Black Americans report high levels of vaccine hesitancy
2021-03-01
Black Americans have a high level of vaccine hesitancy and mistrust of COVID-19 vaccines, including among Black health care workers, according to a new RAND Corporation survey.
Those who expressed vaccine hesitancy also showed high levels of overall mistrust in the vaccine, concerns about potential harm and side effects, and lack of confidence in vaccine effectiveness and safety.
Participants in the RAND survey reported higher trust in COVID-19 information from health care providers and public health officials than from elected local and federal officials.
The findings are based on a survey ...
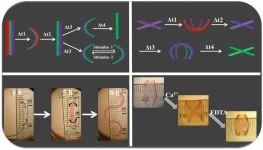
4D bioengineering materials bend, curve like natural tissue
2021-03-01
Tissue engineering has long-depended on geometrically static scaffolds seeded with cells in the lab to create new tissues and even organs. The scaffolding material -- usually a biodegradable polymer structure -- is supplied with cells and the cells, if supplied with the right nutrients, then develop into tissue as the underlying scaffold biodegrades. But this model ignores the extraordinarily dynamic morphological processes that underlie the natural development of tissues.
Now, researchers at the END ...
Deep dive into bioarchaeological data reveals Mediterranean migration trends over 8,000 years
2021-03-01
A team of international researchers led by a Florida State University assistant professor has analyzed reams of data from the Neolithic to Late Roman period looking at migration patterns across the Mediterranean and found that despite evidence of cultural connections, there's little evidence of massive migration across the region.
"Because of the prevailing scholarly attitude of the 'connected' Mediterranean -- one with high degrees of mobility and migration that drive the archaeological patterns we see -- we'd imagined we'd see comparatively high levels of migration reflected in the strontium isotope data," said Thomas Leppard, assistant professor of anthropology at Florida State. "That instead ...
A research group proposes six guidelines for managing the impacts of invasive species
2021-03-01
Invasive alien species, defined as animals and plants that breed and disperse in a landscape beyond their native range, have negative environmental, social, and economic impacts. One example among many is the forage grass genus Brachiaria, originally African and introduced to Brazil to form cattle pasture. It has become a major threat to the survival of native species and biodiversity at several spatial scales.
Complete eradication of invasive species is often impracticable. Attempts to do so have had undesirable consequences and even been damaging because merely withdrawing an invasive ...
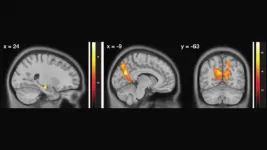
Noisy brain activity contributes to aging-related navigation impairments
2021-03-01
Too much activity in the hippocampus may cause navigation impairments seen in aging adults, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Spatial navigation is one of the cognitive abilities that declines sharply in old age. Older adults often have difficulty navigating new environments and will choose to stick with familiar ones. Plus, key regions in the brain's navigation circuit are some of the first affected by Alzheimer's disease. In a recent study, Diersch et al. examined the neural mechanism behind this decline in spatial learning.
In the study, younger ...
Addressing a complex world of pain in a single gene difference
2021-03-01
A single letter difference in a single gene, inherited from both parents, spells a lifetime of anemia and pain for 20 million people, mostly of African ancestry, worldwide. Sickle cell disease (SCD) causes red blood cells to assume a sickle shape and jam in capillaries, cutting off oxygen to lungs, brain, bones and other organs. Despite the single genetic origin of SCD, each person's disease experience and even life expectancy depend upon where they live, and the social, physical and environmental factors they encounter.
Now, a new review published by Wiley in the journal Advanced Genetics proposes that it is ...
Scientists describe 'hidden biodiversity crisis' as variation within species is lost
2021-03-01
The rapid loss of variation within species is a hidden biodiversity crisis, according to the authors of a new study looking at how this variation supports essential ecological functions and the benefits nature provides for people.
