Allergy season starts earlier each year due to climate change and pollen transport
2021-02-25
Allergy sufferers are no strangers to problems with pollen. But now - due to climate change - the pollen season is lasting longer and starting earlier than ever before, meaning more days of itchy eyes and runny noses. Warmer temperatures cause flowers to bloom earlier, while higher CO2 levels cause more pollen to be produced.
The effects of climate change on the pollen season have been studied at-length, and END ...
Study shows opioid use among US patients with knee osteoarthritis costs 14 billion dollars in societal costs
2021-02-25
Although guidelines do not recommend use of opioids to manage pain for individuals with knee osteoarthritis, a recent study published early online in END ...
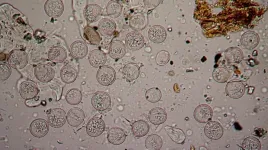
On the line: Watching nanoparticles get in shape
2021-02-25
Liquid structures - liquid droplets that maintain a specific shape - are useful for a variety of applications, from food processing to cosmetics, medicine, and even petroleum extraction, but researchers have yet to tap into these exciting new materials' full potential because not much is known about how they form.
Now, a research team led by Berkeley Lab has captured real-time high-resolution videos of liquid structures taking shape as nanoparticle surfactants (NPSs) - soap-like particles just billionths of a meter in size - jam tightly together, ...
A-maze-ing pheasants have two ways of navigating
2021-02-25
Pheasants fall into two groups in terms of how they find their way around - and the different types prefer slightly different habitats, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists tested whether individual pheasants used landmarks (allocentric) or their own position (egocentric) to learn the way through a maze.
The captive-bred pheasants were later released into the wild, and their choice of habitat was observed.
All pheasants favoured woodland, but allocentric navigators spent more time out in the open, where their landmark-based style is more useful.
"Humans tend to use both of these navigational tactics and quite frequently combine them, ...
CAR T-cell therapy generates lasting remissions in patients with multiple myeloma
2021-02-25
In a major advance in the treatment of multiple myeloma, a CAR T-cell therapy has generated deep, sustained remissions in patients who had relapsed from several previous therapies, an international clinical trial has found.
In a study posted online today by the New England Journal of Medicine, trial leaders report that almost 75% of the participants responded to the therapy, known as idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel), and one-third of them had a complete response, or disappearance of all signs of their cancer. These rates, and the duration of the responses, are significantly ...
Fantastic voyage: Nanobodies could help CRISPR turn genes on and off
2021-02-25
The genetic tool CRISPR has been likened to molecular scissors for its ability to snip out and replace genetic code within DNA.
But CRISPR has a capability that could make it useful beyond genetic repairs. "CRISPR can precisely locate specific genes," says Lacramioara Bintu, an assistant professor of bioengineering at Stanford. "What we did was attach CRISPR to nanobodies to help it perform specific actions when it reached the right spot on DNA."
Her lab recently used this combo technique to transform CRISPR from a gene-editing scissors into a nanoscale control agent that can toggle specific genes on and off, like a light switch, to start or stop the flow of some health-related protein inside a cell.
"There are a lot of things you can't fix ...
Baby mice have a skill that humans want - and this microchip might help us learn it
2021-02-25
Baby mice might be small, but they're tough, too.
For their first seven days of life, they have the special ability to regenerate damaged heart tissue.
Humans, on the other hand, aren't so lucky: any heart injuries we suffer could lead to permanent damage. But what if we could learn to repair our hearts, just like baby mice?
A team of researchers led by UNSW Sydney have developed a microchip that can help scientists study the regenerative potential of mice heart cells. This microchip - which combines microengineering with biomedicine - could help pave the way for new regenerative heart medicine research.
The study is featured on the cover ...
New discoveries on the containment of COVID-19 finds travel bans are of limited value
2021-02-25
BROOKLYN, New York, Wednesday, February 24, 2021 - Travel bans have been key to efforts by many countries to control the spread of COVID-19. But new research aimed at providing a decision support system to Italian policy makers, recently published in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface, suggests that reducing individual activity (i.e., social distancing, closure of non-essential business, etc.) is far superior in controlling the dissemination of Sars-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
The research, which has implications for the United States and other countries, found that limiting personal mobility through travel restrictions and similar tactics is effective only in the first phases of the epidemic, and reduces in proportion to the ...
UM scientists achieve breakthrough in culturing corals and sea anemones cells
2021-02-25
MIAMI--Researchers have perfected the recipe for keeping sea anemone and coral cells alive in a petri dish for up to 12 days. The new study, led by scientists at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, has important applications to study everything from evolutionary biology to human health.
Cnidarians are emerging model organisms for cell and molecular biology research. Yet, successfully keeping their cells in a laboratory setting has proved challenging due to contamination from the many microorganisms that live within these marine organisms or because the whole tissue survive in a culture environment.
UM cell ...
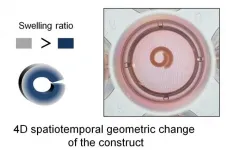
New shape-changing 4D materials hold promise for morphodynamic tissue engineering
2021-02-25
New hydrogel-based materials that can change shape in response to psychological stimuli, such as water, could be the next generation of materials used to bioengineer tissues and organs, according to a team of researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago.
