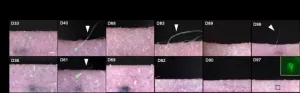
<i>Oncotarget</i>: Combination of copanlisib with cetuximab improves tumor response
2021-02-10
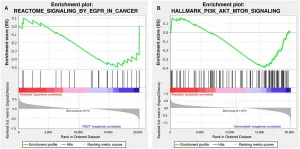
Oncotarget published "Combination of copanlisib with cetuximab improves tumor response in cetuximab-resistant patient-derived xenografts of head and neck cancer" which reported that HNSCC is frequently associated with either amplification or mutational changes in the PI3K pathway, making PI3K an attractive target, particularly in cetuximab-resistant tumors.
Here, the authors explored the antitumor activity of the selective, pan-class I PI3K inhibitor copanlisib with predominant activity towards PI3Kα and δ in monotherapy and in combination with cetuximab using a mouse clinical trial set-up with 33 patient-derived xenograft models with known HPV and PI3K mutational status and available data ...
Researchers unravel what makes someone a COVID-19 super-spreader
2021-02-10
Scientists and public health experts have long known that certain individuals, termed "super-spreaders," can transmit COVID-19 with incredible efficiency and devastating consequences.
Now, researchers at Tulane University, Harvard University, MIT and Massachusetts General Hospital have learned that obesity, age and COVID-19 infection correlate with a propensity to breathe out more respiratory droplets -- key spreaders of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Their findings were published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Using data from an observational study of 194 healthy people and an experimental study of nonhuman primates with COVID-19, researchers found that exhaled aerosol particles vary greatly ...
Sinai team builds first model acute myeloid leukemia progression using CRISPR
2021-02-10
(New York, NY) February 10, 2021 - A research team led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (Icahn Mount Sinai) has built the first cellular model to depict the evolution of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), from its early to late stages. By using gene editing technologies to alter genes that make cells malignant, the team was able to identify potential therapeutic targets for early disease stages. The study was reported in the journal Cell Stem Cell in February.
The therapeutic targets could be applicable not just to AML but also to the blood cancer myelodysplastic syndrome and clonal hematopoiesis, which is often a preleukemic condition.
"We essentially built from scratch a model of leukemia that characterizes the ...
Research shows emissions of banned ozone-depleting substance are back on the decline
2021-02-10
Global emissions of a potent substance notorious for depleting the Earth's ozone layer - the protective barrier which absorbs the Sun's harmful UV rays - have fallen rapidly and are now back on the decline, according to new research.
Two international studies published today in Nature, show emissions of CFC-11, one of the many chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) chemicals once widely used in refrigerators and insulating foams, are back on the decline less than two years after the exposure of their shock resurgence in the wake of suspected rogue production.
Dr Luke Western, from the University of Bristol, a co-lead author of one ...
Novel protein could reverse severe muscle wasting in disease, aging and trauma
2021-02-10
When we tear a muscle " stem cells within it repair the problem. We can see this occurring not only in severe muscle wasting diseases such as muscular dystrophy and in war veterans who survive catastrophic limb injuries, but also in our day to day lives when we pull a muscle.
Also when we age and become frail we lose much of our muscle and our stem cells don't seem to be able to work as well as we age.
These muscle stem cells are invisible engines that drive the tissue's growth and repair after such injuries. But growing these cells in the lab and then using them to therapeutically replace damaged muscle has been frustratingly difficult.
Researchers at the Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute at Monash University in Melbourne, ...
Earliest signs of an immune response found in developing embryos
2021-02-10
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) reveal that newly formed embryos clear dying cells to maximise their chances of survival. It is the earliest display of an innate immune response found in vertebrate animals to date.
The findings, which are published today in the journal Nature, may aid future efforts to understand why some embryos fail to form in the earliest stages of development, and lead to new clinical efforts in treating infertility or early miscarriages.
An embryo is fragile in the first hours after its formation. Rapid cell division and environmental stress make them prone to cellular errors, which in turn cause the sporadic death of embryonic stem cells. This is ...
Scientists develop new, faster method for seeking out dark matter
2021-02-10
For nearly a century, scientists have worked to unravel the mystery of dark matter--an elusive substance that spreads through the universe and likely makes up much of its mass, but has so far proven impossible to detect in experiments. Now, a team of researchers have used an innovative technique called "quantum squeezing" to dramatically speed up the search for one candidate for dark matter in the lab.
The findings, published today in the journal Nature, center on an incredibly lightweight and as-of-yet undiscovered particle called the axion. According to theory, axions are likely billions to trillions of times smaller than electrons and may have been created during the Big Bang in humungous numbers--enough ...
Factors associated with racial differences in deaths among nursing home residents with COVID-19 in US
2021-02-10
What The Study Did: This observational study describes differences in the number of COVID-19 deaths by nursing home racial composition and examines the factors associated with these differences.