Published March 1 in Nature Ecology and Evolution, the study highlights the need to better understand and conserve variation within species in order to safeguard nature's contributions to people.
"Biodiversity means more than the number of species, and when we focus on species-level extinctions we are missing part of the story," said corresponding author Eric Palkovacs, professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at UC Santa Cruz. "Intraspecific variation is a neglected aspect of biodiversity, ...
Reinforced by policies, charters segregate schools
2021-03-01
ITHACA, N.Y. - The expansion of charter schools in the 2000s led to an increase in school segregation and a slight decline in residential segregation, according to new research from Cornell University providing the first national estimates of the diverging trends.
According to the study, the average district to expand charter school enrollment between 2000 and 2010 experienced a 12% increase in white-Black school segregation and a 2% decrease in white-Black residential segregation.
The patterns moved in opposite directions, the research found, because charter ...
Potential target for treating many cancers found within GLI1 gene
2021-03-01
Scientists from the Stanley Manne Children's Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago found that a region within the DNA of the cancer-promoting GLI1 gene is directly responsible for regulating this gene's expression. These findings, published in the journal Stem Cells, imply that this region within GLI1 could potentially be targeted as cancer treatment, since turning off GLI1 would interrupt excessive cell division characteristic of cancer.
"From previous research, we know that GLI1 drives the unrelenting cell proliferation that is responsible for many cancers, and that this gene also stimulates its own expression," says co-senior author Philip Iannaccone, MD, PhD, Professor Emeritus at the Manne Research Institute at Lurie Children's and Northwestern ...
Natural product isolated from sea sponge tested against cancer cells
2021-03-01
Scientists from Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU) together with Russian and German colleagues, continue studying antitumor compounds synthesized based on bioactive molecules isolated from a sea sponge. One of them fights cancer cells resistant to standard chemotherapy, and at the same time has an interesting dual mechanism of action. A related article appears in Marine Drugs.
Scientists have tested the biological effect of the marine alkaloid 3,10-dibromofascaplysin on various prostate cancer cells, including those resistant to standard docetaxel-based chemotherapy. ...
On calm days, sunlight warms the ocean surface and drives turbulence
2021-03-01
CORVALLIS, Ore. - In tropical oceans, a combination of sunlight and weak winds drives up surface temperatures in the afternoon, increasing atmospheric turbulence, unprecedented new observational data collected by an Oregon State University researcher shows.
The new findings could have important implications for weather forecasting and climate modeling, said Simon de Szoeke, a professor in OSU's College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric Sciences and the lead author of the study.
"The ocean warms in the afternoon by just a degree or two, but it is an effect that has largely been ignored," said de Szoeke. ...
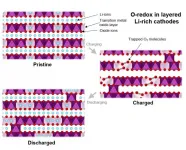
Mechanistic understanding of oxygen-redox processes in lithium-rich battery cathodes
2021-03-01
HARWELL, UK (1 March 2021) Scientists based at the University of Oxford as part of the Faraday Institution CATMAT project researching next-generation cathode materials have made a significant advance in understanding oxygen-redox processes involved in lithium-rich cathode materials. The paper, published in Nature Energy, proposes strategies that offer potential routes to increase the energy density of lithium-ion batteries.
"In the ever more difficult quest to make incremental improvements to Li-ion battery energy density, being able to harness the potential of oxygen-redox cathodes and the bigger improvements they offer relative to the nickel rich cathodes in commercial use today is potentially significant," Prof Peter Bruce, University ...
Socioeconomic status plays a major role in cognitive outcomes
2021-03-01
Childhood cancer and its treatment can result in cognitive struggles. Scientists atSt. Jude Children's Research Hospital are studying the risk factors. They looked at social and economic issues in children with brain tumors treated with radiation.
These patients have the greatest risk of cognitive problems. Scientists followed a group of St. Jude patients for 10 years. The children all had conformal radiation therapy.
For each patient, researchers looked at certain factors. These included the parent's job, education level, and whether it was a single parent home. The children were from different backgrounds.
