Shuffling bubbles reveal how liquid foams evolve
2021-02-06
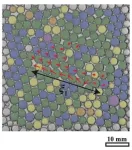
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University studied the dynamics of foams. When a drop of water was added to a foam raft, the bubbles rearranged themselves to reach a new stable state. The team found that bubble movement was qualitatively different depending on the range of bubble sizes present. Along with analogies with soft-jammed materials, these findings may inspire the design of new foam materials for industry.
Foams are everywhere. Whether it's soaps and detergents, meringues, beer foam, cosmetics or insulation for clothing and building, we're surrounded by everyday ...
COVID-19: Schools urgently need guidelines on improving ventilation in classrooms
2021-02-06
There is an urgent need for guidelines on how schools can use ventilation to reduce the risk of COVID-19 transmission in the classroom, according to doctors at Imperial College London and the headteacher of a secondary school in Pinner, Middlesex. In a commentary published by the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, the authors say that improving air quality in classroom spaces should be as important as following government advice regarding social distancing, mask-wearing and hand washing.
The authors point to lessons from the airline industry, where the risk of contracting COVID-19 on a flight ...
Drug 'breakthrough' gives longest-ever survival in nonresectable liver cancer patients
2021-02-06
6 February: The IMbrave150 trial found median overall survival was 19.2 months in patients treated with atezo+bev vs 13.4 months for those treated with sorafenib alone, the current standard treatment (HR, 0.66 [95% CI, 0.52-0.85]; P=0.0009). Survival at 18 months was 52% with atezo+bev and 40% in patients treated with sorafenib.
All patients in the trial had nonresectable HCC - the most common form of liver cancer - and had not previously been treated with systemic therapy. A total of 501 patients were treated in the multicentre, open label, randomised controlled trial and the new follow-up figures confirm the superiority of the atezo+bev combination over sorafenib in this group of patients with HCC.
Atezolizumab is an immune ...
The Lancet Public Health: Survey taken after France's first COVID-19 wave indicates almost one-third of working-age people could reject a vaccine
2021-02-06
Around one in three working-age adults (29%) surveyed in France in July 2020 would refuse any COVID-19 vaccine.
Willingness to receive a COVID-19 vaccination depended upon its country of origin, effectiveness, rate of serious side effects, and site of vaccination.
Although attitudes may have changed since July 2020 with the approval of several vaccines and a second wave of COVID-19, the findings suggest that communicating the collective benefits of herd immunity reduced people's hesitancy about being vaccinated.
Nearly one in three working-age adults in France (29%) surveyed in July 2020 - when lockdown restrictions had been ...
Peginterferon-lambda shows strong antiviral action to accelerate clearance of COVID-19
2021-02-06
TORONTO (February 5, 2021) - A clinical study led by Dr. Jordan Feld, a liver specialist at Toronto Centre for Liver Disease, University Health Network (UHN), showed an experimental antiviral drug can significantly speed up recovery for COVID-19 outpatients - patients who do not need to be hospitalized.
This could become an important intervention to treat infected patients and help curb community spread, while COVID-19 vaccines are rolled out this year.
"This treatment has large therapeutic potential, especially at this moment as we see aggressive variants of the virus spreading around the globe which are less sensitive to both vaccines and treatment ...
Critical flaw found in lab models of the human blood-brain barrier
2021-02-05
NEW YORK, NY (Feb. 5, 2020)--Cells used to study the human blood brain barrier in the lab aren't what they seem, throwing nearly a decade's worth of research into question, a new study from scientists at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and Weill Cornell Medicine suggests.
The team also discovered a possible way to correct the error, raising hopes of creating a more accurate model of the human blood-brain barrier for studying certain neurological diseases and developing drugs that can cross it.
The study was published online Feb. ...
Physical discipline and cognitive deprivation associated with specific types of developmental delay
2021-02-05
Washington, DC, February 5, 2021 - A study in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP), published by Elsevier, reports that in a diverse, cross-national sample of youth, physical discipline and cognitive deprivation had distinct associations with specific domains of developmental delay. The findings are based on the Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys, which is an ongoing, international household survey initiative coordinated and assisted by the United Nations agency, UNICEF.
"Physical discipline and cognitive deprivation are well-established risks to child development. However, it is rare that these experiences are examined in relation to each other," said lead author ...
Tom Hanks' COVID-19 diagnosis likely shaped behaviors, thoughts toward virus
2021-02-05
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa.-- When actor Tom Hanks announced his COVID-19 diagnosis on March 11, 2020, many Americans were still learning about the virus and its severity. According to new research, Hanks' announcement may have affected how some people understood the virus and their behavior toward its prevention.
The day after Hanks posted the news on social media, Jessica Gall Myrick, an associate professor in the Donald P. Bellisario College of Communications at Penn State, and Jessica Fitts Willoughby, associate professor at Washington State University, surveyed 682 people about their attitudes and behaviors toward COVID-19.
Just under 90% of the people surveyed had heard about Hanks' social ...
