Using Nature's strategies in the development of new drugs
2021-02-10
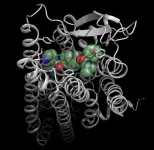
Dimerization (Note: combination of two identical or different molecules) of the human neuropeptides oxytocin and vasopressin can produce new types of bioactive molecules. In a recent study, an international research team led by MedUni Vienna and the University of Vienna demonstrated that dimerized and therefore significantly larger versions of oxytocin and vasopressin are still able to activate their receptors. Such new constructs provide several opportunities to optimize the efficacy of these neuropeptides for therapeutic application. The researchers were inspired for this approach from naturally occurring dimers. The results have been published in the journal "Chemical Science".
Oxytocin/vasopressin receptors are typical examples of so-called G protein-coupled receptors - the most ...
Tailor-made drugs to treat epilepsy or cardiovascular diseases
2021-02-10
In order for a drug to be effective at the right places in the body, it helps if scientists can predict as accurately as possible how the molecules of that drug will interact with human cells. In a joint research project, scientists from Collaborative Research Centre 1423 at Leipzig University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shanghai have succeeded in elucidating such a structure, namely that of the neuropeptide Y receptor Y2 with one of its ligands. This is the first time that a molecular blueprint for this receptor is available, which will enable the development of tailor-made new drugs, for example to treat epilepsy or cardiovascular diseases. The researchers' findings have now been published in Nature Communications.
The Y2 receptor plays ...
The therapeutic potential of peptides
2021-02-10
"Insulin is a prime example for a successful peptide drug that has been essential for the health of millions of diabetic patients in the past 100 years," says Markus Muttenthaler, who leads research groups at the Institute of Biological Chemistry of the Faculty of Chemistry at University in Vienna as well as at the Institute for Molecular Bioscience, at the University of Queensland in Brisbane.
Worldwide, peptide therapeutics account for 5% of the global pharmaceutical market, with global sales exceeding US$ 50 billion. More than 150 peptides are in clinical development and another 400-600 peptides undergoing preclinical ...
'Sleep hygiene' should be integrated into epilepsy diagnosis and management - study
2021-02-10
Children with epilepsy sleep poorly compared to healthy children, and are more likely to experience disruptions such as night terrors, sleep walking or sleep disordered breathing, according to a new study.
A team at the University of Birmingham's Centre for Human Brain Health analysed 19 published studies on sleep and epilepsy in children and adolescents to try to better understand and articulate the links between them.
Their findings, published in Sleep Medicine Reviews, highlight the significantly poorer sleep experienced by children and adolescents with epilepsy, and present a strong argument for screening children for sleep problems as an integral part of diagnosis and management of the condition.
Lead author Alice Winsor explains: "We know that sleep and epilepsy ...
Quantum effects help minimise communication flaws
2021-02-10
Among the most active fields of research in modern physics, both at an academic level and beyond, are quantum computation and communication, which apply quantum phenomena such as superposition and entanglement to perform calculations, or to exchange information. A number of research groups around the world have built quantum devices that are able to perform calculations faster than any classical computer. Yet, there is still a long way to go before these devices can be converted into marketable quantum computers. One reason for this is that both quantum computation and ...
Cell biology - Overseers of cell death
2021-02-10
A new study shows that proteins called IAPs, which can trigger programmed cell death, are inhibited by a specific chemical modification, and reveals that they play a wider role in protein quality control than previously assumed.
N-terminal acetylation - the attachment of an acetyl group (CH3-COO-) directly to the N-terminus of a protein - is one of the most common modifications found in the protein complements of higher organisms. The chemical tag has been linked to a wide variety of cellular signaling pathways. Now researchers led by Tanja Bange (Institute of Medical Psychology, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich) have shown that N-terminal acetylation shields certain proteins from degradation, and inhibits programmed cell death ('apoptosis'). ...
Mediterranean-style diet linked to better thinking skills in later life
2021-02-10
People who eat a Mediterranean-style diet--particularly one rich in green leafy vegetables and low in meat--are more likely to stay mentally sharp in later life, a study shows.
Closely adhering to a Mediterranean diet was associated with higher scores on a range of memory and thinking tests among adults in their late 70s, the research found.
The study found no link, however, between the Mediterranean-style diet and better brain health.
Markers of healthy brain ageing - such as greater grey or white matter volume, or fewer white matter lesions--did not differ between those regularly eating a Mediterranean diet and those who did not.
These ...
Six previously FDA-approved drugs appear promising against SARS-CoV-2 in laboratory testing
2021-02-10
Washington, DC - February 9, 2021 - A team of investigators from the Republic of China has discovered that 6 drugs previously approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for other indications could be repurposed to treat or prevent COVID-19. The research is published in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
Using FDA-approved drugs saves time -- the drugs don't need to go through the FDA approval process again -- making them available quickly to treat patients who need them.
The research shows that the investigators screened 2 large drug libraries cumulatively containing 3,769 FDA-approved drugs and found drugs that can inhibit 2 protein-cutting ...
