Star-shaped brain cells may be linked to stuttering
2021-02-12
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Astrocytes -- star-shaped cells in the brain that are actively involved in brain function -- may play an important role in stuttering, a study led by a University of California, Riverside, expert on stuttering has found.
"Our study suggests that treatment with the medication risperidone leads to increased activity of the striatum in persons who stutter," said Dr. END ...
Young planets with teenage sun give space studies a lift
2021-02-12
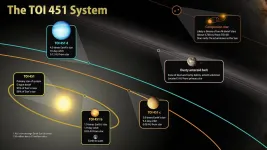
HANOVER, N.H. - February 12, 2021 - A newly discovered planetary system will provide researchers with the rare chance to study a group of growing planets, according to research co-led by Dartmouth.
The new system, named TOI 451, is made up of at least three neighboring planets that orbit the same sun. The planets range in size between that of Earth and Neptune.
According to the research team, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and its planned successor, the James Webb Space Telescope, can be used to study the atmosphere of each planet. Such research could lead to information on how planetary systems like our own solar system evolve.
"The sun in this planetary system is very similar to our own sun, but much younger," ...
Computer love
2021-02-12
In your quest for true love and that elusive happily ever after, are you waiting for the "right" person to come along, or do you find yourself going for the cutest guy or girl in the room, hoping things will work out? Do you leave your options open, hoping to "trade-up" at the next opportunity, or do you invest in your relationship with an eye on the cost-benefits analysis?
For something so fundamental to our existence, mate selection remains one of humanity's most enduring mysteries. It's been the topic of intense psychological research for decades, spawning myriad hypotheses of why we choose whom we choose.
"Mate choice is really complicated, especially in humans," ...
NIH research funding to support surgeon scientists is rising
2021-02-12
CHICAGO (February 12, 2021): Since 2010, National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding to support surgeon scientists has, remarkably, risen significantly while funding to support other non-surgeon physicians has significantly decreased. This growth has occurred despite an overall decrease in NIH funding and an increase in demand for clinical productivity. These findings are according to an " END ...
Bacterial degradation of the MYC oncogene -- a new cancer treatment strategy?
2021-02-12
Scientists at Lund University have discovered how E. coli bacteria target and degrade the well-known oncogene MYC, which is involved in many forms of cancer. The study is now published in Nature Biotechnology.
Cancer cells grow too fast, outcompete normal cells and spread to distant sites, where they cause metastases. Understanding what makes cancer cells so efficient and threatening is critically important and stopping them has always been the goal of cancer research. Early studies identified so-called ''oncogenes''; genes that that normally control cell growth but when mutated may be responsible for the creation of cancer cells and explain their competitive advantage.
The pleiotropic transcription factor MYC has been ...
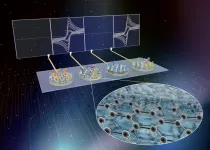
Detecting multiple sepsis biomarkers from whole blood - made fast, accurate, and cheap
2021-02-12
(BOSTON) -- Many life-threatening medical conditions, such as sepsis, which is triggered by blood-borne pathogens, cannot be detected accurately and quickly enough to initiate the right course of treatment. In patients that have been infected by an unknown pathogen and progress to overt sepsis, every additional hour that an effective antibiotic cannot be administered significantly increases the mortality rate, so time is of utmost essence.
The challenge with rapidly diagnosing sepsis stems from the fact that measuring only one biomarker often does not allow a clear-cut diagnosis. Engineers have struggled for decades to simultaneously quantify multiple biomarkers in whole blood with high ...
Medication-based starvation of cancer cells
2021-02-12
The drug thalidomide was sold as a sedative under the trade name Contergan in the 1950s and 1960s. At the time, its side-effects triggered one of the largest pharmaceutical scandals in history: The medication was taken from the market after it became known that the use of Contergan during pregnancy had resulted in over 10,000 cases of severe birth defects.
Currently, the successor preparations lenalidomide and pomalidomide are prescribed under strict supervision by experienced oncologists - the active ingredients are a cornerstone of modern cancer therapies. The use of lenalidomide and pomalidomide has considerably improved the success ...
UTEP professor's study may lead to solutions for overeating
2021-02-12
EL PASO, Texas - Science is a step closer to a new response to obesity, thanks in part to a study conducted by a team that included Sergio Iñiguez, Ph.D., associate professor of psychology at The University of Texas at El Paso.
The 10-member team led by Brandon Warren, Ph.D., assistant professor of pharmacodynamics at the University of Florida, made discoveries about a specific area of the brain tied to recollection and the desire to seek and consume food. It could lead to a way to inhibit the desire to overeat.
