Biological assessment of world's rivers presents incomplete but bleak picture
2021-02-22
An international team of scientists, including two from Oregon State University, conducted a biological assessment of the world's rivers and the limited data they found presents a fairly bleak picture.
"For the places that we have data, the situations are not really that good. There are many species that are declining, threatened or endangered," said Bob Hughes, co-author of the paper and a courtesy associate professor in Oregon State's Department of Fisheries and Wildlife. "But for most of the globe, there just is little rigorous data."
The work by Hughes and the ...
Study quantifying parachute science in coral reef research shows it's 'still widespread'
2021-02-22
By analyzing 50 years' worth of coral reef biodiversity studies, researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on February 22 have quantified the practice of "parachute science," which happens when international scientists, typically from higher-income countries, conduct field studies in another, typically lower-income country, without engaging with local researchers. They found that institutions from several lower-middle- and upper-middle-income countries with abundant coral reefs produced less research than institutions based in high-income countries with fewer or in some cases no reefs. They also found that host-nation scientists (scientists from the nations where field research was conducted) were ...
Tweaking corn kernels with CRISPR
2021-02-22
Corn--or maize--has changed over thousands of years from weedy plants that make ears with less than a dozen kernels to the cobs packed with hundreds of juicy kernels that we see on farms today. Powerful DNA-editing techniques such as CRISPR can speed up that process. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor David Jackson and his postdoctoral fellow Lei Liu collaborated with University of Massachusetts Amherst Associate Professor Madelaine Bartlett to use this highly specific technique to tinker with corn kernel numbers. Jackson's lab is one of the first to apply CRISPR to corn's very complex ...
Ghost particle from shredded star reveals cosmic particle accelerator
2021-02-22
Tracing back a ghostly particle to a shredded star, scientists have uncovered a gigantic cosmic particle accelerator. The subatomic particle, called a neutrino, was hurled towards Earth after the doomed star came too close to the supermassive black hole at the centre of its home galaxy and was ripped apart by the black hole's colossal gravity. It is the first particle that can be traced back to such a 'tidal disruption event' (TDE) and provides evidence that these little understood cosmic catastrophes can be powerful natural particle accelerators, as the team led by DESY scientist Robert Stein reports in the journal Nature Astronomy. The observations also demonstrate the power of exploring the cosmos via ...
'Mini brain' organoids grown in lab mature much like infant brains
2021-02-22
A new study from UCLA and Stanford University researchers finds that three-dimensional human stem cell-derived 'mini brain' organoids can mature in a manner that is strikingly similar to human brain development.
For the new study, published in Nature Neuroscience February 22, senior authors Dr. Daniel Geschwind of UCLA and Dr. Sergiu Pasca of Stanford University conducted extensive genetic analysis of organoids that had been grown for up to 20 months in a lab dish. They found that these 3D organoids follow an internal clock that guides their maturation in sync with the timeline of human development.
"This is novel -- Until now, nobody has grown and characterized these organoids for this amount of time, nor shown they will recapitulate human brain development in a laboratory environment ...
New dating techniques reveal Australia's oldest known rock painting, and it's a kangaroo
2021-02-22
A two-metre-long painting of a kangaroo in Western Australia's Kimberley region has been identified as Australia's oldest intact rock painting.
Using the radiocarbon dating of 27 mud wasp nests, collected from over and under 16 similar paintings, a University of Melbourne collaboration has put the painting at 17,500 and 17,100 years old.
"This makes the painting Australia's oldest known in-situ painting," said Postdoctoral Researcher Dr Damien Finch who pioneered the exciting new radiocarbon technique.
"This is a significant find as through these initial estimates, we can understand something of the ...
Association of timing of school closings, behavioral changes with evolution of COVID-19 pandemic in US
2021-02-22
What The Study Did: Using COVID-19 data, this observational study looked at what are the independent associations of voluntary behavioral change and legal restrictions, such as state-mandated school closings, with the subsequent spread of the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S.
Authors: Frederick J. Zimmerman, Ph.D., of the Fielding School of Public Health at UCLA in Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.6371)
Editor's Note: The article includes ...
Scientists link star-shredding event to origins of universe's highest-energy particles
2021-02-22
A team of scientists has detected the presence of a high-energy neutrino--a particularly elusive particle--in the wake of a star's destruction as it is consumed by a black hole. This discovery, reported in the journal Nature Astronomy, sheds new light on the origins of Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays--the highest energy particles in the Universe.
The work, which included researchers from more than two dozen institutions, including New York University and Germany's DESY research center, focused on neutrinos--subatomic particles that are produced on Earth only in powerful ...
Trauma admissions during COVID-19 pandemic in LA county
2021-02-22
What The Study Did: Researchers examined changes in trauma admissions throughout Los Angeles County during the COVID-19 pandemic in California.