Authors: Rebecca J. Gorges, Ph.D., of the University of Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37431)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
Role of dermatologists in early HIV/AIDS epidemic
2021-02-10
What The Study Did: This article revisits the role of dermatologists in the early HIV/AIDS epidemic for the 40th anniversary of the epidemic.
Authors: Heather Milbar, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.5545)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
Racial, ethnic differences in deceased organ donation
2021-02-10
What The Study Did: Researchers examined changes in how organ donation from deceased donors differed by race and ethnicity in the United States over time.
Authors: Dorry L. Segev, M.D., Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2020.7083)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news ...
Silicon chip provides low cost solution to help machines see the world clearly
2021-02-10
Researchers in Southampton and San Francisco have developed the first compact 3D LiDAR imaging system that can match and exceed the performance and accuracy of most advanced, mechanical systems currently used.
3D LiDAR can provide accurate imaging and mapping for many applications; it is the "eyes" for autonomous cars and is used in facial recognition software and by autonomous robots and drones. Accurate imaging is essential for machines to map and interact with the physical world but the size and costs of the technology currently needed has limited LIDAR's use in ...
Bone marrow 'map' opens path to organoid-like blood stem cell production
2021-02-10
CINCINNATI--Imagine a day when clinicians treating people with blood diseases such as leukemia or multiple myeloma can send in requests for laboratories to custom-produce specific types of blood cells to replace those affected by the disease.
That day became one step closer to reality with a new study led by experts at Cincinnati Children's that provides powerful new insights into how bone marrow tissue works.
The study, published Feb. 10, 2021 in Nature, was led by senior author Daniel Lucas, PhD, and first authors Jizhou Zhang, MD, and Qingqing Wu, PhD, from the Division of Experimental Hematology and Cancer Biology. Co-authors include a team of scientists from Cincinnati Children's and the University of Cincinnati, plus collaborators in Colorado, Texas and Michigan.
The ...
A new method to search for potentially habitable planets
2021-02-10
Imaging planets orbiting around nearby stars, which could potentially harbour life, has become a possibility thanks to the progress made in observational methods by an international team of astronomers. First candidate: Alpha Centauri, a system similar to ours, "only" 4.3 light years away. This study is the subject of a publication in the journal Nature Communications.
Efforts to obtain direct images of exoplanets - planets outside our solar system - have so far been hampered by technological limitations, which have led to a bias towards detecting planets much larger than Jupiter, around very young stars and far from the habitable zone, the area in which a planet may have liquid water on its surface, and thus ...
Difficulties to care for ICU patients caused by COVID-19
2021-02-10
Researchers from the University of Seville's Nursing Department, with the collaboration of professionals from the ICU at Virgen Macarena University Hospital in Seville, have analysed the key factors in caring for critical COVID-19 patients during the first wave of the pandemic. Their study concludes that nursing care was impacted by fear and isolation, which made it difficult to maintain the human experience of health care.
The break down in the humanising trend of ICU care during this period was mainly the result of the isolation of COVID-19 patients. This, along with the personal protection equipment worn by staff to prevent becoming infected ...
Rapid ice retreat during last deglaciation parallels current melt rates
2021-02-10
10,000 km2 of ice disappeared in a blink of an eye from an ice sheet in the Storfjorden Through offshore Svalbard, a new study shows. This dramatic break off was preceded by quite a rapid melt of 2.5 kilometres of ice a year. This parallels the current melt rates in Antarctica and Greenland and worries the scientists behind the study.
"Our measurements of the ice retreat in Storfjorden Through show that the prevailing conditions to the great break off, match what we see in Antarctica and Greenland today. It is uncanny. There are new studies published almost weekly, that show that the retreat of current ice sheets is two to four km a year and that it's speeding up." Says CAGE-professor and first author Tine Lander Rasmussen.
Climatically unstable period
The last deglaciation, ...
A scalable method for the large-area integration of 2D materials
2021-02-10
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have a huge potential for providing devices with much smaller size and extended functionalities with respect to what can be achieved with today's silicon technologies. But to exploit this potential we must be able to integrate 2D materials into semiconductor manufacturing lines - a notoriously difficult step. A team of Graphene Flagship researchers in Sweden and Germany now reports a new method to make this work.
The technique, just published in Nature Communications by researchers from Graphene Flagship partners RWTH Aachen University, Universität der Bundeswehr ...
Young and restless, old and focused: Age-differences in mind-wandering
2021-02-10
New research from Trinity College Dublin suggests that older adults can be more focused, less impeded by anxiety and less mentally restless than younger adults. The team at the Trinity College Institute of Neuroscience (TCIN) (today, Wednesday, 10th February, 2021) show that older adults appear to mitigate the negative aspects of cognitive decline by increasing motivation and adopting more efficient strategies to suspend the wandering mind when focus is required.
The study, published in the journal Psychology and Aging (American Psychological Association) is the first to adjudicate between competing theories of age-related ...