Center for BrainHealth researchers create virtual reality cognitive assessment
2021-02-05
Virtual reality isn't just for gaming. Researchers can use virtual reality, or VR, to assess participants' attention, memory and problem-solving abilities in real world settings. By using VR technology to examine how folks complete daily tasks, like making a grocery list, researchers can better help clinical populations that struggle with executive functioning to manage their everyday lives.
Lead author Zhengsi Chang is a PhD student that works in the lab of Daniel Krawczyk, PhD, deputy director of the Center for BrainHealth®. Along with Brandon Pires, a researcher at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, the team investigated whether VR can be used to effectively test ...
Researchers find peptide that treats, prevents killer citrus disease
2021-02-05
New research affirms a unique peptide found in an Australian plant can destroy the No. 1 killer of citrus trees worldwide and help prevent infection.
Huanglongbing, HLB, or citrus greening has multiple names, but one ultimate result: bitter and worthless citrus fruits. It has wiped out citrus orchards across the globe, causing billions in annual production losses.
All commercially important citrus varieties are susceptible to it, and there is no effective tool to treat HLB-positive trees, or to prevent new infections.
However, new UC Riverside research shows that a naturally occurring peptide found in HLB-tolerant citrus relatives, such as Australian finger lime, can not only kill the bacteria that causes the disease, it can also activate the plant's ...
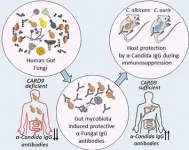
Fungi in the gut prime immunity against infection
2021-02-05
Common fungi, often present in the gut, teach the immune system how to respond to their more dangerous relatives, according to new research from scientists at Weill Cornell Medicine. Breakdowns in this process can leave people susceptible to deadly fungal infections.
The study, published Feb. 5 in Cell, reveals a new twist in the complex relationship between humans and their associated microbes, and points the way toward novel therapies that could help combat a rising tide of drug-resistant pathogens.
The new discovery stemmed from work on inflammatory bowel disease, which often causes patients to carry larger than normal populations of fungi in their guts. ...
Arctic stew: Understanding how high-latitude lakes respond to and affect climate change
2021-02-05
To arrive at Nunavut, turn left at the Dakotas and head north. You can't miss it--the vast tundra territory covers almost a million square miles of northern Canada. Relatively few people call this lake-scattered landscape home, but the region plays a crucial role in understanding global climate change. New research from Soren Brothers, assistant professor in the Department of Watershed Sciences and Ecology Center, details how lakes in Nunavut could have a big impact on carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, and it's not all bad news--at least for now. Brothers examined 23 years of data from lakes near Rankin Inlet. He noted a peculiarity--as the lakes warmed, their carbon dioxide concentrations fell. ...
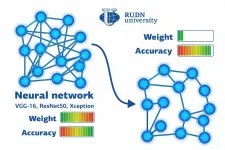
RUDN University mathematicians reduced neural network size six times without post-training
2021-02-05
A team of mathematicians from RUDN University found a way to reduce the size of a trained neural network six times without spending additional resources on re-training it. The approach is based on finding a correlation between the weights of neural connections in the initial system and its simplified version. The results of the work were published in the Optical Memory and Neural Networks journal.
The structures of artificial neural networks and neurons in a living organism are based on the same principles. Nodes in a network are interconnected; some of them receive a signal, and some transmit it by activating or suppressing the next element in the chain. The processing of any signal (for ...
Study identifies 'Achilles heel' of bacteria linked to Crohn's disease
2021-02-05
The discovery of an "Achilles heel" in a type of gut bacteria that causes intestinal inflammation in patients with Crohn's disease may lead to more targeted therapies for the difficult to treat disease, according to Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators.
In a study published Feb. 3 in Cell Host and Microbe, the investigators showed that patients with Crohn's disease have an overabundance of a type of gut bacteria called adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC), which promotes inflammation in the intestine. Their experiments revealed ...
New research sheds light on vision loss in Batten disease
2021-02-05
Progressive vision loss, and eventually blindness, are the hallmarks of juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (JNCL) or CLN3-Batten disease. New research shows how the mutation associated with the disease could potentially lead to degeneration of light sensing photoreceptor cells in the retina, and subsequent vision loss.
"The prominence and early onset of retinal degeneration in JNCL makes it likely that cellular processes that are compromised in JNCL are critical for health and function of the retina," said Ruchira Signh, Ph.D., an associate professor in the Department of Ophthalmology and Center for Visual Science and lead author of the study which appears in the journal Communications Biology. "It is important to understand how vision loss is triggered in this disease, ...
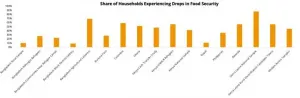
New study shows pandemic's toll on jobs, businesses, and food security in poorer countries
2021-02-05
Washington, D.C.. -- The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic caused a sharp decline in living standards and rising food insecurity in developing countries across the globe, according to a new study by an international team of economists.
The study, published Feb. 5 in the journal Science Advances, provides an in-depth view of the health crisis's initial socioeconomic effects in low- and middle-income countries, using detailed micro data collected from tens of thousands of households across nine countries. The phone surveys were conducted from April through July 2020 of nationally and sub-nationally representative samples in Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Colombia, Ghana, Kenya, Nepal, Philippines, Rwanda, and Sierra Leone. Across the board, study ...
