Transforming urban systems: Toward sustainability
2021-02-23
Urban areas are on the rise and changing rapidly in form and function, with spillover effects on virtually all areas of the Earth. The UN estimates that by 2050, 68% of the world's population will reside in urban areas. In the inaugural issue of npj Urban Sustainability, a new Nature Partner Journal out today, a team of leading urban ecologists outlines a practical checklist to guide interventions, strategies, and research that better position urban systems to meet urgent sustainability goals.
Co-author Steward Pickett of Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies explains, "Urban areas shape demographics, ...
Models to predict dengue, zika and yellow fever outbreaks are developed by researchers
2021-02-23
By Maria Fernanda Ziegler | Agência FAPESP – Yellow fever was the first human disease to have a licensed vaccine and has long been considered important to an understanding of how epidemics happen and should be combated. It was introduced to the Americas in the seventeenth century, and high death rates have resulted from successive outbreaks since then. Epidemics of yellow fever were associated with the slave trade, the US gold rush and settlement of the Old West, the Haitian Revolution, and construction of the Panama Canal, to cite only a few examples.
Centuries after the disease was first reported in the Americas, an international team of researchers will embark on a groundbreaking study to develop ...
Managing suicide risk in research study participants
2021-02-23
What should researchers do if they encounter a study participant who reports suicidal thoughts?
UIC College of Nursing associate professor Susan Dunn explores this question as lead author of "Suicide Risk Management Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial of Cardiac Patients Reporting Hopelessness," a paper published in the January/February edition of Nursing Research.
Suicide is ranked as the 10th leading cause of death for all ages in the U.S. and can be identified through clinical research, according to the paper.
Although suicide screening tools are widely available for patients in emergency, hospital and primary care settings and ...
Dingo effects on ecosystem visible from space
2021-02-23
The environmental impacts of removing dingoes from the landscape are visible from space, a new UNSW Sydney study shows.
The study, recently published in Landscape Ecology, pairs 32 years' worth of satellite imagery with site-based field research on both sides of the Dingo Fence in the Strzelecki Desert.
The researchers found that vegetation inside the fence - that is, areas without dingoes - had poorer long-term growth than vegetation in areas with dingoes.
"Dingoes indirectly affect vegetation by controlling numbers of kangaroos and small mammals," says Professor Mike Letnic, senior author of the study and researcher at UNSW's Centre ...
Reclusive neutron star may have been found in famous supernova
2021-02-23
Since astronomers captured the bright explosion of a star on February 24, 1987, researchers have been searching for the squashed stellar core that should have been left behind. A group of astronomers using data from NASA space missions and ground-based telescopes may have finally found it.
As the first supernova visible with the naked eye in about 400 years, Supernova 1987A (or SN 1987A for short) sparked great excitement among scientists and soon became one of the most studied objects in the sky. The supernova is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small companion galaxy to our own Milky Way, only about 170,000 light-years from Earth.
While astronomers watched debris ...
Scientists propose a new heavy particle similar to the Higgs boson
2021-02-23
Unlike the Higgs boson, discovered at CERN's Large Hadron Collider in 2012 after a 40-year quest, the new particle proposed by these researchers is so heavy that it could not be produced directly even in this collider
The University of Granada is among the participants in this major scientific advancement in Theoretical Physics, which could help unravel the mysteries of dark matter
Scientists from the University of Granada (UGR) and the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (Germany) have recently published a study in which they endeavour to extend the Standard Model of particle physics (the equivalent of 'the periodic table' for particle physics) and answer some of the questions that this model is unable to answer. Such puzzles include: What ...
New comprehensive study on feeding patterns of tiger mosquitos in Europe
2021-02-23
This study, published recently in the international journal Insects, was conducted by researchers from the University of Granada, the Doñana Biological Station, and the Biomedical Research Networking Centre for Epidemiology and Public Health (CIBERESP)
Researchers from the University of Granada (UGR), the Doñana Biological Station (EBD-CSIC), and the Biomedical Research Networking Centre for Epidemiology and Public Health (CIBERESP) have carried out the most comprehensive study to date of the eating patterns of the tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) and other invasive species of the same genus in Europe. The results of the study were recently published in the international journal Insects.
This research, which reviews ...
Targeted delivery of highly toxic anti-cancer drug to brain tumors
2021-02-23
With a survival rate of only five years, the most common and aggressive form of primary brain tumor, glioblastoma multiforme, is notoriously hard to treat using current regimens that rely on surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and their combinations.
"Two of the major challenges in the treatment of gliomas include poor transport of chemotherapeutics across the blood brain barrier and undesired side effects of these therapeutics on healthy tissues," said Sheereen Majd, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Houston. "To get enough medicine across the blood brain barrier, a high dosage ...
