Common dolphin populations at risk
2021-03-03
While consumers look out for the Dolphin Safe mark on seafood purchases, a major research stocktake of Australian-New Zealand waters gives new guidelines to managers of dolphin fisheries.
The extensive new genomic study of almost 500 common dolphins (Delphinus delphis), spanning multiple spatial areas of more than 1500 sq km from the southern and east coast of Australia to Tasmania and New Zealand, calls for greater collaboration between the two countries' conservation and fisheries plans.
Just published in Frontiers in Marine Science, the study of DNA diversity of several dolphin populations in Australia and NZ suggests connectivity between ...
Genomics study identifies routes of transmission of coronavirus in care homes
2021-03-03
Care homes are at high risk of experiencing outbreaks of COVID-19, the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. Older people and those affected by heart disease, respiratory disease and type 2 diabetes - all of which increase with age - are at greatest risk of severe disease and even death, making the care home population especially vulnerable.
Care homes are known to be high-risk settings for infectious diseases, owing to a combination of the underlying vulnerability of residents who are often frail and elderly, the shared living environment with multiple ...
Fluorescent nanodiamonds successfully injected into living cells
2021-03-03
As odd as it sounds, many scientists have attempted to place extremely small diamonds inside living cells. Why? Because nanodiamonds are consistently bright and can give us unique knowledge about the inner life of cells over a long time. Now physics researchers at Lund University in Sweden have succeeded in injecting a large number of nanodiamonds directly to the cell interior.
Diamonds are not only sought after for their beauty, but also for their uniquely luminescent properties, at least among scientists. Unlike other fluorescent materials, they do not bleach.
"We actually think of them as a dye. In addition, they are biocompatible", says Elke Hebisch, researcher at solid state physics at Lund University.
Together ...
80% of sexual abuse victims in Spain who seek public compensation receive nothing
2021-03-03
European Union law rules that Member States must provide fair and appropriate compensation for victims of sexual offences. In some countries, few victims receive any financial compensation, or often the amount received is very low. According to figures from the Spanish Government's Ministry of Finance, obtained by professor of Criminal Law at the UOC, Josep M. Tamarit, between 1998 and 2018 in Spain some 1,356 applications for public compensation were made, of which 272 were favourably settled. "During these two decades, only 20% of the compensation ...
Reconstructing historical typhoons from a 142-year record
2021-03-03
A team of scientists has, for the first time, identified landfalls of tropical cyclones (TCs) in Japan for the period from 1877 to 2019; this knowledge will help prepare for future TC disasters.
In recent years strong TCs have been making landfalls in Japan, such as Typhoon Jebi in 2018, which severely hit the Kinki region, and Typhoon Hagibis in 2019, which severely hit eastern Japan. While Japan has suffered from a number of TC impacts throughout its history, meteorological data for these events has been sparse.
The team, including Specially Appointed Associate Professor Hisayuki Kubota of the Faculty of ...
University students with special educational needs highlight the benefits of e-assessment
2021-03-03
While the digitization process offers an extensive list of opportunities, it also presents a number of challenges for higher education institutions, a primary one of which is learner authentication in online education. More and more higher education establishments are making use of digital learning environments (DLE), and electronic assessment systems are now an increasingly important element in the digital age, both for academic institutions and for students, including those with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND).
David Bañeres is a researcher with the IN3 SOM Research Lab group and professor at the Faculty ...
More extreme short-duration thunderstorms likely in the future due to global warming
2021-03-03
Climate experts have revealed that rising temperatures will intensify future rainfall extremes at a much greater rate than average rainfall, with largest increases to short thunderstorms.
New research by Newcastle University has shown that warming temperatures in some regions of the UK are the main drivers of increases in extreme short-duration rainfall intensities, which tend to occur in summer and cause dangerous flash flooding.
These intensities are increasing at significantly higher rates than for winter storms. A study, led by Professor Hayley Fowler, of Newcastle University's School of Engineering, highlights the urgent need for climate change adaptation measures as heavier short-term rainfall increases ...
Researchers realize the ice inhibition for cryopreservation
2021-03-03
As is sensed in our daily life, jiaozi frozen in domestic refrigerator tastes less delicious than an instant frozen one sold in the supermarket. The formation of the ice crystal is to blame. In scientific researches ranging from aerospace to biology and medicine, the formation, growth and elimination of the ice crystal are of significant importance.
By far, slow freezing and vitrification are generally adopted for cryopreservation. The former method, assembling freezing jiaozi with domestic refrigerator, is accompanied by mass formation of ice crystal which inevitably does irreversible damage to the cell. Vitrification effectively avoids former problems but requires either extremely rapid freezing rate which is too hard to achieve or high ...
Researchers discover SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
2021-03-03
A research team of pharmacists at the University of Bonn has discovered two families of active substances that can block the replication of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. The drug candidates are able to switch off the the key enzyme of the virus, the so-called main protease. The study is based on laboratory experiments. Extensive clinical trials are still required for their further development as therapeutic drugs. The results have now been published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
In order for the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus to replicate, it relies on the main protease as a key enzyme. The virus ...
