International team first to stack virus resistance plus iron & zinc in a non-cereal crop
2021-02-16
ST. LOUIS, MO, February 16, 2021 - Delivering the benefits of agricultural biotechnology to smallholder farmers requires that resources be directed toward staple food crops. To achieve effect at scale, beneficial traits must be integrated into multiple, elite farmer-preferred varieties with relevance across geographical regions. For the first time, an international team of scientists, led by Narayanan Narayanan, Ph.D., senior research scientist, and Nigel Taylor, Ph.D., associate member and Dorothy J. King Distinguished Investigator at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center, and their collaborators in Nigeria, led ...
Breakthrough in the fight against spruce bark beetles
2021-02-16
For the first time, a research team led by Lund University in Sweden has mapped out exactly what happens when spruce bark beetles use their sense of smell to find trees and partners to reproduce with. The hope is that the results will lead to better pest control and protection of the forest in the future.
The Eurasian spruce bark beetle uses its sense of smell to locate trees and partners. The odours are captured via odorant receptors (proteins) in their antennae. Researchers have long understood the connection, but so far they have not known exactly which receptors bind to what pheromones. ...
Secret to how cholera adapts to temperature revealed
2021-02-16
Scientists have discovered an essential protein in cholera-causing bacteria that allows them to adapt to changes in temperature, according to a study published today in eLife.
The protein, BipA, is conserved across bacterial species, which suggests it could hold the key to how other types of bacteria change their biology and growth to survive at suboptimal temperatures.
Vibrio cholerae (V. cholerae) is the bacteria responsible for the severe diarrhoeal disease cholera. As with other species, V. cholerae forms biofilms - communities of bacteria enclosed in a structure made up of sugars and proteins - to protect against predators and stress conditions. V. cholerae forms these biofilms both in their aquatic environment and in the human intestine. There is evidence to suggest that biofilm ...
Solution to puzzling phenomenon may open door to improved Cold Spray efficiency
2021-02-16
An international team of researchers has solved a puzzling phenomenon whereby strangely beautiful, vortex-like structures appear between materials deposited onto engineering components used in multiple settings - from space shuttles to household items and everyday transport vehicles.
The discovery may ultimately improve the efficiency of the "Cold Spray" (CS) deposition process from which these structures are formed - a not-insignificant consideration from a financial perspective, or from a functional one given that some of the materials created by CS are pushed to the limit in outer space.
The discovery is featured on the front cover of international journal, Materials & Design.
Cold Spray (CS) and deposition efficiency (DE)
CS enables the formation of coatings, ...
Silencing by crosstalk
2021-02-16
Why do genes need to be silenced? The "genes" in question are in fact transposons, selfish genetic elements that seek to self-multiply at the host's expense and that need to be controlled. Julius Brennecke's group at IMBA focuses on lifting the mysteries of a specific type of transposon silencing, namely the piRNA pathway in animal gonads. Understanding this ancient silencing system promises to reveal general mechanistic principles of gene expression and chromatin biology.
Gene silencing: either before they "speak", or right as they attempt to
Heterochromatin, a tightly packed form of DNA, plays an essential role in transposon ...
Past earthquakes triggered large rockslides in the Eastern Alps
2021-02-16
Many steep valleys in the European Alps show the relicts of large rockslides, during which several hundreds of million cubic metres of rocks get instable, collapse and impact everything on their path. "For most of these, we still do not know how they are caused, because these rockslides occurred long before the start of written history in the region about 1000 years ago," says Patrick Oswald, PhD student at the Department of Geology of the University of Innsbruck and lead author of the study. "Curiously, many of these ancient rockslides occurred together in clusters, meaning they are found in small regions and have a rather comparable age". This enigmatic pattern has puzzled researchers over the last decades and fuelled some intense debates. Some experts ...
Nanotechnologies reduce friction and improve durability of materials
2021-02-16
"Thin films are solid state substances that can be only several atomic layers thick. Usually, their properties are considerably different from the properties of the original substances on the macroscale. The areas of their application keep expanding and include nanoelectronics, optoelectronics, spintronics, electro-, and photocatalysis, as well as such important fields of economics as space technologies and instrument building. Micromodule devices for space crafts and medical technologies are also promising areas in which thin films can be used," said Vyacheslav Fominski, a project supervisor representing MEPhI.
To reduce friction and solve many ...
Cloudy eyes caused by protein imbalance
2021-02-16
Cataracts are the most common eye ailment in humans. However, the exact processes leading to this condition are not fully understood. A team of researchers headed by the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now discovered that the composition of the protein solution plays a decisive role. Their conclusions are contrary to prevailing opinion in the field.
The cells in the lens consist of a highly concentrated protein solution that is normally clear. "When the balance of the proteins in the lens is destroyed, they clump together and the lens becomes cloudy," says Prof. Johannes Buchner of the Chair of Biotechnology at TUM. This results in the condition known as cataracts.
The clouding can have different causes. Because the proteins in the lens are formed ...
