Sniffing in the name of science
2021-03-02
The lists of Earth's endangered animals and plants are getting increasingly longer. But in order to stop this trend, we require more information. It is often difficult to find out exactly where the individual species can be found and how their populations are developing. According to a new overview study published in Methods in Ecology and Evolution by Dr Annegret Grimm-Seyfarth from the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) and her colleagues, specially trained detection dogs can be indispensable in such cases. With the help of these dogs, the species sought can usually be found faster and more effectively than with other methods.
How many otters are there ...
TPU scientists develop efficient method to create high-strength materials for flexible electronics
2021-03-02
TPU researchers jointly with their colleagues from foreign universities have developed a method that allows for a laser-driven integration of metals into polymers to form electrically conductive composites. The research findings are presented in Ultra-Robust Flexible Electronics by Laser-Driven Polymer-Nanomaterials Integration article Ultra-Robust Flexible Electronics by Laser-Driven Polymer-Nanomaterials Integration, published in Advanced Functional Materials academic journal (Q1, IF 16,836).
"Currently developing breakthrough technologies such as the Internet of Things, flexible electronics, brain-computer interfaces will have a great impact on ...
Ultra-fast electron measurement provides important findings for the solar industry
2021-03-02
The key are the ultra-fast flashes of light, with which the team led by Dr. Friedrich Roth works at FLASH in Hamburg, the world's first free-electron laser in the X-ray region. "We took advantage of the special properties of this X-ray source and expanded them with time-resolved X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (TR-XPS). This method is based on the external photoelectric effect, for the explanation of which Albert Einstein received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
"For the first time, we were able to directly analyze the specific charge separation and subsequent processes when light hits a model system such as an organic solar cell. ...
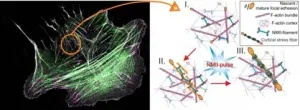
A mechanism by which cells build 'mini-muscles' underneath their nucleus identified
2021-03-02
Research groups at the University of Helsinki uncovered how motor protein myosin, which is responsible for contraction of skeletal muscles, functions also in non-muscle cells to build contractile structures at the inner face of the cell membrane. This is the first time when such 'mini-muscles', also known as stress fibers, have been seen to emerge spontaneously through myosin-driven reorganization of the pre-existing actin filament network in cells. Defects in the assembly of these 'mini-muscles' in cells lead to multiple disorders in humans, and in the most severe cases to cancer progression.
A new study published in eLife, drills into the core mechanisms of stress fiber assembly, and reveals how stress fibers can be built directly ...
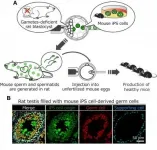
Mouse sperm generated in rats
2021-03-02
Okazaki, Japan - Making gametes such as sperm and eggs from pluripotent stem cells, primitive cells that can make all the tissues, greatly contributes to efficient reproduction of livestock animals and future assisted reproductive medicine. Researchers pave the way to achieve this goal using a body of xenogenic animals.
The researchers previously developed a method to grow stem cells into an entire organ in the body, so-called blastocyst complementation. The blastocyst is a structure of early embryos. If stem cells are transplanted into the blastocyst obtained from animals that cannot make a certain organ, ...
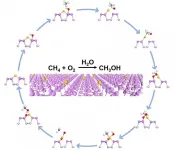
Gold-phosphorus nanosheets catalyzes nature gas to greener energy selectively
2021-03-02
Advances in hydraulic fracturing technology have enabled discovery of large reserves of natural gas which primarily contains methane, which is mainly burned directly and causing global warming potentially. Upgrading methane to greener energy such as methanol through aerobic oxidation is an ideal way to solve the problem and remain 100% atom economy.
Yet the difficulties lie in activating methane and preventing methanol from over-oxidation. Methane takes a stable non-polar tetrahedral structure with high dissociation energy of C-H bond, which requires high energy to be activated. ...
