact with others. In addition, dream narratives in the period include a larger proportion of terms relating to cleanliness and contamination, as well as anger and sadness.
All this is reported in a study published in PLOS ONE. The principal investigator was Natália ...
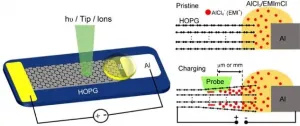
Surface effect of electrodes revealed by operando surface science methodology
2021-02-04
Surface and interface play critical roles in energy storage devices, thus calling for in-situ/operando methods to probe the electrified surface/interface. However, the commonly used in-situ/operando characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray spectroscopy and topography, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are based on the structural, electronic and chemical information in bulk region of the electrodes or electrolytes.
Surface science methodology including electron spectroscopy and scanning probe microscopy can provide rich information about how reactions ...
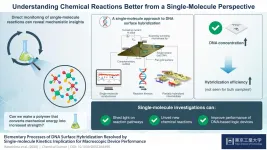
A single-molecule guide to understanding chemical reactions better
2021-02-04
Scientists globally aim to control chemical reactions--an ambitious goal that requires identifying the steps taken by initial reactants to arrive at the final products as the reaction takes place. While this dream remains to be realized, techniques for probing chemical reactions have become sufficiently advanced to render it possible. In fact, chemical reactions can now be monitored based on the change of electronic properties of a single molecule! Thanks to the scanning tunneling microscope (STM), this is also simple to accomplish. Why not then utilize ...
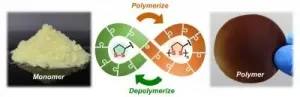
Molecule from nature provides fully recyclable polymers
2021-02-04
Plastics are among the most successful materials of modern times. However, they also create a huge waste problem. Scientists from the University of Groningen (The Netherlands) and the East China University of Science and Technology (ECUST) in Shanghai produced different polymers from lipoic acid, a natural molecule. These polymers are easily depolymerized under mild conditions. Some 87 per cent of the monomers can be recovered in their pure form and re-used to make new polymers of virgin quality. The process is described in an article that was published in the journal Matter on 4 February.
A problem with recycling plastics is that it usually results in a lower-quality product. The best results are obtained by chemical recycling, in which the polymers are broken ...
[1] ... [2664]
[2665]
[2666]
[2667]
[2668]
[2669]
[2670]
[2671]
2672
[2673]
[2674]
[2675]
[2676]
[2677]
[2678]
[2679]
[2680]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.