Sloshing quantum fluids of light and matter to probe superfluidity
2021-02-16
The 'sloshing' of a quantum fluid comprised of light and matter reveals superfluid properties.
An Australian-led team of physicists have successfully created sloshing quantum liquids in a 'bucket' formed by containment lasers.
"These quantum fluids are expected to be as wavy as the oceans, but catching clear pictures of the waves is an experimental challenge," says lead author Dr Eliezer Estrecho.
Led by the Australian National University (ANU), the team serendipitously observed the wavy motion of the quantum fluid in an optically-controlled bucket, gaining new insights of the intriguing superfluid properties of this peculiar, hybrid light-matter system.
Superfluidity ...
Researchers find a novel connection between cell metabolism and cell division
2021-02-16
The processes in living beings follow a finely orchestrated choreography down to the molecular level. Rhythmic processes are found everywhere in biology, for example, the 24-hour circadian cycle, a kind of "internal clock", plays an important role in regulating many processes in living cells, including metabolism and cell division mechanisms.
Scientists from Saarbrücken and Kaiserslautern have now taken a closer look at a similar cycle, the somewhat shorter ultradian cycle of baker's yeast. Under the leadership of Bruce Morgan, Professor of Biochemistry at ...
How healthy lifestyle behaviours can improve cholesterol profiles
2021-02-16
Combining healthy lifestyle interventions reduces heart disease through beneficial effects on different lipoproteins and associated cholesterols, according to a study published February 9 in eLife.
Having a healthy lifestyle has long been associated with a lower risk of developing heart disease. The new study provides more detailed information on how healthy lifestyles improve cholesterol, and suggests that combining cholesterol-lowering medications and lifestyle interventions may yield the greatest benefits to heart health.
Cholesterol-lowering ...
It takes two to tango: When cells interact
2021-02-16
The fact that cells are motile and come into contact with each other is one of biology's fundamental principles. During embryonic development, cells must communicate with their neighbors in order to find their proper place in the differentiating organism. Wound healing is another process in which direct intercellular interactions are essential. In this context, motility enables cells to migrate to the location of the lesion and regenerate lost structures. Cancer cells also make use of this property to leave their site of origin in the primary tumor, which allows them to initiate the formation of metastatic tumors in other tissues.
"In recent years, biologists ...
Small 'window of opportunity' for best recovery after stroke
2021-02-16
An international study has shown, for the first time, that the capacity of the human brain to recover and rewire itself peaks around two weeks after a stroke and diminishes over time.
The finding, published today in the Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair journal, is the result of a study in London and Adelaide that followed the recovery of 60 stroke patients up to one year after their stroke.
Lead author Dr Brenton Hordacre, from the University of South Australia, says the multi-site study showed conclusive evidence that the brain only has a small window of opportunity to more easily repair itself after stroke.
"Earlier animal studies suggested ...
How icebergs really melt -- and what this could mean for climate change
2021-02-16
Icebergs are melting faster than current models describe, according to a new study by mathematicians at the University of Sydney. The researchers have proposed a new model to more accurately represent the melt speed of icebergs into oceans.
Their results, published in Physical Review Fluids, have implications for oceanographers and climate scientists.
Lead author and PhD student Eric Hester said: "While icebergs are only one part of the global climate system, our improved model provides us with a dial that we can tune to better capture the reality of Earth's changing climate."
Current models, which are incorporated into the methodology used by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, ...
A performance leap for Graphene modulators in next generation datacom and telecom
2021-02-16
Over the past years, global data traffic has experienced a boom, with over 12.5 billion connected devices all over the world. The current world-wide deployment of the 5G telecommunications standard is triggering the need for smaller devices with enhanced performances, such as higher speed, lower power consumption and reduced cost as well as easier manufacturability.
In search for the appropriate technology, photonic devices emerged as the leading technology for the evolution of such information and communication technologies, already surpassing ...
Army researchers expand study of ethics, artificial intelligence
2021-02-16
ADELPHI, Md. -- The Army of the future will involve humans and autonomous machines working together to accomplish the mission. According to Army researchers, this vision will only succeed if artificial intelligence is perceived to be ethical.
Researchers, based at the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, now known as DEVCOM, Army Research Laboratory, Northeastern University and the University of Southern California, expanded existing research to cover moral dilemmas and decision making that has not been pursued elsewhere.
This research, featured in Frontiers in Robotics and AI, tackles the fundamental challenge of developing ethical artificial intelligence, ...
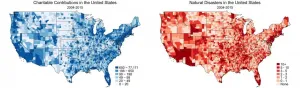
The effect of natural disasters on criminal--and charitable--activity in the USA
2021-02-16
The human condition is riddled with extreme events, which bring chaos into our lives. Natural disasters leave a trail of destruction, causing direct and horrible pain and suffering - costing lives, creating injuries, destroying houses, livelihoods, crops and broken infrastructures. While extensive research has been conducted on the economic and public healthcare costs of these types of disasters around the world, their effect does not end there. A team of researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem sought to better understand the behavioral and social implications ...
