Bottling the world's coldest plasma
2021-03-01
HOUSTON - (March 1, 2021) - Rice University physicists have discovered a way to trap the world's coldest plasma in a magnetic bottle, a technological achievement that could advance research into clean energy, space weather and astrophysics.
"To understand how the solar wind interacts with the Earth, or to generate clean energy from nuclear fusion, one has to understand how plasma -- a soup of electrons and ions -- behaves in a magnetic field," said Rice Dean of Natural Sciences Tom Killian, the corresponding author of a published study about the work in Physical Review Letters.
Using laser-cooled strontium, ...
Visiting water bodies worth £700bn to economies, study finds
2021-03-01
Europeans spend more than £700 billion (€800bn) a year on recreational visits to water bodies - but perceived poor water quality costs almost £90 billion (€100bn) in lost visits, a new study has found.
The new research - led by a European collaboration involving the University of Exeter and the University of Stirling - used data from 11,000 visits in 14 different countries to analyse the economic value of water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, waterfalls, beaches and seaside promenades.
The research team estimated that people spend an average of £35 (€40) travelling to and from these sites, with a typical family making 45 such trips each year.
The team also found ...
Microplastic sizes in Hudson-Raritan Estuary and coastal ocean revealed
2021-03-01
Rutgers scientists for the first time have pinpointed the sizes of microplastics from a highly urbanized estuarine and coastal system with numerous sources of fresh water, including the Hudson River and Raritan River.
Their study of tiny pieces of plastic in the Hudson-Raritan Estuary in New Jersey and New York indicates that stormwater could be an important source of the plastic pollution that plagues oceans, bays, rivers and other waters and threatens aquatic and other life.
"Stormwater, an understudied pathway for microplastics to enter waterways, had similar or higher concentrations of ...
The right '5-a-day' mix is 2 fruit and 3 vegetable servings for longer life
2021-03-01
DALLAS, March 1, 2021 — Studies representing nearly 2 million adults worldwide show that eating about five daily servings of fruits and vegetables, in which 2 are fruits and 3 are vegetables, is likely the optimal amount for a longer life, according to new research published today in the American Heart Association’s flagship journal Circulation.
Diets rich in fruits and vegetables help reduce risk for numerous chronic health conditions that are leading causes of death, including cardiovascular disease and cancer. Yet, only about one in 10 adults eat enough fruits or vegetables, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“While groups like the ...
Single cell sequencing opens new avenues for eradicating leukemia at its source
2021-03-01
A new method, described in a study published today in the journal Nature Communications, has the potential to boost international research efforts to find drugs that eradicate cancer at its source.
Most cancerous tissue consists of rapidly dividing cells with a limited capacity for self-renewal, meaning that the bulk of cells stop reproducing after a certain number of divisions. However, cancer stem cells can replicate indefinitely, fuelling long-term cancer growth and driving relapse.
Cancer stem cells that elude conventional treatments like chemotherapy are one of the reasons ...
'Overwhelming' international support for more government action on environment, message-testing experiment finds
2021-03-01
With eight months to go before the UN Climate Change Conference (COP26), an international survey experiment has found evidence of "overwhelming" support across seven major countries for governments to "do more" to protect the environment.
The survey directly asks the public about policies they want to see backed by governments at COP26, when the UK and Italy will gather world leaders in Glasgow from 1 November to commit to urgent global climate action.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge worked with polling agency YouGov on a message-testing experiment involving 14,627 adults, with ...
Top diversity and equity leaders in psychiatry offer guidelines for academic medicine
2021-03-01
Diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) leaders in academic medicine are subject to increasing expectations with limited resources and there is an urgent need for psychiatry departments to commit to fully supporting their efforts, according to an article now available in the American Journal of Psychiatry written by top DEI leaders in academic psychiatry from across the country.
The authors, representing prominent public and private institutions, include Ayana Jordan, M.D., Ph.D., Yale University, and current APA ECP Trustee-at-Large; Ruth S. Shim, M.D., M.P.H. University ...
Why COVID-19 vaccine distribution methods fall short and 3 ways to improve them
2021-03-01
BINGHAMTON, NY - Several proposals have emerged on how to distribute the COVID-19 vaccine, but they fall short in ensuring that the vaccine is distributed fairly. A team including Binghamton University professor Nicole Hassoun suggests three ways to more fairly and effectively distribute the vaccine so that people in poor countries get the vaccine as soon as possible.
"Although many people in rich countries will receive a vaccine for COVID-19 this year, many people in poor countries will likely have to wait years to get one," said Hassoun. "Ethical vaccine allocation requires closing this gap and ensuring that everyone can access a vaccine ...
Financial incentives for hospitals boost rapid changes to opioid use disorder treatment
2021-03-01
PHILADELPHIA-- Hospital emergency departments (EDs) not only care for patients with overdose and other complications from opioid use, but they also serve as vital touch points to engage patients into longer-term treatment. After an overdose, patients are at risk for repeat overdose and death. Pennsylvania is unique in establishing a voluntary incentive program to improve the rate at which patients with opioid use disorder receive follow-up treatment after emergency department care. Evaluations of the program show that financial incentives are effective in producing rapid treatment innovations for opioid use disorder.
