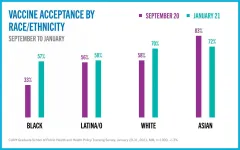Elderly esophageal cancer patients often receive suboptimal therapy due to perceived risks
2021-02-09
CHICAGO: Elderly patients (70 years and over) with locally advanced esophageal (E) and esophagogastric junction (EGJ) cancer (located in the stomach and esophagus) should be considered for optimal therapy that has the potential to cure. This therapy regimen includes initial chemoradiotherapy (NACR) and surgical resection, an operation that removes the cancerous part of the organ.
According to researchers, this recommended therapy is often not offered to elderly patients out of concern that they will not tolerate such an intensive treatment regimen. In a new study, they found that older patients who received the therapy had outcomes comparable with those of younger patients (under 70 years old). The single-institution study from the Ochsner Clinic Foundation and The University of ...
Reimbursing hospitals for postpartum contraception could prevent unintended pregnancies
2021-02-09
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- A new study finds that providing people who have recently given birth access to long-acting reversible methods of contraception, such as intrauterine devices and contraceptive implants, could help prevent them from unintentionally falling pregnant in the following months.
The study -- which analyzed the effects of a 2012 Medicaid policy implemented in South Carolina -- found that expanded access to particular forms of birth control were especially helpful in preventing unintended pregnancies among adolescents who had just given birth, giving them more control over their own futures.
"The ...
Early study points to potential therapeutic avenue for a pair of rare pediatric diseases
2021-02-09
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Feb. 9, 2021) -- Scientists have devised a new approach for detecting and potentially heading off the effects of two rare pediatric diseases before birth.
The study, performed in mouse models of the diseases and published today in Cell Reports, represents an important step toward much-needed early interventions for Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Silver-Russell syndrome.
Both diseases result in growth-related symptoms in children and often lead to additional problems later in life, such as increased cancer risk from Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome ...
A new modifier increases the efficiency of perovskite solar cells
2021-02-09
The research team of NUST MISIS has presented an improved structure of perovskite solar cells. Scientists have modified perovskite-based solar cells using MXenes -- thin two-dimensional titanium carbides with high electrical conductivity. The MXenes-based modified cells showed superior performance, with power conversion efficiency exceeding 19% (the reference demonstrated 17%) and improved stabilized power output with respect to reference devices. The results have been published in the Nano energy international scientific journal.
Perovskite solar cells ...
Nitrate in maternal drinking water may impair fetal growth
2021-02-09
Women whose household drinking water contained nitrate had babies that weighed, on average, 10 grams less than babies born to mothers where household water had no detectible nitrate, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago and Aarhus University.
The study, which is published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, followed pregnant women living in Denmark. The researchers found that even low nitrate levels -- about half of the allowable level set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, or EPA -- caused an adverse effect.
"While ...
Vaccine confidence grows under new administration, latest CUNY SPH Survey reveals
2021-02-09
Under the Biden Administration, New Yorkers' acceptance of the Covid-19 vaccine has increased significantly. In September, 55% of residents reported they would take the vaccine when it became available and this January, 64% reported they would take it.
Differences in vaccine acceptance persist across racial and ethnic groups. Among Whites and Asians acceptance is 70-72%; among Blacks and Latina/os it is 57-58%. On a positive note, the largest increase in rate of acceptance was seen among Black respondents, up from 33% in September to 57% in January.
These are key findings from the most recent tracking survey of public perceptions and experiences in New York City during the Covid-19 pandemic, conducted January 29-31 by the City University of New York Graduate School of ...
Color is in the eye of the beholder
2021-02-09
The colors in a flower patch appear completely different to a bear, a honeybee, a butterfly and humans. The ability to see these colors is generated by specific properties of opsins - light-sensitive proteins in the retina of our eyes. The number of opsins expressed and the molecular structure of the receptor proteins determines the colors we see.
In a paper published February 9 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences a team of researchers led by Harvard University develop a novel method to express long wavelength invertebrate opsin proteins in vitro and detail the molecular structure of redshift (long-wavelength) ...
Poorer mental health smolders after deadly, devastating wildfire
2021-02-09
In 2018, a faulty electric transmission line ignited the Camp Fire in Northern California, ultimately consuming 239 square miles and several communities, including the town of Paradise, which was 95 percent destroyed. At least 85 people died.
Structures have been rebuilt, but some things are worse. In a paper published February 2, 2021 in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, scientists at University of California San Diego, with colleagues elsewhere, describe chronic mental health problems among some residents who experienced the Camp Fire in varying degrees.
Direct exposure to large-scale fires significantly ...
