Hospital hygiene: A closer look reveals realistic frequency of infection
2021-02-18
The incidence of surgical site infections after an operation is an important quality indicator for hospitals. An overview from six European countries published in 2017 documented increased costs and, in some cases, significantly poorer surgical outcomes due to SSIs. The European Center for Disease Control (ECDC) and authorities in the U.S. have therefore defined criteria for recording and documenting the rate of surgical site infections per procedure. Swissnoso has issued binding guidelines for Switzerland based on these criteria. The study investigated to what extent surgical site ...
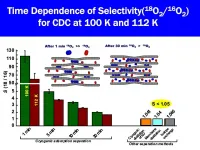
An efficient method for separating O-18 from O-16, essential for use in cancer treatment
2021-02-18
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) plays a major role in the early detection of various types of cancer. A research group led by Specially Appointed Professor Katsumi Kaneko of the Research Initiative for Supra-Materials (RISM), Shinshu University have discovered a method to separate oxygen-18 from oxygen-16, an essential isotope for PET diagnosis, at high speed and high efficiency. The results of this research were recently published online in the journal Nature Communications.
The novel method for the rapid and efficient separation of O-18 from O2-16, which ...
Climate change concern unaffected by pandemic, study shows
2021-02-18
Covid-19 has not made people any less concerned about climate change - despite the pandemic disrupting and dominating many aspects of their lives, a study suggests.
Over a period of 14 months - including the first three months of the Covid-19 lockdown - neither concern about climate change nor belief in the severity of the problem declined in the UK, the research found.
Researchers compared responses to the pandemic with the financial crisis of 2008 to better understand how worries and priorities can change in a crisis.
In contrast to the economic collapse of 2008, which led to reduced concern with environmental issues, the pandemic has not decreased people's belief in the severity of climate change.
The findings shed light on how a concept called the finite pool ...
Smartphone study points to new ways to measure food consumption
2021-02-18
A team of researchers has devised a method using smartphones in order to measure food consumption--an approach that also offers new ways to predict physical well-being.
"We've harnessed the expanding presence of mobile and smartphones around the globe to measure food consumption over time with precision and with the potential to capture seasonal shifts in diet and food consumption patterns," explains Andrew Reid Bell, an assistant professor in New York University's Department of Environmental Studies and an author of the paper, which appears in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Food consumption ...
Study reveals a new potential mechanism underlying loss of muscle mass during menopause
2021-02-18
Menopause is associated with several physiological changes, including loss of skeletal muscle mass. However, the mechanisms underlying muscle wasting are not clear. A new study conducted in collaboration between the universities of Minnesota (USA) and Jyväskylä (Finland) reveals that estrogen deficiency alters the microRNA signalling in skeletal muscle, which may activate signalling cascades leading to loss of muscle mass.
Menopause leads to an estrogen deficiency that is associated with decreases in skeletal muscle mass and strength. This is likely due to changes in both muscle function and the size of muscle cells commonly referred to as fibers.
"The mechanistic role of estrogen in the loss of muscle mass had not been established. In our study, we focused on signaling cascades ...
Penn-developed CAR T therapy shows long-lasting remissions in non-hodgkin lymphoma
2021-02-18
PHILADELPHIA--A significant number of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patients in a Penn Medicine-initiated clinical trial continue to be in remission five years after receiving the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy Kymriah™, researchers in Penn's Abramson Cancer Center reported today in the END ...
Electrons living on the edge
2021-02-18
Tsukuba, Japan - Scientists at the University of Tsukuba demonstrated the possibility of electrons moving as if they were massless when certain materials called "topological insulators" are irradiated with laser beams. This work may lead to a new class of highly efficient electronic devices and photonic crystals.
Conventional electronic devices rely primarily on silicon crystals. From the point of view of electrons that make up the electrical signals coursing through these materials, the systems are so big as to be practically endless. This causes most of the electronic structures ...
Discovery of biomarker could help predict Alzheimer's years before symptoms emerge
2021-02-18
A unique brain protein measured in the blood could be used to diagnose Alzheimer's disease decades before symptoms develop, according to new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research.
Published in Nature journal Translational Psychiatry, the study is the first to find that people with elevated glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the blood also have increased amyloid beta in the brain, a known indicator of Alzheimer's disease.
GFAP is a protein normally found in the brain, but it is released into the blood when the brain is damaged by early Alzheimer's disease.
Alzheimer's disease affects more than 340,000 Australians and more than 35 million people in the world. Current ...
A new piece of the HIV infection puzzle explored
2021-02-18
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg and at the Zentrum für Infektiologie at Heidelberg University Hospital have succeeded for the first time in imaging HIV during transport into the nucleus of an infected cell. The electron tomographic images show the protein envelope of the virus passing through one of the nuclear pores - the openings in the membrane around the nucleus that allow molecules in and out. The scientists found that the virus passes through the nuclear pore intact, only breaking apart inside the nucleus, where it releases its genetic information. This clarifies an important mechanism by which the virus's genetic material is integrated into the genome of the infected cell.
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) - which was ...
