Metallic state of Ag nanoclusters in oxidative dispersion identified in situ
2021-03-04
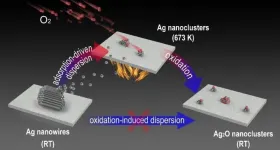
Oxidative dispersion has been widely used in the regeneration of sintered metal catalysts as well as the fabrication of single-atom catalysts.
The consensus on the oxidative dispersion process includes the formation of mobile metal oxide species from large metal particles and the capture of these species on a support surface. Nevertheless, the mechanism of oxidation-induced dispersion has yet to be confirmed via in situ electron microscopic and/or spectroscopic characterizations.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. FU Qiang and Prof. BAO Xinhe from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. YANG Bing from DICP and Prof. GAO Yi ...
Administering zinc to covid-19 patients could help towards their recovery
2021-03-04
Administering zinc supplements to covid-19 patients with low levels of this element may be a strategy to reduce mortality and recovery time. At the same time, it could help to prevent risk groups, like the elderly, from suffering the worst effects of the disease. These are the findings of a study by physicians and researchers from the Hospital del Mar, Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM) and Pompeu Fabra University (UPF), led by Dr. Robert Güerri, a physician at the Infectious Diseases Service of Hospital del Mar, which has just been published in the journal Nutrients.
The study analysed the zinc levels of 249 adult patients treated at the centre between 9 March and 1 April 2020, with an average age of 65 years. The most common symptoms presented at the time of ...
Researchers discover how to control zinc in plants: Could help the world's malnourished
2021-03-04
Researchers discover how to control zinc content in plants: Could help the world's malnourished
Over 2 billion people worldwide are malnourished due to zinc deficiency. Led by the University of Copenhagen, an international team of researchers has discovered how plants sense zinc and use this knowledge to enhance plant zinc uptake, leading to an increase in seed zinc content by 50 percent. The new knowledge might one day be applied towards the cultivation of more nutritious crops.
A deficiency of zinc and other essential dietary nutrients is one of the greatest causes of malnutrition worldwide. More than two billion people are estimated to suffer from zinc deficiency, a problem that can lead to impaired immune systems, mental disorders and stunting. Among other things, ...
Determination of glycine transporter opens new avenues in development of psychiatric drugs
2021-03-04
Glycine can stimulate or inhibit neurons in the brain, thereby controlling complex functions. Unraveling the three-dimensional structure of the glycine transporter, researchers have now come a big step closer to understanding the regulation of glycine in the brain. These results, which have been published in Nature, open up opportunities to find effective drugs that inhibit GlyT1 function, with major implications for the treatment of schizophrenia and other mental disorders.
Glycine is the smallest amino acid and a building block of proteins, and also a critical neurotransmitter that can both stimulate or inhibit ...
Sea butterflies already struggle in acidifying Southern Ocean
2021-03-04
The oceans are becoming more acidic because of the rapid release of carbon dioxide (CO2) caused by anthropogenic (human) activities, such as burning of fossil fuels. So far, the oceans have taken up around 30% of all anthropogenic CO2 released to the atmosphere. The continuous increase of CO2 has a substantial effect on ocean chemistry because CO2 reacts with water and carbonate molecules. This process, called 'ocean acidification', lowers pH, and calcium carbonate becomes less available. This is a problem for calcifying organisms, such as corals and molluscs, that use calcium carbonate as the main building blocks of their exoskeleton.
In particular, organisms that build their shells from a type of calcium carbonate known as 'aragonite' are in trouble because aragonite is ...
Preventing injuries and improving recovery with micro-Doppler radars
2021-03-04
?Micro-Doppler radars could soon be used in clinical settings to predict injury risk and track recovery progress, according to Penn State researchers.?
Being able to view subtle differences in human movement?would allow health care workers to more accurately identify individuals who may be at risk for injury and to track progress precisely while individuals are recovering from an injury. In an effort to find an accurate, reliable and cost-effective way to measure these subtleties ?in human movement, College of Engineering and College of Medicine researchers teamed up to develop a radar in front ...
