Take-at-home tests boost colorectal cancer screening 10x for the underserved
2021-02-08
Colorectal cancer screening rates jumped by more than 1,000 percent when researchers sent take-at-home tests to patients overdue for testing at a community health center that predominantly serves people of color. Instead of the oft-standard text message that simply reminds a patient that they are overdue for screening, researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania made it the default to send a take-at-home test to the patient's home unless they opted out via a text message prompt. The research was published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
"Colorectal cancer screening rates remain limited ...
WVU biologists uncover forests' unexpected role in climate change
2021-02-08
New research from West Virginia University biologists shows that trees around the world are consuming more carbon dioxide than previously reported, making forests even more important in regulating the Earth's atmosphere and forever shift how we think about climate change.
In a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Professor Richard Thomas and alumnus Justin Mathias (BS Biology, '13 and Ph.D. Biology, '20) synthesized published tree ring studies. They found that increases in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere over the past century have caused ...
Distinctness of mental disorders traced to differences in gene readouts
2021-02-08
A new study suggests that differences in the expression of gene transcripts - readouts copied from DNA that help maintain and build our cells - may hold the key to understanding how mental disorders with shared genetic risk factors result in different patterns of onset, symptoms, course of illness, and treatment responses. Findings from the study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), part of the National Institutes of Health, appear in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology.
"Major mental disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder, share common genetic roots, but each disorder presents differently in each individual," said Francis J. McMahon, M.D., a senior author of the ...
Addressing breastfeeding disparities for African American mothers
2021-02-08
PHILADELPHIA (February 8, 2021) - An abundance of data underscore the importance of breastfeeding and human milk for the optimal health of infants, children, mothers, and society. But while breastfeeding initiation rates have increased to more than 80% in the U.S., a disparity exists for African American mothers and infants. In this group, breastfeeding is initiated only about 69% of the time.
A new study to help identify the best strategies and practices to improve breastfeeding in the African American community leverages the opinions, knowledge, and experiences of subject matter exerts (SMEs) with national and international exposure to policies and practices influencing African ...
Mount Sinai study finds wearable devices can detect COVID-19 symptoms and predict diagnosis
2021-02-08
Wearable devices can identify COVID-19 cases earlier than traditional diagnostic methods and can help track and improve management of the disease, Mount Sinai researchers report in one of the first studies on the topic. The findings were published in the END ...
How humans can build better teamwork with robots
2021-02-08
As human interaction with robots and artificial intelligence increases exponentially in areas like healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, space exploration, defense technologies, information about how humans and autonomous systems work within teams remains scarce.
Recent findings from human systems engineering research demonstrate that human-autonomy teaming comes with interaction limitations that can leave these teams less efficient than all-human teams.
Existing knowledge about teamwork primarily is based on human-to-human or human-to-automation interaction, which positions humans as supervisors of automated partners.
But as autonomy has increasingly ...
How rocks rusted on Earth and turned red
2021-02-08
How did rocks rust on Earth and turn red? A Rutgers-led study has shed new light on the important phenomenon and will help address questions about the Late Triassic climate more than 200 million years ago, when greenhouse gas levels were high enough to be a model for what our planet may be like in the future.
"All of the red color we see in New Jersey rocks and in the American Southwest is due to the natural mineral hematite," said lead author Christopher J. Lepre, an assistant teaching professor in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences in the School of Arts and Sciences at Rutgers University-New Brunswick. ...
Synchronization of brain hemispheres changes what we hear
2021-02-08
How come we don't hear everything twice: After all, our ears sit on opposite sides of our head and most sounds do not reach both our ears at exactly the same time. "While this helps us determine which direction sounds are coming from, it also means that our brain has to combine the information from both ears. Otherwise, we would hear an echo," explains Basil Preisig of the Department of Psychology at the University of Zurich.
In addition, input from the right ear reaches the left brain hemisphere first, while input from the left ear reaches the right brain hemisphere first. The two hemispheres ...
Cleaning Up the Mississippi River
2021-02-08
Louisiana State University College of the Coast & Environment Boyd Professor R. Eugene Turner reconstructed a 100-year record chronicling water quality trends in the lower Mississippi River by compiling water quality data collected from 1901 to 2019 by federal and state agencies as well as the New Orleans Sewerage and Water Board. The Mississippi River is the largest river in North America with about 30 million people living within its watershed. Turner focused on data that tracked the water's acidity through pH levels and concentrations of bacteria, oxygen, lead and sulphate in this study published in Ambio, a journal of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
Rivers ...