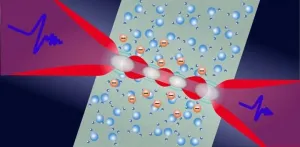
THz spectroscopy tracks electron solvation in photoionized water
2021-02-09
Photoionization of water involves the migration and solvation of electrons, with many transient and highly active intermediates. The process results in a large blue shift in the absorption spectrum, from the THz or gigahertz region to the visible range. While the behavior of low-density quasifree electrons excited by small pump power density has been investigated extensively, we still know little about the transient evolution of photoexcited plasma in liquid water. Valuable insights were recently provided by an international research team in a study published in Advanced Photonics.
According to Liangliang Zhang, physics professor at Capital Normal University in Beijing and one of the senior authors on the study, the physical mechanism of plasma evolution on the ...
Chemists developed a simplified method for pharmaceutical compounds synthesizing
2021-02-09
The structure of organic substances tetrahydroisoquinolines (THIQ) includes a benzene ring fused with a nitrogen-containing cycle. These compounds are in high demand in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the synthesis of myorelaxants, antidepressants, and drugs against hypertension, cough, and insomnia. Although different variations of THIQ structures can be found in natural sources (for example, as parts of phytotoxins), modern-day pharmaceutical manufacturers are also interested in their rare types, such as spirocyclic THIQs. In their molecules, two adjacent cycles share one common atom, thus creating an unusual and very stable 3D structure. This feature ...
Chemists identified necessary conditions for successful synthesis of small molecules
2021-02-09
The development of the so-called small molecules is a promising field of the pharmaceutical industry. Small molecules are organic compounds with a small molecular mass. They are often based on heterocycles--carbon rings that also include atoms of nitrogen and other elements. The synthesis of small molecules is much cheaper than the development of drugs based on antibodies or other biological molecules; however, their properties are still understudied. Even the slightest modifications can change the characteristics of a small molecule and open a whole new range of its practical applications. Therefore, many research teams working in the field of chemical pharmacology improve synthesis methods to create libraries of ...
The pandemic lockdown leads to cleaner city air across Canada, Concordia paper reveals
2021-02-09
The COVID-19 pandemic that shuttered cities around the world did not just affect the way we work, study and socialize. It also affected our mobility. With millions of workers no longer commuting, vehicle traffic across Canada has plummeted. This has had a significant impact on the quality of air in major Canadian cities, according to a new study by Concordia researchers.
A paper published in the journal Science of the Total Environment looked at downtown air quality monitoring station data from Vancouver, Edmonton, Saskatoon, Winnipeg, Toronto, Montreal, Halifax ...
Scientists suggested using non-symmetrical magnets for target drug delivery
2021-02-09
To achieve target delivery of drugs to cells and organs, scientists have to be able to transport the molecules of pharmaceutical substances to targets using a controllable carrier. The role of such a carrier can be played by special particles, such as lipid droplets or magnetic nanoparticles. Among the latter, the most popular are the ones based on iron oxides. Their sizes range from 1 to 100 nm, which is dozens of times smaller than animal cells, and they can be moved within a body using an external magnetic field.
However, in practice, it is quite difficult to control nanoparticles with magnets, as the magnetic field quickly becomes weaker when the distance from the magnet increases. This problem ...
Porous materials unfavorable for coronavirus survival
2021-02-09
WASHINGTON, February 9, 2021 -- As COVID-19 spreads via respiratory droplets, researchers have become increasingly interested in the drying of droplets on impermeable and porous surfaces. Surfaces that accelerate evaporation can decelerate the spread of the COVID-19 virus.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from IIT Bombay show a droplet remains liquid for a much shorter time on a porous surface, making it less favorable to survival of the virus.
The researchers found the coronavirus can survive for four days on glass, seven days on plastic, and seven days on stainless steel. But on paper and cloth, the virus survived for only three hours and two days, respectively.
"Based on our study, we recommend that furniture in hospitals and offices, ...
SARS-CoV-2 infection among migrant workers in Singapore
2021-02-09
What The Study Did: Researchers examined how common SARS- CoV-2 infection was among migrant workers in Singapore.
Authors: Vernon J. Lee, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., of the Ministry of Health in Singapore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24071)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full article is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
Advanced simulations reveal how air conditioning spreads COVID-19 aerosols
2021-02-09
WASHINGTON, February 9, 2021 -- The detailed physical processes and pathways involved in the transmission of COVID-19 are still not well understood. Researchers decided to use advanced computational fluid dynamics tools on supercomputers to deepen understanding of transmission and provide a quantitative assessment of how different environmental factors influence transmission pathways and airborne infection risk.
A restaurant outbreak in China was widely reported as strong evidence of airflow-induced transmission of COVID-19. But it lacked a detailed investigation about exactly how transmission occurred.
Why did some people get infected while others within the same area did not? ...
COVID-19 pandemic as opportunity to ensure more successful future for science, public health
2021-02-09
What The Viewpoint Says: The missteps and miscommunications that have stymied a more effective U.S. and global response to the COVID-19 pandemic bring into sharp focus the deficiencies in governance systems of the U.S. public health and scientific institutions.