Authors: Kazuhide Matsushima, M.D., of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1320)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
New technique reveals switches in RNA
2021-02-22
Scientists at the University of Groningen (The Netherlands), in collaboration with colleagues from the University of Torino (Italy), have developed a method to visualize and quantify alternative structures of RNA molecules. These alternative RNA 'shapes' can have important functional relevance in viruses and bacteria. The researchers used an algorithm to rapidly analyse large quantities of chemically modified RNA molecules and calculate how many differently folded conformations were present. This technique was used to identify a conserved structural switch in the ...
Patient page: Teen vaping
2021-02-22
What The Article Says: How parents can identify whether their teens are vaping, how to help prevent it, and what to do if their teen is addicted are discussed in this JAMA Pediatrics Patient Page.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.6689)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full article is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.6689?guestAccessKey=8fe3a04c-4e0a-40f3-a883-916eaadb05bb&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=022221
...
State legislation related to abortion services
2021-02-22
What The Study Did: This survey study looked at changes in abortion policies among states by examining legislation enacted between January 2017 and November 2020.
Authors: Phillip M. Singer, Ph.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.8781)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
Genomic insights into the origin of pre-historic populations in East Asia
2021-02-22
Diverse East Asians derive ancestry from a coastal expansion tens of thousands of years ago
Researchers have long debated whether the peopling of East Asia by modern humans occurred mainly via a coastal or interior route. The answer is probably both. "Indigenous Andaman islanders of the Bay of Bengal, Indigenous Tibetans, ancient Taiwanese, and ancient and modern Japanese all derive ancestry from a deep shared lineage that split from other East Asian lineages more than 40,000 years ago," says David Reich, co-senior author of the study, who is a Professor of Genetics ...
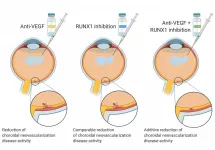
New therapeutic approach may help treat age-related macular degeneration effectively
2021-02-22
Philadelphia, February 22, 2021 - Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) has been linked to retinal neovascularization and the development of abnormal blood vessels, which result in vision loss in diabetic retinopathy. Now, scientists have found that RUNX1 inhibition presents a new therapeutic approach in the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), which is the leading cause of blindness in the elderly worldwide. Their END ...
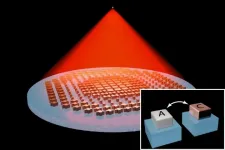
New "metalens" shifts focus without tilting or moving
2021-02-22
Polished glass has been at the center of imaging systems for centuries. Their precise curvature enables lenses to focus light and produce sharp images, whether the object in view is a single cell, the page of a book, or a far-off galaxy.
Changing focus to see clearly at all these scales typically requires physically moving a lens, by tilting, sliding, or otherwise shifting the lens, usually with the help of mechanical parts that add to the bulk of microscopes and telescopes.
Now MIT engineers have fabricated a tunable "metalens" that can focus on objects at multiple depths, without changes to its physical position or shape. The lens is made not of solid glass but of a ...
Air pollution puts children at higher risk of disease in adulthood
2021-02-22
Children exposed to air pollution, such as wildfire smoke and car exhaust, for as little as one day may be doomed to higher rates of heart disease and other ailments in adulthood, according to a new Stanford-led study. The analysis, published in Nature Scientific Reports, is the first of its kind to investigate air pollution's effects at the single cell level and to simultaneously focus on both the cardiovascular and immune systems in children. It confirms previous research that bad air can alter gene regulation in a way that may impact long-term health - a finding that could change the way medical experts and parents think about the air children ...
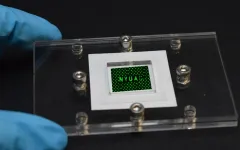
NYUAD researchers develop high throughput paper-based arrays of 3D tumor models
2021-02-22
Abu Dhabi, UAE, February 22: By engineering common filter papers, similar to coffee filters, a team of NYU Abu Dhabi researchers have created high throughput arrays of miniaturized 3D tumor models to replicate key aspects of tumor physiology, which are absent in traditional drug testing platforms. With the new paper-based technology, the formed tumor models can be safely cryopreserved and stored for prolonged periods for on-demand drug testing use. These cryopreservable tumor models could provide the pharmaceutical industry with an easy and low cost method for investigating the outcomes of drug efficacy, potentially bolstering personalized ...
Parents of children with cancer have additional worries during COVID
2021-02-22
DURHAM, N.C. - The COVID-19 pandemic has heaped additional financial strains, childcare complications and other problems on already-burdened caregivers of children diagnosed with cancer, according to a study from researchers at Duke Health and other institutions.
Surveying 360 parents and caregivers of children currently in treatment or still being monitored for cancer, the researchers found that half had to cancel or delay appointments, 77% reported increased feelings of anxiety and of those who had lost jobs or wages, 11% struggled to pay for basic needs.