Locked MOFs are the key to high porosity
2021-02-18
A highly porous metal organic framework, assembled from molecular building blocks designed to lock together in a specific orientation, has been developed by researchers at KAUST.
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are crystalline materials made from metal ions connected by organic linkers. Their internal structure is like a repeating array of tiny identical cages, which are ideal for hosting various molecules. MOFs have found potential uses from gas sensing to molecular separations to storage, depending on the dimensions and structure of their pores.
One family of MOFs has been inspired by inorganic porous materials called zeolites. Zeolites are a special class of porous material with ...
How location dictates biological clocks of species: Study in beetles offers new insights
2021-02-18
One of the most intriguing features in all living beings is the "biological clock", an internal time-keeping mechanism that governs our behavioral pattern (such as the sleep-wake cycle). In fact, the biological clock dictates the developmental timing of various processes, such as when flowers bloom and insects reproduce. Biologists refer to these activities collectively as "circadian rhythms," owing to the rhythmic pattern in which they occur.
Since their discovery, circadian rhythms have been studied extensively, and today we know a great deal about how they work. ...
Perception critical to women's breast reconstruction decision making
2021-02-18
When women undergo surgical treatment for breast cancer, they often also have reconstructive surgery but new QUT research reveals many women feel left out of the decision making.
An interdisciplinary study from researchers in QUT's Centre for Behavioural Economics, Society and Technology (BEST), Engineering Faculty, and School of Nursing, along with Dr Jeremy Hunt a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons and Dr Tim Peltz from the University of New South Wales, on Knowledge, consultation time and choice in breast reconstruction has just been published in the British Journal of Surgery.
"Approximately one in seven Australian women will be diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime," ...
Unexpected decrease in ammonia emissions due to COVID-19 lockdowns
2021-02-18
Most Chinese working in the cities return to work today after a 7-day public holiday of Spring Festival. The annual Spring Festival, which also marks the start of Chinese New Year, traditionally begins with the second new moon following the winter solstice, usually in January or February. Like westerners on Thanksgiving and Christmas, people across China return to their hometown to reunite with family and friends. However, the sudden outbreak of COVID-19 last year halted the largest holiday mobilization in the world. In response to the crisis, in late 2019, local governments launched ...
Magnetic attraction: Breakthrough test for malaria
2021-02-18
After nearly a decade of research, a new test that detects the magnetic properties of malaria-infected blood could soon be used to help eliminate the mosquito-borne disease.
Dr Stephan Karl, a Senior Research Fellow in Malaria and Vector Biology at James Cook University's Australian Institute of Tropical Health and Medicine, has led an international study to field-test a new tool in the fight to eliminate the disease, which had 229 million reported cases in 2019.
"Malaria is easily treated but it is actually hard to diagnose, and because of that there ...
Quantum computing: when ignorance is wanted
2021-02-18
Quantum computers promise not only to outperform classical machines in certain important tasks, but also to maintain the privacy of data processing. The secure delegation of computations has been an increasingly important issue since the possibility of utilizing cloud computing and cloud networks. Of particular interest is the ability to exploit quantum technology that allows for unconditional security, meaning that no assumptions about the computational power of a potential adversary need to be made.
Different quantum protocols have been proposed, all of which make trade-offs between computational performance, security, and resources. Classical protocols, for example, are either limited ...
Selective concentration of cationic species
2021-02-18
Sample pretreatment processes such as concentration or classification are essential to finding trace substances present in a fluid. In scientific communities recently, prolific research is being conducted on sample pretreatment techniques utilizing electrokinetics.1 However, due to the lack of commercial anion-permselective material - an essential component - its potential application is limited to only negatively charged particles. To this, a research team at POSTECH has found a way to isolate and concentrate only the cationic samples.
A POSTECH research team led by Professor Geunbae Lim, Ph.D. candidate Minsoo Lee, and Dr. Hyukjin J. Kwon of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a novel type of multiscale-porous anion exchange ...
New revelations of tiger genomes
2021-02-18
Genetic variation is like money in the bank: the more you have, the better your chances of survival in the future. Population bottlenecks decrease genetic variation, especially in endangered species. An individual's genome comprises the events that have impacted genetic variation over time, and relatively recent sequencing technologies allow us to read and interpret genetic variation across the genome. Although tigers have received significant conservation attention, little is known about their evolutionary history and genomic variation. This is especially true for Indian tigers, and ...
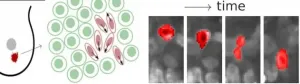
Physics of tumours: Cancer cells become fluidised and squeeze through tissue
2021-02-18
Working with colleagues from Germany and the US, researchers at Leipzig University have achieved a breakthrough in research into how cancer cells spread. In experiments, the team of biophysicists led by Professor Josef Alfons Käs, Steffen Grosser and Jürgen Lippoldt demonstrated for the first time how cells deform in order to move in dense tumour tissues and squeeze past neighbouring cells. The researchers found that motile cells work together to fluidise tumour tissue.
