Controlling adhesions in the abdomen
2021-03-05
Scars inside the abdomen, known as adhesions, form after inflammation or surgery. They can cause chronic pain and digestive problems, lead to infertility in women, or even have potentially life-threatening consequences such as intestinal obstruction. If adhesions develop, they must be operated on again. They also make subsequent surgical interventions more difficult. This leads to substantial suffering for those affected and is also a significant financial burden for the healthcare system. In the USA alone, adhesions in the abdomen result in healthcare costs of 2.3 billion dollars per year.
Knowledge ...
Sports information on social networks leaves out women, disabled and minority disciplines
2021-03-05
Researchers from the University of Seville and Pompeu Fabra University argue that sports information on social media is dominated by men and football. This leaves out women's sports, sports featuring athletes with disabilities and minority disciplines, thus repeating the reality of the traditional media. That is the main conclusion of a study analysing more than 7,000 tweets published by the profiles of four public media in four European countries.
The study analysed the posts by the Twitter profiles providing sports news of the public broadcasters of Spain (RTVE), France (France TV), Ireland (RTÉ) and Italy (RAI). Between 30% and 58% of the tweets by these media related to football. However, differences were observed ...
What can stream quality tell us about quality of life?
2021-03-05
As the source of most of the water we drink and a place where we often go to recreate and enjoy nature, streams represent a crucial point-of-contact between human beings and the environment.
Now researchers in the College of Natural Resources and Environment and the Department of Biological Systems Engineering are using stream quality data to find new insights into the interactions between the health of our natural spaces and human well-being.
Their findings, published in the journal Ecological Indicators, reveal that demographics such as race and population density, as well as health indices such as cancer rates and food insecurity, show strong correlations with water quality across the Commonwealth of Virginia.
"We started off wanting to explore the general, intuitive ...
New method facilitates development of antibody-based drugs
2021-03-05
In recent years, therapeutic antibodies have transformed the treatment of cancer and autoimmune diseases. Now, researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed a new, efficient method based on the genetic scissors CRISPR-Cas9, that facilitates antibody development. The discovery is published in Nature Communications.
Antibody drugs are the fastest growing class of drug, and several therapeutic antibodies are used to treat cancer. They are effective, often have few side effects and benefit from the body's own immune system by identifying foreign substances in the body. ...
Life's rich pattern: Researchers use sound to shape the future of printing
2021-03-05
Researchers in the UK have developed a way to coax microscopic particles and droplets into precise patterns by harnessing the power of sound in air. The implications for printing, especially in the fields of medicine and electronics, are far-reaching.
The scientists from the Universities of Bath and Bristol have shown that it's possible to create precise, pre-determined patterns on surfaces from aerosol droplets or particles, using computer-controlled ultrasound. A paper describing the entirely new technique, called 'sonolithography', is published in Advanced Materials Technologies.
Professor Mike Fraser from the Department of Computer Science at the University of Bath, explained: "The power of ultrasound has already been shown to levitate small ...
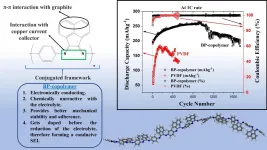
Built to last: New copolymer binder to extend the life of lithium ion batteries
2021-03-05
Anyone who has owned a smartphone for over a year is most likely aware that its built-in lithium (Li)-ion battery does not hold as much charge as when the device was new. The degradation of Li-ion batteries is a serious issue that greatly limits the useful life of portable electronic devices, indirectly causing huge amounts of pollution and economic losses. In addition to this, the fact that Li-ion batteries are not very durable is a massive roadblock for the market of electric vehicles and renewable energy harvesting. Considering the severity of these issues, it is no surprise that researchers have been actively ...
When peeking at your brain may help with mental illness
2021-03-05
In recent years, researchers have begun using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) not just for better understanding the neural bases of psychiatric illness, but also for experimental treatment of depression, ADHD, anxiety, PTSD, substance use disorder, and schizophrenia with a technique called real-time fMRI neurofeedback.
While rtfMRI-NF has emerged in recent years as a promising experimental intervention, it's also a costly procedure that requires extensive technical setup to allow for real-time analysis. That's why a quantitative data review was overdue.
A team of END ...
Improved tool to help understand the brain, one section at a time
2021-03-05
In the brain, billions of neurons reach to each other, exchanging information, storing memories, reacting to danger and more. Scientists have barely scratched the surface of the most complex organ, but a new device to automatically collect tissue for analysis may allow for a quicker, deeper dive into the brain.
Their approach was published in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, a joint publication of the IEEE and the Chinese Association of Automation.
"The ultimate goal of this study is to further promote the speed and quality of 3D-reconstruction of brain neural connections," said the author Long ...