Effective treatment for insomnia delivered in a few short phone calls
2021-02-23
Insomnia -- trouble falling asleep, staying asleep or waking up too early -- is a common condition in older adults. Sleeplessness can be exacerbated by osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis causing joint pain. While there are effective therapies for treating insomnia in older adults, many people cannot get the treatment they need because they live in areas with limited access to health care, either in person or over the internet.
With telephones nearly universal among the elderly, however, researchers at the University of Washington and Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute sought to determine if therapy using only a phone connection ...
Like wine, environmental conditions impact flavor of whiskey, study finds
2021-02-23
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Flavor differences in whiskey can be discerned based solely on the environment in which the barley used to make the whiskey is grown, a new study co-authored by an Oregon State University researcher found.
This is first scientific study that found the environmental conditions, or terroir, of where the barley is grown impacts the flavor of whiskey, said Dustin Herb, an author of the study and a courtesy faculty member in the Department of Crop and Soil Science at Oregon State University.
"Terroir is increasingly being used to differentiate and market agricultural products, most commonly wine, as consumers grow more interested in the origins of their food," Herb said. "Understanding terroir ...
Distinguishing between two very similar pediatric brain conditions
2021-02-23
Slight differences in clinical features can help physicians distinguish between two rare but similar forms of autoimmune brain inflammation in children, a new study by UT Southwestern scientists suggests. The findings, published online in Pediatric Neurology, could provide patients and their families with a better prognosis and the potential to target treatments specific to each condition in the future.
About half of all cases of encephalitis - a rare type of brain inflammation that affects about 1 of every 200,000 people in the U.S. each year - can be traced to an infection. For a portion of other cases in which the cause isn't initially clear, researchers have discovered a link with the patients' ...
Markey's ACTION program develops cancer education curriculum for Appalachian schools
2021-02-23
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Feb. 19, 2021) - After conducting a study to assess the need for cancer education materials in Appalachian Kentucky, members of the University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center's Appalachian Career Training in Oncology (ACTION) program worked with faculty from the UK College of Education to create a three-part cancer education curriculum for middle and high school teachers in the region.
Kentucky is home to the highest rates of cancer incidence and mortality in the country, and that problem is further concentrated in the Appalachian region of the state. Funded by a grant from the National Cancer Institute, ACTION is a two-year program designed to prepare undergraduate and high school students for cancer-focused careers and is open to students who hail ...
Agile underwater glider could quietly survey the seas
2021-02-23
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- Autonomous underwater vehicles have become versatile tools for exploring the seas. But they can be disruptive to the environment or have trouble traveling through confined spaces.
Purdue University researchers are studying an alternative: highly maneuverable, low-cost underwater gliders that operate silently. Components and sensors of the glider also can be easily swapped out or added according to a wide range of mission specifications.
"Our goal is persistent operation of mobile robots in challenging environments," said Nina Mahmoudian, associate professor of mechanical engineering. "Most underwater robots ...
College students displaced from campus due to COVID-19 show worse psychological outcomes
2021-02-23
BOSTON -- Numerous psychiatric studies have documented increased rates of depression and anxiety among those forced to relocate, with sudden moves often affecting individuals' social support and sense of identity and control. As the COVID-19 pandemic spread through the U.S. in March of 2020, universities evacuated students from their campuses, and thousands quickly relocated. Few studies have examined the mental health impact of the sudden disruption. In a new study of 791 undergraduate and graduate students, surveyed between April 9 and August 4, 2020, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston University's School of Social Work, and McLean Hospital revealed that students forced to relocate during the spring were more likely to report COVID-19-related ...
Study finds COVID risk communication targeting younger adults may have biggest impact
2021-02-23
A study of adults in the United States finds that - broadly speaking - the older you are, the more concerned you are about COVID-19, and the more steps you take to reduce your risk from COVID-19. The study suggests that the biggest boost in risk reduction would stem from communication efforts aimed at raising awareness of COVID-19 risks among U.S. adults under the age of 40.
"Our study reinforces the idea that different generations perceive the risks associated with COVID-19 very differently," says Yang Cheng, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of communication at North Carolina State University. "It also highlights the need to do more to communicate the need for preventive measures ...
Alaska thunderstorms may triple with climate change
2021-02-23
Warming temperatures will potentially alter the climate in Alaska so profoundly later this century that the number of thunderstorms will triple, increasing the risks of widespread flash flooding, landslides, and lightning-induced wildfires, new research finds.
In a pair of new papers, a research team led by scientists at the Paris Sciences and Letters University and the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) show that the sea ice around Alaska could largely give way to open water in the warmer months, creating an ample source of moisture for the atmosphere. This moisture, combined with warmer temperatures that can hold more water vapor, would turbocharge summertime storms over Alaska by the end of ...
UIC researchers invent new gene-editing tool
2021-02-23
Researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago have discovered a new gene-editing technique that allows for the programming of sequential cuts -- or edits -- over time.