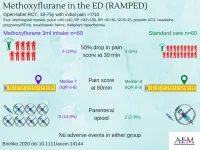
Rapid administration of methoxyflurane versus standard care for pain management in the ED
2021-03-02
Des Plaines, IL - Initial management with inhaled methoxyflurane in the emergency department did not achieve the prespecified substantial reduction in pain, but was associated with clinically significant lower pain scores compared to standard therapy. That is the conclusion of a study titled Rapid Administration of Methoxyflurane to Patients in the Emergency Department (RAMPED) Study: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Methoxyflurane Versus Standard Care that was published recently in the February 2021 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
According to findings of the controlled randomized trial, secondary outcomes included the pain ...
Designing soft materials that mimic biological functions
2021-03-02
Northwestern Engineering researchers have developed a theoretical model to design soft materials that demonstrate autonomous oscillating properties that mimic biological functions. The work could advance the design of responsive materials used to deliver therapeutics as well as for robot-like soft materials that operate autonomously.
The design and synthesis of materials with biological functions require a delicate balance between structural form and physiological function. During embryonic development, for instance, flat sheets of embryonic cells morph through a series of folds into intricate three-dimensional structures such as branches, tubes, and furrows. These, in turn, become dynamic, three-dimensional building blocks for organs performing vital functions ...
Parents' school reviews correlated with test scores and demographics, not school effectiveness
2021-03-02
Washington, March 2, 2021--A first-of-its-kind analysis of parents' reviews of U.S. public K-12 schools, posted primarily from 2009 to 2019 on the popular school information site GreatSchools.org, found that most reviews were written by parents at schools in affluent neighborhoods and provided information that correlated strongly with test scores, a measure that closely tracks race and family income. Language associated with school effectiveness, which measures how much students improve in their test scores over time and is less correlated with demographics, was ...
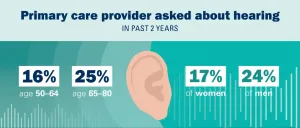
Most older adults haven't gotten screened or tested for hearing loss, poll finds
2021-03-02
Eighty percent of Americans over 50 say their primary care doctor hasn't asked about their hearing in the past two years, and nearly as many - 77% -- haven't had their hearing checked by a professional in that same time, according to a new national poll report.
That's despite a growing body of evidence about the importance of hearing to other aspects of life, from dementia and risk of falls to the ability to stay connected to friends and family.
Men were more likely than women to say they'd had a recent hearing screening or test, and so were people ages 65 to 80 compared with those in ...
Black NBA players have shorter careers than white players
2021-03-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Black players in the NBA have 30% greater odds of leaving the league in any given season than white players who have equivalent performance on the court, a new study finds.
The results were driven mostly by bench players, who are the majority of those in the league, but who average less than 20 minutes of action per game.
These findings suggest that even in the NBA - a league in which Black players make up 70-75% of those on the court - African Americans face discrimination, said Davon Norris, lead author of the study and a doctoral student in sociology at The Ohio State University.
"If there is going to be anywhere in America where you would expect there wouldn't be racial ...
Common bacteria modified to make designer sugar-based drug
2021-03-02
TROY, N.Y. -- Envisioning an animal-free drug supply, scientists have -- for the first time -- reprogrammed a common bacterium to make a designer polysaccharide molecule used in pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. Published today in Nature Communications, the researchers modified E. coli to produce chondroitin sulfate, a drug best known as a dietary supplement to treat arthritis that is currently sourced from cow trachea.
Genetically engineered E. coli is used to make a long list of medicinal proteins, but it took years to coax the bacteria into producing even ...
Meeting the meat needs of the future
2021-03-02
Tokyo, Japan - Humans are largely omnivores, and meat in various forms has always featured in the diet of most cultures. However, with the increasing population and pressure on the environment, traditional methods of meeting this fundamental food requirement are likely to fall short. Now, researchers at the University of Tokyo report innovative biofabrication of bovine muscle tissue in the laboratory that may help meet escalating future demands for dietary meat.
