The GRANTECAN discovers the largest cluster of galaxies known in the early universe
2021-02-26
A study, led by researchers at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) and carried out with OSIRIS, an instrument on the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC), has found the most densely populated galaxy cluster in formation in the primitive universe. The researchers predict that this structure, which is at a distance of 12.5 billion light years from us, will have evolved becoming a cluster similar to that of Virgo, a neighbour of the Local Group of galaxies to which the Milky Way belongs. The study is published in the specialized journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).
Clusters of galaxies are groups of galaxies which remain together because of the action of gravity. To understand the evolution of these "cities of galaxies" scientists look ...
A missing protein promotes genetic instability in patients with Mulibrey syndrome
2021-02-26
Researchers from the Andalusian Centre for Molecular Biology and Regenerative Medicine (CABIMER), in collaboration with the Swiss Institute for Experimental Cancer Research (ISREC) have studied the mechanisms behind the higher tendency of people with Mulibrey syndrome to develop tumours. Their results point to the important role of the TRIM37 protein, whose absence explains the appearance of tumour cells.
Mulibrey syndrome is a so-called rare disease as it occurs in less than 5 out of every 10,000 inhabitants. Some of these diseases usually have a very definite genetic basis. ...
From microsaws to nanodrills: laser pulses act as subtle machining tools
2021-02-26
If light is strongly concentrated in time and space, resulting in extreme photon densities, it can enable interaction with all conceivable materials. By using these ultrashort laser foci, even transparent materials can be modified, even though they ordinarily would not interact. Short, focused laser pulses can overcome this transparency and allow energy to be deposited completely contact-free. The exact response of the material to the radiation can be very diverse, ranging from marginal refractive index changes to destructive microscale explosions that evacuate entire areas.
Using the laser pulses for optical machining allows for equally diverse material modification, such as separating or joining using the same laser system. Due to the extremely short exposure time and low degree ...
Ancient Egyptian manual reveals new details about mummification
2021-02-26
Based on a manual recently discovered in a 3,500-year-old medical papyrus, University of Copenhagen Egyptologist Sofie Schiødt has been able to help reconstruct the embalming process used to prepare ancient Egyptians for the afterlife. It is the oldest surviving manual on mummification yet discovered.
In ancient Egypt, embalming was considered a sacred art, and knowledge of the process was the preserve of very few individuals. Most secrets of the art were probably passed on orally from one embalmer to the other, Egyptologists believe, so written evidence is scarce; until recently, only two texts on mummification had been identified.
Egyptologists were therefore surprised to find a short manual on embalming in a medical text that is primarily concerned with ...
Dinosaur species: 'Everyone's unique'
2021-02-26
"Everyone's unique" is a popular maxim. All people are equal, but there are of course individual differences. This was no different with dinosaurs. A study by researchers at the University of Bonn and the Dinosaur Museum Frick in Switzerland has now revealed that the variability of Plateosaurus trossingensis was much greater than previously assumed. The paleontologists examined a total of 14 complete skulls of this species, eight of which they described for the first time. The results have now been published in the scientific journal "Acta Palaeontologica Polonica".
Plateosaurus lived during the Late Triassic, about 217 to 201 million years ago. "With well over 100 skeletons, some of them completely preserved, ...
How photoblueing disturbs microscopy
2021-02-26
The latest developments in fluorescence microscopy make it possible to image individual molecules in cells or molecular complexes with a spatial resolution of up to 20 nanometres. However, under certain circumstances, an effect occurs that falsifies the results: the laser light used can cause very reactive oxygen molecules to form in the sample. These can then damage the fluorescent dyes used to such an extent that they no longer fluoresce. Among microscopy experts, this effect is known as photobleaching.
However, various fluorescent dyes can also be transformed by photobleaching so that they absorb light of shorter wavelengths. "A previously red fluorescent dye then glows green. Its fluorescence ...
Warming may promote spread of invasive blue catfish
2021-02-26
A study by researchers at William & Mary's Virginia Institute of Marine Science suggests that continued warming of Atlantic coastal waters may enhance the spread of invasive blue catfish within the Chesapeake Bay and other estuaries along the U.S. East Coast.
