Retinal implants can give artificial vision to the blind
2021-03-05
Being able to make blind people see again sounds like the stuff of miracles or even science fiction. And it has always been one of the biggest challenges for scientists. Diego Ghezzi, who holds the Medtronic Chair in Neuroengineering (LNE) at EPFL's School of Engineering, has made this issue a research focus. Since 2015, he and his team have been developing a retinal implant that works with camera-equipped smart glasses and a microcomputer. "Our system is designed to give blind people a form of artificial vision by using electrodes to stimulate their retinal cells," says Ghezzi.
Read more: https://actu.epfl.ch/news/a-retinal-implant-that-is-more-effective-against-b/
Star-spangled sky
The camera embedded in the smart glasses captures images in the wearer's field of vision, and ...
Tracking proteins in the heart of cells
2021-03-05
In order to stay alive, the cell must provide its various organelles with all the energy elements they need, which are formed in the Golgi apparatus, its centre of maturation and redistribution of lipids and proteins. But how do the proteins that carry these cargoes - the kinesins - find their way and direction within the cell's "road network" to deliver them at the right place? Chemists and biochemists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, have discovered a fluorescent chemical dye, making it possible for the first time to track the transport ...
Antarctic seals reveal worrying threats to disappearing glaciers
2021-03-05
More Antarctic meltwater is surfacing than was previously known, modifying the climate, preventing sea ice from forming and boosting marine productivity- according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA).
For the first time, researchers have been able to obtain full-depth glacial meltwater observations in winter, using instruments attached to the heads of seals living near the Pine Island Glacier, in the remote Amundsen Sea in the west of Antarctica.
The harsh environmental conditions in the Antarctic limit the use of most traditional observation systems, such as ships and airplanes, especially ...
Fine particulate matter from wildfire smoke more harmful than pollution from other sources
2021-03-05
Researchers at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego examining 14 years of hospital admissions data conclude that the fine particles in wildfire smoke can be several times more harmful to human respiratory health than particulate matter from other sources such as car exhaust. While this distinction has been previously identified in laboratory experiments, the new study confirms it at the population level.
This new research work, focused on Southern California, reveals the risks of tiny airborne particles with diameters of up to 2.5 microns, about one-twentieth that of a human hair. These particles - termed PM2.5 - are the ...
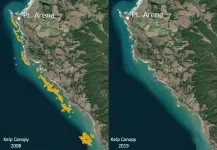
The collapse of Northern California kelp forests will be hard to reverse
2021-03-05
Satellite imagery shows that the area covered by kelp forests off the coast of Northern California has dropped by more than 95 percent, with just a few small, isolated patches of bull kelp remaining. Species-rich kelp forests have been replaced by "urchin barrens," where purple sea urchins cover a seafloor devoid of kelp and other algae.
A new study led by researchers at UC Santa Cruz documents this dramatic shift in the coastal ecosystem and analyzes the events that caused it. This was not a gradual decline, but an abrupt collapse of the kelp forest ecosystem in the aftermath of unusual ocean warming along the West Coast starting in 2014, part of a series of events that combined to decimate the kelp forests.
Published March 5 in Communications Biology, ...
New Corona test developed
2021-03-05
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) is the most widely used diagnostic method to detect RNA viruses such as SARS-CoV-2. However, it requires expensive laboratory equipment and global shortages of reagents for RNA purification has increased the need to find simple but reliable alternatives. One alternative to the qPCR technology is RT-LAMP (reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification). This test amplifies the desired target sequences of the virus at a constant temperature, using minimal equipment compared to qPCR. In 2020, it was adapted to the detection of SARS-CoV-2. It was also shown that instead of a swab, which many people find unpleasant, it can be performed on gargle lavage samples.
First author Lukas Bokelmann and colleagues have now ...
