The Lancet Public Health: Jail incarceration strongly linked with several causes of premature death in US counties </p>
2021-02-24
Unique analysis of US county-level data finds a strong association between jail incarceration and death rates at the county level from infectious diseases, chronic lower respiratory disease, drug use, and suicide; and to a lesser extent heart disease and cancer.
Findings underscore public health benefits of reducing jail incarceration and importance of interventions to mitigate the harmful effects of mass imprisonment on community health including treatment for substance use disorder and greater investment in social services.
County jail incarceration rates in the USA are potential drivers of many causes of death in the communities where they are located, with particularly pronounced effects on the number of deaths caused by infectious and respiratory diseases, drug overdose, and suicide, ...
Fighting fit cockroaches have 'hidden strength'
2021-02-24
A new study has discovered that not all cockroaches are equal and "super athletes", with larger respiratory systems, are more likely to win physical mating battles.
The research, published in the journal Animal Behaviour and led by Dr Sophie Mowles of Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), studied aggressive interactions between male wide-horned hissing cockroaches (Gromphadorhina oblongonota).
Animal contests are usually won by the larger opponent and physical fighting is often avoided if clear differences exist between competitors. However, during a series of laboratory contests, the researchers closely matched the cockroaches ...
Global travellers vulnerable to drug-resistant bacteria - study
2021-02-24
International travellers are particularly vulnerable to virulent strains of drug-resistant bacteria - often picking up several different types during a trip through spending time in the company of other tourists, a new study reveals.
The global spread of intestinal multidrug resistant gram-negative (MDR-GN) bacteria poses a serious threat to human health worldwide, with MDR clones of E.coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae threatening more antibiotic resistant infections around the world.
Researchers monitored a group of European travellers visiting Lao People's Democratic Republic for three weeks - analysing daily returns of ...
Incarceration is strongly linked with premature death in US
2021-02-24
An analysis of U.S. county-level data found a strong association between jail incarceration and death rates from infectious diseases, chronic lower respiratory disease, drug use, and suicide, in a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The researchers found this was the case to a lesser extent for heart disease and cancer. The study is the first to examine the link between the expansion of the jail population and multiple specific causes of death at the county level, and adds to the growing body of evidence suggesting that decarceration strategies would improve public health. Findings are published online in the journal Lancet ...
Waitlist policies may contribute to racial disparities in kidney transplant access
2021-02-24
Highlight
Racial disparities in access to kidney transplantation persist in the United States. New research indicates that registering Black patients on the kidney transplant waitlist at a slightly higher level of kidney function compared with white patients might lessen racial inequality in patients' wait time prior to kidney failure onset, and ultimately improve racial equity in access to kidney transplantation.
Washington, DC (February 23, 2021) -- Despite efforts to address them, racial disparities in access to kidney transplantation persist in the United States. New research published in an upcoming issue of JASN indicates that policy changes surrounding patients' eligibility to be put on kidney transplant waitlists might help address these disparities.
There are studies ...
Do people with migraine get enough exercise?
2021-02-23
MINNEAPOLIS - More than two-thirds of people with migraine do not get enough exercise, according to a preliminary study released today, February 23, 2021, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 73rd Annual Meeting being held virtually April 17 to 22, 2021. The study found that people who do get a minimum of two-and-a-half hours of moderate to vigorous exercise a week had a reduced rate of migraine triggers like stress, depression and sleep problems.
"Migraine is a disabling condition that affects millions of people in the United States, and yet regular exercise may be an effective way to reduce the frequency and intensity of some migraines," said study author Mason Dyess, D.O., of the University ...
You've got to move it, move it
2021-02-23
One in four women over age 65 is unable to walk two blocks or climb a flight of stairs. Known as mobility disability, it is the leading type of incapacity in the United States and a key contributor to a person's loss of independence. New research from Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Sciences at UC San Diego suggests that light-intensity physical activity, including shopping or a casual walk, may protect mobility in older women.
Published in the February 23, 2021 online issue of JAMA Network Open, researchers found that women ...
