Slow motion precursors give earthquakes the fast slip
2021-02-16
Ithaca, N.Y. - At a glacier near the South Pole, earth scientists have found evidence of a quiet, slow-motion fault slip that triggers strong, fast-slip earthquakes many miles away, according to Cornell University research published in Science Advances.
During an earthquake, a fast slip happens when energy builds up underground and is released quickly along a fault. Blocks of earth rapidly slide against one another.
However, at an Antarctic glacier called Whillans Ice Plain, the earth scientists show that "slow slips" precede dozens of large magnitude 7 earthquakes. "We found that there is almost always a precursory 'slow slip' before an earthquake," ...
Combination treatment for common glioma type shows promise in mice
2021-02-16
WHAT
Gliomas are common brain tumors that comprise about one third of all cancers of the nervous system. In a study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers tested a novel combination treatment approach on mice with tumors with characteristics similar to human astrocytomas--a type of slow-growing glioma--and found tumor regression in 60 percent of the mice treated. These encouraging results, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, could be the first step toward developing a treatment for this type of brain cancer.
Led by senior authors Maria Castro, Ph.D. and Pedro Lowenstein, M.D., Ph.D. along with a team of researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Centerb in Ann Arbor specifically ...
High public support for strict COVID measures but lower level of trust in gov
2021-02-16
High levels of public support for strict measures to control COVID-19 during the first wave of the pandemic did not reflect high levels of public trust in the UK government's honesty, transparency or motives, suggests a new study published in PLOS One.
The 'mixed-methods' project, a collaboration between the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) and University College London (UCL), involved collecting data from more than 9,000 adults living in the UK using an online survey.
It found that during the first wave of COVID-19 (April 2020) 95% of participants were in support of the government having powers to enforce behaviour change. However, only around half (52%) thought that the government was actually doing a good job of controlling COVID-19. Even fewer (36%) thought ...
A genetic variant inherited from Neanderthals reduces the risk of severe COVID-19
2021-02-16
New research has found that a group of genes that reduces the risk of developing severe COVID-19 by around 20% is inherited from Neanderthals
These genes, located on chromosome 12, code for enzymes that play a vital role in helping cells destroy the genomes of invading viruses
The study suggests that enzymes produced by the Neanderthal variant of these genes are more efficient which helps protect against severe COVID-19
This genetic variant was passed to humans around 60,000 years ago via interbreeding between modern humans and Neanderthals
The genetic variant has increased in frequency over the last millennium and is now found ...
Biodegradable microcapsules deliver nerve growth factor to guide neuronal development
2021-02-16
Researchers from Skoltech and their colleagues have demonstrated that nanoengineered biodegradable microcapsules can guide the development of hippocampal neurons in an in vitro experiment. The microcapsules deliver nerve growth factor, a peptide necessary for neuron growth. The paper describing this work was published in the journal Pharmaceutics.
Many neurodegenerative conditions that can lead to severe disorders are associated with depleted levels of growth factors in the brain - neuropeptides that help neurons grow, proliferate and survive. Some clinical studies of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases have shown that delivering these growth factors to specific degenerating neurons can have a therapeutic effect. ...
NREL heats up thermal energy storage with new solution meant to ease grid stress
2021-02-16
Scientists from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have developed a simple way to better evaluate the potential of novel materials to store or release heat on demand in your home, office, or other building in a way that more efficiently manages the building's energy use.
Their work, featured in Nature Energy, proposes a new design method that could make the process of heating and cooling buildings more manageable, less expensive, more efficient, and better prepared to flexibly manage power from renewable energy sources that do not always deliver ...
Neandertal gene variants both increase and decrease the risk for severe COVID-19
2021-02-16
Last year, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany showed that a major genetic risk factor for severe COVID-19 is inherited from Neandertals. Now the same researchers show, in a study published in PNAS, that Neandertals also contributed a protective variant. Half of all people outside Africa carry a Neandertal gene variant that reduces the risk of needing intensive care for COVID-19 by 20 percent.