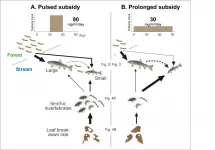
'Falling insect' season length impacts river ecosystems
2021-03-05
Insects that fall from the surrounding forest provide seasonal food for fish in streams. Researchers at Kobe University and The University of Tokyo have shown that the lengthening of this period has a profound effect on food webs and ecosystem functions present in streams.
These research results provide proof that changes in forest seasonality also affect the ecosystems of nearby rivers. This finding highlights the importance of predicting the effects of climate change on ecosystems.
The research group consisted of Associate Professor SATO Takuya and post-graduate student UEDA Rui of Kobe University's Graduate ...
Study shows combined liver-cytokine humanization rescues circulating red blood cells
2021-03-05
In a new study by the Yale Department of Immunobiology and Yale Cancer Center, researchers report combined liver and growth factor humanization enhances human red blood cell production and survival in circulation the immunodeficient murine host. The discovery could help in the development of treatments of life-threatening blood disorders, such as myelodysplastic syndrome, and diseases afflicting red blood cells, including sickle cell disease and malaria. The study is published online today in the journal Science.
"Red blood cell diseases, such as thalassemia and sickle cell disease involve approximately 5% of ...
Speeding up commercialization of electric vehicles
2021-03-05
Professor Byoungwoo Kang develops a high-density cathode material through controlling local structures of the Li-rich layered materials.
Researchers in Korea have developed a high-capacity cathode material that can be stably charged and discharged for hundreds of cycles without using the expensive cobalt (Co) metal. The day is fast approaching when electric vehicles can drive long distances with Li- ion batteries.
Professor Byoungwoo Kang and Dr. Junghwa Lee of POSTECH's Department of Materials Science and Engineering have successfully developed a high energy-density cathode material that can stably maintain charge and discharge for over 500 cycles without the expensive ...
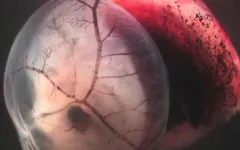
HSC transplants in embryos: Opening the door for hematopoiesis research
2021-03-05
Most people have heard of stem cells, cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the architects of blood cell development and are responsible for blood cell formation throughout the life of an organism. HSCs are also used in the treatment of cancer and immune disturbances.
Previous research into HSC transplantation has involved the use of adult and fetal mice. This has involved the removal of recipient HSCs using approaches including irradiation and the administration of DNA damaging drugs. In a first of its kind, researchers from the University of Tsukuba devised a novel approach for HSC deletion in mouse embryos. This report provides the first description of embryonic HSC depletion and transplantation of donor HSCs ...
The negative effects of powerful political connections
2021-03-05
SMU Office of Research and Tech Transfer - One of the motivations for the recently published Journal of Accounting Research paper "Politically Connected Governments" was the daily experience with the subway system in New York City.
The author of the paper, SMU Assistant Professor of Accounting Kim Jungbae, told the Office of Research & Tech Transferthe research question for the paper which examines the consequences of powerful political connections for local governments, was inspired by the New York Times article "The Most Expensive Mile of Subway Track on Earth" (January 24, 2018).
"The article suggests that the NYC subway system is ...
When more Covid-19 data doesn't equal more understanding
2021-03-05
Since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, charts and graphs have helped communicate information about infection rates, deaths, and vaccinations. In some cases, such visualizations can encourage behaviors that reduce virus transmission, like wearing a mask. Indeed, the pandemic has been hailed as the breakthrough moment for data visualization.
But new findings suggest a more complex picture. A study from MIT shows how coronavirus skeptics have marshalled data visualizations online to argue against public health orthodoxy about the benefits of mask mandates. Such "counter-visualizations" are often quite sophisticated, using datasets from official sources and state-of-the-art visualization ...
Bringing AI into the real world
2021-03-05
SMU Office of Research & Tech Transfer - Even before countries began rolling out their vaccination campaigns, Pfizer, Moderna and AstraZeneca's announcements had already proved fortifying shots. Stocks rallied and healthcare workers celebrated in the wake of the vaccine news late last year. But months on, that early euphoria has somewhat evaporated, replaced by uncertainty and debate over vaccine safety, possible side effects and varying degrees of citizen reluctance.
Artificial intelligence (AI) researchers and health experts modelling COVID-19's spread ...
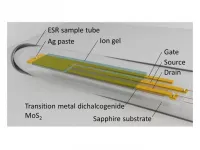
Taking 2D materials for a spin
2021-03-05
Tsukuba, Japan and Warsaw, Poland - Scientists from the University of Tsukuba and a scientist from the Institute of High Pressure Physics detected and mapped the electronic spins moving in a working transistor made of molybdenum disulfide. This research may lead to much faster computers that take advantage of the natural magnetism of electrons, as opposed to just their charge.
Spintronics is a new area of condensed matter physics that attempts to use the intrinsic magnetic moment of electrons, called "spins," to perform calculations. This would be a major advance ...
