Cabozantinib most effective treatment for metastatic papillary kidney cancer
2021-02-13
In a SWOG Cancer Research Network trial that put three targeted drugs to the test, the small molecule inhibitor cabozantinib was found most effective in treating patients with metastatic papillary kidney cancer - findings expected to change medical practice.
These findings will be presented at ASCO's virtual 2021 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium on Feb. 13, 2021 at 1 p.m. ET. The findings will be simultaneously published in The Lancet.
There are currently no effective treatments for metastatic papillary kidney cancer, or metastatic pRCC, a rare subtype of kidney cancer. One study of 38 patients found that the average survival ...
Immunotherapy -- targeted drug combination improves survival in advanced kidney cancer
2021-02-13
Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab yields better overall survival than single-agent sunitinib when given as first-line therapy in untreated patients with metastatic kidney cancer
The combination also improved progression-free survival and overall response rate
BOSTON - Patients with advanced kidney cancer, who received a targeted drug combined with a checkpoint-blocker immunotherapy agent had longer survival than patients treated with the standard targeted drug, said an investigator from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, reporting results from a phase 3 clinical trial.
The survival benefit demonstrates that an immune checkpoint inhibitor together with a targeted kinase inhibitor drug "is important ...
Gene-based blood test for melanoma spread evaluates treatment progress
2021-02-13
A test that monitors blood levels of DNA fragments released by dying tumor cells may serve as an accurate early indicator of treatment success in people in late stages of one of the most aggressive forms of skin cancer, a new study finds.
Led by NYU Grossman School of Medicine and Perlmutter Cancer Center researchers, the investigation looked at adults with undetectable levels of freely circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) four weeks into drug treatment for metastatic melanoma tumors that cannot be removed surgically (unresectable). The study showed that these patients, all of whom had common genetic changes (BRAFV600 mutations) linked to cancer, were living ...
<i>The Lancet</i>: COVID-19 vaccination potential will not be achieved without increased production, affordable pricing, global availability, and successful rollout
2021-02-13
Peer-reviewed / Review, Survey and Opinion piece
To ensure an effective global immunisation strategy against COVID-19, vaccines need to be produced at scale, priced affordably, and allocated globally so that they are available where needed, and successfully rolled out.
Review of evidence includes a comparison of 26 leading vaccines on their potential contribution to achieving global vaccine immunity, and a new survey of COVID-19 vaccine confidence in 32 countries.
Having new COVID-19 vaccines will mean little if people around the world are unable to get vaccinated in a timely manner. ...
Liquid biopsy for colorectal cancer could guide therapy for tumors
2021-02-12
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis demonstrates that a liquid biopsy examining blood or urine can help gauge the effectiveness of therapy for colorectal cancer that has just begun to spread beyond the original tumor. Such a biopsy can detect lingering disease and could serve as a guide for deciding whether a patient should undergo further treatments due to some tumor cells evading an initial attempt to eradicate the cancer.
The study appears online Feb. 12 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology Precision Oncology, a journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
While a few liquid biopsies have been approved ...
Study suggests sounds influence the developing brain earlier than previously thought
2021-02-12
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Scientists have yet to answer the age-old question of whether or how sound shapes the minds of fetuses in the womb, and expectant mothers often wonder about the benefits of such activities as playing music during pregnancy. Now, in experiments in newborn mice, scientists at Johns Hopkins report that sounds appear to change "wiring" patterns in areas of the brain that process sound earlier than scientists assumed and even before the ear canal opens.
The current experiments involve newborn mice, which have ear canals that open 11 days after birth. In human fetuses, the ear canal opens prenatally, at about 20 weeks gestation.
The findings, published online Feb. 12 in END ...
Dark-skinned teens, females prime targets of acne's psychological fallout
2021-02-12
A more aggressive approach to treating acne that marries the disciplines of psychology and dermatology is needed, according to two UC Riverside psychology researchers.