Some people become seriously ill when infected with SARS-CoV-2 while others get only mild or no symptoms. In addition to ...
Researchers solve riddle of plant immune system
2021-02-16
How do plants build resilience? An international research team led by the University of Göttingen studied the molecular mechanisms of the plant immune system. They were able to show a connection between a relatively unknown gene and resistance to pathogens. The results of the study were published in the journal The Plant Cell.
Scientists from "PRoTECT" - Plant Responses To Eliminate Critical Threats - investigated the molecular mechanisms of the immune system of a small flowering plant known as thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana). PRoTECT ...
Nursing home staff responses to pandemic reveal resilience, shortcomings: Concordia study
2021-02-16
The ongoing health disaster of the past 12 months has exposed the crises facing nursing homes in Canada and the United States and the struggles of the staff working in them.
Writing in the Journal of Comparative Policy Analysis: Research and Practice, PhD student Daniel Dickson, his supervisor Patrik Marier, professor of political science, and co-author Robert Henry Cox of the University of South Carolina perform a comparative analysis of those workers' experiences. In it, they look at Quebec (including those at government-run CHSLDs), British Columbia, Washington State and Ohio ...
Researchers take early step toward leukemia drug therapy
2021-02-16
Hamilton, ON (February 16, 2021) - A McMaster stem cell research team has made an important early step in developing a new class of therapeutics for patients with a deadly blood cancer.
The team has discovered that for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients, there is a dopamine receptor pathway that becomes abnormally activated in the cancer stem cells. This inspired the clinical investigation of a dopamine receptor-inhibiting drug thioridazine as a new therapy for patients, and their focus on adult AML has revealed encouraging results.
AML is a particularly deadly cancer that starts with a DNA mutation in the blood stem cells of the bone marrow that produce too many infection-fighting white blood cells. According ...
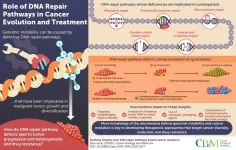
Fixer-upper: Understanding the DNA repair toolkit to chart cancer evolution
2021-02-16
The ongoing fight of science against cancer has made great strides, but cancer cells have not made it easy. The complexity of cancer cells and their adaptive evolutionary nature complicate the search for effective cures. Multiple DNA repair pathways in healthy cells typically work to rectify DNA damages caused by sources within the organism, like spontaneous DNA mutations, or from outside, like ultraviolet radiation.
But what happens when these pathways malfunction? It is known that deficiencies in these pathways increase the instability of the genes, and this causes cancer to develop. Therefore, detailed knowledge of how DNA repair pathways participate in this process is crucial for tracking tumor progression, understanding the emergence of drug ...
Identifying "ugly ducklings" to catch skin cancer earlier
2021-02-16
Melanoma is by far the deadliest form of skin cancer, killing more than 7,000 people in the United States in 2019 alone. Early detection of the disease dramatically reduces the risk of death and the costs of treatment, but widespread melanoma screening is not currently feasible. There are about 12,000 practicing dermatologists in the US, and they would each need to see 27,416 patients per year to screen the entire population for suspicious pigmented lesions (SPLs) that can indicate cancer.
Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems have been developed in recent years to try to solve this problem by analyzing images of ...
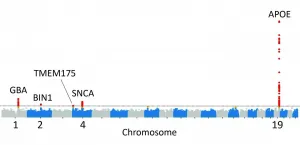
Genetic study of Lewy body dementia supports ties to Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases
2021-02-16
In a study led by National Institutes of Health (NIH) researchers, scientists found that five genes may play a critical role in determining whether a person will suffer from Lewy body dementia, a devastating disorder that riddles the brain with clumps of abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies. Lewy bodies are also a hallmark of Parkinson's disease. The results, published in Nature Genetics, not only supported the disease's ties to Parkinson's disease but also suggested that people who have Lewy body dementia may share similar genetic profiles to those who have Alzheimer's disease.
"Lewy body dementia is a devastating brain disorder for which we have no effective treatments. Patients often appear to suffer the worst of both Alzheimer's ...