In a new paper published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, the research team -- led by Eben Alsberg, the Richard and Loan Hill Professor of Biomedical Engineering -- that developed the substances show that the unique materials can curl into tubes in response to water, making the materials good candidates for bioengineering blood vessels or other tubular structures.
In nature, embryonic development and tissue healing often involve ...
Apollo rock samples capture key moments in the Moon's early history, study find
2021-02-24
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Volcanic rock samples collected during NASA's Apollo missions bear the isotopic signature of key events in the early evolution of the Moon, a new analysis found. Those events include the formation of the Moon's iron core, as well as the crystallization of the lunar magma ocean -- the sea of molten rock thought to have covered the Moon for around 100 million years after the it formed.
The analysis, published in the journal Science Advances, used a technique called secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) to study volcanic glasses returned ...
COVID-19 isolation linked to increased domestic violence, researchers suggest
2021-02-24
While COVID-19-related lockdowns may have decreased the spread of a deadly virus, they appear to have created an ideal environment for increased domestic violence.c
Data collected in surveys of nearly 400 adults for 10 weeks beginning in April 2020 suggest that more services and communication are needed so that even front-line health and food bank workers, for example -- rather than only social workers, doctors and therapists -- can spot the signs and ask clients questions about potential intimate partner violence. They could then help lead victims to resources, said Clare Cannon, assistant professor of social and environmental justice in the Department of Human Ecology and the lead author of the study.
The paper, "COVID-19, intimate partner violence, and communication ...
What to do when a mammogram shows swollen lymph nodes in women just vaccinated for COVID
2021-02-24
BOSTON - Swelling of lymph nodes in the armpit area is a normal response to COVID-19 vaccinations, but when they are seen on mammograms, they can be mistaken for nodes that are swollen because of cancer. In some cases, the nodes are biopsied to confirm they are not cancer. To avoid confusion by patients and their providers, and to avoid delays in either vaccinations or recommended mammograms through the pandemic, radiologists at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have published an approach to manage what is expected to be a fairly common occurrence as vaccination programs ramp up. The approach is described in the American Journal of Roentgenology.
"We had started ...
After Hurricane Irma, soundscape reveals resilient reef ecosystem
2021-02-24
A new study from North Carolina State University reveals that the soundscapes of coral reef ecosystems can recover quickly from severe weather events such as hurricanes. The work also demonstrates that non-invasive monitoring is an important tool in shedding further light on these key ecosystems.
Soundscape ecology is a relatively new way for researchers to keep tabs on a variety of habitats without direct interference. In underwater habitats like coral reefs, soundscapes allow continual monitoring of an ecosystem that is difficult to access. By deploying underwater microphones, or hydrophones, researchers can get an acoustic picture of the types of animals in the ecosystem, as well as their behavior patterns.
Kayelyn Simmons, a Ph.D. student at NC State, used soundscapes and ...
Parker Solar Probe offers stunning view of Venus
2021-02-24
NASA's Parker Solar Probe captured stunning views of Venus during its close flyby of the planet in July 2020.
Though Parker Solar Probe's focus is the Sun, Venus plays a critical role in the mission: The spacecraft whips by Venus a total of seven times over the course of its seven-year mission, using the planet's gravity to bend the spacecraft's orbit. These Venus gravity assists allow Parker Solar Probe to fly closer and closer to the Sun on its mission to study the dynamics of the solar wind close to its source.
But -- along with the orbital dynamics -- these passes can also yield some unique and even unexpected views of the inner solar system. During the mission's third ...
Ancient skeletal hand could reveal evolutionary secrets
2021-02-24
Evolutionary expert Charles Darwin and others recognized a close evolutionary relationship between humans, chimps and gorillas based on their shared anatomies, raising some big questions: how are humans related to other primates, and exactly how did early humans move around? Research by a Texas A&M University professor may provide some answers.
Thomas Cody Prang, assistant professor of anthropology, and colleagues examined the skeletal remains of Ardipithecus ramidus ("Ardi"), dated to 4.4 million years old and found in Ethiopia. One of Ardi's hands was exceptionally well-preserved.
The researchers compared the shape of Ardi's hand to hundreds of other hand specimens representing recent humans, apes and monkeys (measured ...
Study finds human-caused North Atlantic right whale deaths are being undercounted
2021-02-24
A study co-authored by scientists at the New England Aquarium has found that known deaths of critically endangered North Atlantic right whales represent a fraction of the true death toll. This comes as the death of a calf and recent sightings of entangled right whales off the southeastern United States raise alarm.
The study, published this month in END ...
Bearded seals are loud -- but not loud enough
2021-02-24
Ithaca, NY-- During mating season, male bearded seals make loud calls to attract a mate--even their "quiet" call could still be as ear-rattling as a chainsaw. Bearded seals have to be loud to be heard over the cacophony of their equally loud brethren. And, increasingly, the noise humans make is adding to the underwater din and could have serious consequences. A study conducted by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology's Center for Conservation Bioacoustics (CCB) aims to understand how resilient bearded seals can be to changes in ambient underwater noise. The results are published in Proceedings of the Royal Society: Biological Science.