In a study, researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at ...
March SLAS Discovery explores COVID-19 drug therapies six months later
2021-03-01
Oak Brook, IL - The March edition of SLAS Discovery features the cover article, "Therapeutic and Vaccine Options for COVID-19: Status After 6 Months of the Disease Outbreak" by Christian Ogaugwu (Federal University Oye-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria ), Dawid Maciorowski, Subba Rao Durvasula, Ph.D., Ravi Durvasula, M.D., and Adinarayana Kunamneni, Ph.D. (Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, IL, USA).
This cover article focuses on the therapeutic and vaccine options available against the novel coronavirus, roughly six months after the outbreak; because the COVID-19-related death toll worldwide had reached 500,000 in six months (and ballooned to over 2,000,000 at the time of publishing) the importance of options to temper the disease cannot be overemphasized. The article ...
'Silent epidemic of grief' leaves bereaved and bereavement care practitioners struggling
2021-03-01
Major changes in bereavement care have occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic, amid a flood of demand for help from bereaved people, according to new research from the University of Cambridge. The first major study of pandemic-related changes in bereavement care has found that the switch to remote working has helped some services to reach out, but many practitioners feel they do not have capacity to meet people's needs.
It is estimated that for every death, nine people are affected by bereavement. The scale of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on those ...
Study: Treatable sleep disorder common in people with thinking and memory problems
2021-02-28
MINNEAPOLIS - Obstructive sleep apnea is when breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep. Research has shown people with this sleep disorder have an increased risk of developing cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Yet, it is treatable. A preliminary study released today, February 28, 2021, has found that obstructive sleep apnea is common in people with cognitive impairment. The study will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 73rd Annual Meeting being held virtually April 17 to 22, 2021.
Cognitive impairment includes memory and thinking problems that affect ...
Sensing suns
2021-02-28
Red supergiants are a class of star that end their lives in supernova explosions. Their lifecycles are not fully understood, partly due to difficulties in measuring their temperatures. For the first time, astronomers develop an accurate method to determine the surface temperatures of red supergiants.
Stars come in a wide range of sizes, masses and compositions. Our sun is considered a relatively small specimen, especially when compared to something like Betelgeuse which is known as a red supergiant. Red supergiants are stars over nine times the mass of our sun, and all this mass means that when they die they do so with extreme ferocity in an enormous explosion known as a supernova, in particular what is known as a Type-II supernova.
Type II supernovae seed the cosmos with elements ...
When foams collapse (and when they don't)
2021-02-27
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have revealed how liquid foams collapse by observing individual collapse "events" with high-speed video microscopy. They found that cracks in films led to a receding liquid front which sweeps up the original film border, inverts its shape, and releases a droplet which hits and breaks other films. Their observations and physical model provide key insights into how to make foams more or less resistant to collapse.
Understanding how foams collapse is serious business. Whether it's ensuring fire extinguishing foams stay long enough to put out flames, cleaning up toxic foams in seas and rivers, or simply getting the perfect rise on a cake, getting to grips with how foam materials collapse is vital to tailoring their properties, ...
Predicts the onset of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) using deep learning-based Splice-AI
2021-02-27
Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI, President Suh Pann-ghill) announced that the research team led by Dr. Jae-Yeol Joo discovered new cryptic splice variants and SNVs in PLCg1 gene of AD-specific models for the first time using Splice-AI.
This research outcome was published in PNAS, a world-renowned academic journal.
* (Title) Prediction of Alzheimer's Disease-Specific phospholipase c gamma-1 SNV by Deep Learning-Based Approach for High-Throughput Screening
Alternative splicing variant regulates gene expression and influences diverse phenotypes. Especially, genetic ...
Oahu marine protected areas offer limited protection of coral reef herbivorous fishes
2021-02-26
Marine protected areas (MPAs) around O?ahu do not adequately protect populations of herbivorous reef fishes that eat algae on coral reefs. That is the primary conclusion of a study published in Coral Reefs by researchers from the University of Hawai?i at Mānoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST).
There are over 20 species of herbivorous fishes and ten species of herbivorous urchins commonly observed on Hawaiian reefs. These species eat algae that grows on reefs, a process called herbivory, that contributes to the resilience of coral reefs by preventing algae dominance that can lead to overgrowth of corals.
The team of researchers found that of the four marine protected areas around O?ahu they assessed in the study, ...
'Explicit instruction' provides dramatic benefits in learning to read
2021-02-26
The ability to read is foundational to education, but prolonged school closures and distance learning due to the pandemic have imposed unique challenges on the teaching of many fundamental skills. When in-person classes resume, many students will likely need a period of catch-up learning, especially those who lag behind in basic reading skills.
New research published in the journal Psychological Science shows that people who were taught to read by receiving explicit instructions on the relationship between sounds and spelling experienced a dramatic improvement compared to learners who discovered this relationship naturally through the reading process. These results contribute to an ongoing debate about how best to teach children to ...