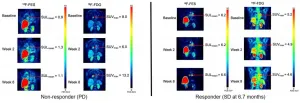
Molecular imaging determines effectiveness of novel metastatic breast cancer treatment
2021-02-16
Reston, VA--Molecular imaging can successfully predict response to a novel treatment for ER-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer patients who are resistant to hormonal therapy. According to research published in the February issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine, positron emission tomography (PET) imaging using an imaging agent called 18F-fluoroestradiol can help to determine which patients could benefit from treatments that could spare them from unnecessary chemotherapy.
Nearly two-thirds of invasive breast cancers are ER-positive, and endocrine therapy is the mainstay of treatment for these tumors because of its favorable toxicity profile and efficacy. Should cancer progress in these patients, however, salvage endocrine therapy with molecularly targeted agents ...
Antibody-based COVID-19 treatments work best in concert with immune cells
2021-02-16
Of the nine treatments and preventives for COVID-19 authorized for emergency use by the Food and Drug Administration, three are drugs made from so-called monoclonal antibodies. Such drugs provide patients with ready-made antibodies that neutralize the virus, bypassing the body's slower and sometimes less effective process of making its own antibodies.
But such therapies were developed without detailed information about how antibodies interact with the rest of the immune system during COVID-19. Faced with a new, deadly and fast-spreading disease, drug designers started work ...
Radioactive bone cement found to be safer in treating spinal tumors
2021-02-16
Irvine, Calif., Feb. 16, 2021 -- A radioactive bone cement that's injected into bone to provide support and local irradiation is proving to be a safer alternative to conventional radiation therapy for bone tumors, according to a study led by University of California, Irvine researchers.
The study shows that this brachytherapy cement can be placed into spinal bones to directly irradiate tumors without harming the spinal cord, and the radioactive material will stay localized in the bones, which promises to virtually eliminate side effects.
Lead researcher Joyce Keyak, UCI professor of radiological sciences, presented the results at the 2021 annual meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society, which was held virtually Feb. 12-16.
Cancers ...
Star employees get most of the credit - and blame
2021-02-16
ITHACA, N.Y. - Working with a "star" employee - someone who demonstrates exceptional performance and enjoys broad visibility relative to industry peers - offers both risks and rewards, according to new research from the Cornell University's ILR School.
In collaborations, stars tend to get more than their share of the credit when things go well - and more of the blame when projects don't succeed, according to "Shadows and Shields: Stars Limit Their Collaborators' Exposure to Attributions of Both Credit and Blame," published Dec. 10, 2020, by Personnel Psychology.
"We look at ...
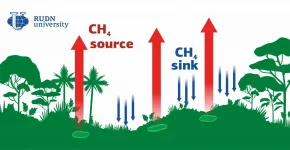
RUDN University biologists studied the effect of jungles on global warming
2021-02-16
Biologists from RUDN University described the role of tropical rainforests in the production of methane, the second most harmful greenhouse gas after CO2. It turned out that some areas of rainforests not only consumed methane but also emitted it. The results of the study were published in the Forests journal.
Although the share of methane in the atmosphere is relatively small (less than 1%), its contribution to the greenhouse effect is 20 to 30 times bigger than that of the same amount of carbon dioxide. The tropics are one of the main sources of methane. Previously, soil scientists used to focus only on swampy tropical areas, because methane-producing microorganisms live and multiply in the anaerobic conditions of swamps. As for ...
Model helps predict which patients will benefit most from PSMA PET scan
2021-02-16
UCLA RESEARCH ALERT
FINDINGS
A new study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center helps identify which patients with prostate cancer will benefit most from the use of prostate-specific membrane antigen PET imaging, PSMA PET, a novel imaging technique that recently was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
By studying different variables and risk factors, researchers created a model that can be used in the clinic to identify patients who may have more extensive disease than anticipated and identify patients who are at higher risk of prostate cancer spreading to lymph nodes in the pelvis and beyond. The team found the percent ...
