Agile underwater glider could quietly survey the seas
2021-02-23
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- Autonomous underwater vehicles have become versatile tools for exploring the seas. But they can be disruptive to the environment or have trouble traveling through confined spaces.
Purdue University researchers are studying an alternative: highly maneuverable, low-cost underwater gliders that operate silently. Components and sensors of the glider also can be easily swapped out or added according to a wide range of mission specifications.
"Our goal is persistent operation of mobile robots in challenging environments," said Nina Mahmoudian, associate professor of mechanical engineering. "Most underwater robots ...
College students displaced from campus due to COVID-19 show worse psychological outcomes
2021-02-23
BOSTON -- Numerous psychiatric studies have documented increased rates of depression and anxiety among those forced to relocate, with sudden moves often affecting individuals' social support and sense of identity and control. As the COVID-19 pandemic spread through the U.S. in March of 2020, universities evacuated students from their campuses, and thousands quickly relocated. Few studies have examined the mental health impact of the sudden disruption. In a new study of 791 undergraduate and graduate students, surveyed between April 9 and August 4, 2020, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston University's School of Social Work, and McLean Hospital revealed that students forced to relocate during the spring were more likely to report COVID-19-related ...
Study finds COVID risk communication targeting younger adults may have biggest impact
2021-02-23
A study of adults in the United States finds that - broadly speaking - the older you are, the more concerned you are about COVID-19, and the more steps you take to reduce your risk from COVID-19. The study suggests that the biggest boost in risk reduction would stem from communication efforts aimed at raising awareness of COVID-19 risks among U.S. adults under the age of 40.
"Our study reinforces the idea that different generations perceive the risks associated with COVID-19 very differently," says Yang Cheng, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of communication at North Carolina State University. "It also highlights the need to do more to communicate the need for preventive measures ...
Alaska thunderstorms may triple with climate change
2021-02-23
Warming temperatures will potentially alter the climate in Alaska so profoundly later this century that the number of thunderstorms will triple, increasing the risks of widespread flash flooding, landslides, and lightning-induced wildfires, new research finds.
In a pair of new papers, a research team led by scientists at the Paris Sciences and Letters University and the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) show that the sea ice around Alaska could largely give way to open water in the warmer months, creating an ample source of moisture for the atmosphere. This moisture, combined with warmer temperatures that can hold more water vapor, would turbocharge summertime storms over Alaska by the end of ...
UIC researchers invent new gene-editing tool
2021-02-23
Researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago have discovered a new gene-editing technique that allows for the programming of sequential cuts -- or edits -- over time.
CRISPR is a gene-editing tool that allows scientists to change the DNA sequences in cells and sometimes add a desired sequence or genes. CRISPR uses an enzyme called Cas9 that acts like scissors to make a cut precisely at a desired location in the DNA. Once a cut is made, the ways in which cells repair the DNA break can be influenced to result in different changes or edits to the DNA sequence.
The discovery of the gene-editing capabilities ...
The unveiling of a novel mechanism of resistance to immunotherapy targeting HER2
2021-02-23
Redirection of lymphocytes, via T-cell bispecific antibodies (TCBs) and chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), is already approved to treat some hematologic malignancies. In solid tumors these immune-based strategies continue to fail.
Research led by Joaquín Arribas, co-Program Director of Preclinical and Translational Research at VHIO, has now shown how HER2 breast cancer cells adopt a strategy to resist clearance by redirected lymphocytes. Findings evidence that the disruption of interferon-gamma signaling confers resistance to these immunotherapies and promotes disease ...
Study shows new treatment pathway to prevent and treat endometrial cancer recurrence
2021-02-23
In a new study led by Yale Cancer Center, researchers demonstrate sex hormones and insulin growth factors are associated with recurrence risk of endometrial cancer. The findings suggest endocrine-targeted therapies and an assessment of biomarkers in hormone and insulin signaling pathways may be useful in the prevention and treatment of endometrial cancer recurrence. The study is a collaboration with researchers at the University of Hawaii and The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and is published online today in the journal Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention.
"These findings are very ...
Measuring hemoglobin levels with AI microscope, microfluidic chips
2021-02-23
WASHINGTON, February 23, 2021 -- One of the most performed medical diagnostic tests to ascertain the health of patients is a complete blood count, which typically includes an estimate of the hemoglobin concentration. The hemoglobin level in the blood is an important biochemical parameter that can indicate a host of medical conditions including anemia, polycythemia, and pulmonary fibrosis.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers from SigTuple Technologies and the Indian Institute of Science describe a new AI-powered imaging-based tool to estimate hemoglobin levels. The setup was developed in conjunction with a microfluidic chip and ...
Effect of layperson-delivered, empathy-focused program of telephone calls on loneliness, depression, anxiety during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-02-23
What The Study Did: A randomized clinical trial, this study reports that a layperson-delivered, empathy-oriented telephone call program reduced loneliness, depression and anxiety compared with the control group and improved the general mental health of participants within four weeks.