CRISPR is a gene-editing tool that allows scientists to change the DNA sequences in cells and sometimes add a desired sequence or genes. CRISPR uses an enzyme called Cas9 that acts like scissors to make a cut precisely at a desired location in the DNA. Once a cut is made, the ways in which cells repair the DNA break can be influenced to result in different changes or edits to the DNA sequence.
The discovery of the gene-editing capabilities ...
The unveiling of a novel mechanism of resistance to immunotherapy targeting HER2
2021-02-23
Redirection of lymphocytes, via T-cell bispecific antibodies (TCBs) and chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), is already approved to treat some hematologic malignancies. In solid tumors these immune-based strategies continue to fail.
Research led by Joaquín Arribas, co-Program Director of Preclinical and Translational Research at VHIO, has now shown how HER2 breast cancer cells adopt a strategy to resist clearance by redirected lymphocytes. Findings evidence that the disruption of interferon-gamma signaling confers resistance to these immunotherapies and promotes disease ...
Study shows new treatment pathway to prevent and treat endometrial cancer recurrence
2021-02-23
In a new study led by Yale Cancer Center, researchers demonstrate sex hormones and insulin growth factors are associated with recurrence risk of endometrial cancer. The findings suggest endocrine-targeted therapies and an assessment of biomarkers in hormone and insulin signaling pathways may be useful in the prevention and treatment of endometrial cancer recurrence. The study is a collaboration with researchers at the University of Hawaii and The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and is published online today in the journal Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention.
"These findings are very ...
Measuring hemoglobin levels with AI microscope, microfluidic chips
2021-02-23
WASHINGTON, February 23, 2021 -- One of the most performed medical diagnostic tests to ascertain the health of patients is a complete blood count, which typically includes an estimate of the hemoglobin concentration. The hemoglobin level in the blood is an important biochemical parameter that can indicate a host of medical conditions including anemia, polycythemia, and pulmonary fibrosis.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers from SigTuple Technologies and the Indian Institute of Science describe a new AI-powered imaging-based tool to estimate hemoglobin levels. The setup was developed in conjunction with a microfluidic chip and ...
Effect of layperson-delivered, empathy-focused program of telephone calls on loneliness, depression, anxiety during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-02-23
What The Study Did: A randomized clinical trial, this study reports that a layperson-delivered, empathy-oriented telephone call program reduced loneliness, depression and anxiety compared with the control group and improved the general mental health of participants within four weeks.
Authors: Maninder K. Kahlon, Ph.D., of the University of Texas at Austin, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.0113)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
COVID-19 communication
2021-02-23
What The Article Says: In this narrative medicine essay, a medical school professor expresses gratitude for the caring and empathy expressed by the team caring for her mother hospitalized with COVID-19 and emphasizes the importance of humanity and compassion over facts and statistics for families physically separated from their critically ill loved ones.
Authors: Lisa M. Meeks, Ph.D., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0119)
Editor's ...
Tobacco exposure in kids, risk of increased blood pressure
2021-02-23
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated whether children and adolescents who smoked or lived with a smoker had an increased risk of elevated blood pressure.
Authors: Rebecca V. Levy, B.M., B.Ch., M.Sc., of the Montefiore Medical Center in Bronx, New York is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37936)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Simply speaking while infected can potentially spread COVID-19
2021-02-23
WASHINGTON, February 23, 2021 -- COVID-19 can spread from asymptomatic but infected people through small aerosol droplets in their exhaled breath. Most studies of the flow of exhaled air have focused on coughing or sneezing, which can send aerosols flying long distances.
However, speaking while near one another is also risky since the virus can be ejected by merely talking.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, scientists in Japan use smoke and laser light to study the flow of expelled breath near and around two people conversing in various relative postures commonly found in the service industry, such as in hair salons, medical exam rooms, or long-term care facilities. ...
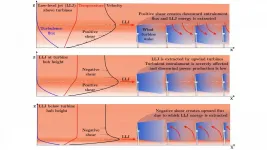
Low-level jets create winds of change for turbines
2021-02-23
WASHINGTON, February 23, 2021 -- As one of the leading sources of clean and renewable energy, global wind power capacity has increased more than fivefold over the past decade, leading to larger turbines and pushing wind technology to its limits.
"These much larger turbines are operating in very different atmospheric layers than smaller turbines used 5-10 years ago," said Srinidhi Gadde, one of the authors of a paper in the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, from AIP Publishing, that examines the impacts of turbine height. "At these scales, local meteorology and extreme shear events, which frequently occur, can impact ...
[1] ... [2603]
[2604]
[2605]
[2606]
[2607]
[2608]
[2609]
[2610]
2611
[2612]
[2613]
[2614]
[2615]
[2616]
[2617]
[2618]
[2619]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.