Vitamin D supplementation: possible gain in life years combined with cost savings
2021-02-10
In recent years, three meta-analyses of clinical studies have come to the conclusion that vitamin D supplementation was associated with a reduction in the mortality rate from cancer of around 13 percent. Scientists at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) have now transferred these results to the situation in Germany and calculated: If all Germans over the age of 50 were to take vitamin D supplements, up to 30,000 cancer deaths per year could possibly be avoided and more than 300,000 years of life could be gained - in addition, health care costs could be saved.
For several years now, scientists have been investigating the influence of an adequate supply of vitamin D on the ...
Why overfishing leads to smaller cod
2021-02-10
Overfishing, hunting and intensive agriculture and forestry can sometimes contribute to plants and animals becoming endangered. New research from Lund University in Sweden and University of Toronto can now show why this leads to entire populations becoming smaller in size, as well as reproducing earlier. The study is published in the journal PNAS.
Researchers from Lund and Toronto are behind the study conducted on five different species of damselflies. They have studied how different environmental factors affect when and at what size the damselflies begin to reproduce. In the study, the researchers also shed light on how overfishing off the coast ...
A rare observation of a vampire bat adopting an unrelated pup
2021-02-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio - The death of a vampire bat 19 days after giving birth presented scientists studying the animals in 2019 with an unexpected chance to observe a rare event: a female bat's adoption of an unrelated baby.
The researchers had captured common vampire bats in Panama as part of ongoing studies of the formation of cooperative relationships among strangers. The team used infrared surveillance cameras to observe six hours of vampire bat activity spaced over the span of each day.
Two unrelated and unfamiliar female bats were observed forming a social bond based on mutual grooming and food sharing that increased over time. The researchers had named them BD and Lilith.
Lilith ...
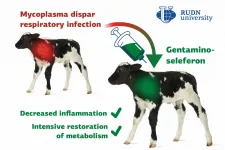
RUDN University veterinarians tested a new drug against pneumonia in calves
2021-02-10
Respiratory tract diseases in young animals of the cattle are a big issue for world agriculture and food safety because a bacterium that causes them is resistant to most antibiotics. A team of veterinarians from RUDN University developed and tested a complex preparation called gentaminoseleferon that could help treat respiratory infection in calves. The results of the study were published in the Veterinary World journal.
Bacteria of the genus Mycoplasma cause many infectious diseases in animals, including atypical pneumonia, other respiratory tract conditions, reproductive pathologies, arthritis, keratoconjunctivitis, mastitis, and so on. The genus includes about 200 species of bacteria, and all of them ...
New weapon against resistant bacteria
2021-02-10
Every day, people die from simple infections even though they have been treated with antibiotics. This is because more and more bacteria have become resistant to the types of antibiotics that doctors can prescribe.
- It's a huge societal problem and a crisis that we must solve. For example, by developing new antibiotics that can defeat the resistant bacteria, says professor of chemistry at the Department of Physics, Chemistry and Pharmacy, University of Southern Denmark, Poul Nielsen.
Resistant bacteria are not only known from pig farms, where it is becoming increasingly difficult to keep the pigsties disease-free. Hospitals are also experiencing with increasing regularity that, for example, infectious diseases cannot be controlled in patients. Thus, ...
Long-term stress linked to increased risk of heart attack
2021-02-10
Can long-term stress lead to heart attacks? Most people would probably answer in the affirmative, but the scientific evidence of this is scarce. A new study by researchers from Linköping University in Sweden reveals that the levels of the stress hormone cortisol were increased in the months preceding a heart attack. The results, published in Scientific Reports, suggest that long-term stress is a risk factor for heart attacks.
"The levels of the stress hormone cortisol differed between people who have had a heart attack and those not affected. This suggests that cortisol in hair may be a new risk marker for heart attacks. We must take stress seriously", says Professor Tomas Faresjö from the Department of Health, ...
Endovascular aneurysm repair linked to higher readmission rates
2021-02-10
Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (rAAA) are responsible for nearly 2% of all deaths in U.S. men over the age of 65. Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) has emerged as a newer and less invasive alternative to open repair for rAAA, and current guidelines recommend EVAR as a first-line option for treatment of rAAA when certain criteria are met. But researchers from the University of Missouri School of Medicine have discovered that while EVAR is more commonly utilized for rAA, shortens hospital stay and has a lower initial mortality rate, the odds of ...
A recipe for regenerating bioengineered hair
2021-02-10
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research in Japan have discovered a recipe for continuous cyclical regeneration of cultured hair follicles from hair follicle stem cells.
Scientists have been making waves in recent years by developing ways to grow a variety of useful items in laboratories, from meat and diamonds to retinas and other organoids. At the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research in Japan, a team led by Takashi Tsuji has been working on ways to regenerate lost hair from stem cells. In an important step, a new study identifies a population of hair follicle stem cells in the skin and a recipe for normal cyclical regeneration in the lab.
The researchers took fur and whisker cells ...
[1] ... [2646]
[2647]
[2648]
[2649]
[2650]
[2651]
[2652]
[2653]
2654
[2655]
[2656]
[2657]
[2658]
[2659]
[2660]
[2661]
[2662]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.