Positive reinforcements help algorithm forecast underground natural reserves
2021-02-23
Texas A&M University researchers have designed a reinforcement-based algorithm that automates the process of predicting the properties of the underground environment, facilitating the accurate forecasting of oil and gas reserves.
Within the Earth's crust, layers of rock hold bountiful reservoirs of groundwater, oil and natural gas. Now, using machine learning, researchers at Texas A&M University have developed an algorithm that automates the process of determining key features of the Earth's subterranean environment. They said this research might help with accurate forecasting of our natural reserves.
Specifically, the researchers' algorithm ...
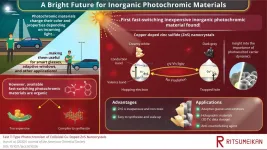
Transformed by light: Fast photochromism discovered in an inexpensive inorganic material
2021-02-23
Isn't it convenient when office building windows adaptively darken according to the intensity of sunlight? Or when standard glasses turn into sunglasses under the sun and switch back as you enter a building? Such feats are possible thanks to photochromic materials, whose optical (and other) properties change radically when irradiated by visible or ultraviolet light.
Today, virtually all fast-switching photochromic materials are made using organic compounds. Unfortunately, this makes them considerably expensive and complex to synthesize, requiring multi-step processes that are difficult to scale up for mass production. So, despite the myriad ...
Oxidation processes in combustion engines and in the atmosphere take the same routes
2021-02-23
Thuwal/Helsinki/Leipzig. Alkanes, an important component of fuels for combustion engines and an important class of urban trace gases, react via another reaction pathways than previously thought. These hydrocarbons, formerly called paraffins, thus produce large amounts of highly oxygenated compounds that can contribute to organic aerosol and thus to air pollution in cities. An international research team has now been able to prove this through laboratory experiments with state-of-the-art measurement technology at the University of Helsinki and the Leibniz Institute for Tropospheric ...
Machine learning aids in simulating dynamics of interacting atoms
2021-02-23
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., February 23, 2021--A revolutionary machine-learning (ML) approach to simulate the motions of atoms in materials such as aluminum is described in this week's Nature Communications journal. This automated approach to "interatomic potential development" could transform the field of computational materials discovery.
"This approach promises to be an important building block for the study of materials damage and aging from first principles," said project lead Justin Smith of Los Alamos National Laboratory. "Simulating the dynamics of interacting atoms is a cornerstone of understanding and developing new materials. Machine learning methods are providing computational scientists new tools to accurately and efficiently conduct these atomistic ...
Abundance of iron drives cell death and could inform novel treatments for neuroblastoma
2021-02-23
Neuroblastoma is a cancer that develops in nerve tissue, most commonly in the glands around the kidneys. The gene MYCN is overexpressed in 20-25% of neuroblastoma, and MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma contributes to a considerable percentage of pediatric cancer-related deaths.
Anthony Faber, Ph.D., and a team of researchers at VCU Massey Cancer Center were awarded a grant from the American Cancer Society to study how MYCN and an abundance of iron can drive cancer cell death in neuroblastoma and potentially be targeted with novel treatments. This award is the first part of a potential two-stage grant worth a combined total of $600,000.
"Iron is a double-edged sword in a cancer cell. It can help the cancer grow and survive, but it also creates ...
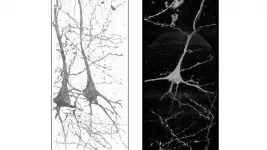
Seeing schizophrenia: X-rays shed light on neural differences, point toward treatment
2021-02-23
Schizophrenia, a chronic, neurological brain disorder, affects millions of people around the world. It causes a fracture between a person's thoughts, feelings and behavior. Symptoms include delusions, hallucinations, difficulty processing thoughts and an overall lack of motivation. Schizophrenia patients have a higher suicide rate and more health problems than the general population, and a lower life expectancy.
There is no cure for schizophrenia, but the key to treating it more effectively is to better understand how it arises. And that, according to Ryuta Mizutani, professor of applied biochemistry at Tokai University in Japan, means studying the structure of brain tissue. Specifically, it means comparing the brain tissues of schizophrenia patients with those ...