The research, by Drs. Vaskar Nepal and Mary Fabrizio of VIMS, appeared in a recent issue of PLOS ONE. It builds on an earlier study by the two authors showing that blue catfish can better tolerate salinity spikes than most freshwater fishes, and thus may be able to expand their range downstream into mainstem Chesapeake waters, and from there into new Bay tributaries and even Delaware Bay. "Blue cats" were introduced to tidal freshwater stretches of the James, York, and Rappahannock rivers during the 1970s and 1980s ...
Discovery: Neanderthal-derived protein may reduce the severity of COVID-19
2021-02-26
Researchers at the Lady Davis Institute (LDI) at the Jewish General Hospital have discovered that increased levels of the protein OAS1 are associated with reduced mortality and less severe disease requiring ventilation among patients with COVID-19. Using drugs that boost OAS1 levels could be explored to try to improve these outcomes. The findings are published today in Nature Medicine.
"Our analysis shows evidence that OAS1 has a protective effect against COVID-19 susceptibility and severity," explains Dr. Brent Richards, a senior investigator at the LDI's Centre for Clinical Epidemiology and Professor of Medicine, Human Genetics, Epidemiology and Biostatistics at McGill University. "This is a very ...
Pioneering prehistoric landscape reconstruction reveals early dinosaurs lived on tropical islands
2021-02-26
A new study using leading edge technology has shed surprising light on the ancient habitat where some of the first dinosaurs roamed in the UK around 200 million years ago.
The research, led by the University of Bristol, examined hundreds of pieces of old and new data including historic literature vividly describing the landscape as a "landscape of limestone islands like the Florida Everglades" swept by storms powerful enough to "scatter pebbles, roll fragments of marl, break bones and teeth."
The evidence was carefully compiled and digitised so it could be used to generate for the first time ...
Statin use associated with increased survival in severe COVID-19
2021-02-26
NEW YORK, NY (Feb. 26, 2021)--People who took statins to lower cholesterol were approximately 50% less likely to die if hospitalized for COVID-19, a study by physicians at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and NewYork-Presbyterian has found.
"Our study is one of the larger studies confirming this hypothesis and the data lay the groundwork for future randomized clinical trials that are needed to confirm the benefit of statins in COVID-19," says Aakriti Gupta, MD, a cardiologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center and one of the co-lead authors of the study.
"If their beneficial effect bears out in randomized clinical trials, statins could potentially prove to be a low-cost and effective therapeutic ...
Male lyrebirds create an 'acoustic illusion' to snare potential mates
2021-02-26
Ithaca, NY--Famous for their uncanny ability to imitate other birds and even mechanical devices, researchers find that Australia's Superb Lyrebird also uses that skill in a totally unexpected way. Lyrebirds imitate the panicked alarm calls of a mixed-species flock of birds while males are courting and even while mating with a female. These findings are published in the journal Current Biology.
"The male Superb Lyrebird creates a remarkable acoustic illusion," says Anastasia Dalziell, currently a Cornell Lab of Ornithology Associate and recent Cornell Lab Rose Postdoctoral Fellow, now at the University of Wollongong, Australia. "Birds gather in mobbing flocks and the ruckus they make is a potent cue of a predator nearby. The ...
Could a common barnacle help find missing persons lost at sea?
2021-02-26
A common barnacle could be used to help trace missing persons lost at sea, according to research by UNSW Science.
Researchers from the Centre for Marine Science and Innovation have developed an equation that can estimate the minimum time an object has spent drifting at sea by counting the number of Lepas anserifera attached to the object.
They also developed an equation which can help plot possible drift paths of a missing boat.
"We saw this opportunity that Lepas could possibly fill in this gap in that marine forensic process and possibly contribute (to finding missing people)," study lead author Thomas ...
