Upending complex crystal formation
2021-02-17
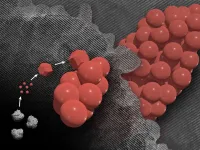
When materials reach extremely small size scales, strange things begin to happen. One of those phenomena is the formation of mesocrystals.
Despite being composed of separate individual crystals, mesocrystals come together to form a larger, fused structure that behaves as a pure, single crystal. However, these processes happen at scales far too small for the human eye to see and their creation is extremely challenging to observe.
Because of these challenges, scientists had not been able to confirm exactly how mesocrystals form.
Now new research by a Pacific ...
Fueling the future: Novel two-polymer membrane boosts hydrogen fuel cell performance
2021-02-17
A considerable portion of the efforts to realize a sustainable world has gone into developing hydrogen fuel cells so that a hydrogen economy can be achieved. Fuel cells have distinctive advantages: high energy-conversion efficiencies (up to 70%) and a clean by-product, water. In the past decade, anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFC), which convert chemical energy to electrical energy via the transport of negatively charged ions (anions) through a membrane, have received attention due to their low-cost and relative environment friendliness compared ...
3D microscopy clarifies understanding of body's immune response to obesity
2021-02-17
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Researchers who focus on fat know that some adipose tissue is more prone to inflammation-related comorbidities than others, but the reasons why are not well understood. Thanks to a new analytical technique, scientists are getting a clearer view of the microenvironments found within adipose tissue associated with obesity. This advance may illuminate why some adipose tissues are more prone to inflammation - leading to diseases like type 2 diabetes, cancer and cardiovascular disorders - and help direct future drug therapies to treat obesity.
In a new study, University of Illinois ...
NASA-funded network tracks the recent rise and fall of ozone depleting pollutants
2021-02-17
A short-lived resurgence in the emission of ozone depleting pollutants in eastern China will not significantly delay the recovery of Earth's protective "sunscreen" layer, according to new research published Feb. 10 in Nature.
Stratospheric ozone, also known as Earth's ozone layer, helps shield us from the Sun's harmful Ultraviolet (UV) rays. Compounds like CFC-11 (Trichlorofluoromethane, also known as Freon-11), a chemical once considered safe and widely used as a refrigerant and in the production of insulation for buildings, rise to the stratosphere after emission on Earth's surface. Once in the atmosphere, CFC's are broken down by the UV light and result in the destruction of ozone molecules, both reducing stratospheric ozone concentrations globally ...
Neural network could help clinicians look for 'ugly duckling' pre-cancerous skin lesions
2021-02-17
A neural network system that analyzes photographs can rank and distinguish suspicious, potentially precancerous skin lesions, which can turn into the deadly skin malignancy melanoma if not caught and removed early. The system accurately scoped out suspicious lesions from 68 patients in a manner that mostly matched tried-and-true evaluations from dermatologists. The results suggest the platform could help clinicians spot suspicious lesions during clinical visits faster and on a larger scale, potentially allowing for earlier diagnosis and treatment. Melanoma is ...
Dr. Frederick Boop presents at the ISPN 2020 Virtual Meeting
2021-02-17
Understanding the molecular biology of brain tumors is key to prognosis and treatment said Le Bonheur Neuroscience Institute Co-Director Frederick Boop, MD, in his presentation "How Molecular Biology Impacts Clinical Practice" at the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery (ISPN) 2020 Virtual Meeting.
"Historically we have depended on what we see under a microscope to differentiate tumor types and determine prognosis and therapy," said Boop. "We know now that what we see doesn't necessarily predict how these tumors are going to behave."
Physicians are able to send a piece of a child's tumor to FoundationOne, an FDA-approved tissue-based broad companion diagnostic (CDx) for solid tumors, which provides the genomic alterations of that particular tumor. ...
Friends fur life help build skills for life
2021-02-17
A new UBC Okanagan study finds children not only reap the benefits of working with therapy dogs-they enjoy it too.
"Dog lovers often have an assumption that canine-assisted interventions are going to be effective because other people are going to love dogs," says Nicole Harris, who conducted this research while a master's student in the School of Education. "While we do frequently see children improve in therapy dog programs, we didn't have data to support that they enjoyed the time as well."
Harris was the lead researcher in the study that explored how children reacted while participating in a social skill-training program with therapy dogs.
The research saw 22 children from the Okanagan Boys and Girls ...
SuperAger brains resist protein tangles that lead to Alzheimer's
2021-02-17
Resistance to tangle formation may help preserve memory
SuperAgers have fewer tangles than normally aging individuals
Future research to see how SuperAgers are protected
CHICAGO - A new Northwestern Medicine study showed cognitive SuperAgers have resistance to the development of fibrous tangles in a brain region related to memory and which are known to be markers of Alzheimer's disease.
The tangles are made of the tau protein which forms structures that transport nutrients within the nerve cell. These tangles disrupt the cell's transport system, ...
FSU College of Medicine researcher develops new possibilities to prevent sudden cardiac death
2021-02-17
Nearly a half-million people a year die from sudden cardiac death (SCD) in the U.S. -- the result of malfunctions in the heart's electrical system.