Deep brain stimulation and exercise restore movement in ataxia
2021-02-26
New research from Baylor College of Medicine scientists shows that a combination of deep brain stimulation (DBS) and exercise has potential benefits for treating ataxia, a rare genetic neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive irreversible problems with movement.
Working with a mouse model of the human condition, researchers at Baylor and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital discovered that combining DBS targeted to the cerebellum, a major motor center in the brain, and exercise rescued limb coordination and stepping and that the benefits persisted without further stimulation. In addition, the study reports that stimulating mice with early-stage ataxia showed the most dramatic improvements. These and other ...
Atherosclerosis can accelerate the development of clonal hematopoiesis, study finds
2021-02-26
BOSTON -- Billions of peripheral white blood cells are produced every day by the regular divisions of hematopoietic stem cells and their descendants in the bone marrow. Under normal circumstances, thousands of stem cells contribute progeny to the blood at any given time, making white blood cells a group with diverse ancestry.
Clonal hematopoiesis is a common age-related condition in which the descendants of one of these hematopoietic stem cells begin to dominate substantial portions of the blood. Genome-wide analyses have determined that clonal ...
Picture books can boost physical activity for youth with autism
2021-02-26
COLUMBIA, Mo. - While physical activity is important for everyone, research has shown people with developmental disabilities do not exercise as often as their typically developed peers. In an effort to close this disparity, a researcher at the University of Missouri recently created fitness picture books that help youth with autism exercise more frequently while offering low-income families a simple resource for workout motivation when outdoor fitness equipment might not be accessible.
"There is so much research geared toward helping individuals with autism improve their academic ...
Cancer: a new killer lymphocyte enters the ring
2021-02-26
Treatments for beating tumours are mainly based on CD8 T lymphocytes, which specialise in detecting and eliminating intracellular infections and in killing cancer cells. A large proportion of patients, however, do not respond to these treatments. This prompted a research team from the Swiss Cancer Centre Léman (SCCL, Switzerland) to bring together the universities of Geneva (UNIGE) and Lausanne (UNIL), the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research (LICR), EPFL and CHUV to investigate CD4 T lymphocytes. While these play a supporting role with CD8 T cells, their ability to eliminate tumour cells directly has been a matter of controversy. Using innovative nanoimaging technologies designed at the EPFL laboratory, the scientists found that when the CD4 T lymphocytes ...
When using pyrite to understand Earth's ocean and atmosphere: Think local, not global
2021-02-26
The ocean floor is vast and varied, making up more than 70% of the Earth's surface. Scientists have long used information from sediments at the bottom of the ocean -- layers of rock and microbial muck -- to reconstruct the conditions in oceans of the past.
These reconstructions are important for understanding how and when oxygen became available in Earth's atmosphere and ultimately increased to the levels that support life as we know it today.
Yet reconstructions that rely on signals from sedimentary rocks but ignore the impact of local sedimentary processes do so at their own peril, according to geoscientists including David Fike in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis.
Their new study published Feb. ...
New insights into an ancient protein complex
2021-02-26
Cells rely on membranes to protect themselves from the outside world. But these membranes can't be fully closed because nutrients and other molecules have to be able to pass through. To achieve this, cell membranes have many types of channels and pores. Also, there are receptors, antennas if you like, imbedded in the membrane that continuously monitor the outside world and signal to the cell interior. Extensive collaboration between five VIB groups resulted in a better understanding of the machinery that plants use to regulate the protein composition of their outer membrane. This discovery, published in Science Advances, enhances our basic knowledge of how the plasma membrane composition can be adapted based on external stimuli, an essential ...
Meteorites remember conditions of stellar explosions
2021-02-26
A team of international researchers went back to the formation of the solar system 4.6 billion years ago to gain new insights into the cosmic origin of the heaviest elements on the period-ic table.
Led by scientists who collaborate as part of the International Research Network for Nuclear Astrophysics (IReNA) (irenaweb.org) and the Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics - Center for the Evolution of the Elements (JINA-CEE) (jinaweb.org), the study is published in the lat-est issue of the journal Science (science.sciencemag.org/content/371/6532/945).
Heavy elements we encounter in our everyday life, ...
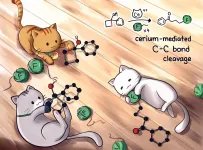
Cerium sidelines silver to make drug precursor
2021-02-26
HOUSTON - (Feb. 26, 2021) - Save your silver! It's better used for jewelry than as a catalyst for drugs.
Rice University scientists have developed a greatly simplified method to make fluoroketones, precursors for drug design and manufacture that typically require a silver catalyst.
Rice chemist Julian West and graduate students Yen-Chu Lu and Helen Jordan introduced a process for the rapid and scalable synthesis of fluoroketones that have until now been challenging and expensive to make.
Their open-access work graces the cover of the Feb. 21 issue of the Royal Society of ...
[1] ... [2590]
[2591]
[2592]
[2593]
[2594]
[2595]
[2596]
[2597]
2598
[2599]
[2600]
[2601]
[2602]
[2603]
[2604]
[2605]
[2606]
... [8827]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.