What to do when a mammogram shows swollen lymph nodes in women just vaccinated for COVID
2021-02-24
BOSTON - Swelling of lymph nodes in the armpit area is a normal response to COVID-19 vaccinations, but when they are seen on mammograms, they can be mistaken for nodes that are swollen because of cancer. In some cases, the nodes are biopsied to confirm they are not cancer. To avoid confusion by patients and their providers, and to avoid delays in either vaccinations or recommended mammograms through the pandemic, radiologists at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have published an approach to manage what is expected to be a fairly common occurrence as vaccination programs ramp up. The approach is described in the American Journal of Roentgenology.
"We had started ...
After Hurricane Irma, soundscape reveals resilient reef ecosystem
2021-02-24
A new study from North Carolina State University reveals that the soundscapes of coral reef ecosystems can recover quickly from severe weather events such as hurricanes. The work also demonstrates that non-invasive monitoring is an important tool in shedding further light on these key ecosystems.
Soundscape ecology is a relatively new way for researchers to keep tabs on a variety of habitats without direct interference. In underwater habitats like coral reefs, soundscapes allow continual monitoring of an ecosystem that is difficult to access. By deploying underwater microphones, or hydrophones, researchers can get an acoustic picture of the types of animals in the ecosystem, as well as their behavior patterns.
Kayelyn Simmons, a Ph.D. student at NC State, used soundscapes and ...
Parker Solar Probe offers stunning view of Venus
2021-02-24
NASA's Parker Solar Probe captured stunning views of Venus during its close flyby of the planet in July 2020.
Though Parker Solar Probe's focus is the Sun, Venus plays a critical role in the mission: The spacecraft whips by Venus a total of seven times over the course of its seven-year mission, using the planet's gravity to bend the spacecraft's orbit. These Venus gravity assists allow Parker Solar Probe to fly closer and closer to the Sun on its mission to study the dynamics of the solar wind close to its source.
But -- along with the orbital dynamics -- these passes can also yield some unique and even unexpected views of the inner solar system. During the mission's third ...
Ancient skeletal hand could reveal evolutionary secrets
2021-02-24
Evolutionary expert Charles Darwin and others recognized a close evolutionary relationship between humans, chimps and gorillas based on their shared anatomies, raising some big questions: how are humans related to other primates, and exactly how did early humans move around? Research by a Texas A&M University professor may provide some answers.
Thomas Cody Prang, assistant professor of anthropology, and colleagues examined the skeletal remains of Ardipithecus ramidus ("Ardi"), dated to 4.4 million years old and found in Ethiopia. One of Ardi's hands was exceptionally well-preserved.
The researchers compared the shape of Ardi's hand to hundreds of other hand specimens representing recent humans, apes and monkeys (measured ...
Study finds human-caused North Atlantic right whale deaths are being undercounted
2021-02-24
A study co-authored by scientists at the New England Aquarium has found that known deaths of critically endangered North Atlantic right whales represent a fraction of the true death toll. This comes as the death of a calf and recent sightings of entangled right whales off the southeastern United States raise alarm.
The study, published this month in END ...
Bearded seals are loud -- but not loud enough
2021-02-24
Ithaca, NY-- During mating season, male bearded seals make loud calls to attract a mate--even their "quiet" call could still be as ear-rattling as a chainsaw. Bearded seals have to be loud to be heard over the cacophony of their equally loud brethren. And, increasingly, the noise humans make is adding to the underwater din and could have serious consequences. A study conducted by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology's Center for Conservation Bioacoustics (CCB) aims to understand how resilient bearded seals can be to changes in ambient underwater noise. The results are published in Proceedings of the Royal Society: Biological Science.
"We wanted to know whether bearded seals would call louder when ...
Tool that more efficiently analyzes ocean color data will become part of NASA program
2021-02-24
Researchers at Stevens Institute of Technology have developed a new machine learning-powered platform, known as OC-SMART, that can process ocean color in satellite images 10 times faster than the world's leading platform. The work, which will be adopted by NASA, is one of the first machine learning-based platforms in ocean color analysis that can process both coastal and open ocean regions globally to reveal data on sea health and the impact of climate change.