How to choose low glycaemic index (GI) foods? A GI 'glossary' of Asian foods released
2021-03-04
Professor Christiani Jeyakumar Henry, Senior Advisor of Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation (SIFBI), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) and his team have developed a Glycaemic Index (GI) glossary of non-Western foods. The research paper was published in Nutrition & Diabetes on 6 Jan 2021: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-020-00145-w.
Observational studies have shown that the consumption of low glycaemic index (GI) foods is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), significantly less insulin resistance and a lower prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. However, most published GI values focus on Western foods with minimal inclusion of other foods from non-Western countries, hence their application ...
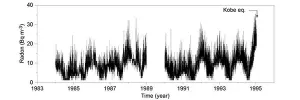
Revisiting the Kobe earthquake and the variations of atmospheric radon concentration
2021-03-04
Tohoku University researchers have unearthed further details about radon concentration in the atmosphere before and after earthquakes, moving us closer to being able to anticipate when large earthquakes may hit.
The results of their research were published in the journal Science Reports on February 18, 2021.
Radon is a radioactive noble gas derived from radioactive decays of radium-226 in the ground. Radon bubbles up to the surface and is expelled into the atmosphere.
It has long been known that elevated levels of radon underneath the ground can be detected before and after earthquakes. But the relationship between the mechanisms that cause abnormal changes in radon concentration and the occurrence of earthquakes requires greater ...
Scientists discover how microorganisms evolve cooperative behaviors
2021-03-04
Interspecies interactions are the foundation of ecosystems, from soil to ocean to human gut. Among the many different types of interactions, syntrophy is a particularly important and mutually beneficial interspecies interaction where one partner provides a chemical or nutrient that is consumed by the other in exchange for a reward.
Syntrophy plays an essential role in global carbon cycles by mediating the conversion of organic matter to methane, which is about 30 times more potent than carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas and is a source of sustainable energy. And in the human gut, trillions of microbial cells also interact ...
Nanoprinted high-neuron density optical linear perceptrons performing near-infrared inference on a C
2021-03-04
Intelligent holographic nanostructures on CMOS sensors for energy-efficient AI security schemes
Today, machine learning permeates our everyday life, with millions of users every day unlocking their phones through facial recognition or passing through AI-enabled automated security checks at airports and train stations. These tasks are possible thanks to sensors that collect optical information to feed it to a neural network in a computer. Imagine to empower the sensors in the devices you use every day to perform artificial intelligence functions without a computer - as simply as putting glasses on them.
The integrated holographic perceptrons developed by a research team at University of Shanghai for Science and Technology led ...
UN: 17% of all food available at consumer levels is wasted
2021-03-04
Nairobi/Paris, 4 March 2021 - An estimated 931 million tonnes of food, or 17% of total food available to consumers in 2019, went into the waste bins of households, retailers, restaurants and other food services, according to new UN research conducted to support global efforts to halve food waste by 2030.
The weight roughly equals that of 23 million fully-loaded 40-tonne trucks -- enough bumper-to-bumper to circle the Earth 7 times.
The Food Waste Index Report 2021, from the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and partner organization WRAP, looks at food waste that occurs in retail outlets, restaurants and homes - ...
Higher income predicts feelings such as pride and confidence
2021-03-04
People with higher incomes tend to feel prouder, more confident and less afraid than people with lower incomes, but not necessarily more compassionate or loving, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
In a study of data from 162 countries, researchers found consistent evidence that higher income predicts whether people feel more positive "self-regard emotions," including confidence, pride and determination. Lower income had the opposite effect, and predicted negative self-regard emotions, such as sadness, fear and shame. The research was published online in the journal Emotion. ...
Misinformation, polarization impeding environmental protection efforts
2021-03-04
A group of researchers, spanning six universities and three continents, are sounding the alarm on a topic not often discussed in the context of conservation--misinformation.