Breastfeeding mothers produce COVID-19 antibodies capable of neutralizing virus
2021-02-10
MOSCOW, Idaho -- Feb. 9, 2021 -- Breastfeeding women with COVID-19 do not pass along the SARS-CoV-2 virus in their milk but do transfer milk-borne antibodies that are able to neutralize the virus, a multi-institutional team of researchers led by the University of Idaho reported.
The team analyzed 37 milk samples submitted by 18 women diagnosed with COVID-19. None of the milk samples were found to contain the virus, but nearly two-thirds of the samples did contain two antibodies specific to the virus.
"Taken together, our data do not support maternal-to-infant transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via milk," the researchers reported ...
International research team begins uncovering Arctic mystery
2021-02-10
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Something lurks beneath the Arctic Ocean. While it's not a monster, it has largely remained a mystery.
According to 25 international researchers who collaborated on a first-of-its-kind study, frozen land beneath rising sea levels currently traps 60 billion tons of methane and 560 billion tons of organic carbon. Little is known about the frozen sediment and soil -- called submarine permafrost -- even as it slowly thaws and releases methane and carbon that could have significant impacts on climate.
To put into perspective the amount of greenhouse gases in submarine permafrost, humans have released about 500 billion tons of carbon into the atmosphere since the Industrial Revolution, said Sandia National Laboratories geosciences engineer ...
Texas Heart Institute develops breakthrough heart ablation evaluation system
2021-02-10
The Texas Heart Institute (THI) has announced that a research team led by Dr. Mehdi Razavi, Director of Electrophysiology Clinical Research & Innovations, has developed a breakthrough new ex vivo benchtop system for evaluating the effects of ablation systems on excised tissues and assessing potential damage to collateral heart tissues. The unique system allows for fast and easy benchtop assessments rather than using costly in vivo tests. Critical findings associated with this innovation are outlined in a study published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Physiology.
The new ablation method evaluated by Dr. Razavi and team is being ...
After COVID-19 hit, federal financial aid applications dropped sharply among first-year students
2021-02-10
Washington, February 10, 2021--After the COVID-19 crisis hit last March, federal student aid applications among potential college freshmen in California dropped 14 percent between mid-March and mid-August, relative to prior years. While there were also initial declines in applications among current undergraduates and graduate students, these quickly recovered and ended 8 percent higher relative to prior years. The findings, published today in Educational Researcher, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association, are from the first academic study conducted on this topic.
Using data from the ...
New study identifies top-performing point-of-care COVID-19 tests
2021-02-10
ANN ARBOR, Mich. and VANCOUVER, B.C. (February 10, 2021) - After screening more than 1,100 independently assessed, point-of-care COVID-19 tests, researchers at NSF International and Novateur Ventures have identified 5 direct (antigen/RNA) tests for detection of acute infection and 6 indirect (antibody) tests for detection of prior infection that meet the recently published World Health Organization (WHO) "desirable" Target Product Profile (TPP) criteria. The researchers hope their work will help communities and healthcare systems make more informed decisions when choosing rapid, point-of-care COVID-19 ...
Depressed moms who breastfeed boost babies' mood, neuroprotection and mutual touch
2021-02-10
About 1 in 9 mothers suffers from maternal depression, which can affect the mother-infant bond as well as infant development. Touch plays an important role in an infant's socio-emotional development. Mothers who are depressed are less likely to provide their babies with soothing touch, less able to detect changes in facial expressions, and more likely to have trouble regulating their own emotions. In addition, infants of depressed mothers exhibit similar brain functioning patterns as their depressed mothers, which also are linked to temperament characteristics. Infants of depressed mothers are at a high risk of atypical and ...
Genetic markers show Pacific albacore intermingle across equator
2021-02-10
NEWPORT, Ore. - Analyzing thousands of genetic markers in albacore tuna from the Pacific Ocean, researchers at Oregon State University have learned that just seven dozen of those markers are needed to determine which side of the equator a fish comes from.
The scientists also discovered that fish from different hemispheres intermingle and sometimes breed with each other.
Published Tuesday in Evolutionary Applications, the findings are an important step toward better understanding the population structure of a species that's a vital and inexpensive source of protein for people around the globe.
Albacore in the North and South Pacific Oceans are currently managed as separate ...
White contours induce red hue
2021-02-10
Overview:
A color illusion that strongly induces color contrast effect has been found by a research team at the Toyohashi University of Technology Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary Research Institute (EIIRIS). The powerful visual illusion clarified a century-old contradiction relating to simultaneous color contrast theory. Through a human psychophysical experiment, the team demonstrated that the presence or absence of flanking contours formed from extremely thin white lines could be used to switch between contradictory visual phenomena (Figure 1), enabling consistent explanation for both discrepant ...
Cell-selective nanotherapy prevents post-angioplasty restenosis, promotes artery healing
2021-02-10
Tampa, FL (Feb. 10, 2021) - Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), commonly known as angioplasty with a stent, opens clogged arteries and saves lives. Despite its benefit in treating atherosclerosis that causes coronary artery disease, this common minimally-invasive procedure still poses severe complications for some patients.