The work, led by Knut Stamnes, a physics professor at Stevens, and spearheaded by Yongzhen Fan Ph.D. '16, a visiting physics scholar in Stamnes' lab, solves a 30-year-old problem in retrieving data from both coastal regions and open ocean areas. For decades, NASA's SeaDAS platform exceled at analyzing ocean color ...
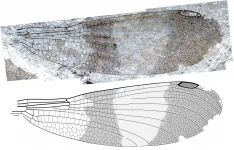
Paleontologists discover new insect group after solving 150-year-old mystery
2021-02-24
For more than 150 years, scientists have been incorrectly classifying a group of fossil insects as damselflies, the familiar cousins of dragonflies that flit around wetlands eating mosquitoes. While they are strikingly similar, these fossils have oddly shaped heads, which researchers have always attributed to distortion resulting from the fossilization process.
Now, however, a team of researchers led by Simon Fraser University (SFU) paleontologist Bruce Archibald has discovered they aren't damselflies at all, but represent a major new insect group closely related to them.
The findings, published today in Zootaxa, show that the distinctive shape of the insect's non-protruding, ...
'Miracle poison' for novel therapeutics
2021-02-24
When people hear botulinum toxin, they often think one of two things: a cosmetic that makes frown lines disappear or a deadly poison.
But the "miracle poison," as it's also known, has been approved by the F.D.A. to treat a suite of maladies like chronic migraines, uncontrolled blinking, and certain muscle spasms. And now, a team of researchers from Harvard University and the Broad Institute have, for the first time, proved they could rapidly evolve the toxin in the laboratory to target a variety of different proteins, creating a suite of bespoke, super-selective ...
Over 80% of Atlantic Rainforest remnants have been impacted by human activity
2021-02-24
A Brazilian study published (http://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20217-w) in Nature Communications shows that human activities have directly or indirectly caused biodiversity and biomass losses in over 80% of the remaining Atlantic Rainforest fragments.
According to the authors, in terms of carbon storage, the biomass erosion corresponds to the destruction of 70,000 square kilometers (km²) of forest - almost 10 million soccer pitches - or USD 2.3 billion-USD 2.6 billion in carbon credits. "These figures have direct implications for mechanisms of climate change mitigation," they state in the article.
Atlantic Rainforest remnants ...
Researchers use machine learning to identify autism blood biomarkers
2021-02-24
DALLAS - Feb. 24, 2021 - Using machine learning tools to analyze hundreds of proteins, UT Southwestern researchers have identified a group of biomarkers in blood that could lead to an earlier diagnosis of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and, in turn, more effective therapies sooner.
The identification of nine serum proteins that strongly predict ASD were reported in a study published today by PLOS ONE.
Earlier diagnosis, followed by prompt therapeutic support and intervention, could have a significant impact on the 1 in 59 children diagnosed with autism in the United States. Being able to identify children on the autism spectrum when they are toddlers could make a big difference, says Dwight German, Ph.D., professor of psychiatry at UT Southwestern ...
The risks of communicating extreme climate forecasts
2021-02-24
For decades, climate change researchers and activists have used dramatic forecasts to attempt to influence public perception of the problem and as a call to action on climate change. These forecasts have frequently been for events that might be called "apocalyptic," because they predict cataclysmic events resulting from climate change.
In a new paper published in the International Journal of Global Warming, Carnegie Mellon University's David Rode and Paul Fischbeck argue that making such forecasts can be counterproductive. "Truly apocalyptic forecasts can only ever be observed in their failure--that is the world did not end as predicted," says Rode, adjunct research faculty with the Carnegie Mellon Electricity Industry Center, "and observing ...