They also assert that women and people with darker skin disproportionately suffer from acne's psychological impacts.
"Acne is pervasive, physically harmless, and painless, so we all-too-often underestimate its impacts as the quintessential nuisance of adolescence and puberty," said UCR psychology professor Misaki Natsuaki, who authored the paper along with Tuppett Yates, also a UCR psychology professor.
The insinuation, including by developmental scientists, can be that hurtful monikers such as "pizza face" and "crater face" are best shrugged off.
But psychological ...
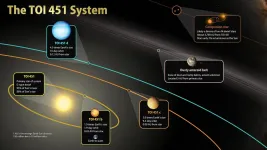
NASA's TESS discovers new worlds in a river of young stars
2021-02-12
Using observations from NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), an international team of astronomers has discovered a trio of hot worlds larger than Earth orbiting a much younger version of our Sun called TOI 451. The system resides in the recently discovered Pisces-Eridanus stream, a collection of stars less than 3% the age of our solar system that stretches across one-third of the sky.
The planets were discovered in TESS images taken between October and December 2018. Follow-up studies of TOI 451 and its planets included observations made in 2019 and 2020 using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, ...
Researchers propose that humidity from masks may lessen severity of COVID-19
2021-02-12
Masks help protect the people wearing them from getting or spreading SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, but now researchers from the National Institutes of Health have added evidence for yet another potential benefit for wearers: The humidity created inside the mask may help combat respiratory diseases such as COVID-19.
The study, led by researchers in the NIH's National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), found that face masks substantially increase the humidity in the air that the mask-wearer breathes in. This higher level of humidity in inhaled air, the researchers suggest, could help explain why wearing masks has been linked to lower disease severity in people infected with SARS-CoV-2, because hydration of the respiratory ...
Disease epidemic possibly caused population collapse in Central Africa 1600-1400 years ago
2021-02-12
A new study published in the journal Science Advances shows that Bantu-speaking communities in the Congo rainforest underwent a major population collapse from 1600 to 1400 years ago, probably due to a prolonged disease epidemic, and that significant resettlement did not restart until around 1000 years ago. These findings revise the population history of no less than seven present-day African countries (Cameroon, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, and Angola) and challenges the commonly held belief that the settlement of Central Africa by Bantu-speaking communities was a continuous process from about 4000 years ago until the start of the transatlantic ...
'See through soil' could help farmers deal with future droughts
2021-02-12
In research that may eventually help crops survive drought, scientists at Princeton University have uncovered a key reason that mixing material called hydrogels with soil has sometimes proven disappointing for farmers.
Hydrogel beads, tiny plastic blobs that can absorb a thousand times their weight in water, seem ideally suited to serve as tiny underground reservoirs of water. In theory, as the soil dries, hydrogels release water to hydrate plants' roots, thus alleviating droughts, conserving water, and boosting crop yields.
Yet mixing hydrogels into farmers' fields has had spotty results. Scientists have struggled to explain these uneven performances in large part because soil--being opaque --has thwarted attempts at observing, analyzing, and ultimately improving hydrogel ...
ACC urges COVID-19 vaccine prioritization for highest risk heart disease patients
2021-02-12
COVID-19 vaccine prioritization should prioritize those with advanced cardiovascular (CVD) disease over well-managed CVD disease, according to an American College of Cardiology (ACC) health policy statement published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC). All CVD patients face a higher risk of COVID-19 complications and should receive the vaccine quickly, but recommendations in this paper serve to guide clinicians in prioritizing their most vulnerable patients within the larger CVD group, while considering disparities in COVID-19 outcomes among different racial/ethnic groups and socioeconomic ...
New class of drug leads to 30% reduced risk of death for bladder cancer patients
2021-02-12
A new type of drug that helps target chemotherapy directly to cancer cells has been found to significantly increase survival of patients with the most common form of bladder cancer, according to results from a phase III clinical trial led in the UK by Queen Mary University of London and Barts Health NHS Trust.