A leading cause of SCD in young athletes is arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM), a genetic disease in which healthy heart muscle is replaced over time by scar tissue (fibrosis) and fat.
Stephen Chelko, an assistant professor of biomedical sciences at the Florida State University College of Medicine, has developed a better understanding of the pathological characteristics behind the disease, as well as promising avenues for ...
'Smart' asthma inhaler sensors improve pediatric asthma control
2021-02-17
The trial found that using sensor-based asthma inhalers may improve control of the condition and improve the quality of life for caregivers.
Greatest gains were among non-Hispanic Black participants, who experience more frequent and severe asthma than other groups.
Based on the study results, this asthma intervention should be considered for use by primary care, allergy and pulmonary care providers, to help engage diverse populations of pediatric asthma patients and their caregivers.
CHICAGO (February 17, 2021) -- Sensor-based inhalers integrated into health care providers' clinical workflows may help improve medication adherence and support children with asthma - and their families - to more effectively manage this condition, according ...
Toward a disease-sniffing device that rivals a dog's nose
2021-02-17
Numerous studies have shown that trained dogs can detect many kinds of disease -- including lung, breast, ovarian, bladder, and prostate cancers, and possibly Covid-19 -- simply through smell. In some cases, involving prostate cancer for example, the dogs had a 99 percent success rate in detecting the disease by sniffing patients' urine samples.
But it takes time to train such dogs, and their availability and time is limited. Scientists have been hunting for ways of automating the amazing olfactory capabilities of the canine nose and brain, in a compact device. Now, a team of researchers at MIT and other institutions has come up with a system that can detect the chemical and microbial content of an air sample with ...
Protein linked to Alzheimer's, strokes cleared from brain blood vessels
2021-02-17
As people age, a normal brain protein known as amyloid beta often starts to collect into harmful amyloid plaques in the brain. Such plaques can be the first step on the path to Alzheimer's dementia. When they form around blood vessels in the brain, a condition known as cerebral amyloid angiopathy, the plaques also raise the risk of strokes.
Several antibodies that target amyloid plaques have been studied as experimental treatments for Alzheimer's disease. Such antibodies also may have the potential to treat cerebral amyloid angiopathy, although they haven't yet been evaluated in clinical trials. ...
World's oldest DNA reveals how mammoths evolved
2021-02-17
An international team led by researchers at the Centre for Palaeogenetics in Stockholm has sequenced DNA recovered from mammoth remains that are up to 1.2 million years old. The analyses show that the Columbian mammoth that inhabited North America during the last ice age was a hybrid between the woolly mammoth and a previously unknown genetic lineage of mammoth. In addition, the study provides new insights into when and how fast mammoths became adapted to cold climate. These findings are published today in Nature.
Around one million years ago there were no woolly or Columbian mammoths, as they had not yet evolved. This was the time of their predecessor, the ...
Mentally ill kids become less healthy adults
2021-02-17
DURHAM, N.C. -- A new pair of studies from a Duke research team's long-term work in New Zealand make the case that mental health struggles in early life can lead to poorer physical health and advanced aging in adulthood.
But because mental health problems peak early in life and can be identified, the researchers say that more investment in prompt mental health care could be used to prevent later diseases and lower societal healthcare costs.
"The same people who experience psychiatric conditions when they are young go on to experience excess age-related physical diseases and neurodegenerative diseases when they are older adults," explained Terrie Moffitt, the Nannerl O. Keohane professor ...
A 'twisted elevator' could be key to understanding neurological diseases
2021-02-17
A University of Sydney-led international team of scientists has revealed the shape of one of the most important molecular machines in our cellsthe glutamate transporter, helping to explain how our brain cells communicate with one another.
Glutamate transporters are tiny proteins on the surface of all our cells that shut on and off the chemical signals that have a big role in making sure all cell-to-cell talk runs smoothly. They are also involved in nerve signalling, metabolism and learning and memory.
The researchers captured the transporters in exquisite detail using cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM), showing they look like a 'twisted elevator' embedded in the cell membrane.
This world-first discovery ...
One in five has a mutation that provides superior resilience to cold
2021-02-17
Almost one in five people lacks the protein α-actinin-3 in their muscle fibre. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden now show that more of the skeletal muscle of these individuals comprises slow-twitch muscle fibres, which are more durable and energy-efficient and provide better tolerance to low temperatures than fast-twitch muscle fibres. The results are published in the scientific journal The American Journal of Human Genetics.
Skeletal muscle comprises fast-twitch (white) fibres that fatigue quickly and slow-twitch (red) fibres that are more resistant to fatigue. The protein α-actinin-3, which is found only ...
Robotic dogs & laughter therapy: combating loneliness & isolation while social distancing
2021-02-17
Robotic dogs, laughter therapy and mindfulness are some of the ways that might help people - particularly the elderly - cope with loneliness and social isolation while social distancing, say researchers at the University of Cambridge.
A team at Cambridge's School of Medicine carried out a systematic review looking at the existing evidence on different approaches to tackling loneliness and social isolation. While all the individual studies were carried out pre-pandemic, the team considered which approaches might be feasible when people are still required to socially distance. Their results are published today in PLOS ONE.