Unequal parenthood impacts may explain academia's publication gender gap
2021-02-24
Parenthood leads to greater reductions in short-term research productivity for mothers across three disciplines than for fathers, largely explaining the publication gender gap between women and men in academia, according to an analysis of survey data from 3,064 tenure track faculty at PhD-granting universities in the U.S. and Canada. The findings suggest that policies designed to boost workplace flexibility for parents, including easily accessible lactation rooms and affordable childcare, may help to ease the impact of parenthood on mothers in academia, giving them more time for research. While a large body of previous research across academic fields has shown that men tend to publish more papers than women, the reasons for this have remained uncertain. ...
Potential biomarker predicts the risk of kidney transplant rejection in patients
2021-02-24
Scientists have found that comparing the ratio of two immune molecules helped predict the likelihood of transplant rejection in 339 patients who received kidney transplants, the only curative treatment for late-stage kidney failure. Their results suggest that monitoring this ratio could help distinguish high-risk patients early on, before long-term organ rejection becomes inevitable, allowing clinicians to intervene accordingly with new treatments. Kidney transplants often grant immediate benefits to patients with end-stage kidney disease, but long-term outcomes are mixed, as 35% of transplant recipients lose their new kidney within ...
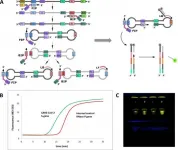
A gearbox for tumor cell identity changes
2021-02-24
Cancer cells can experience stress. They have to contend with attacks by the immune system or with anti-cancer therapeutics. If they attempt to colonize other tissues, they have to break away from the extracellular matrix, enter the bloodstream and survive during the travel through the body. Then exit and start building a new colony. The ability of cells to adapt their properties to face all the challenges they encounter is called plasticity. In epithelial solid tumors, including the very common lung, breast, colon and pancreatic cancers, tumor cells plasticity hijacks a cellular development process known as epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
EMT is commonly associated to kinases - enzymes that act like a switch, turning biochemical ...
University of Chicago study uncovers inhibitory role of 'Ter cells' in cancer therapies
2021-02-24
Targeted radiation is often used to study and treat diverse cancer types. A multidisciplinary research team based at the University of Chicago Medicine has recently focused on a type of cell that releases a protein that enhances resistance to cancer therapies and promotes tumor progression.
The study focused on Ter cells, which are extra medullary erythroid precursers that secrete the neuropeptide artemin. In the study, published February 24, 2020, in Science Translational Medicine, the researchers showed that local tumor radiotherapy, systemic immunotherapy or the combination of both treatments were able to deplete Ter cells in the spleen, reduce artemin production and limit tumor progression both in the locally irradiated tumors as well as outside ...
Asteroid dust found in crater closes case of dinosaur extinction
2021-02-24
Researchers believe they have closed the case of what killed the dinosaurs, definitively linking their extinction with an asteroid that slammed into Earth 66 million years ago by finding a key piece of evidence: asteroid dust inside the impact crater.
Death by asteroid rather than by a series of volcanic eruptions or some other global calamity has been the leading hypothesis since the 1980s, when scientists found asteroid dust in the geologic layer that marks the extinction of the dinosaurs. This discovery painted an apocalyptic picture of dust from the vaporized asteroid and rocks from impact circling the planet, blocking ...
Politicized pandemic shaped compliance with social distancing
2021-02-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Politicization of the COVID-19 pandemic had a powerful influence over adherence to social distancing guidelines in the United States and why people did, or did not, comply during the lockdown days, a new study has found.
The analysis boiled down to whom study participants trusted most: scientists or President Donald Trump.
"People who expressed a great deal of faith in President Trump, who thought he was doing an effective job of guiding us through the pandemic, were less likely to socially distance," said Russell Fazio, senior author of the study and a professor ...
Ultra-rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 in public workspace environments
2021-02-24
Ultra-fast, cheap LAMP-based COVID tests could be performed by non-experts at work and in public spaces, giving results in under an hour
INFORMATION:
Article Title: "Ultra-rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 in public workspace environments"
Funding: This project was made possible through the support of a grant from Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry, LLC, The funder provided support in the form of salaries and supplies for authors OY, ZY, JM, and BO, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific ...