Role of aspirating system type in SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity among dental staff
2021-02-08
Alexandria, Va., USA -- High-volume aspirators are recommended in dental clinics during the COVID-19 pandemic, but the study "SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity Among Dental Staff and the Role of Aspirating Systems" published in the JDR Clinical & Translational Research (JDR CTR), shows that the type of aspirating system significantly affects the incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among dental specialists.
In this retrospective cohort study of 157 healthcare workers in Ekaterinburg, Russia, data on the seroprevalence of COVID-19 from dental clinics using three different types of aspirating systems were compared. Clinic A and B used a V6000 aspirating system with a vacuum controller and high-efficiency ...
Deepfake detectors can be defeated, computer scientists show for the first time
2021-02-08
Systems designed to detect deepfakes --videos that manipulate real-life footage via artificial intelligence--can be deceived, computer scientists showed for the first time at the WACV 2021 conference which took place online Jan. 5 to 9, 2021.
Researchers showed detectors can be defeated by inserting inputs called adversarial examples into every video frame. The adversarial examples are slightly manipulated inputs which cause artificial intelligence systems such as machine learning models to make a mistake. In addition, the team showed that the attack still works after videos are ...
Scientists discover how a group of caterpillars became poisonous
2021-02-08
The Atala butterfly (Eumaeus atala) and its five closest relatives in the genus Eumaeus like to display their toxicity. This sextet's toxicity comes from what they eat as caterpillars: plants called cycads that have been around since before dinosaurs roamed the Earth and contain a potent liver toxin called cycasin.
Because they are filled with poison, Eumaeus are big, gaudily iridescent and flap about like they have no place to go. Even their caterpillars are conspicuous, congregating in groups to munch cycad plants all while sporting flashy red and gold ...
Researchers develop platform to identify cancer mutations that may be responsive to drug therapies
2021-02-08
CLEVELAND - A Cleveland Clinic-led team of researchers has developed a personalized genomic medicine platform that will help advance accelerate genomic medicine research and genome-informed drug discovery, according to new study results published recently in END ...
Northwestern researcher to discuss consequences of incarceration at AAAS annual meeting
2021-02-08
CHICAGO --- Northwestern University professor and researcher Linda Teplin will discuss the psychosocial outcomes of incarcerated youth at the virtual 2021 American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) annual meeting.
Teplin will moderate the scientific session "Consequences of Incarceration on Health Inequity and Racial Injustice" at 2 p.m. EST, Monday, Feb. 8. During the session, she will also present "Consequences of Incarceration in Detained Youth: A 15-Year Longitudinal Study."
Nearly 2.2 million Americans are incarcerated annually, ...
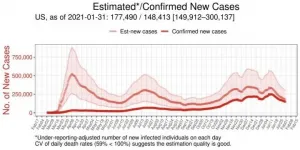
Severe undercounting of COVID-19 cases in U.S., other countries estimated via model
2021-02-08
A new machine-learning framework uses reported test results and death rates to calculate estimates of the actual number of current COVID-19 infections within all 50 U.S. states and 50 countries. Jungsik Noh and Gaudenz Danuser of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on February 8, 2021.
During the ongoing pandemic, U.S. states and many countries have reported daily counts of COVID-19 infections and deaths confirmed by testing. However, many infections have gone undetected, resulting in under-counting of the total number of people currently infected at any ...
3D printing polymers
2021-02-08
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) -- Researchers in the labs of Christopher Bates, an assistant professor of materials at UC Santa Barbara, and Michael Chabinyc, a professor of materials and chair of the department, have teamed to develop the first 3D-printable "bottlebrush" elastomer. The new material results in printed objects that have unusual softness and elasticity -- mechanical properties that closely resemble those of human tissue.
Conventional elastomers, i.e. rubbers, are stiffer than many biological tissues. That's due to the size and shape of their constituent polymers, which are long, linear molecules that easily entangle like cooked spaghetti. In contrast, bottlebrush polymers ...
Death by suicide? Drug overdoses muddy waters for investigators, amplify mental health crisis
2021-02-08
Classifying a death as suicide may be easiest for medical examiners and coroners in the western United States, which reports the highest suicide rates officially. Suicide by firearm is the leading method there, and usually clear in terms of evidence.
By contrast, suicides by drug overdose, spurred primarily by the opioid epidemic in the remainder of the country, are less obvious to investigators.
But a new West Virginia University-led injury mortality study combines most drug overdose deaths with all suicides into an expanded self-injury category. Exposing a mental health crisis that has unraveled across the United States over the past two decades, study data have direct implications for suicide prevention efforts.
Ian Rockett, professor ...
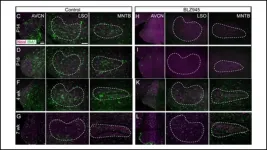
Auditory brainstem pathways do not develop properly without microglia
2021-02-08
Auditory pathways in the brainstem do not fully mature without microglia clearing away extra cell connections. This crucial function occurs even when pruning by microglia is delayed, according to new research published in eNeuro.