Attending consecutive mammography screens protects against breast cancer death
2021-03-03
For women who had participated in both of their previous two screening examinations, the incidence of breast cancers proving fatal within 10 years of diagnosis was 50 per cent lower than in women who did not attend either of the last two screening examinations. Compared with women who attended only one of the two previous screens, women who attended both had a significant 22-33 per cent reduction in breast cancer mortality.
Lead author, Professor Stephen Duffy of Queen Mary University of London, said: "While there is ample evidence that breast cancer mortality is reduced in those who attend screening, these results demonstrate that repeated attendance ...
USTC detects a sharp rise in detection rate of broad absorption line variations
2021-03-03
Gas around black holes and interstellar medium distribution are key factors in understanding the growth of supermassive black holes and the evolution of their host galaxies. However, as a crucial parameter, gas density is hard to be determined reliably, because the general method is not applicable to all quasars.
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) for the first time detected a "sharp rise" signature in the detection rate of broad absorption line (BAL) variations, which in turn deduced ionized gas density. The work was published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters on January 11, 2021.
The ionization state of a gaseous outflow requires a ...
Diagnosis of genetic condition could help patients stop smoking and prevent lung disease
2021-03-03
New research shows that people diagnosed with a genetic condition, called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), are far more likely to stop smoking and therefore prevent the development of lung disease.
The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Science, is published in COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
It is estimated that 265,000 people on the island of Ireland are affected by either severe or moderate AATD, but the vast majority of people with AATD have not been diagnosed.
Previously, it was assumed that only people with severe AATD were at risk of lung disease. Recent Irish research has shown that people with the far more common moderate form ...
Chemists develop a new technology to prevent lithium-ion batteries from catching fire
2021-03-03
Lithium-ion battery fire hazards are extensive worldwide and such failure can have a severe implication for both smartphones and electric cars, says the head of the group and Professor in the Department of Electrochemistry at St Petersburg University Oleg Levin. 'From 2012 to 2018, 25,000 cases of catching fire by a wide range of devices in the USA only were reported. Earlier, from 1999 to 2012, only 1,013 cases were reported. The number of fire incidents is increasing as is the number of the batteries being used,' he said.
Among the main reasons why lithium ion batteries catch fire or explode are overcharging, short circuit, and others. As a result, the battery is overheated and the battery ...
Drug found effective for weight loss in patients with obesity and diabetes, international study show
2021-03-03
Semaglutide, an injectable medication taken once a week, offers a nonsurgical way to reduce weight and treat obesity. It could help the more than 70 million adults in the United States who struggle with this chronic condition, says Ildiko Lingvay, M.D., M.P.H., M.S.C.S., professor of internal medicine and population and data sciences at UTSW and lead author of the study, published today in The Lancet.
People with diabetes benefit greatly from weight loss, yet they have a much harder time losing weight compared with those without diabetes, Lingvay says. This ...
Key steps discovered in production of critical immune cell
2021-03-03
WEHI researchers have uncovered a process cells use to fight off infection and cancer that could pave the way for precision cancer immunotherapy treatment.
Through gaining a better understanding of how this process works, researchers hope to be able to determine a way of tailoring immunotherapy to better fight cancer.
Led by Dr Dawn Lin and Dr Shalin Naik and published in Nature Cell Biology, the research provides new insight into the way cells adapt to fight infection.
This research lays the foundation for future studies into the body's response to environmental stressors, such as injury, infection or cancer, at a single cell level.
At a glance
WEHI researchers have studied dendritic ...
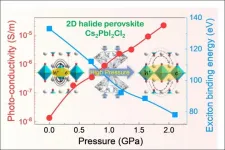
Pressure-regulated excitonic feature enhances photocurrent of all-inorganic 2D perovskite
2021-03-03
HPSTAR scientists Dr. Songhao Guo and Dr. Xujie Lü report three orders of magnitude increase in the photoconductivity of Cs2PbI2Cl2 from its initial value, at the industrially achievable level of 2 GPa, using pressure regulation. Impressively, pressure regulating the 2D perovskite's excitonic features gains it 3D compound characteristics without diminishing its own advantages, making it a more promising material for photovoltaic and photodetector applications. Their study is published as a Cover article in the latest issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Two-dimensional (2D) halide perovskites have recently emerged for photovoltaic and optoelectronic ...
Forecast: the impacts of vaccines and variants on the U.S. COVID trajectory
2021-03-03
In a report summary released today Thomas McAndrew, a computational scientist and assistant professor at Lehigh University's College of Health includes probabilistic forecasts of the impact of vaccines and variants on the U.S. COVID trajectory over the next few weeks. The goal of the report, says McAndrew, is "to support public health officials, infectious disease modeling groups, and the general public"
Report highlights:
A consensus of 91 forecasters predicts that the B.1.1.7. variant will be found in 42% of all genetic sequences with an S-gene mutation in the first two weeks of March and in 72% in all sequences between ...