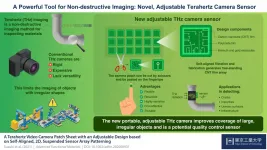
Novel flexible terahertz camera can inspect objects with diverse shapes
2021-02-16
In today's digital age, the use of "Internet-of-things" (devices embedded with softwares and sensors) has become widespread. These devices include wireless equipment, autonomous machinery, wearable sensors, and security systems. With their intricate structures and properties stems the need to scrutinize them closely to assess their safety and utility and rule out any potential defects. But, at the same time, damage to the device during inspection must be avoided.
Terahertz (THz) imaging, based on radiation with frequencies between 0.1 and 10 THz, is one such non-destructive method that is rapidly gaining popularity owing ...
Unexpected findings on weight loss and breast cancer from international study in JNCCN
2021-02-16
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [February 16, 2021] -- New research in the February 2021 issue of JNCCN--Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network examined body mass index (BMI) data for people with HER2-positive early breast cancer, and found a 5% weight loss in patients over two years in was associated with worse outcomes. Weight gain over the same time period did not affect survival rates.
"The finding that weight loss, and not weight gain, was associated with worse outcomes is unexpected," said lead researcher Samuel Martel, MD, Universitè de Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada, who worked with researchers in Belgium, Brazil, Germany, Italy, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom, as well as the ...
A sharper look at the interior of semiconductors
2021-02-16
Images provide information - what we can observe with our own eyes enables us to understand. Constantly expanding the field of perception into dimensions that are initially hidden from the naked eye, drives science forward. Today, increasingly powerful microscopes let us see into the cells and tissues of living organisms, into the world of microorganisms as well as into inanimate nature. But even the best microscopes have their limits. "To be able to observe structures and processes down to the nanoscale level and below, we need new methods and technologies," says Dr Silvio Fuchs from the Institute of Optics and Quantum Electronics at the University of Jena. This applies in particular to technological ...
Study sheds light on how people cope with health challenges and medical debt
2021-02-16
A recent qualitative study sheds light on how people cope with health and financial challenges, highlighting the important role that communication plays in these coping strategies.
"This is one of the first studies to look at how people respond to the combination of financial uncertainties and health uncertainties," says Lynsey Romo, first author of the study and an associate professor of communication at North Carolina State University. "And it drives home that uncertainty about money and uncertainty about health go hand in hand. Financial limitations created significant health challenges - such as an inability to afford prescription medications. And health problems created significant expenses leading to serious financial challenges.
"The study also highlights that these ...
New dataset opens Estonian soil information for versatile use
2021-02-16
A comprehensive database of Estonian soils and a map application has been completed in cooperation with researchers of the University of Tartu and the Estonian University of Life Sciences. The database makes Estonian soil information easily accessible and can be used from local farm-scale to national-level big data statistical analysis and machine-learning models.
"Soil data is possibly the most undervalued and yet complicated type of environmental data there is. The diversity of organic, chemical, living and dead materials that make up a handful of dirt is astounding," said Alexander Kmoch, ...
It's morally wrong for rich nations to hoard COVID-19 vaccine
2021-02-16
BINGHAMTON, NY -- Rich nations should not engage in "vaccine nationalism" and keep the COVID-19 vaccine to themselves when poorer nations need them, according to Nicole Hassoun, professor of philosophy at Binghamton University, State University of New York. Hassoun's paper, "Against Vaccine Nationalism," was published in the Journal of Medical Ethics.
While rich countries like the US and UK are starting to vaccinate their populations against COVID-19, poor countries may lack access to a vaccine for years. Canada, for instance, has already secured enough to vaccinate its entire population nine times over, and the US, European Union, UK, Australia, and Japan can vaccinate their populations between 2-8x.
"Vaccine nationalism ...
[1] ... [2639]
[2640]
[2641]
[2642]
[2643]
[2644]
[2645]
[2646]
2647
[2648]
[2649]
[2650]
[2651]
[2652]
[2653]
[2654]
[2655]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.