The survey findings appear online this month in the journal Pediatric Blood & Cancer.
"Parents and caregivers ...
Study could explain tuberculosis bacteria paradox
2021-02-22
HOUSTON - (Feb. 22, 2021) -Tuberculosis bacteria have evolved to remember stressful encounters and react quickly to future stress, according to a study by computational bioengineers at Rice University and infectious disease experts at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School (NJMS).
Published online in the open-access journal mSystems, the research identifies a genetic mechanism that allows the TB-causing bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, to respond to stress rapidly and in manner that is "history-dependent," said corresponding author Oleg Igoshin, a professor of bioengineering at Rice.
Researchers have long suspected that the ability of TB bacteria to remain dormant, sometimes for decades, ...
Tricking the novel coronavirus with a fake "handshake"
2021-02-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Fool the novel coronavirus once and it can't cause infection of cells, new research suggests.
Scientists have developed protein fragments - called peptides - that fit snugly into a groove on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein that it would normally use to access a host cell. These peptides effectively trick the virus into "shaking hands" with a replica rather than with the actual protein on a cell's surface that lets the virus in.
Previous research has determined that the novel coronavirus binds to a receptor protein on a target cell's surface called ACE2. This receptor is located on certain types of human cells in the lung and nasal cavity, providing SARS-CoV-2 many access points to infect the body.
For this work, Ohio State University scientists designed and tested peptides ...
Yale scientists repair injured spinal cord using patients' own stem cells
2021-02-22
Intravenous injection of bone marrow derived stem cells (MSCs) in patients with spinal cord injuries led to significant improvement in motor functions, researchers from Yale University and Japan report Feb. 18 in the Journal of Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery.
For more than half of the patients, substantial improvements in key functions -- such as ability to walk, or to use their hands -- were observed within weeks of stem cell injection, the researchers report. No substantial side effects were reported.
The patients had sustained, non-penetrating spinal cord injuries, in many cases from falls or minor trauma, several weeks prior to implantation of the stem cells. Their symptoms ...
'Jumping genes' repeatedly form new genes over evolution
2021-02-22
ITHACA, N.Y. - In the same way that Lego pieces can be arranged in new ways to build a variety of structures, genetic elements can be mixed and matched to create new genes, according to new research.
A long-proposed mechanism for creating genes, called exon shuffling, works by shuffling functional blocks of DNA sequences into new genes that express proteins.
A study, "Recurrent Evolution of Vertebrate Transcription Factors by Transposase Capture," published Feb. 19 in Science, investigates how genetic elements called transposons, or "jumping genes," are added into the mix during evolution to assemble new genes through exon shuffling.
Transposons, first discovered in the 1940s by Cornell alum and Nobel Prize-winner Barbara McClintock '23, M.A. '25, Ph.D. '27, are ...
Antibiotic tolerance study paves way for new treatments
2021-02-22
ITHACA, N.Y. - A new study identifies a mechanism that makes bacteria tolerant to penicillin and related antibiotics, findings that could lead to new therapies that boost the effectiveness of these treatments.
Antibiotic tolerance is the ability of bacteria to survive exposure to antibiotics, in contrast to antibiotic resistance, when bacteria actually grow in the presence of antibiotics. Tolerant bacteria can lead to infections that persist after treatment and may develop into resistance over time.
The study in mice, "A Multifaceted Cellular Damage Repair and Prevention Pathway Promotes ...
Focus on the positive to improve classroom behavior
2021-02-22
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- When teachers encounter disruptive or noncompliant students in the classroom, they typically respond by focusing on the negative behavior. However, new research from the University of Missouri found that offering students more positive encouragement not only reduces disruptive classroom behavior, but can improve students' academic and social outcomes.
"As educators, we often focus on communicating what we don't want our students to be doing in class, but we have found that just doesn't work," said Keith Herman, a professor in the University of Missouri College of Education. "Instead, we need to be setting clear expectations ...
Sleep is vital to associating emotion with memory, according to U-M study
2021-02-22
When you slip into sleep, it's easy to imagine that your brain shuts down, but University of Michigan research suggests that groups of neurons activated during prior learning keep humming, tattooing memories into your brain.
U-M researchers have been studying how memories associated with a specific sensory event are formed and stored in mice. In a study conducted prior to the coronavirus pandemic and recently published in Nature Communications, the researchers examined how a fearful memory formed in relation to a specific visual stimulus.
They found that not only did the neurons activated by the visual ...
[1] ... [2621]
[2622]
[2623]
[2624]
[2625]
[2626]
[2627]
[2628]
2629
[2630]
[2631]
[2632]
[2633]
[2634]
[2635]
[2636]
[2637]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.