At the start of the pandemic in the UK, over 1.5 million people were told they must self-isolate ...
Lakes isolated beneath Antarctic ice could be more amenable to life than thought
2021-02-17
Lakes underneath the Antarctic ice sheet could be more hospitable than previously thought, allowing them to host more microbial life.
This is the finding of a new study that could help researchers determine the best spots to search for microbes that could be unique to the region, having been isolated and evolving alone for millions of years. The work could even provide insights into similar lakes beneath the surfaces of icy moons orbiting Jupiter and Saturn, and the southern ice cap on Mars.
Lakes can form beneath the thick ice sheet of Antarctica where the weight of ice causes immense pressure at the base, lowering the melting point of ice. This, coupled with gentle heating from rocks below and the insulation provided by the ice from the cold air above, allows pools of liquid water ...
Researchers find diverse supportive partnerships among older gay men with and without HIV
2021-02-17
WASHINGTON --- Recent data reveals that gay men living with HIV report having supportive relationships with family, friends, or in informal relationships rather than with primary romantic partners, while gay men who are HIV negative report having relationships mainly with primary partners. Additionally, gay men living with HIV were more likely to report no primary or secondary supportive partnerships compared to men who are HIV negative. The analysis was led by researchers at Georgetown University Medical Center.
Along with successful HIV treatments, it is known that the presence of social support impacts long-term survival among men living with HIV. However, little has been known about the types of ...
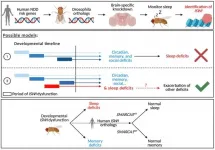
High-risk gene for neurodevelopmental disorders linked to sleep problems in flies
2021-02-17
PHILADELPHIA - The mutation of a gene that has been associated with neurodevelopmental disorders like autism spectrum disorder led to marked sleep disturbances in fruit flies, according to a new study from scientists in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The findings, published Wednesday in Science Advances, provide further evidence that sleep is linked to early neurodevelopmental processes and could guide future treatments for patients.
While sleep disruption is a commonly reported symptom across neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism, it is often treated clinically as a "secondary effect" ...
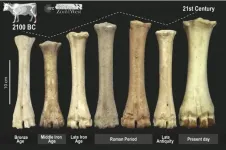
Changing livestock in ancient Europe reflect political shifts
2021-02-17
In ancient European settlements, livestock use was likely primarily determined by political structure and market demands, according to a study published February 17, 2021 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ariadna Nieto-Espinet and colleagues of the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Barcelona.
Zooarchaeology - the study of animal remains from archaeological sites - has great potential to provide information on past human communities. Livestock preferences are known to have changed over time in Europe, but little is known about how much these changes are influenced by environmental, economic, or political conditions of ancient settlements.
In ...
More sustainable recycling of plastics
2021-02-17
The new method works without extremely high temperatures, is therefore more energy-efficient and has a significantly higher recovery rate (approx. 96 per cent of the starting material) than established processes. These findings will be published on 17 February 2021 in the scientific journal Nature.
Mechanical recycling vs. chemical recycling
"The direct re-utilization of plastics is often hampered by the fact that, in practice, mechanical recycling only functions to a limited degree - because the plastics are contaminated and mixed with additives, which impairs the properties ...
This robot doesn't need any electronics
2021-02-17
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have created a four-legged soft robot that doesn't need any electronics to work. The robot only needs a constant source of pressurized air for all its functions, including its controls and locomotion systems.
The team, led by Michael T. Tolley, a professor of mechanical engineering at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego, details its findings in the Feb. 17, 2021 issue of the journal Science Robotics.
"This work represents a fundamental yet significant step towards fully-autonomous, electronics-free walking robots," said Dylan Drotman, a Ph.D. student in Tolley's research group and the paper's first author.
Applications include low-cost robotics for entertainment, such ...
Climate change and fire suppression
2021-02-17
The unprecedented and deadly blazes that engulfed the American West in 2020 attest to the increasing number, size and severity of wildfires in the region. And while scientists predict the climate crisis will exacerbate this situation, there's still much discussion around its contributing factors.
With this in mind, scientists at five western universities, including UC Santa Barbara, investigated the effects of human-driven climate change and more than a century of fire suppression, which has produced dense forests primed to burn. Their research, published in the journal Environmental ...
On the quest for other Earths
2021-02-17
In the search for planets capable of sustaining life, an international research team with members from ETH has taken a significant step forward. As the researchers reported recently in the journal Nature Communications, they found signs of a Neptune-sized planet in the Alpha Centauri star system, a mere 4.4 light years away from Earth. This exoplanet is located in a zone that may offer suitable conditions for life. The team was able to collect data with unprecedented sensitivity, thus registering even very weak signals.
Earth is a disruptive factor
Thanks to the new process, the researchers have advanced one step closer to ...
[1] ... [2634]
[2635]
[2636]
[2637]
[2638]
[2639]
[2640]
[2641]
2642
[2643]
[2644]
[2645]
[2646]
[2647]
[2648]
[2649]
[2650]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.