Käs led the research project in cooperation with Professor Lisa Manning from Syracuse University (US) and Professor Bahriye Aktas from Leipzig University Hospital. They have now ...
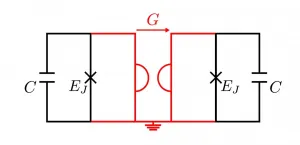
Blueprint for fault-tolerant qubits
2021-02-18
Building a universal quantum computer is a challenging task because of the fragility of quantum bits, or qubits for short. To deal with this problem, various types of error correction have been developed. Conventional methods do this by active correction techniques. In contrast, researchers led by Prof. David DiVincenzo from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University, together with partners from the University of Basel and QuTech Delft, have now proposed a design for a circuit with passive error correction. Such a circuit would already be inherently fault protected and could significantly accelerate the construction of a quantum computer with a large number of qubits.
In order to encode quantum information ...
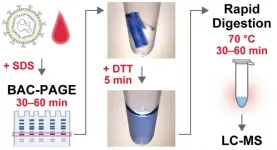
A novel gel electrophoresis technique for rapid biomarker diagnosis via mass spectrometry
2021-02-18
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful method for biomarker analysis because it enables highly sensitive and accurate measurement of target molecules in clinical samples. The application of MS to clinical diagnosis, such as neonatal metabolic screening, has been progressing with a focus on metabolite markers. MS measurement of proteins is currently mainly used for novel marker discovery studies, but there is a growing interest in its application in clinical marker diagnosis as an alternative to immunoassays.
MS-based quantification of protein biomarkers is mainly performed by a bottom-up approach using peptide fragments obtained by enzymatic ...
Youth exposed to natural disasters report low post-traumatic stress
2021-02-18
A study of over 1,700 U.S. young people exposed to four major hurricanes found that just a few of them reported chronic stress, and the trajectories among most youth reflected recovery or low-decreasing post-traumatic stress (PTS) symptoms, according to research recently published in JAMA Network Open.
Titled "Trajectories of Post-traumatic Stress in Youths After Natural Disasters," the inquiry, conducted from August 2017 to August 2020, combined data from four studies of youths ages six to 16 who attended schools near the respective destructive paths of Hurricanes Andrew (1992), Charley (2004), Ike (2005) and Katrina (2008), from three to 26 months following the disasters. Fifty-four percent of ...
Waste into wealth: Harvesting useful products from microbial growth
2021-02-18
Ancient alchemists dreamed of transforming base materials like lead into gold and other valuable commodities. While such efforts generally came to naught, researchers today are having some success in extracting a variety of useful products like aviation fuels, lubricants, solvents, food additives and plastics from organic waste.
The trick is accomplished with the aid of specialized bacteria, whose metabolic activities can convert simpler chemicals into useful products through a microbial growth process knows as chain elongation.
Anca Delgado, a researcher in the Biodesign Swette Center for Environmental Biotechnology at Arizona State University, has been exploring the phenomenon. In a new study, she describes ...
Immunosuppressive cell and cytokine response linked to bone nonunion
2021-02-18
EUGENE, Ore. -- Feb. 18, 2021 -- An abnormal suppression of the immune system linked to the onset of numerous diseases has been associated with poor functional regeneration of traumatic bone injuries.
Levels of immune cells and proteins circulating in the blood following traumatic injury combined with advanced data analytics could predict whether patients are likely to respond to treatment, said Robert Guldberg, executive director of the Phil and Penny Knight Campus for Accelerating Scientific Impact.
The project -- detailed in a paper published online ahead of print in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences -- identified ...
Study finds risk factor for blood clots occurs in more than 10 percent of transgender men using testosterone
2021-02-18
WASHINGTON--A potentially dangerous side effect of testosterone therapy for transgender men is an increase in red blood cells that can raise the risk of blood clots, heart attack or stroke, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Gender diverse people make up an estimated 0.6% of the U.S. population and are defined as having gender identity that is not aligned with their sex recorded at birth. Transgender men often undergo testosterone therapy as part of their gender-affirming treatment. Erythrocytosis, a condition where your body makes too many red blood cells, is a common side effect of testosterone therapy that can increase the risk of blood clots, heart attack or stroke.
"Erythrocytosis is common ...
Increasingly fragmented tiger populations may require 'genetic rescue'
2021-02-18
Despite being one of the world's most charismatic species, tigers face uncertain futures primarily due to habitat fragmentation, human-wildlife conflict and poaching. As global tiger populations decline, so does their genetic diversity. But until now it's been unclear how the animals' dwindling numbers are affecting them at the genetic level.
To find out, researchers at Stanford University, the National Centre for Biological Sciences, India, and various zoological parks and NGOs sequenced 65 genomes from four of the surviving tiger subspecies. Their findings confirmed that strong genetic differences exist between different tiger subspecies but showed, surprisingly, that these differences emerged relatively recently, ...
[1] ... [2619]
[2620]
[2621]
[2622]
[2623]
[2624]
[2625]
[2626]
2627
[2628]
[2629]
[2630]
[2631]
[2632]
[2633]
[2634]
[2635]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.