The results are published in the New England Journal of Medicine and were presented at the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology's Genitourinary Cancers Symposium.
Urothelial cancer is the most common type of bladder cancer (90 percent of cases) and can also be found in the renal pelvis (where urine collects inside the kidney), ureter (tube that connects the kidneys ...
More trees do not always create a cooler planet, Clark University geographer finds
2021-02-12
WORCESTER, Mass. -- New research by Christopher A. Williams, an environmental scientist and professor in Clark University's Graduate School of Geography, reveals that deforestation in the U.S. does not always cause planetary warming, as is commonly assumed; instead, in some places, it actually cools the planet. A peer-reviewed study by Williams and his team, "Climate Impacts of U.S. Forest Loss Span Net Warming to Net Cooling," published today (Feb. 12) in Science Advances. The team's discovery has important implications for policy and management efforts that are turning to forests to mitigate climate change.
It ...
Star-shaped brain cells may be linked to stuttering
2021-02-12
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Astrocytes -- star-shaped cells in the brain that are actively involved in brain function -- may play an important role in stuttering, a study led by a University of California, Riverside, expert on stuttering has found.
"Our study suggests that treatment with the medication risperidone leads to increased activity of the striatum in persons who stutter," said Dr. END ...
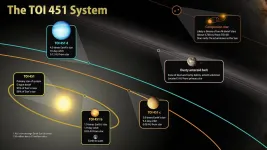
Young planets with teenage sun give space studies a lift
2021-02-12
HANOVER, N.H. - February 12, 2021 - A newly discovered planetary system will provide researchers with the rare chance to study a group of growing planets, according to research co-led by Dartmouth.
The new system, named TOI 451, is made up of at least three neighboring planets that orbit the same sun. The planets range in size between that of Earth and Neptune.
According to the research team, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and its planned successor, the James Webb Space Telescope, can be used to study the atmosphere of each planet. Such research could lead to information on how planetary systems like our own solar system evolve.
"The sun in this planetary system is very similar to our own sun, but much younger," ...
Computer love
2021-02-12
In your quest for true love and that elusive happily ever after, are you waiting for the "right" person to come along, or do you find yourself going for the cutest guy or girl in the room, hoping things will work out? Do you leave your options open, hoping to "trade-up" at the next opportunity, or do you invest in your relationship with an eye on the cost-benefits analysis?
For something so fundamental to our existence, mate selection remains one of humanity's most enduring mysteries. It's been the topic of intense psychological research for decades, spawning myriad hypotheses of why we choose whom we choose.
"Mate choice is really complicated, especially in humans," ...
NIH research funding to support surgeon scientists is rising
2021-02-12
CHICAGO (February 12, 2021): Since 2010, National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding to support surgeon scientists has, remarkably, risen significantly while funding to support other non-surgeon physicians has significantly decreased. This growth has occurred despite an overall decrease in NIH funding and an increase in demand for clinical productivity. These findings are according to an " END ...
Bacterial degradation of the MYC oncogene -- a new cancer treatment strategy?
2021-02-12
Scientists at Lund University have discovered how E. coli bacteria target and degrade the well-known oncogene MYC, which is involved in many forms of cancer. The study is now published in Nature Biotechnology.
Cancer cells grow too fast, outcompete normal cells and spread to distant sites, where they cause metastases. Understanding what makes cancer cells so efficient and threatening is critically important and stopping them has always been the goal of cancer research. Early studies identified so-called ''oncogenes''; genes that that normally control cell growth but when mutated may be responsible for the creation of cancer cells and explain their competitive advantage.
The pleiotropic transcription factor MYC has been ...
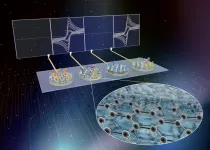
Detecting multiple sepsis biomarkers from whole blood - made fast, accurate, and cheap
2021-02-12
(BOSTON) -- Many life-threatening medical conditions, such as sepsis, which is triggered by blood-borne pathogens, cannot be detected accurately and quickly enough to initiate the right course of treatment. In patients that have been infected by an unknown pathogen and progress to overt sepsis, every additional hour that an effective antibiotic cannot be administered significantly increases the mortality rate, so time is of utmost essence.