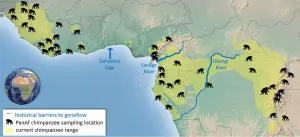
Chimpanzees without borders
2021-03-05
Researchers from the Pan African Programme: The Cultured Chimpanzee (PanAf) at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (MPI-EVA) and a team of international researchers, collected over 5000 fecal samples from 55 sites in 18 countries across the chimpanzee range over 8 years. This is by far the most complete sampling of the species to date, with a known location of origin for every sample, thus addressing the sampling limitations of previous studies. "Collecting these samples was often a daunting task for our amazing field teams. The chimpanzees were almost all unhabituated to human presence, so it took a lot of patience, skill and luck to find chimpanzee dung at each of the sites," explains ...
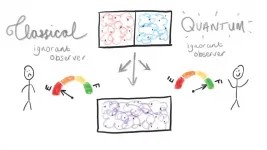
New quantum theory heats up thermodynamic research
2021-03-05
Researchers have developed a new quantum version of a 150-year-old thermodynamical thought experiment that could pave the way for the development of quantum heat engines.
Mathematicians from the University of Nottingham have applied new quantum theory to the Gibbs paradox and demonstrated a fundamental difference in the roles of information and control between classical and quantum thermodynamics. Their research has been published today in Nature Communications.
The classical Gibbs paradox led to crucial insights for the development of early thermodynamics and emphasises the need to consider an experimenter's ...
RCSI researchers discover new way to halt excessive inflammation
2021-03-05
DUBLIN, Friday, 5 March 2021: RCSI researchers have discovered a new way to 'put the brakes' on excessive inflammation by regulating a type of white blood cell that is critical for our immune system.
The discovery has the potential to protect the body from unchecked damage caused by inflammatory diseases.
The paper, led by researchers at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is published in Nature Communications.
When immune cells (white blood cells) in our body called macrophages are exposed to potent infectious agents, powerful inflammatory proteins ...
Overweight children exposed to lead in utero may have poor future kidney function
2021-03-05
New York, NY (March 5, 2021) - Overweight children who were exposed to lead in utero and during their first weeks of life have the potential for poorer kidney function in adulthood, according to an Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai study published in Environment International in March.
The study found that children with high body mass indexes who had been exposed to lead had lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), a measure of how well the kidneys are filtering or cleaning the blood. The researchers measured blood levels during mothers' pregnancy and later measured eGFR levels in the children when they were between 8 and 12 years old.
Decreased ...
Beauty is in the brain: AI reads brain data, generates personally attractive images
2021-03-05
Researchers have succeeded in making an AI understand our subjective notions of what makes faces attractive. The device demonstrated this knowledge by its ability to create new portraits on its own that were tailored to be found personally attractive to individuals. The results can be utilised, for example, in modelling preferences and decision-making as well as potentially identifying unconscious attitudes.
Researchers at the University of Helsinki and University of Copenhagen investigated whether a computer would be able to identify the facial features we consider attractive and, based on this, create new images matching our criteria. The researchers used artificial intelligence to interpret brain signals and combined the resulting brain-computer interface with a ...
Variable compensation and salesperson health
2021-03-05
Researchers from University of Houston and University of Bochum published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how variable compensation plans for salespeople can lead to lower health.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Variable Compensation and Salesperson Health" and is authored by Johannes Habel, Sascha Alavi, and Kim Linsenmayer.
Sales compensation plans typically comprise a variable component. Variable compensation is issued on top of a base salary and the amount is contingent on performance. For example, a salesperson with an annual target salary ...
Study shows that regular physical activity is an effective strategy to prevent
2021-03-05
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [EASD]) shows that regular physical activity is a safe diabetes prevention strategy for people residing in relatively polluted regions.
The study, which is the first to investigate the combined effects of physical activity and pollution exposure on type 2 diabetes risk, is by Dr Cui Guo and Professor Lao Xiang Qian, Faculty of Medicine at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China, and Dr Hsiao Ting Yang, Institute for Risk Assessment Sciences, Utrecht University, Utrecht, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
An increasing body of evidence has shown that air pollution ...