The findings show social and economic status is linked to IQ, academics, attention ...
The role of human behavior is critical for advancing comfort knowledge
2021-03-01
Amsterdam, March 1, 2021 - Comfort is a daily human experience central to the perception of our environment and the continuous processing of sensory input. Environmental factors such as smell, temperature and light can influence comfort, as can our interaction with products, such as the design of a chair or a mattress. Increasingly, researchers investigating the science of comfort and discomfort are focusing on the role of human behavior. A special supplement to the journal WORK presents the latest advances, from optimal seat design in offices and transportation to the influence of smell on comfort and the interaction between time and comfort.
"This special supplement adds unique findings to comfort knowledge. ...
Mutant gene-targeted immunotherapy approach developed
2021-03-01
A novel targeted immunotherapy approach developed by researchers at the Ludwig Center, the Lustgarten Laboratory, and Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center employs new antibodies against genetically altered proteins to target cancers.
The researchers targeted their immunotherapy approach to alterations in the common cancer-related p53 tumor suppressor gene, the RAS tumor-promoting oncogene or T-cell receptor genes. They also tested the therapy on cancer cells in the laboratory and in animal tumor models. Their findings are reported in three related studies published March 1 in Science Immunology, Science and Science Translational Medicine.
Two ...
Transmission risk of COVID-19 from sewage spills into rivers can now be quickly quantified
2021-03-01
Scientists have identified that the COVID-19 virus could be transmitted through faecal contaminated river water.
A team of researchers, including water quality, epidemiology, remote sensing and modelling experts, led by Dr Jamie Shutler at the University of Exeter, have developed a fast and simple way to assess the potential risk of water-borne transmission of the COVID-19 virus, posed by sewage spills into open and closed freshwater networks.
The new study, published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology - Water, identifies the relative risk of viral transmission by sewerage spills, across 39 different counties.
The study used information on the environment, a population's infection rate, and water usage to calculate the potential potency of ...
How a plant regulates its growth
2021-03-01
Plants grow towards the light. This phenomenon, which already fascinated Charles Darwin, has been observed by everyone who owns houseplants. Thus, the plant ensures that it can make the best use of light to photosynthesize and synthesize sugars. Similarly, the roots grow into the soil to ensure that the plant is supplied with water and nutrients.
These growth processes are controlled by a hormone called "auxin", which plays a key role in the formation of polarity in plants. To do this, auxin is transported in the plant body polar, from the shoot through the plant body into the roots. In this process, a family of polar transport proteins distributes the auxin throughout the plant. To ...
Oncotarget: Identification intermediate-risk subgroups in metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
2021-03-01
The cover for issue 49 of Oncotarget features Figure 4, "CART-Tree analysis for overall survival in IMDC intermediate risk group," by Guida, et al.recently published in "Identification of international metastatic renal cell carcinoma database consortium (IMDC) intermediate-risk subgroups in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma" which reported that as these patients have different prognosis, the aim of this study is to better characterize IR patients in order to better tailor the treatment.
A multivariable Cox model with backward selection procedure and a Classification and Regression Tree analysis were performed to identify which prognostic factors were associated to OS in IR patients.
Median OS for patients with ...
Oncotarget: Exploiting the metabolic dependencies of the broad amino acid transporter SLC6A14
2021-03-01
Oncotarget recently published "Exploiting the metabolic dependencies of the broad amino acid transporter SLC6A14" which reported that Tumor cells typically enhance their metabolic capacity to sustain their higher rate of growth and proliferation.
One way to elevate the nutrient intake into cancer cells is to increase the expression of genes encoding amino acid transporters, which may represent targetable vulnerabilities.
The Oncotarget authors analyze the pattern of transcriptional changes in a panel of breast cancer cell lines upon metabolic stress and found that SLC6A14 expression levels are increased in the absence of methionine.