Angioplasty involves inflating a balloon at the tip of a catheter to compress fatty deposits (plaques) against the artery wall, thereby restoring blood flow to the narrowed or blocked vessels. The image-guided procedure is often combined with the placement of either uncoated stents -- tiny expandable mesh devices- or stents coated with slowly-released antiproliferative ...
Where and when is economic decision-making represented in the brain?
2021-02-10
Tsukuba, Japan -- Economists have been using game theory to study decision-making since the 1950s. More recently, the interdisciplinary field of neuroeconomics has gained popularity as scientists try to understand how economic decisions are made in the brain. Researchers led by Professor Masayuki Matsumoto and Assistant Professor Hiroshi Yamada at the University of Tsukuba in Japan studied populations of neurons across the monkey brain reward network to find out where and when expected value is calculated.
The team trained monkeys to perform a lottery task for a reward. The monkeys saw two pie charts on a computer screen. The colors in the charts told the monkeys the size of the reward and the probability of getting it. ...
Black carbon aerosols in Beijing become "slim"
2021-02-10
Black carbon (BC) is the product of incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, biofuel, and biomass. By strongly absorbing solar radiation, BC can heat the atmosphere, affect its stability, and further deteriorate air quality.
The climatic and environmental effects of BC are determined by its loading in the atmosphere. Scientists find that microphysical characteristics of BC, such as particle size and mixing state, can also influence these effects.
The team pointed out that the reduction of the thickly coated BC would further lead to a decline of solar radiation absorption by atmospheric aerosols, besides the decline resulting from the BC loading ...
Pooping out miracles: scientists reveal mechanism behind fecal microbiota transplantation
2021-02-10
Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI) occurs in the gut and is caused by the Gram-positive, spore-forming anaerobic bacterium, C. difficile when its spores attach to fecal matter and are transferred from hand to mouth by health care workers. Patients undergoing antibiotic treatment are especially susceptible as the microorganisms that maintain a healthy gut are greatly damaged by the antibiotics.
Treatment of rCDI involves withdrawing the causative antibiotics and initiating antibiotic therapy, although this can be very challenging. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is considered an effective alternative therapy as it addresses the issue from the ground up by replacing the damaged microflora with a healthy one through a stool transplant.
However, two deaths caused by antibiotic-resistant ...
Novel analytical tools developed by SMART key to next-generation agriculture
2021-02-10
Plant nanosensors and Raman spectroscopy are two emerging analytical technologies and tools to study plants and monitor plant health, enabling research opportunities in plant science that have so far been difficult to achieve with conventional technologies such as genetic engineering techniques
The species-independent analytical tools are rapid and non-destructive, overcoming current limitations and providing a wealth of real-time information, such as early plant stress detection and hormonal signalling, that are important to plant growth and yield ...
Time perception and sense of touch: a new connection
2021-02-10
The percept of time relates to the sense of touch. A new SISSA study "A sensory integration account for time perception" published in PLOS Computational Biology uncovers this connection. "The challenge to neuroscience posed by the sense of time lies, first and foremost, in the fact there do not exist dedicated receptors - the passage of time is a sensory experience constructed without sensors," notes Mathew Diamond, director of the Tactile Perception and Learning Lab. "One might imagine a precise clock in the brain, a sort of stopwatch that registers the start and stop and computes the elapsed ...
Arizona economic burden of valley fever totals $736 million
2021-02-10
A University of Arizona Health Sciences study has estimated total lifetime costs at $736 million for the 10,359 valley fever patients diagnosed in Arizona in 2019, underscoring the economic burden the disease places on the state and its residents.
The prevalence of valley fever, formally known as coccidioidomycosis or cocci, has increased in recent years, from 5,624 cases diagnosed in Arizona in 2014 to 10,359 cases in 2019. There currently are no certain means of prevention or vaccination for the fungal disease, which is caused by spores of Coccidioides, a family of fungi found in soils of the Southwest.
The findings highlight the need ...
Virtual post-sepsis recovery program may also help recovering COVID-19 patients
2021-02-10
Feb. 10, 2021 - A new paper published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society describes a "virtual" recovery program for sepsis patients that may also help post-COVID-19 patients and survivors of other serious illnesses.
In " END ...
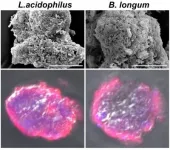
Smectite promotes probiotic biofilm formation in gut for cancer immunotherapy
2021-02-10
Scientists from Nanjing University and the University of Macau have devised a new approach to extend the survival of transplanted probiotics in vivo, enhancing the efficacy of cancer chemo-/immunotherapies in mice. The paper entitled "Smectite promotes probiotic biofilm formation in the gut for cancer immunotherapy" appears online today in Cell Reports.
The gut contains trillions of symbiotic bacteria. Disturbing the balance of intestinal flora may increase the occurrence of major diseases, including cancers. The gut microbiome plays an essential role in regulating the host immunity, which has inspired strategies to modulate intestinal microorganisms ...
[1] ... [2656]
[2657]
[2658]
[2659]
[2660]
[2661]
[2662]
[2663]
2664
[2665]
[2666]
[2667]
[2668]
[2669]
[2670]
[2671]
[2672]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.