Iñiguez, who directs UTEP's Iñiguez Behavioral Neuroscience Lab and helped design novel experimental techniques for the research, said that people tend to overeat when exposed to cues or environments that remind them of treats, which is one reason ...
Study contradicts belief that whales learn songs from one another
2021-02-12
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Humpback and bowhead whales are the only mammals other than humans thought to progressively change the songs they sing through a process of cultural learning.
But maybe the humpbacks are no longer part of that trio. Humpbacks might be singing songs that are not as "cultured" as once assumed.
A new study by a University at Buffalo researcher is directly contradicting the widely accepted cultural transmission hypothesis suggesting that whales learn their songs from other whales.
"It seems like that is not correct," says Eduardo Mercado, a professor of psychology in UB's College of Arts and Sciences. "Our findings indicate that neither cultural transmission nor social learning contributes significantly to how humpback whales ...
'Sex, lasers and male competition:' fruit flies win genetic race with rivals
2021-02-12
Scientists have accepted natural selection as a driver of evolution for more than 160 years, thanks to Charles Darwin.
But University of Cincinnati biologist Michal Polak says Darwin's book "The Descent of Man" only tells part of the story. Sometimes when the victor vanquishes his sexual rival, the quest to pass genes to the next generation is just beginning.
According to a new UC study published in the journal Current Biology, male fruit flies with the most impressive sexual ornamentation also have super sperm that can outcompete that of rivals in the post-mating fertilization game.
UC studied Drosophila bipectinata, a tiny red-eyed fruit fly ...
The effects of antidepressant drugs evaluated through the analysis of patients' tweet
2021-02-12
Researchers of the Research Programme on Biomedical Informatics (GRIB) from UPF and Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM) in Barcelona, Spain, have identified behavioural and linguistic changes in tweets in Spanish published by users suffering from depression and who are taking medication to treat this disease.
Their work has been published in Journal of Medical Internet Research and was led by Ferran Sanz; with Angela Leis and Francesco Ronzano as first authors, who conducted the work together with Miguel Angel Mayer and Laura I Furlong, all from the Integrative Biomedical Informatics research ...
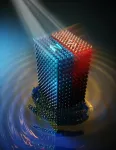
Scientists manipulate magnets at the atomic scale
2021-02-12
Fast and energy-efficient future data processing technologies are on the horizon after an international team of scientists successfully manipulated magnets at the atomic level.
Physicist Dr Rostislav Mikhaylovskiy from Lancaster University said: "With stalling efficiency trends of current technology, new scientific approaches are especially valuable. Our discovery of the atomically-driven ultrafast control of magnetism opens broad avenues for fast and energy-efficient future data processing technologies essential to keep up with our data hunger."
Magnetic materials are heavily used in modern life with applications ranging from fridge magnets to Google and Amazon's ...
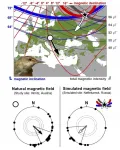
Birds can 'read' the Earth's magnetic signature well enough to get back on course
2021-02-12
Birdwatchers get very excited when a 'rare' migratory bird makes landfall having been blown off-course and flown beyond its normal range. But these are rare for a reason; most birds that have made the journey before are able to correct for large displacements and find their final destination.
Now, new research by an international team shows for the first time, how birds displaced in this way are able to navigate back to their migratory route and gives us an insight into how they accomplish this feat.
Writing in Current Biology, the team from Bangor and Keele Universities describe how reed warblers can navigate from a 'magnetic position' beyond what they have ...
Effect of high-dose zinc, ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length, reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection
2021-02-12
What The Study Did: These findings suggest that treatment with zinc, ascorbic acid or both doesn't affect SARS-CoV-2 symptoms.
Authors: Milind Y. Desai, M.D., M.B.A., of the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to ...
Pediatric hospital admissions in 2020 compared with decade before COVID-19
2021-02-12
What The Study Did: Pediatric admissions to U.S. hospitals decreased last year across an array of pediatric conditions and some may represent unmet needs in pediatric care during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Christopher M. Horvat, M.D., M.H.A., of UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37227)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
Variations in sensitivity of serological tests among individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2
2021-02-12
What The Study Did: This observational study investigated the sensitivity of antibody tests to detect previous SARS-CoV-2 infection using existing clinical data across the University of California Health system.
Authors: Atul J. Butte, M.D. Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0337)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please ...
Green tea compound aids tumor-suppressing, DNA-repairing protein
2021-02-12
TROY, N.Y. -- An antioxidant found in green tea may increase levels of p53, a natural anti-cancer protein, known as the "guardian of the genome" for its ability to repair DNA damage or destroy cancerous cells. Published today in END ...