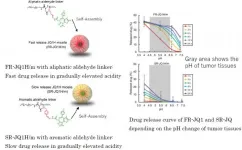
Nanomedicine activation profile determines efficacy depending on tumor c-Myc expression
2021-02-26
February 26, 2021 - Kawasaki, Japan: The Innovation Center of NanoMedicine (Director General: Prof. Kazunori Kataoka, Location: Kawasaki in Japan, Abbreviation: iCONM) reported in ACS Nano (Impact Factor: 14.588 in 2019) together with the group of Prof. Yu Matsumoto of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery (Prof. Tatsuya Yamasoba) and the group of Prof. Horacio Cabral of the Department of Bioengineering (Prof. Ryo Miyake) in the University of Tokyo that the efficacy of polymeric nano-micelles with different drug activation profile depends on the expression level of c-Myc, one of the major proto-oncogene, has been developed. See: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.1c00364
It ...
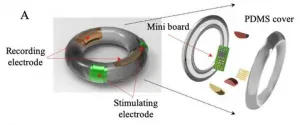
Development of an electroceutical to drastically reduce high-risk, preterm labor
2021-02-26
Preterm labor comprises 12.7% of all pregnancies. Although the overall rate of pregnancy is decreasing, the occurrence of premature birth due to preterm labor in south korea has been increasing over the past 7 years. Not only is preterm birth accountable for about a half of all neonatal mortality cases, the neurological deficits in surviving premature infants often lead to problems later in life, such as developmental disorders and respiratory complications. Currently, preterm labor is detected only when expecting mothers experience abnormal symptoms, or when they undergo a routine test like abdominal ultrasound or a laboratory test for ...
OHSU study advances field of precision medicine
2021-02-26
Researchers at Oregon Health & Science University have demonstrated a new method of quickly mapping the genome of single cells, while also clarifying the spatial position of the cells within the body.
The discovery, published in the journal Nature Communications, builds upon previous advances by OHSU scientists in single-cell genome sequencing. The study represents another milestone in the field of precision medicine.
"It gives us a lot more precision," said senior author Andrew Adey, Ph.D., associate professor of molecular and medical genetics in the OHSU School of Medicine. "The single-cell aspect gives us the ability to track the molecular changes within each cell type. Our new study also allows the capture of where those ...
Can a robot operate effectively underwater?
2021-02-26
If you've ever watched Planet Earth, you know the ocean is a wild place to live. The water is teaming with different ecosystems and organisms varying in complexity from an erudite octopus to a sea star. Unexpectedly, it is the sea star, a simple organism characterized by a decentralized nervous system, that offers insights into advanced adaptation to hydrodynamic forces--the forces created by water pressure and flow.
Researchers from the USC Viterbi School of Engineering found that sea stars effectively stay attached to surfaces under extreme hydrodynamic loads by altering their shape. The researchers, including the Henry Salvatori Early Career Chair in Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering Mitul Luhar and doctoral ...
Early-warning for seizures could be a game-changer for epilepsy patients
2021-02-26
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological conditions, affecting more than 65 million worldwide. For those dealing with epilepsy, the advent of a seizure can feel like a ticking time bomb. It could happen at any time or any place, potentially posing a fatal risk when a seizure strikes during risky situations, such as while driving.
A research team at USC Viterbi School of Engineering and Keck Medicine of USC is tackling this dangerous problem with a powerful new seizure predicting mathematical model that will give epilepsy patients an accurate warning five minutes to one hour before they are likely to experience a seizure, offering enhanced freedom for the patient and cutting the need for medical intervention.
The research, ...
MicroRNA testing of healthy kids could provide a window on future heart and kidney health
2021-02-26
New York, NY (February 26, 2020) - Molecules called microRNAs (miRNAs) that are measurable in urine have been identified by researchers at Mount Sinai as predictors of both heart and kidney health in children without disease. The epidemiological study of Mexican children was published in February in the journal Epigenomics.
"For the first time, we measured in healthy children the associations between urinary miRNAs and cardiorenal outcomes, including blood pressure, urinary sodium and potassium levels, and eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate, a measure of how well the kidneys are filtering or cleaning the blood]," says lead author Yuri Levin-Schwartz, ...