Authors: Maninder K. Kahlon, Ph.D., of the University of Texas at Austin, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.0113)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
COVID-19 communication
2021-02-23
What The Article Says: In this narrative medicine essay, a medical school professor expresses gratitude for the caring and empathy expressed by the team caring for her mother hospitalized with COVID-19 and emphasizes the importance of humanity and compassion over facts and statistics for families physically separated from their critically ill loved ones.
Authors: Lisa M. Meeks, Ph.D., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0119)
Editor's ...
Tobacco exposure in kids, risk of increased blood pressure
2021-02-23
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated whether children and adolescents who smoked or lived with a smoker had an increased risk of elevated blood pressure.
Authors: Rebecca V. Levy, B.M., B.Ch., M.Sc., of the Montefiore Medical Center in Bronx, New York is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37936)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Simply speaking while infected can potentially spread COVID-19
2021-02-23
WASHINGTON, February 23, 2021 -- COVID-19 can spread from asymptomatic but infected people through small aerosol droplets in their exhaled breath. Most studies of the flow of exhaled air have focused on coughing or sneezing, which can send aerosols flying long distances.
However, speaking while near one another is also risky since the virus can be ejected by merely talking.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, scientists in Japan use smoke and laser light to study the flow of expelled breath near and around two people conversing in various relative postures commonly found in the service industry, such as in hair salons, medical exam rooms, or long-term care facilities. ...
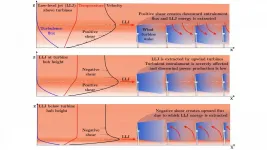
Low-level jets create winds of change for turbines
2021-02-23
WASHINGTON, February 23, 2021 -- As one of the leading sources of clean and renewable energy, global wind power capacity has increased more than fivefold over the past decade, leading to larger turbines and pushing wind technology to its limits.
"These much larger turbines are operating in very different atmospheric layers than smaller turbines used 5-10 years ago," said Srinidhi Gadde, one of the authors of a paper in the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, from AIP Publishing, that examines the impacts of turbine height. "At these scales, local meteorology and extreme shear events, which frequently occur, can impact ...
Parasitic plants conspire to keep hosts alive
2021-02-23
The plant that encourages kissing at Christmas is in fact a parasite, and new research reveals mistletoe has an unusual feeding strategy.
Like other plants, mistletoe is capable of using sunlight to create its own food, a process called photosynthesis. However, it prefers to siphon water and nutrients from other trees and shrubs, using "false roots" to invade its hosts.
"Plants are autotrophic, they make their own food. Humans are heterotrophic, we eat it," explained UC Riverside plant-insect ecologist Paul Nabity. "Mistletoe are mostly heterotrophic, but they can switch if they want to."
Nabity's team found when two mistletoes invade the same tree, they increase photosynthesis to get the nutrients they need, essentially sharing the ...
Kittens could hold key to understanding deadly diarrheal disease in children
2021-02-23
Kittens could be the model for understanding infectious, sometimes deadly, diarrheal disease in both animals and children, according to new research from North Carolina State University.
Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli (DEC) bacteria cause lethal diarrheal disease in children worldwide, killing up to 120,000 children under the age of five annually. Atypical enteropathic Escherichia coli (aEPEC) are a form of DEC increasingly associated with diarrheal disease in humans and in kittens.
"We were looking for causes of infectious diarrhea in kittens, which has a high mortality rate, and came across this pathogen," says Jody Gookin, FluoroScience Distinguished Professor in Veterinary Scholars Research Education at NC State and corresponding ...
Genetic tool improves estimation of prostate cancer risk in diverse ethnic/racial groups
2021-02-23
Building upon previous research, an international team led by scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, has validated a more inclusive and comprehensive genetic tool for predicting age of onset of aggressive prostate cancer, a disease that killed more than 33,000 American men in 2020.
Reporting in the February 23, 2021 online edition of Nature Communications, the researchers describe the performance of a polygenic hazard score (PHS) -- a mathematical estimate of an individuals' age-specific genetic risk for developing a disease -- in a multi-ethnic patient population.
"Genetic tools to predict a man's lifetime risk of prostate cancer might allow us to target cancer screening efforts to the men who are most likely to need it. We are ...
University of Minnesota researchers develop two new rapid COVID-19 diagnostic tests
2021-02-23
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (02/23/2021) -- University of Minnesota Medical School researchers have developed two new rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 - one to detect COVID-19 variants and one to help differentiate with other illnesses that have COVID-19-like symptoms. The findings were recently published in the journal Bioengineering.
Although many people are hopeful about COVID-19 vaccines, widespread vaccine distribution isn't predicted to be available until several months from now. Until that happens, the ability to diagnose COVID-19 quickly and accurately is crucial to help minimize loss of life and ...