New drug targets for childhood cancer neuroblastoma identified
2021-02-05
The largest single cell study to date of the childhood cancer, neuroblastoma, has answered important questions about the genesis of the disease. The researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) and the Princess Máxima Center for Pediatric Oncology, discovered that all neuroblastomas arise from a single type of embryonic cell called sympathoblasts.
The study, published today (5 February 2021) in Science Advances, sought to understand why neuroblastomas range in severity, with some easy to treat and others having relatively low five-year survival rates. The fact that all neuroblastomas arise from sympathoblasts makes them an attractive ...
Pandemic caused 'staggering' economic, human impact in developing counties, research says
2021-02-05
Berkeley -- The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic last year led to a devastating loss of jobs and income across the global south, threatening hundreds of millions of people with hunger and lost savings and raising an array of risks for children, according to new research co-authored at the University of California, Berkeley.
The research, to be published Friday Feb. 5, 2021, in the journal Science Advances, found "staggering" income losses after the pandemic emerged last year, with a median 70% of households across nine countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America reporting financial losses. By April last year, roughly 50% ...
Fingerprint for the formation of nitrous oxide emissions
2021-02-05
Scientists led by Eliza Harris and Michael Bahn from the Institute of Ecology at the University of Innsbruck have succeeded in studying emissions of the greenhouse gas N2O under the influence of environmental impacts in an unprecedented level of detail. The study, which has now been published in Science Advances, is thus also a starting point for the creation of models that could predict future trends in the greenhouse gas emission dynamics of ecosystems under global climate change.
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a potent greenhouse gas whose atmospheric growth rate has accelerated over the past decade. The largest share of anthropogenic N2O emissions results from the fertilization of soils with nitrogen, which is converted into N2O via various abiotic ...
Genes for face shape identified
2021-02-05
Genes that determine the shape of a person's facial profile have been discovered by a UCL-led research team.
The researchers identified 32 gene regions that influenced facial features such as nose, lip, jaw, and brow shape, nine of which were entirely new discoveries while the others validated genes with prior limited evidence.
The analysis of data from more than 6,000 volunteers across Latin America was published today in Science Advances.
The international research team, led from UCL, Aix-Marseille University and The Open University, found that one of the genes appears ...
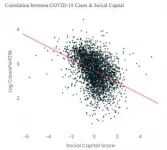
US counties with more social capital have fewer COVID-19 infections and deaths
2021-02-05
US counties with more social capital have fewer COVID-19 infections and deaths - perhaps because these communities have greater concern for the health of others.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: "How social capital helps communities weather the COVID-19 pandemic"
Funding: This research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research [CIHR, FRN-170368; PI: Cary Wu].
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0245135
...
Women's voices in the media still outnumbered by those of men - study
2021-02-05
New research from Simon Fraser University shows that women's voices continue to be underrepresented in the media, despite having prominent female leaders across Canada and internationally. Researchers in SFU's Discourse Processing Lab found that men outnumber women quoted in Canadian news media about three to one. The findings from the team's Gender Gap Tracker study were published this week in the journal PLOS ONE.
The research team collected data from seven major Canadian media outlets from October 2018 to September 2020. Over the two-year period, 29 per cent of people ...
New microscopy concept enters into force
2021-02-05
The development of scanning probe microscopes in the early 1980s brought a breakthrough in imaging, throwing open a window into the world at the nanoscale. The key idea is to scan an extremely sharp tip over a substrate and to record at each location the strength of the interaction between tip and surface. In scanning force microscopy, this interaction is -- as the name implies -- the force between tip and structures on the surface. This force is typically determined by measuring how the dynamics of a vibrating tip changes as it scans over objects deposited on a substrate. A common analogy is tapping a finger across a table and sensing objects placed ...
Gap between the 'haves' and 'have nots' widened by the COVID pandemic, an IU study found
2021-02-05
A new study by Indiana University found women, younger individuals, those with lower levels of formal education, and people of color are being hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal, found that Black adults were three times as likely as whites to report food insecurity, being laid off, or being unemployed during the pandemic. Additionally, residents without a college degree were twice as likely to report food insecurity (compared to those with some college) while those not completing high school are four times as likely to report it, compared ...
COVID-19 transmission extremely low at group of North Carolina day camps
2021-02-05
Cases of symptomatic COVID-19 were extremely low among children and staff at a network of YMCA summer camps held last year in North Carolina that took precautions like masking and physical distancing, with close to zero transmissions occurring at the camps, according to researchers at Duke Health, Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian.
In the camps' 2020 sessions, there were 19 cases of COVID-19 among 5,344 staff and 1,486 youth, only two of which were linked to possible on-site transmission at a group of YMCA of the Triangle camps, at a time ...
[1] ... [2660]
[2661]
[2662]
[2663]
[2664]
[2665]
[2666]
[2667]
2668
[2669]
[2670]
[2671]
[2672]
[2673]
[2674]
[2675]
[2676]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.