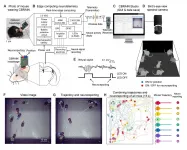
Flickering the neural activities with LED lights
2021-02-26
Living in a group has clear benefits. As a member of a societal group, one can share resources with the others, seek protection from predators, and forage in an efficient manner. In a 2020 paper published in Science Advances, the neuroscientist Jee Hyun Choi and her student Jisoo Kim of the Brain Science Institute in the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) argue that there are much more stories about the advantages of group living and social behaviors to the mammalian brain yet to be discovered. Their research was conducted using CBRAIN (Collective Brain Research Aided by Illuminating Neural activity), a unique neuro-telemetric device equipped with LED lights, which enables the ...
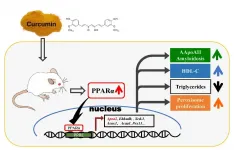
Curcumin for amyloidosis and lipid metabolism -- a novel insight
2021-02-26
Curcumin is a polyphenol compound produced by plants of the Curcuma longa species and has been reported to have many physiological activities, which include anti-oxidation, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-amyloid properties. However, the mechanism and network of action are not completely clear. Amyloidosis is a group of diseases characterized by abnormal aggregates of proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, and subsequent deposition in various tissues and organs, such as Alzheimer's disease, immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis.
In previous studies, curcumin has been ...
Changing the silkworm's diet to spin stronger silk
2021-02-26
Tohoku University researchers have produced cellulose nanofiber (CNF) synthesized silk naturally through a simple tweak to silkworms' diet. Mixing CNF with commercially available food and feeding the silkworms resulted in a stronger and more tensile silk.
The results of their research were published in the journal Materials and Design on February 1, 2021.
"The idea for our research came to us when we realized the flow-focusing method by which silkworms produce silk is optimal for the nanofibril alignment of CNF," said Tohoku University materials engineer Fumio Narita and co-author of the study.
Silk is usually associated with clothes. But its usage is incredibly diverse thanks to its strength and elastic properties. Its biocompatibility makes it even safe to ...
New open-source platform accelerates research into the treatment of heart arrhythmia's
2021-02-26
An open-source platform, OpenEP co-developed by researchers from the School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences at King's College London has been made available to advance research on atrial fibrillation, a condition characterised by an irregular and often fast heartbeat. It can cause significant symptoms such as breathlessness, palpitations and fatigue, as well as being a major contributor to stroke and heart failure.
Current research into the condition involves the interpretation of large amounts of clinical patient data using software written by individual ...
Using artificial intelligence to hunt for breast cancer
2021-02-26
The centre is part of the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR). With the help of microscopy and artificial intelligence, the "E-Morph" test reliably identifies substances that can have oestrogen-like or even opposing effects, according to the research team's report in the specialist journal "Environment International". "E-Morph is a milestone on the way to, one day, replacing animal experiments currently required to detect hormone-like effects," says BfR President Prof. Dr. Dr. Andreas Hensel.
Link to the specialist publication (ScienceDirect):
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160412021000350
Link ...
Advantageous preparation of movement via independent control of muscle sensors
2021-02-26
A number of brain areas change their activity before we execute a planned voluntary movement. A new study by Umeå University identifies a novel function of this preparatory neural activity, highlighting another mechanism the nervous system can use to achieve its goals.
Voluntary movements are prepared before they are executed. For example, such 'preparation' occurs in the period between seeing a coffee cup and starting to reach for it. Neurons in many areas of the brain change their activity during movement preparation in ways that reflect different aspects of ...
"Stark warning": Combating ecosystem collapse from the tropics to the Antarctic
2021-02-26
Eminent scientists warn that key ecosystems around Australia and Antarctica are collapsing, and propose a three-step framework to combat irreversible global damage.
Their report, authored by 38 Australian, UK and US scientists from universities and government agencies, is published today in the international journal Global Change Biology. Researchers say I heralds a stark warning for ecosystem collapse worldwide, if action if not taken urgently.
Lead author, Dr Dana Bergstrom from the Australian Antarctic Division, said that the project emerged from a conference inspired by her ecological research in polar environments.
"I was seeing unbelievably rapid, widespread dieback in the alpine tundra of World Heritage-listed Macquarie Island and started wondering if this ...
[1] ... [2589]
[2590]
[2591]
[2592]
[2593]
[2594]
[2595]
[2596]
2597
[2598]
[2599]
[2600]
[2601]
[2602]
[2603]
[2604]
[2605]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.