Improving road safety to tackle crime
2021-02-24
Improving road safety in cities could result in a lower rate of violent crime, according to research from UCL.
Experts analysing crime and car accident data in Mexico City found a surprisingly high level of synchronicity between the two on a weekly cycle, suggesting that applying more resources to prevent road accidents would improve crime rates by enabling more efficient policing.
For the paper, published today in Cities as Complex Systems special issue in PLOS ONE, experts plotted the time and locations of nearly one million car accidents and 200,000 ...
New research at UH Rainbow studies the impact of face masks on heart ra
2021-02-24
CLEVELAND, Ohio - Researchers at University Hospitals Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital (UH Rainbow) published new findings today that wearing a face mask - either a cloth mask or a surgical mask - did not impair the ability of subjects to get air in and out of their bodies.
The study measured heart rate, transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension, and oxygen levels in 50 adult volunteers at the conclusion of six 10-minute phases: Sitting quietly and then walking briskly without a mask; sitting quietly and then walking briskly while wearing a cloth mask; and sitting quietly and then walking ...
New technology shows potential to improve potency and durability benefits in gene therapy
2021-02-24
WATERTOWN, Mass. - Gene therapy has traditionally been conceptualized as a one-time, curative treatment option; however, research shows that there may be a need for subsequent doses years after initial treatment. While adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors are a core part of this powerful therapeutic approach, they present two key challenges in gene therapy.
The first challenge is their immunogenicity. In gene therapy, the formation of neutralizing antibodies (Nabs) in response to AAV vector administration precludes retreatment of a patient due to the potentially dangerous immune response that would occur after a second or third administration of the therapy.
The second obstacle relates to their durability. AAV vectors ...
Scientists describe earliest primate fossils
2021-02-24
A new study published Feb. 24 in the journal Royal Society Open Science documents the earliest-known fossil evidence of primates.
A team of 10 researchers from across the U.S. analyzed several fossils of Purgatorius, the oldest genus in a group of the earliest-known primates called plesiadapiforms. These ancient mammals were small-bodied and ate specialized diets of insects and fruits that varied by species. These newly described specimens are central to understanding primate ancestry and paint a picture of how life on land recovered after the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago that wiped out all dinosaurs -- except for birds -- and led to the rise of mammals.
Gregory Wilson Mantilla, a University of Washington professor of biology and curator of vertebrate ...
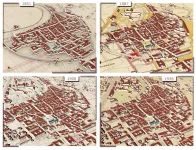
Revive the map: 4D building reconstruction with machine learning
2021-02-24
A research team from Skoltech and FBK (Italy) presented a methodology to derive 4D building models using historical maps and machine learning. The implemented method relies on the geometric, neighbourhood, and categorical attributes to predict building heights. The method is useful for understanding urban phenomena and changes contributing to defining our cities' actual shapes. The results were published in the MDPI Applied Sciences journal.
Historical maps are the most powerful source used to analyze changes in urban development. Nevertheless, maps represent the 3D world ...
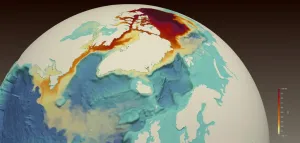
Record-high Arctic freshwater will flow to Labrador Sea, affecting local and global oceans
2021-02-24
Freshwater is accumulating in the Arctic Ocean. The Beaufort Sea, which is the largest Arctic Ocean freshwater reservoir, has increased its freshwater content by 40% over the past two decades. How and where this water will flow into the Atlantic Ocean is important for local and global ocean conditions.
A study from the University of Washington, Los Alamos National Laboratory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration shows that this freshwater travels through the Canadian Archipelago to reach the Labrador Sea, rather than through the wider marine passageways that connect to seas in Northern Europe. The open-access study was published Feb. 23 ...
[1] ... [2609]
[2610]
[2611]
[2612]
[2613]
[2614]
[2615]
[2616]
2617
[2618]
[2619]
[2620]
[2621]
[2622]
[2623]
[2624]
[2625]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.