Authors: K. M. Venkat Narayan, M.D., M.Sc., of the Rollins School of Public Health and School of Medicine at Emory University in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.23479)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
School closures may not reduce coronavirus deaths as much as expected
2021-02-09
WASHINGTON, February 9, 2021 -- School closures, the loss of public spaces, and having to work remotely due to the coronavirus pandemic have caused major disruptions in people's social lives all over the world.
Researchers from City University of Hong Kong, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute suggest a reduction in fatal coronavirus cases can be achieved without the need for so much social disruption. They discuss the impacts of the closures of various types of facilities in the journal Chaos, from AIP Publishing.
After running thousands of simulations of the pandemic response in New York City with variations in social distancing behavior at home, in schools, at public facilities, and in the workplace ...
Disparities in SARS-CoV-2 testing in Massachusetts during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-02-09
What The Study Did: To mitigate subsequent waves of COVID-19, allocating testing resources to locations of greatest need is important. Researchers in this study examined the alignment of testing to epidemic intensity in Massachusetts.
Authors: Scott Dryden-Peterson, M.D., M.Sc., of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37067)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
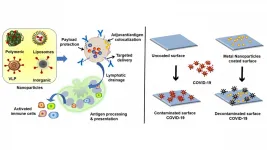
Biomaterials could mean better vaccines, virus-fighting surfaces
2021-02-09
WASHINGTON, February 9, 2021 -- Advances in the fields of biomaterials and nanotechnology could lead to big breakthroughs in the fight against dangerous viruses like the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the Indian Institute of Science describe two possibilities being explored by scientists in the field to make vaccines more effective and build surfaces that could fight and kill viruses on their own.
"It is important not just in terms of COVID," said author Kaushik Chatterjee. "We've seen SARS, ...
Regular walnut consumption may reduce negative outcomes of H. pylori infection
2021-02-09
FOLSOM, Calif., February 9, 2021 - A new animal study, published in the Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, suggests regular walnut consumption may be a promising intervention for reducing negative outcomes associated with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, a widespread bacterial infection that affects more than half of the world's population.
Using mice models, researchers from the CHA Cancer Prevention Research Center in Korea found preliminary evidence that eating a diet rich in walnuts may help protect against negative outcomes associated with H. pylori infection. Specifically, the research found that walnut extracts, formed from ...
Embry-Riddle alumna helps unravel key mysteries of rare stars
2021-02-09
Within the constellation Cygnus, an elderly star and its massive companion are having one last hurrah, flinging off mass at an incredible rate before they explode as supernovae and collapse into a black hole.
Now, researchers including recent Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University graduate Laura M. Lee have mapped the elderly star's orbit around its oversized and equally ancient partner. In a scientific first, they have also determined the dynamical mass of both stars that make up a binary system called Wolf-Rayet 133.
The team's findings, published Feb. 9, 2021 by Astrophysical Journal ...
Bats & pangolins in Southeast Asia harbour SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses, reveals new study
2021-02-09
While the World Health Organization (WHO) continues its mission to Wuhan investigating the origin and early transmission of SARS-CoV-2, a new study led by scientists from Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, and Chulalongkorn University, Thailand, shows that SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses (SC2r-CoVs) are circulating in animals as far away as Thailand. The study, published in Nature Communications today, reported that high levels of neutralising antibodies against the virus were present in both bats and pangolins found in the Southeast Asian country. The study further indicates that more SC2r-CoVs are likely to be discovered ...
Expanded spina bifida guidelines cover care from newborn to adult
2021-02-09
Amsterdam, NL, February 9, 2021 - Globally, nearly 300,000 babies are born with neural tube defects including spina bifida (SB) each year. This openly available special issue of the Journal of Pediatric Rehabilitation Medicine (JPRM) provides 20 important evidence- and consensus-based updates to key sections of the 2018 "Guidelines for the Care of People with Spina Bifida" issued by the Spina Bifida Association (SBA). These reflect current recommendations for the care of patients with SB across the entire lifespan, from prenatal counseling to adult care.
As a result of research advancements and improved team-based patient care, approximately 80%-90% of children with SB now live to adulthood in the United ...
Paid maternity leave has long-term health benefits
2021-02-09
A study of women who were new mothers in the late 1970s found that those who were given longer, paid maternity leave lived healthier lives as they entered middle age.
While universal paid maternity leave is now available in many Western European nations, this has not always been the case. A new study by University of Georgia economist Meghan Skira looked at the health of Norwegian mothers before and after paid maternity leave became law in 1977. She found that the health benefits of leave continued for years after their children were born.
Skira, an associate professor in the Terry College of Business, worked with economist Aline Bütikofer of the Norwegian School of Economics and Julie Riise of the University of Bergen on the study. Their paper, "The Impact of Paid ...
[1] ... [2651]
[2652]
[2653]
[2654]
[2655]
[2656]
[2657]
[2658]
2659
[2660]
[2661]
[2662]
[2663]
[2664]
[2665]
[2666]
[2667]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.