Stanford researchers identify four causes of "Zoom fatigue" and their simple fixes
2021-02-23
Even as more people are logging onto popular video chat platforms to connect with colleagues, family and friends during the COVID-19 pandemic, Stanford researchers have a warning for you: Those video calls are likely tiring you out.
Prompted by the recent boom in videoconferencing, communication Professor Jeremy Bailenson, founding director of the Stanford Virtual Human Interaction Lab (VHIL), examined the psychological consequences of spending hours per day on these platforms. Just as "Googling" is something akin to any web search, the term "Zooming" has become ubiquitous and a generic verb to replace videoconferencing. Virtual meetings have skyrocketed, with hundreds of millions happening daily, as social distancing protocols have kept people apart physically.
In ...
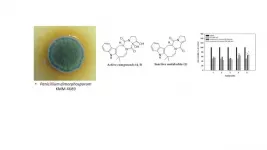
Scientists found in marine mold substance that antidotes paraquat
2021-02-23
Biologically active compounds from the marine fungus Penicillium dimorphosporum protect cells from paraquat, the highly toxic herbicide with no remedy, and might enhance the action of some drugs. The fungus was isolated from soft coral collected in the South China Sea during an expedition on the Akademik Oparin research vessel. Scientists of Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU) and G. B. Elyakov Pacific Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry reported the results in Marine Drugs.
Paraquat a herbicide compound highly toxic for animals and humans. About a hundred countries, including the United States, apply it for crop cultivation and weed control. Dozens of countries, including Russia, have banned the ...
School of Community Health Sciences publishes study on sugar-sweetened beverage taxes
2021-02-23
A new research study out of the University of Nevada, Reno's School of Community Health Sciences has just been published by the American Journal of Public Health and addresses state preemption of local sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) taxes, issuing an emerging public health threat. Assistant Professor Eric Crosbie examines commercial determinants of health and public health policy, specifically in industries like tobacco and food and beverage.
"The beverage industry is aggressively attempting to preempt sugar-sweetened beverage taxes at the state level to prevent the diffusion of progressive policies at the local level throughout the United States," Crosbie, an affiliate of the University's Ozmen Institute for Global Studies, said. "Once preemption laws are enacted, ...
Give the heart a ketone? It may be beneficial
2021-02-23
There is growing evidence that ketone bodies may be beneficial to heart disease patients regardless of the method of delivery used to increase ketone delivery to the heart. A Journal of the American College of Cardiology review paper examines emerging evidence regarding ketone bodies' effects on the heart and the potential for ketone therapy as a cardiovascular intervention in heart disease patients.
In recent years ketone bodies entered the popular lexicon through the "keto diet," which consists of a very low carbohydrate and high fat diet that endeavors to force the body into ketosis. This is a metabolic ...
Monoclonal antibodies against MERS coronavirus show promise in phase 1 NIH-sponsored trial
2021-02-23
WHAT:
A randomized, placebo-controlled Phase 1 clinical trial of two monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed against the coronavirus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) found that they were well tolerated and generally safe when administered simultaneously to healthy adults. The experimental mAbs, REGN3048 and REGN3051, target the MERS coronavirus (MERS CoV) spike protein used by the virus to attach to and infect target cells. The mAbs were discovered and developed by scientists at the biopharmaceutical company Regeneron, located in Tarrytown, New York. The trial was sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
The trial was the first to test the experimental antibodies
Hyperlink Code ...
New strategy blocks chronic lung disease in mice
2021-02-23
Inflammatory lung diseases such as asthma, COPD and, most recently, COVID-19, have proven difficult to treat. Current therapies reduce symptoms and do little to stop such diseases from continuing to damage the lungs. Much research into treating chronic inflammatory diseases has focused on blocking chemicals called cytokines, which trigger cascades of molecular events that fuel damaging inflammation.