In a recent study published in FACETS, the team, including Dr. Adam Ford, Canada Research Chair in Wildlife Restoration Ecology, and Dr. Clayton Lamb, Liber Ero Fellow, both based in the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Science, explain how the actions of some scientists, advocacy groups and the public are eroding efforts to conserve biodiversity.
"Outcomes, not intentions, should be the basis for how we view success in conservation," says Dr. Ford.
"Misinformation related to vaccines, climate change, and links between smoking ...
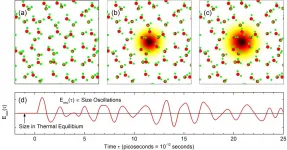
Terahertz waves from electrons oscillating in liquid water
2021-03-04
Ionization of water molecules by light generates free electrons in liquid water. After generation, the so-called solvated electron is formed, a localized electron surrounded by a shell of water molecules. In the ultrafast localization process, the electron and its water shell display strong oscillations, giving rise to terahertz emission for tens of picoseconds.
Ionization of atoms and molecules by light is a basic physical process generating a negatively charged free electron and a positively charged parent ion. If one ionizes liquid water, the free electron undergoes a sequence of ultrafast processes by which it loses energy and eventually localizes at a new site in ...
Engineered safety switch curbs severe side effects of CAR-T immunotherapy
2021-03-04
CHAPEL HILL, North Carolina--UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers have successfully used an experimental safety switch, incorporated as part of a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, a type of immunotherapy, to reduce the severity of treatment side effects that sometimes occur. This advance was seen in a patient enrolled in a clinical trial using CAR-T to treat refractory acute B-cell leukemia. It demonstrates a proof-of-principle for possible expanded use of CAR-T immunotherapy paired with the safety switch.
The researchers published their findings in the journal Blood as an ahead-of-print publication.
With CAR-T therapy, T-cells from a patient's immune system ...
'PopDel' detects deletions in our genomes
2021-03-04
The human genome contains roughly three million letters. On average, the genome sequences of any two people differ from each other by about one in every 1,000 letters. Yet different variants occur, from substituted letters to entire missing sections of DNA. Scientists from the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) and the Regensburg Center for Interventional Immunology (RCI) have teamed up with Icelandic researchers to develop software that reliably and quickly identifies large deletions in ten-thousands of genomes simultaneously. The researchers have now published their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
The human genome contains roughly three million letters ...
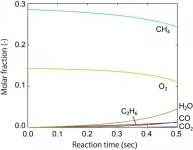
Performance of methane conversion solid catalyst is predicted by theoretical calculation
2021-03-04
Japanese researchers have developed a simulation method to theoretically estimate the performance of heterogeneous catalyst by combining first-principles calculation (1) and kinetic calculation techniques. Up to now, simulation studies mainly focused on a single or limited number of reaction pathways, and it was difficult to estimate the efficiency of a catalytic reaction without experimental information.
Atsushi Ishikawa, Senior Researcher, Center for Green Research on Energy and Environmental Materials, National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), performed computation of reaction kinetic information from first-principles calculations based on quantum mechanics, and developed methods and programs to carry out kinetic simulations ...
Quick to smile - study shows speed of expression offers vital visual cues
2021-03-04
The speed at which we produce facial expressions plays an important role in our ability to recognise emotions in others, according to new research at the University of Birmingham.
A team in the University's School of Psychology carried out research which showed that people tend to produce happy and angry expressions more rapidly, while sad expressions are produced more slowly.
The team found that our ability to form judgements about people's facial expressions has close links with the speeds at which those expressions are produced and is also closely related to the ways in which we would produce those expressions ourselves. The study is published in Emotion.
"Being able to recognise and interpret ...
Advance in 'optical tweezers' to boost biomedical research
2021-03-04
Much like the Jedis in Star Wars use 'the force' to control objects from a distance, scientists can use light or 'optical force' to move very small particles.
The inventors of this ground-breaking laser technology, known as 'optical tweezers', were awarded the 2018 Nobel Prize in physics.
Optical tweezers are used in biology, medicine and materials science to assemble and manipulate nanoparticles such as gold atoms. However, the technology relies on a difference in the refractive properties of the trapped particle and the surrounding environment.