With global urbanization, the economics of animal husbandry are becoming unsustainable. From an environmental viewpoint, the land and water costs of modern mega-scale ...
Secrets of sealed 17th century letters revealed by dental X-ray scanners
2021-03-02
In a world first, an international team of researchers has read an unopened letter from Renaissance Europe - without breaking its seal or damaging it in any way.
The research, published in Nature Communications, describes how an X-ray scanner used in dental research and 'virtual unfolding' allowed the interdisciplinary team to read the contents of a securely and intricately folded letter which has remained unopened for 300 years, while preserving its valuable physical evidence.
A highly sensitive X-ray microtomography scanner, developed at ...
First ever detailed description of a volcanic eruption from Sierra Negra
2021-03-02
A volcanic eruption in the Galápagos Islands has given scientists a fresh insight into how volcanoes behave and provided vital information that will help to predict future hazards on the islands.
Irish scientists, based at Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies (DIAS) and Trinity College Dublin respectively, were members of an international research team from Ireland, United Kingdom, United States, France and Ecuador that made the discovery.
The research published today (02.03.21) in Nature Communications reveals the first ever detailed description of a volcanic eruption from Sierra Negra - one ...
Lead up to volcanic eruption in Galapagos captured in rare detail
2021-03-02
Hours before the 2018 eruption of Sierra Negra, the Galápagos Islands' largest volcano, an earthquake rumbled and raised the ground more than 6 feet in an instant. The event, which triggered the eruption, was captured in rare detail by an international team of scientists, who said it offers new insights into one of the world's most active volcanoes.
"The power of this study is that it's one of the first times we've been able to see a full eruptive cycle in this detail at almost any volcano," said Peter La Femina, associate professor of geosciences ...
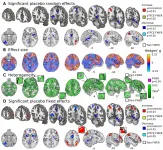
New study gives the most detailed look yet at the neuroscience of placebo effects
2021-03-02
A large proportion of the benefit that a person gets from taking a real drug or receiving a treatment to alleviate pain is due to an individual's mindset, not to the drug itself. Understanding the neural mechanisms driving this placebo effect has been a longstanding question. A meta-analysis published in Nature Communications finds that placebo treatments to reduce pain, known as placebo analgesia, reduce pain-related activity in multiple areas of the brain.
Previous studies of this kind have relied on small-scale studies, so until now, researchers did not know if the neural mechanisms underlying ...
New technology allows scientists first glimpse of intricate details of Little Foot's life
2021-03-02
In June 2019, an international team brought the complete skull of the 3.67-million-year-old Little Foot Australopithecus skeleton, from South Africa to the UK and achieved unprecedented imaging resolution of its bony structures and dentition in an X-ray synchrotron-based investigation at the UK's national synchrotron, Diamond Light Source. The X-ray work is highlighted in a new paper in e-Life, published today (2nd March 2021) focusing on the inner craniodental features of Little Foot. The remarkable completeness and great age of the Little Foot skeleton makes it a crucially important ...
Ecology: The scientific literature dominated by men and a handful of countries
2021-03-02
Publishing in peer-reviewed scientific journals is crucial for the development of a researcher's career. The scientists that publish the most often in the most prestigious journals generally acquire greater renown, as well as higher responsibilities. However, a team involving two CNRS researchers* has just shown that the vast majority of scientific articles in the fields of ecology and conservation biology are authored by men working in a few Western countries. They represent 90% of the 1,051 authors that have published the most frequently in the 13 major scientific journals in the field since 1945. ...
New report offers detailed analysis of Capitol Hill siege
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON (Mar. 2, 2021) -- A report released today by the George Washington University Program on Extremism reveals new information about the 257 people charged in federal court for playing a role in the Jan. 6 attack on the United States Capitol. The report, "This is Our House!" A Preliminary Assessment of the Capitol Hill Siege Participants," also provides several recommendations aimed at combating domestic extremism.