Now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found that such cytokines can drive inflammation in more ways than previously understood, perhaps revealing new routes ...
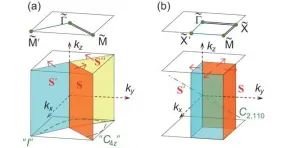
High-throughput screening for Weyl semimetals with S4 symmetry
2021-02-23
Using the symmetries of the systems, people can define various topological invariants to describe different topological states. The topological materials can be accurately discovered by calculating the topological invariants. Recently, researchers found that irreducible representations and compatibility relationships can be used to determine whether a material is topological nontrivial/trivial insulator (satisfying the compatibility relations) or topological semimetal (violating the compatibility relations), which leads to a large number of topological materials predicted by theoretical calculations. However, Weyl semimetals go beyond this paradigm because the existence of Weyl fermions does not need any symmetry protections (except for lattice translation symmetries). At present, ...
Transforming urban systems: Toward sustainability
2021-02-23
Urban areas are on the rise and changing rapidly in form and function, with spillover effects on virtually all areas of the Earth. The UN estimates that by 2050, 68% of the world's population will reside in urban areas. In the inaugural issue of npj Urban Sustainability, a new Nature Partner Journal out today, a team of leading urban ecologists outlines a practical checklist to guide interventions, strategies, and research that better position urban systems to meet urgent sustainability goals.
Co-author Steward Pickett of Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies explains, "Urban areas shape demographics, ...
Models to predict dengue, zika and yellow fever outbreaks are developed by researchers
2021-02-23
By Maria Fernanda Ziegler | Agência FAPESP – Yellow fever was the first human disease to have a licensed vaccine and has long been considered important to an understanding of how epidemics happen and should be combated. It was introduced to the Americas in the seventeenth century, and high death rates have resulted from successive outbreaks since then. Epidemics of yellow fever were associated with the slave trade, the US gold rush and settlement of the Old West, the Haitian Revolution, and construction of the Panama Canal, to cite only a few examples.
Centuries after the disease was first reported in the Americas, an international team of researchers will embark on a groundbreaking study to develop ...
Managing suicide risk in research study participants
2021-02-23
What should researchers do if they encounter a study participant who reports suicidal thoughts?
UIC College of Nursing associate professor Susan Dunn explores this question as lead author of "Suicide Risk Management Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial of Cardiac Patients Reporting Hopelessness," a paper published in the January/February edition of Nursing Research.
Suicide is ranked as the 10th leading cause of death for all ages in the U.S. and can be identified through clinical research, according to the paper.
Although suicide screening tools are widely available for patients in emergency, hospital and primary care settings and ...
Dingo effects on ecosystem visible from space
2021-02-23
The environmental impacts of removing dingoes from the landscape are visible from space, a new UNSW Sydney study shows.
The study, recently published in Landscape Ecology, pairs 32 years' worth of satellite imagery with site-based field research on both sides of the Dingo Fence in the Strzelecki Desert.
The researchers found that vegetation inside the fence - that is, areas without dingoes - had poorer long-term growth than vegetation in areas with dingoes.
"Dingoes indirectly affect vegetation by controlling numbers of kangaroos and small mammals," says Professor Mike Letnic, senior author of the study and researcher at UNSW's Centre ...
Reclusive neutron star may have been found in famous supernova
2021-02-23
Since astronomers captured the bright explosion of a star on February 24, 1987, researchers have been searching for the squashed stellar core that should have been left behind. A group of astronomers using data from NASA space missions and ground-based telescopes may have finally found it.
As the first supernova visible with the naked eye in about 400 years, Supernova 1987A (or SN 1987A for short) sparked great excitement among scientists and soon became one of the most studied objects in the sky. The supernova is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small companion galaxy to our own Milky Way, only about 170,000 light-years from Earth.
While astronomers watched debris ...
[1] ... [2611]
[2612]
[2613]
[2614]
[2615]
[2616]
[2617]
[2618]
2619
[2620]
[2621]
[2622]
[2623]
[2624]
[2625]
[2626]
[2627]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.