"We wanted to know whether bearded seals would call louder when ...
Tool that more efficiently analyzes ocean color data will become part of NASA program
2021-02-24
Researchers at Stevens Institute of Technology have developed a new machine learning-powered platform, known as OC-SMART, that can process ocean color in satellite images 10 times faster than the world's leading platform. The work, which will be adopted by NASA, is one of the first machine learning-based platforms in ocean color analysis that can process both coastal and open ocean regions globally to reveal data on sea health and the impact of climate change.
The work, led by Knut Stamnes, a physics professor at Stevens, and spearheaded by Yongzhen Fan Ph.D. '16, a visiting physics scholar in Stamnes' lab, solves a 30-year-old problem in retrieving data from both coastal regions and open ocean areas. For decades, NASA's SeaDAS platform exceled at analyzing ocean color ...
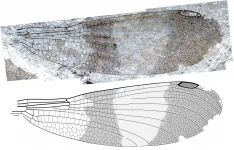
Paleontologists discover new insect group after solving 150-year-old mystery
2021-02-24
For more than 150 years, scientists have been incorrectly classifying a group of fossil insects as damselflies, the familiar cousins of dragonflies that flit around wetlands eating mosquitoes. While they are strikingly similar, these fossils have oddly shaped heads, which researchers have always attributed to distortion resulting from the fossilization process.
Now, however, a team of researchers led by Simon Fraser University (SFU) paleontologist Bruce Archibald has discovered they aren't damselflies at all, but represent a major new insect group closely related to them.
The findings, published today in Zootaxa, show that the distinctive shape of the insect's non-protruding, ...
'Miracle poison' for novel therapeutics
2021-02-24
When people hear botulinum toxin, they often think one of two things: a cosmetic that makes frown lines disappear or a deadly poison.
But the "miracle poison," as it's also known, has been approved by the F.D.A. to treat a suite of maladies like chronic migraines, uncontrolled blinking, and certain muscle spasms. And now, a team of researchers from Harvard University and the Broad Institute have, for the first time, proved they could rapidly evolve the toxin in the laboratory to target a variety of different proteins, creating a suite of bespoke, super-selective ...
Over 80% of Atlantic Rainforest remnants have been impacted by human activity
2021-02-24
A Brazilian study published (http://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20217-w) in Nature Communications shows that human activities have directly or indirectly caused biodiversity and biomass losses in over 80% of the remaining Atlantic Rainforest fragments.
According to the authors, in terms of carbon storage, the biomass erosion corresponds to the destruction of 70,000 square kilometers (km²) of forest - almost 10 million soccer pitches - or USD 2.3 billion-USD 2.6 billion in carbon credits. "These figures have direct implications for mechanisms of climate change mitigation," they state in the article.
Atlantic Rainforest remnants ...
Researchers use machine learning to identify autism blood biomarkers
2021-02-24
DALLAS - Feb. 24, 2021 - Using machine learning tools to analyze hundreds of proteins, UT Southwestern researchers have identified a group of biomarkers in blood that could lead to an earlier diagnosis of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and, in turn, more effective therapies sooner.
The identification of nine serum proteins that strongly predict ASD were reported in a study published today by PLOS ONE.
Earlier diagnosis, followed by prompt therapeutic support and intervention, could have a significant impact on the 1 in 59 children diagnosed with autism in the United States. Being able to identify children on the autism spectrum when they are toddlers could make a big difference, says Dwight German, Ph.D., professor of psychiatry at UT Southwestern ...
The risks of communicating extreme climate forecasts
2021-02-24
For decades, climate change researchers and activists have used dramatic forecasts to attempt to influence public perception of the problem and as a call to action on climate change. These forecasts have frequently been for events that might be called "apocalyptic," because they predict cataclysmic events resulting from climate change.
In a new paper published in the International Journal of Global Warming, Carnegie Mellon University's David Rode and Paul Fischbeck argue that making such forecasts can be counterproductive. "Truly apocalyptic forecasts can only ever be observed in their failure--that is the world did not end as predicted," says Rode, adjunct research faculty with the Carnegie Mellon Electricity Industry Center, "and observing ...
Unequal parenthood impacts may explain academia's publication gender gap
2021-02-24
Parenthood leads to greater reductions in short-term research productivity for mothers across three disciplines than for fathers, largely explaining the publication gender gap between women and men in academia, according to an analysis of survey data from 3,064 tenure track faculty at PhD-granting universities in the U.S. and Canada. The findings suggest that policies designed to boost workplace flexibility for parents, including easily accessible lactation rooms and affordable childcare, may help to ease the impact of parenthood on mothers in academia, giving them more time for research. While a large body of previous research across academic fields has shown that men tend to publish more papers than women, the reasons for this have remained uncertain. ...
[1] ... [2596]
[2597]
[2598]
[2599]
[2600]
[2601]
[2602]
[2603]
2604
[2605]
[2606]
[2607]
[2608]
[2609]
[2610]
[2611]
[2612]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.