Key task in computer vision and graphics gets a boost
2021-03-05
Kanazawa, Japan - Non-rigid point set registration is the process of finding a spatial transformation that aligns two shapes represented as a set of data points. It has extensive applications in areas such as autonomous driving, medical imaging, and robotic manipulation. Now, a method has been developed to speed up this procedure.
In a study published in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, a researcher from Kanazawa University has demonstrated a technique that reduces the computing time for non-rigid point set registration relative to other approaches.
Previous ...
New test enables rapid detection of mild cognitive impairment as well as dementia
2021-03-05
Kanazawa, Japan - As the global population ages, the rate of dementia is increasing worldwide. Given that early detection is critical for treatment, effective ways to screen for dementia are a high research priority. Now, researchers from Japan have developed a new screening tool that can be administered in a matter of minutes.
In a study published in PLOS ONE, researchers from Kanazawa University have revealed a new computerized cognitive test, termed the computerized assessment battery for cognition (C-ABC), which they found to be effective in screening for both dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in just 5 minutes.
Computerized cognitive tests are frequently chosen over paper-and-pencil ...
How heavy snow reduces road injuries: less bicycling, safer transport
2021-03-05
Tsukuba, Japan - Heavy snowfall slows things down and makes it harder to get from point A to point B. But snow clouds have a silver lining--heavy snow may prevent serious road injuries and even save lives. How? By getting people off bicycles and switching to safer modes of transport.
Japanese researchers examined 10 years of police data on road injuries among commuting junior high school students. They found that areas with monthly snowfall of at least 100 cm had almost no bicycling-related injuries. Total injuries among cyclists and pedestrians also fell by 68%. The findings were published in the Journal of Epidemiology.
The logic is quite simple. ...
Texas A&M study finds no link between gender and physics course performance
2021-03-05
A new data-driven study from Texas A&M University casts serious doubt on the stereotype that male students perform better than female students in science -- specifically, physics.
A team of researchers in the Department of Physics and Astronomy analyzed both the midterm exam scores and final grades of more than 10,000 Texas A&M students enrolled in four introductory physics courses across more than a decade, finding no evidence that male students consistently outperform female students in these courses.
The work was led by Texas A&M physicist ...
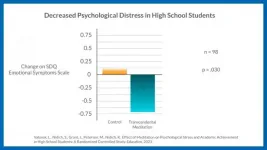
New study shows Transcendental Meditation reduces teacher burnout and improves resilience
2021-03-05
Teachers who participated in a meditation-based teacher development program utilizing the Transcendental Meditation (TM) technique for four months, had significant improvements in emotional exhaustion (the leading factor in burnout), resilience, perceived stress, fatigue, and depression according to a new randomized controlled trial published today in Frontiers in Education.
"Teachers are under high levels of stress as they are asked every day to support their students' learning amidst numerous challenges," said Laurent Valosek, lead author of the study and executive director of the Center for Wellness and Achievement in Education. "This study demonstrates the benefits ...
Decreases in exercise closely linked with higher rates of depression during the pandemic
2021-03-05
Exercise has long-been recommended as a cognitive-behavioral therapy for patients of depression, yet new evidence from the University of California of San Diego suggests that the COVID-19 pandemic changed the nature of the relationship between physical activity and mental health.
In a study of college students conducted before and during the pandemic, findings revealed the average steps of subjects declined from 10,000 to 4,600 steps per day and rates of depression increased from 32% to 61%.
The research, recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, also revealed short-term restoration of exercise does not meaningfully ...
SRL focus section explores U.S. Intermountain West earthquakes in 2020
2021-03-05
During the first half of 2020, the U.S. Intermountain West region of the United States experienced four significant earthquake sequences, spanning multiple states. In the new issue of SRL, 15 papers characterize these major earthquakes and discuss how they are helping seismologists gain new insights into the tectonics of the region.
The Intermountain West is bounded by the eastern margin of the Sierra Nevada and Cascade Mountains to the west and the Rocky Mountains to the east. While its earthquake risk is often overlooked in comparison to those in California and the Pacific Northwest, the region ...
Pandemic ratchets up pressure on people with substance use disorder
2021-03-05
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound effect across society, but it has been especially devastating for people with substance use disorder.
A new study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, sheds light on the experience of patients with substance use disorder who were hospitalized during the initial surge of COVID-19 cases in Oregon last spring. Researchers with Oregon Health & Science University conclude that health systems nationwide could benefit from a better understanding of people who struggle with the basics.
"We need the system to be designed and implemented for patients who may lack phone access, who may not have access to WiFi or may be living on the streets," said lead ...
Food security: Irradiation and essential oil vapors for cereal treatment
2021-03-05
A combined treatment of irradiation and essential oil vapors could effectively destroy insects, bacteria and mold in stored grains. A team from the END ...
[1] ... [2568]
[2569]
[2570]
[2571]
[2572]
[2573]
[2574]
[2575]
2576
[2577]
[2578]
[2579]
[2580]
[2581]
[2582]
[2583]
[2584]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.