Now scientists have discovered a new technique that allows them to manipulate particles that have the same refractive ...
Does a vegan diet lead to poorer bone health?
2021-03-04
The vegan diet is on trend. How this type of diet affects health is the subject of scientific studies. In a new study from the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), the bone health of 36 vegans as well as 36 people following a mixed-food diet was determined with an ultrasound measurement of the heel bone. The result: on average, people following a vegan diet had lower ultrasound values compared to the other group. This indicates poorer bone health.
In the study, the scientists also determined biomarkers in blood and urine. This aims ...
Limiting invasive species may be a better goal than eliminating them
2021-03-04
Managing invasive species--not eliminating them altogether--is a better use of time and conservation resources in many cases, according to a study led by a University of Alberta biologist.
Every year, hundreds of introduced species cause billions of dollars in damage to ecosystems, agriculture and infrastructure in North America alone. The research, led by Stephanie Green, makes a case for working smarter, not harder, to temper the impact of destructive and widespread invasive species using a strategy called functional eradication.
"Rather than trying to completely eliminate invasive species that have spread over large areas, which is very ...
An ultra-degree-of-freedom structured vector beam
2021-03-04
Typically, light emitted from standard lasers has a controllable degree of freedom (DoF) which may be polarisation or beam shape. By suitably manipulating a laser with the introduction of specialised optical components, an output with 2 DoFs, such as vector vortex beams with controllable polarisation and orbital angular momentum (OAM). The term 'vector' describes a structured change in the polarisation across the beam and 'vortex' describes the twisting of the phase in the beam (OAM), much like a twisting tornado. Transcending 2 DoFs from a laser was not possible. By exploiting ray-wave duality in a frequency-degenerate laser, ...
Nerve damage after chemo: potential risk factors revealed
2021-03-04
Being older, overweight and having low haemoglobin levels (fewer red blood cells) could increase a patient's risk of developing debilitating nerve damage following chemotherapy, a research team led by UNSW Sydney has revealed.
The researchers aimed to identify pre-treatment clinical and blood-based risk factors in patients who developed chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) - nerve damage in peripheral body parts, like hands or feet, as a result of chemotherapy.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open recently, examined patients - mostly women - who received paclitaxel or oxaliplatin chemotherapy treatment, which are common treatments for breast, colorectal and gynaecological ...
Scientists adapt solar energy technology to detect chemical warfare agents & pesticides
2021-03-04
In a colourful solution to a dangerous problem, Australian scientists are adapting a component from cutting-edge solar cells to design a rapid, light-based detection system for deadly toxins.
While use of chemical warfare agents like sulfur mustard - better known as mustard gas - is banned internationally, we do rely on other strictly-controlled chemicals for agriculture, industry and throughout our daily lives, including fumigants like methyl iodide, which is used to control insects and fungi. The wrong amounts or incorrect use of these fumigants can be harmful to people and degrade the ozone layer.
Because it's invisible and doesn't smell, it's hard to tell whether there are dangerous amounts of methyl iodide present, and until ...
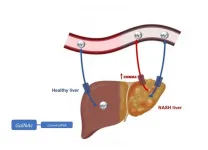
Protein controlling magnesium identified as therapeutic target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
2021-03-04
An international team of researchers has identified the CNNM4 protein as a key regulator of magnesium in the liver and potential therapeutic target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, according to a study published in the Journal of Hepatology.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, a form of fatty liver disease characterized by inflammation and liver fibrosis, is associated with obesity and has a worldwide prevalence of 1.7 billion people.
Unhealthy nutritional habits and dietary imbalances are recognized as causes of many diseases. Magnesium is widely available in both plant and animal foods; most vegetables, legumes, peas, beans, and nuts are rich in magnesium, as are some ...
[1] ... [2581]
[2582]
[2583]
[2584]
[2585]
[2586]
[2587]
[2588]
2589
[2590]
[2591]
[2592]
[2593]
[2594]
[2595]
[2596]
[2597]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.