Assessing brain capillaries in COVID-19
2021-02-12
What The Study Did: This case series analyzes brains from autopsies of patients who died of COVID-19 as confirmed by nucleic acid test and with severe pulmonary pathology.
Authors: David W. Nauen, M.D., Ph.D., of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.0225)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Study explores neurocognitive basis of bias against people who look different
2021-02-12
PHILADELPHIA--The "scarred villain" is one of the oldest tropes in film and literature, from Scar in "The Lion King" to Star Wars' Darth Vader and the Joker in "The Dark Knight." The trope is likely rooted in a long-evolved human bias against facial anomalies -- atypical features such as growths, swelling, facial paralysis, and scars. A new brain-and-behavior study from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania illuminates this bias on multiple levels.
The researchers, whose findings were published this week in the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, used surveys, social simulations, and functional MRI (fMRI) studies to study hundreds of participants' responses and attitudes towards ...
Flowers of St. John's Wort serve as green catalyst
2021-02-12
Since ancient times, St. John's Wort has been used as a medicinal herb covering a wide range of applications such as the treatment of burns, skin injuries, neuralgia, fibrosis, sciatica and depression. Due to its high medicinal potential, the plant known in technical terminology as Hypericum perforatum even became "Medicinal Plant of the Year" in 2015. Now, scientists at TU Dresden have shown that there is much more to the herb than its healing properties.
To this end, two interdisciplinary groups from biology and inorganic chemistry have joined forces and thus achieved astonishing results.
Originally, the research groups led by botanist Prof. Stefan Wanke ...
Here comes the new generation of climate models: the future of rainfall in the Alps
2021-02-12
Less intense mean daily precipitation, more intense and localised extreme events. This is what the future climate scenarios indicate for the Eastern Alps, according to the study "Evaluation and Expected Changes of Summer Precipitation at Convection Permitting Scale with COSMO-CLM over Alpine Space", published by the CMCC Foundation in the journal Atmosphere. The research is conducted in the context of the European project H2020 EUCP (European Climate Prediction system) and contributes to the work of the international scientific community for the development of climate models that can support ...
Biodiversity protects bee communities from disease
2021-02-12
Photos
A new analysis of thousands of native and nonnative Michigan bees shows that the most diverse bee communities have the lowest levels of three common viral pathogens.
University of Michigan researchers netted and trapped more than 4,000 bees from 60 species. The bees were collected at winter squash farms across Michigan, where both managed honeybee colonies and wild native bees pollinate the squash flowers.
All but one species--Apis mellifera, the common European honeybee--are native bees. The number of bee species found at each farm ranged from seven to 49.
Consistently, lower virus levels were strongly linked to greater species richness among the local bee communities. ...
New insight into protein structures that could treat Huntington's disease
2021-02-12
In Huntington's disease, a faulty protein aggregates in brain cells and eventually kills them. Such protein aggregates could, in principle, be prevented with a heat shock protein. However, it is not well known how these proteins interact with the Huntington's disease protein. New research by Patrick van der Wel (University of Groningen, the Netherlands) and colleagues at the University of Texas has partially resolved the structure of heat shock proteins that bind to such aggregating proteins, helping us to understand how they work. The results were published on 11 February in the journal Nature Communications.
Heat shock proteins (Hsp) are produced by cells that are exposed to stressful conditions. The Hsp family is diverse, and quite a few of the ...
Identifying risk factors for elevated anxiety in young adults during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-02-12
A new study has identified early risk factors that predicted heightened anxiety in young adults during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. The findings from the study, supported by the National Institutes of Health and published in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, could help predict who is at greatest risk of developing anxiety during stressful life events in early adulthood and inform prevention and intervention efforts.
The investigators examined data from 291 participants who had been followed from toddlerhood to young adulthood as part of a larger study on temperament and socioemotional development. The researchers ...
Sweet coating for sour bones
2021-02-12
Osteoporosis is a leading global health challenge. Besides its own adverse effects, it also impairs the function of bone implants - normally made of a metal called titanium (Ti). Because there is less bone than normal in the implantation site, the implants could easily loosen, and persistent inflammation often accompanies.
Recently, Chinese scientists from the University of Macau and Nanjing University, in collaboration with National Dental Centre Singapore, invent a bioactive coating that can be chemically linked onto normal Ti surface. This coating, ...
[1] ... [2636]
[2637]
[2638]
[2639]
[2640]
[2641]
[2642]
[2643]
2644
[2645]
[2646]
[2647]
[2648]
[2649]
[2650]
[2651]
[2652]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.