The GW Program on Extremism tracked and categorized the people charged so far in the attack and the resulting report provides a preliminary assessment of the siege participants.
"The events of Jan. 6 may mark a watershed moment for domestic violent ...
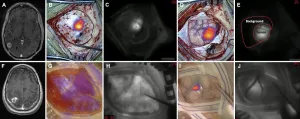
2nd window ICG predicts gross-total resection/progression-free survival in brain metastasis
2021-03-02
Charlottesville, VA (March 2, 2021). Researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania conducted a prospective cohort study utilizing their technique of delayed near-infrared imaging with high-dose indocyanine green (called "second window ICG" or "SWIG") in the identification of brain metastases during surgery. In this study, all metastatic lesions enhanced under near-infrared light with application of SWIG. The researchers compared near-infrared SWIG images obtained at the end of tumor resection with postoperative gadolinium-enhanced MRIs, considered the gold standard for imaging. The comparison demonstrated that SWIG can be used to predict the extent of gross-total resection and, ...
Coffee for the birds: connecting bird-watchers with shade-grown coffee
2021-03-02
Since 1970, bird populations in North America have declined by approximately 2.9 billion birds, a loss of more than one in four birds. Factors in this decline include habitat loss and ecosystem degradation from human actions on the landscape.
At the same time, enthusiasm for bird-watching has grown, with more than 45 million recreational participants in the United States alone. Now, researchers are looking into how to mobilize these bird enthusiasts to help limit bird population declines.
Enter bird-friendly coffee.
Bird-friendly coffee is certified organic, but its impact on the environment goes further than that: it is cultivated specifically to maintain bird habitats instead of clearing vegetation that birds and other animals rely on.
Researchers ...
New study proposes a low cost, high efficiency mask design
2021-03-02
A new paper in Oxford Open Materials Science, published by Oxford University Press, presents low cost modifications to existing N95 masks that prolongs their effectiveness and improves their reusability post disinfectants.
The COVID-19 crisis has increased demand for respiratory masks, with various models of DIY masks becoming popular alongside the commercially available N95. The utility of such masks is primarily based on the size of aerosols that they are capable of filtering out and how long they can do so effectively.
Conventional masks like the N95 use a layered system and have an efficiency ...
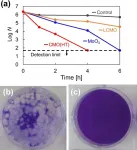
A materials science approach to combating coronavirus
2021-03-02
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology working in collaboration with colleagues at the Kanagawa Institute of Industrial Science and Technology and Nara Medical University in Japan have succeeded in preparing a material called cerium molybdate (γ-Ce2Mo3O13 or CMO), which exhibits high antiviral activity against coronavirus.
The ongoing coronavirus pandemic has highlighted the urgency not only of vaccine development and rollout but also of developing innovative materials and technologies with antiviral properties that could play a vital role in helping to contain the spread of the virus.
Conventional inorganic antimicrobial materials are often prepared with metals such as copper or photocatalysts ...
High fat diets may over-activate destructive heart disease protein
2021-03-02
Peer Reviewed
Experimental
Animals
Consumption of a high fat diet may be activating a response in the heart that is causing destructive growth and lead to greater risk of heart attacks, according to new research.
In a paper published in Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, researchers looked at the effect of feeding mice a high fat diet on oxidative stress levels on heart cells. The team from the University of Reading found that cells from the mice had twice the amount of oxidative stress, and led to heart cells being up to 1.8 times bigger due to cardiac hypertrophy which is associated with heart disease.
Named first author Dr Sunbal Naureen ...
[1] ... [2580]
[2581]
[2582]
[2583]
[2584]
[2585]
[2586]
[2587]
2588
[2589]
[2590]
[2591]
[2592]
[2593]
[2594]
[2595]
[2596]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.