Sensitive hearing requires precise connections between neurons in the auditory brainstem. Early in development, support cells called microglia prune away unnecessary connections and encourage others to expand. Microglia finish their job around two weeks after birth, but the rigidity of this developmental timeframe is unknown.
Milinkeviciute et al. eliminated microglia from the brains of newborn mice using a drug. They stopped the treatment after 10 days, and microglia returned to the brainstem. Initially, the mice with delayed microglia development ...
Microbiota transfer therapy for autism: Multi-omic approaches and lessons learned
2021-02-08
During every instant of life, over a hundred trillion microbes, collectively known as the microbiome, reside on skin surfaces and course through the human body. In the human gut, vast colonies of bacteria, belonging to around 1000 different species, carry out duties ranging from the digestion of food and the management of body weight to effects on the brain and behavior, many of these still elusive to science.
Recent studies in mice and humans have revealed intriguing links between the composition of gut microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a disease believed to affect ...
Radiative cooling and solar heating from one system, no electricity needed
2021-02-08
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Passive cooling, like the shade a tree provides, has been around forever.
Recently, researchers have been exploring how to turbo charge a passive cooling technique -- known as radiative or sky cooling -- with sun-blocking, nanomaterials that emit heat away from building rooftops. While progress has been made, this eco-friendly technology isn't commonplace because researchers have struggled to maximize the materials' cooling capabilities.
New research led by University at Buffalo engineers makes significant progress in this area.
A study published Feb. 8 in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science describes a uniquely designed radiative cooling system that:
Lowered the temperature inside ...
New drug target for Ebola, Marburg viruses
2021-02-08
Ebola and Marburg are among the most deadly viruses, with mortality rates from these infections ranging from 25% to 90%. While no drugs currently are available on the market to prevent infection from these viruses -- they belong to a category of viruses called filoviruses, which are known to cause hemorrhagic fever -- researchers have identified a few small drug molecules that can block filoviruses from infecting cells by occupying a single site on a glycoprotein in the virus.
Now, researchers at the END ...
AI researchers ask: What's going on inside the black box?
2021-02-08
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Peter Koo and collaborator Matt Ploenzke reported a way to train machines to predict the function of DNA sequences. They used "neural nets", a type of artificial intelligence (AI) typically used to classify images. Teaching the neural net to predict the function of short stretches of DNA allowed it to work up to deciphering larger patterns. The researchers hope to analyze more complex DNA sequences that regulate gene activity critical to development and disease.
Machine-learning researchers can train a brain-like "neural net" computer to recognize objects, ...
What happens in the mouth ... doesn't stay in the mouth
2021-02-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio - We know that what happens in the mouth doesn't stay in the mouth - but the oral cavity's connection to the rest of the body goes way beyond chewing, swallowing and digestion.
The healthy human oral microbiome consists of not just clean teeth and firm gums, but also energy-efficient bacteria living in an environment rich in blood vessels that enables the organisms' constant communication with immune-system cells and proteins.
A growing body of evidence has shown that this system that seems so separate from the rest of our bodies is actually highly influential on, and influenced by, our overall health, said Purnima Kumar, professor of periodontology at The Ohio State University, speaking at a science conference this week.
For example, type 2 diabetes has long ...
Brain changed by caffeine in utero, study finds
2021-02-08
New research finds caffeine consumed during pregnancy can change important brain pathways that could lead to behavioral problems later in life. Researchers in the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) analyzed thousands of brain scans of nine and ten-year-olds, and revealed changes in the brain structure in children who were exposed to caffeine in utero.
"These are sort of small effects and it's not causing horrendous psychiatric conditions, but it is causing minimal but noticeable behavioral issues that should make us consider long term effects ...
Mixed and matched: Integrating metal-organic frameworks into polymers for CO2 separation
2021-02-08
One of humanity's biggest challenges right now is reducing our emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Research groups worldwide are trying to find ways to efficiently separate carbon dioxide (CO2) from the mixture of gases emitted from industrial plants and power stations. Among the many strategies for accomplishing this, membrane separation is an attractive, inexpensive option; it involves using polymer membranes that selectively filter CO2 from a mix of gases.
Recent studies have focused on adding low amounts of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) into polymer matrices to enhance their properties. MOFs are compounds made of a metallic center bonded to organic molecules in a very orderly fashion, producing porous crystals. When added to polymer ...
[1] ... [2655]
[2656]
[2657]
[2658]
[2659]
[2660]
[2661]
[2662]
2663
[2664]
[2665]
[2666]
[2667]
[2668]
[2669]
[2670]
[2671]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.