The challenge with rapidly diagnosing sepsis stems from the fact that measuring only one biomarker often does not allow a clear-cut diagnosis. Engineers have struggled for decades to simultaneously quantify multiple biomarkers in whole blood with high ...
Medication-based starvation of cancer cells
2021-02-12
The drug thalidomide was sold as a sedative under the trade name Contergan in the 1950s and 1960s. At the time, its side-effects triggered one of the largest pharmaceutical scandals in history: The medication was taken from the market after it became known that the use of Contergan during pregnancy had resulted in over 10,000 cases of severe birth defects.
Currently, the successor preparations lenalidomide and pomalidomide are prescribed under strict supervision by experienced oncologists - the active ingredients are a cornerstone of modern cancer therapies. The use of lenalidomide and pomalidomide has considerably improved the success ...
UTEP professor's study may lead to solutions for overeating
2021-02-12
EL PASO, Texas - Science is a step closer to a new response to obesity, thanks in part to a study conducted by a team that included Sergio Iñiguez, Ph.D., associate professor of psychology at The University of Texas at El Paso.
The 10-member team led by Brandon Warren, Ph.D., assistant professor of pharmacodynamics at the University of Florida, made discoveries about a specific area of the brain tied to recollection and the desire to seek and consume food. It could lead to a way to inhibit the desire to overeat.
Iñiguez, who directs UTEP's Iñiguez Behavioral Neuroscience Lab and helped design novel experimental techniques for the research, said that people tend to overeat when exposed to cues or environments that remind them of treats, which is one reason ...
Study contradicts belief that whales learn songs from one another
2021-02-12
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Humpback and bowhead whales are the only mammals other than humans thought to progressively change the songs they sing through a process of cultural learning.
But maybe the humpbacks are no longer part of that trio. Humpbacks might be singing songs that are not as "cultured" as once assumed.
A new study by a University at Buffalo researcher is directly contradicting the widely accepted cultural transmission hypothesis suggesting that whales learn their songs from other whales.
"It seems like that is not correct," says Eduardo Mercado, a professor of psychology in UB's College of Arts and Sciences. "Our findings indicate that neither cultural transmission nor social learning contributes significantly to how humpback whales ...
'Sex, lasers and male competition:' fruit flies win genetic race with rivals
2021-02-12
Scientists have accepted natural selection as a driver of evolution for more than 160 years, thanks to Charles Darwin.
But University of Cincinnati biologist Michal Polak says Darwin's book "The Descent of Man" only tells part of the story. Sometimes when the victor vanquishes his sexual rival, the quest to pass genes to the next generation is just beginning.
According to a new UC study published in the journal Current Biology, male fruit flies with the most impressive sexual ornamentation also have super sperm that can outcompete that of rivals in the post-mating fertilization game.
UC studied Drosophila bipectinata, a tiny red-eyed fruit fly ...
The effects of antidepressant drugs evaluated through the analysis of patients' tweet
2021-02-12
Researchers of the Research Programme on Biomedical Informatics (GRIB) from UPF and Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM) in Barcelona, Spain, have identified behavioural and linguistic changes in tweets in Spanish published by users suffering from depression and who are taking medication to treat this disease.
Their work has been published in Journal of Medical Internet Research and was led by Ferran Sanz; with Angela Leis and Francesco Ronzano as first authors, who conducted the work together with Miguel Angel Mayer and Laura I Furlong, all from the Integrative Biomedical Informatics research ...
[1] ... [2648]
[2649]
[2650]
[2651]
[2652]
[2653]
[2654]
[2655]
2656
[2657]
[2658]
[2659]
[2660]
[2661]
[2662]
[2663]
[2664]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.