Psychotherapy for panic disorder shows positive long-term effects
2021-02-16
Psychotherapy for panic disorder produces good results, and the effects are lasting. That is the result from a large long-term study from Lund University in Sweden. Two years after treatment were 70 per cent of the patients clearly improved and 45 per cent were remitted.
Panic disorder is one of the most common causes of mental illness in Sweden and worldwide. Approximately 2 per cent have panic disorder. When untreated, the condition is associated with emotional distress and social isolation. Panic attacks often debut in adolescence or early adulthood and many of those affected ...
Highway tunnel for ions
2021-02-16
We live in modern times, that is full of electronics. Smartphones, laptops, tablets, and many other devices need electrical energy to operate. Portable devices made our lives easier, so novel solutions in clean energy and its storage are desirable. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the most common solutions that dominate the global market and are a huge problem due to their insufficient recovery. Because of their limited power, short cycle life, and non-environment-friendly nature, scientists recently focused on novel solutions like supercapacitors that offer much more than batteries. Why? Let's take a look closer at these devices.
Supercapacitors bring together the properties of a standard capacitor and the Li-ion battery. In practice, ...
Delayed medical treatment of high-impact injuries: A lesson from the Syrian civil war
2021-02-16
Following the civil war outbreak in Syria nearly ten years ago, Israel began admitting wounded Syrians into the country for humanitarian medical treatment.
In accordance with the Israeli government's decision, the Israel Defense Forces, medical corps, health care system and hospitals in the north of the country joined together to provide medical treatment to thousands of wounded Syrians. The logistics of evacuating the injured from the battlefield and transferring them to Israeli territory was often prolonged due to the fact that Israel and Syria are defined as enemy countries.
Most of the wounded were brought to the Galilee ...
Cells use concentration gradients as a compass
2021-02-16
Biophysicists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munch have developed a new theory, which accounts for the observation that cells can perceive their own shapes, and use this information to direct the distribution of proteins inside the cell.
Many cellular processes are critically dependent on the precise distribution and patterning of proteins on the cell membrane. Diverse studies have shown that, in addition to protein-protein interactions and transport processes, cell shape can also have a considerable impact on intracellular pattern formation. Conversely, there are patterning processes in which any dependence on cell form would be deleterious. Using starfish oocytes as a model system, LMU physicists led by Professor Erwin ...
Observations at a shed light on how hard coral survives without light
2021-02-16
In shallow water, less than 30 metres, the survival of hard corals depends on photosynthetic unicellular algae (zooxanthellae) living in their tissues. But how does the coral adapt at depth when the light disappears? French researchers from the CNRS, EPHE-PSL and their international collaborators, associated with Under the Pole (Expedition III), have studied for the first time the distribution of these so-called mesophotic corals in the French Polynesian archipelago, from the surface to 120 metres deep (with a record descent of 172 metres). As the amount of light decreases, the coral associates ...
CPAP treatment increases physical activity in adults with sleep apnea, heart disease
2021-02-16
DARIEN, IL - A new study found that treating obstructive sleep apnea with CPAP therapy increased self-reported physical activity in adults with a history of heart disease.
During a mean follow-up period of 3.7 years, the group treated with CPAP therapy reported approximately 20% higher levels of moderate physical activity compared with the control group. The study also found the CPAP group was more likely to report activity levels consistent with expert recommendations.
"We were pleased to find that our CPAP users reported that they were better able to maintain their levels of activity over the four years of the study, and that they reported fewer limitations in moderate and vigorous activities including those that are important for independent aging, like walking up the stairs," ...
Finding coronavirus's helper proteins
2021-02-16
The researchers used a biophysical method called thermal proteome profiling (TPP) to gain a comprehensive overview of which human proteins are functionally altered during SARS-CoV-2 infection. TPP monitors protein amounts and denaturation temperatures - the points at which proteins heat up so much that they lose their 3D structure. A shift in denaturation temperature indicates that a particular protein has undergone a functional change upon infection, possibly due to the virus hijacking the protein for use in its own replication.
The scientists observed that infection with SARS-CoV-2 changed the abundance and thermal stability of hundreds of cellular proteins. This included ...
Predicting words' grammatical properties helps us read faster
2021-02-16
Psycholinguists from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain found that when reading, people are not only able to predict specific words, but also words' grammatical properties, which helps them to read faster. Researchers have also discovered that predictability of words and grammatical features can be successfully modelled with the use of neural networks. The study was published in the journal PLOS ONE.
The ability to predict the next word in another person's speech or in reading has been described by many psycho- and neurolinguistic studies over the last 40 years. It is assumed that this ability allows us to process the information faster. Some recent publications on the English language have demonstrated evidence that while reading, people can ...
[1] ... [2628]
[2629]
[2630]
[2631]
[2632]
[2633]
[2634]
[2635]
2636
[2637]
[2638]
[2639]
[2640]
[2641]
[2642]
[2643]
[2644]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.