First detailed insight into newborn babies' lungs at birth
2021-03-03
Researchers have captured the first detailed images of newborn babies' lungs as they take their first breaths.
The research, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, provides a breakthrough in understanding the events around a baby's first breath, why healthy babies cry at birth and provides clues to improving preterm babies' survival chances and long term health outcomes.
About 10 per cent of newborns, and almost all preterm infants, need resuscitation because their lungs do not properly fill with air at birth (a process called lung aeration). Despite ...
UBC study finds high life satisfaction linked to better overall health
2021-03-03
New research from UBC finds that higher life satisfaction is associated with better physical, psychological and behavioural health.
The research, published recently in The Milbank Quarterly, found that higher life satisfaction is linked to 21 positive health and well-being outcomes including:
a 26 per cent reduced risk of mortality
a 46 per cent reduced risk of depression
a 25 per cent reduced risk of physical functioning limitations
a 12 per cent reduced risk of chronic pain
a 14 per cent reduced risk of sleep problem onset
an eight per cent higher likelihood of frequent physical activity
better psychological well-being on ...
Researchers introduce a new generation of tiny, agile drones
2021-03-03
If you've ever swatted a mosquito away from your face, only to have it return again (and again and again), you know that insects can be remarkably acrobatic and resilient in flight. Those traits help them navigate the aerial world, with all of its wind gusts, obstacles, and general uncertainty. Such traits are also hard to build into flying robots, but MIT Assistant Professor Kevin Yufeng Chen has built a system that approaches insects' agility.
Chen, a member of the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and the Research Laboratory of Electronics, has developed insect-sized drones with unprecedented dexterity and resilience. The aerial robots ...
Green tea supplements modulate facial development of children with Down syndrome
2021-03-03
Green tea supplements modulate facial development of children with Down syndrome
A new study led by Belgian and Spanish researchers published in Scientific Reports adds evidence about the potential benefits of green tea extracts in Down syndrome. The researchers observed that the intake of green tea extracts can reduce facial dysmorphology in children with Down syndrome when taken during the first three years of life. Additional experimental research in mice confirmed the positive effects at low doses. However, they also found that high doses of the extract can disrupt facial and bone development. More research is needed to fully understand the effects of green tea extracts and therefore they should ...
Helping soft robots turn rigid on demand
2021-03-03
Imagine a robot.
Perhaps you've just conjured a machine with a rigid, metallic exterior. While robots armored with hard exoskeletons are common, they're not always ideal. Soft-bodied robots, inspired by fish or other squishy creatures, might better adapt to changing environments and work more safely with people.
Roboticists generally have to decide whether to design a hard- or soft-bodied robot for a particular task. But that tradeoff may no longer be necessary.
Working with computer simulations, MIT researchers have developed a concept for a soft-bodied robot that can turn rigid on demand. The approach could enable a new generation of robots that combine the strength and precision of rigid robots with the fluidity and safety of ...
Climate models may significantly overestimate savings from improved energy efficiency
2021-03-03
The models used to produce global climate scenarios may overestimate the energy and emission savings from improved energy efficiency, warns new research led by academics at the University of Sussex Business School and the University of Leeds.
In a review of 33 studies, the researchers find that economy wide rebound effects may erode around half of the energy and emission savings from improved energy efficiency.
These rebound effects result from individuals and businesses responding to the benefits of improved energy efficiency - such as cheaper heating, lighting and travel. These responses improve quality-of-life, raise productivity and boost industrial competitiveness, ...
How to choose low glycaemic index (GI) foods? A GI "glossary" of Asian foods released
2021-03-03
Professor Christiani Jeyakumar Henry, Senior Advisor of Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation (SIFBI), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) and his team have developed a Glycaemic Index (GI) glossary of non-Western foods. The research paper (attached PDF) was published in Nutrition & Diabetes on 6 Jan 2021: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-020-00145-w.
Observational studies have shown that the consumption of low glycaemic index (GI) foods is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), significantly less insulin resistance and a lower prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. ...
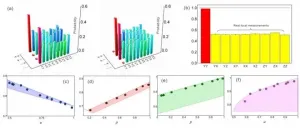
Researchers investigate imaginary part in quantum resource theory
2021-03-03
Recently, research team led by academician GUO Guangcan from CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information of the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of CAS, has made an important progress in quantum information theory. Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Prof. XIANG Guoyong from the team, cooperated with Dr. Strelstov from University of Warsaw, investigated the imaginary part of quantum theory as a resource, and several important results have been obtained. Relevant results are now jointly published as Editors' Suggestion in Physical Review Letters and Physical Review A.
Complex number is a mathematical ...
[1] ... [2573]
[2574]
[2575]
[2576]
[2577]
[2578]
[2579]
[2580]
2581
[2582]
[2583]
[2584]
[2585]
[2586]
[2587]
[2588]
[2589]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.