Protective ship coatings as an underestimated source of microplastic pollution
2021-02-23
Shipping traffic can be a major source of tiny plastic particles floating in the sea, especially out in the open ocean. In a paper published in the scientific journal Environmental Science & Technology, a team of German environmental geochemists based at the University of Oldenburg's Institute of Chemistry and Biology of the Marine Environment and led by Dr Barbara Scholz-Boettcher for the first time provides an overview of microplastics mass distribution in the North Sea.
The scientists found that most of the plastic particles in water samples taken from the German Bight, an area in the south-eastern corner of the North Sea which encompasses some of the world's busiest shipping lanes, originate from binders used in marine paints. "Our hypothesis is that ships leave ...
New blood pressure-lowering guidelines could benefit 25 million americans with chronic kidney disease
2021-02-23
A recommendation for more intensive blood pressure management from an influential global nonprofit that publishes clinical practice guidelines in kidney disease could, if followed, benefit nearly 25 million Americans, according to an analysis led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The new recommendation from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes, a global nonprofit that develops evidence-based clinical practice guidelines in kidney disease, is aimed at doctors to help them to reduce blood pressure for chronic kidney disease patients whose systolic blood pressure levels are over 120 mmHg. Blood pressure can be reduced using antihypertensive medications and lifestyle modifications. ...
Multi-ethnic neighborhoods in England retain diversity unlike in the U.S.
2021-02-23
Multi-ethnic neighborhoods in England retain their diversity and are much more stable than such neighborhoods in the U.S., according to geographers from the U.S. and U.K. The team examined how neighborhood diversity has changed on a national scale from 1991 to 2011 using U.K. Census data.
Past studies of this kind have often focused on neighborhoods in which the presence of two or three different ethnic groups constituted a diverse neighborhood but this study applied a more rigorous standard. A multi-ethnic neighborhood had to have at least five or more ethnic groups represented and no group could represent more ...
'Good bacteria' in breast milk changes over time
2021-02-23
The cocktail of beneficial bacteria passed from mother to infant through breast milk changes significantly over time and could act like a daily booster shot for infant immunity and metabolism. The research, conducted by scientists from Montreal and Guatemala and published in Frontiers in Microbiology, has important implications for infant development and health.
Researchers discovered a range of microbiome species never before identified in human milk. Until now, relatively little was known about the role microbiome bacteria play in breast milk. These bacteria are thought to protect the infant gastrointestinal tract and improve aspects of long-term health, such as allergy ...
Toxins from one bacterial species contribute to genetic diversity of others
2021-02-23
A toxin produced by bacteria as a defence mechanism causes mutations in target bacteria that could help them survive, according to a study published today in eLife.
The finding suggests that competitive encounters between bacterial cells could have profound consequences on the evolution of bacterial populations.
When bacterial cells come into contact, they often produce toxins as a defence mechanism. Although it is known that the bacteria producing these toxins have a competitive advantage, exactly how the toxins affect the recipient cells is less clear.
"Undergoing intoxication is not always detrimental for cells - there are scenarios in which encountering a toxin could provide a benefit, such as generating antibiotic ...
Biopolymer-coated nanocatalyst can help realize a hydrogen fuel-driven future
2021-02-23
To combat climate change, shifting from fossil fuels to clean and sustainable energy sources is imperative. A popular candidate in this regard is hydrogen, an eco-friendly fuel that produces only water when used. However, the efficient methods of hydrogen production are usually not eco-friendly. The eco-friendly alternative of splitting water with sunlight to produce hydrogen is inefficient and suffers from low stability of the photocatalyst (material that facilitates chemical reactions by absorbing light). How does one address the issue of developing a stable and efficient photocatalyst?
In a study recently published in Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, ...
A memory without a brain
2021-02-23
Having a memory of past events enables us to take smarter decisions about the future. Researchers at the Max-Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS) and the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have now identified how the slime mold Physarum polycephalum saves memories - although it has no nervous system.
The ability to store and recover information gives an organism a clear advantage when searching for food or avoiding harmful environments. Traditionally it has been attributed to organisms that have a nervous system.
A new study authored by Mirna Kramar (MPI-DS) and Prof. Karen Alim (TUM and MPI-DS) challenges this view by uncovering the surprising abilities of a highly dynamic, single-celled organism to store and ...
'Problem of missing ice' finally solved by movement of the earth's crust
2021-02-23
During ice ages, the global mean sea level falls because large amounts sea water are stored in the form of huge continental glaciers. Until now, mathematical models of the last ice age could not reconcile the height of the sea level and the thickness of the glacier masses: the so-called Missing Ice Problem. With new calculations that take into account crustal, gravitational and rotational perturbation of the solid Earth, an international team of climate researchers has succeeded in resolving the discrepancy, among them Dr. Paolo Stocchi from the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ). The study, now published in the ...
[1] ... [2616]
[2617]
[2618]
[2619]
[2620]
[2621]
[2622]
[2623]
2624
[2625]
[2626]
[2627]
[2628]
[2629]
[2630]
[2631]
[2632]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.