Methionine deprivation, which can be achieved via modulation of dietary methionine intake in tumor cells, in turn leads to a heightened ...
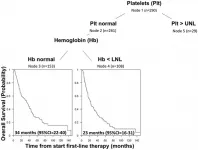
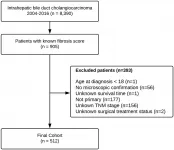
Oncotarget: Effect of liver fibrosis on survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
2021-03-01
Oncotarget recently published "Effect of liver fibrosis on survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a SEER population-based study" which reported that the impact of fibrosis on overall and cancer-specific survival 12, 36, and 60 months following diagnosis, was evaluated in the entire cohort and in subgroups stratified according to treatment approach and the American Joint Committee on Cancer tumor stage using a Cox proportional-hazards model.
After adjusting for age, sex, race, year of diagnosis, AJCC stage, and surgical treatment strategy, advanced fibrosis was associated with worse cancer-specific survival across follow-up periods.
Similar effects were observed for overall survival.
Among patients that underwent surgical resection, ...
AI shows public attitude toward COVID-19 is more 'infectious' than disease itself
2021-03-01
CHICAGO --- Public attitude toward COVID-19 and its treatments is more "infectious" than the disease itself, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to analyze tweets about the virus. Researchers studied the influence of Twitter on COVID-19 health beliefs as well as the competing influence of scientific evidence versus the speeches of politicians.
The study's key findings:
People's biases are magnified when they read tweets about COVID-19 from other users, and the more times it has been retweeted, the more they tend to believe it and retweet it themselves.
Scientific ...
Medical school curriculum takes aim at social determinants of health
2021-03-01
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 1, 2021 - There is a growing recognition in health care that social factors such as racial bias, access to care and housing and food insecurity, have a significant impact on people's health. Compounding and amplifying those underlying inequalities are the ongoing disruptions related to the COVID-19 pandemic and social unrest in our country.
Although many health care organizations (National Academy of Medicine, American College of Physicians and the American Academy of Pediatrics) currently recommend that screening for social determinants of health (SDH) be included in clinical care, medical education has lagged ...
COVID-19 RCTs registered in 1st 100 days of pandemic
2021-03-01
What The Study Did: Researchers assessed the recruitment and results reporting of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to treat or prevent COVID-19 registered within 100 days of the first case reported to the World Health Organization.
Authors: Lars G. Hemkens, M.D., M.P.H., of the University Hospital Basel in Basel, Switzerland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0330)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please ...
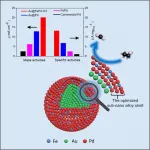
High-performance electrocatalysts to propel development of direct ethanol fuel cells
2021-03-01
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Nanjing Normal University recently reported a strategy for boosting the electrocatalytic performance of palladium (Pd) in ethanol oxidation reaction, the key anodic reaction of direct ethanol fuel cells (DEFCs), offering a rational concept for finely engineering the surface of electrocatalysts used in high-efficiency energy conversion devices and beyond.
The study was published in Cell Reports Physical Science on Mar. 1.
DEFCs, with ethanol as fuel, have the advantage of high energy density, low toxicity and easy operation. However, the lack of active and robust electrocatalysts ...
Global warming poses threat to food chains
2021-03-01
Rising temperatures could reduce the efficiency of food chains and threaten the survival of larger animals, new research shows.
Scientists measured the transfer of energy from single-celled algae (phytoplankton) to small animals that eat them (zooplankton).
The study - by the University of Exeter and Queen Mary University of London, and published in the journal Nature - found that 4°C of warming reduced energy transfer in the plankton food webs by up to 56%.
Warmer conditions increase the metabolic cost of growth, leading to less efficient energy flow through the ...
[1] ... [2591]
[2592]
[2593]
[2594]
[2595]
[2596]
[2597]
[2598]
2599
[2600]
[2601]
[2602]
[2603]
[2604]
[2605]
[2606]
[2607]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.