Culturally tailored intervention boosts safe sex, reduces drinking among young Black women
2021-03-04
A series of weekend workshops that integrate strategies for both reducing risky alcohol use and preventing sexually transmitted infections (STIs) led to an increase in safe sex and decrease in drinking among young Black women, according to a new study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
"By designing an intervention that didn't treat sex and alcohol use as two separate risk factors, young women were empowered to make healthier decisions and better communicate with their partners," said Ralph DiClemente, professor and chair of the Department of Social and Behavioral Sciences at NYU School of Global Public Health and the study's lead author.
"This groundbreaking study illustrates ...
Twistoptics--A new way to control optical nonlinearity
2021-03-04
Columbia researchers engineer first technique to exploit the tunable symmetry of 2D materials for nonlinear optical applications, including laser, optical spectroscopy, imaging, and metrology systems, as well as next-generation optical quantum information processing and computing.
New York, NY--March 4, 2021--Nonlinear optics, a study of how light interacts with matter, is critical to many photonic applications, from the green laser pointers we're all familiar with to intense broadband (white) light sources for quantum photonics that enable optical quantum computing, super-resolution imaging, optical sensing and ranging, and more. Through nonlinear optics, researchers are discovering new ways to use light, from getting a closer look at ultrafast processes in physics, ...
An unstable working life affects the future mental health of young people
2021-03-04
A new study reveals that a precarious, unstable initiation by young people to working life is associated with poorer future mental health. The study was conducted by researchers from the Center for Research in Occupational Health (CISAL, a joint group of UPF and the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute) in Barcelona, Spain. Amaya Ayala-Garcia, Laura Serra and Mònica Ubalde-López are the authors of the study, which has been published in the journal BMJ Open.
Since the 1990s, Spain has been among the European countries with the lowest employment rates, which are accentuated in the young active population. Moreover, in 2017, Spain ...
COVID-19 lockdown linked to uptick in tobacco use
2021-03-04
March 4, 2021 -- Pandemic-related anxiety, boredom, and irregular routines were cited as major drivers of increased nicotine and tobacco use during the initial COVID-19 "lockdown," according to research just released by Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health. The study highlights ways that public health interventions and policies can better support quit attempts and harm reduction, both during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond. The findings are published in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
Between April-May 2020, the researchers conducted ...
Team of bioethicists and scientists suggests revisiting 14-day limit on human embryo
2021-03-04
CLEVELAND (March 5, 2021)--An international team of bioethicists and scientists, led by a researcher at Case Western Reserve University, contends it may be justified to go beyond the standing 14-day limit that restricts how long researchers can study human embryos in a dish. Going beyond this policy limit could lead to potential health and fertility benefits, and the authors provide a process for doing so.
In an article published March 5 in Science, Insoo Hyun, a bioethics professor at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and the paper's lead author, and colleagues urge policymakers and the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) to consider "a cautious, stepwise approach" to scientific exploration beyond the 14-day limit.
"But first," ...
Why we're so bad at daydreaming, and how to fix it
2021-03-04
Did you daydream as a kid, maybe even get in trouble for it? If you find it harder to be pleasantly lost in your thoughts these days, you're not alone.
"This is part of our cognitive toolkit that's underdeveloped, and it's kind of sad," said Erin Westgate, Ph.D., a University of Florida psychology professor.
The ability to think for pleasure is important, and you can get better at it, Westgate says. The first step is recognizing that while it might look easy, daydreaming is surprisingly demanding.
"You have to be the actor, director, screenwriter and audience of a mental performance," she said. "Even though it looks like you're doing nothing, it's cognitively ...
Latinos, Blacks less swayed by college-bound friends
2021-03-04
ITHACA, N.Y. - Close friends are important drivers of adolescent behavior, including college attendance, according to Steven Alvarado, assistant professor of sociology in the College of Arts and Sciences.
In new research published March 4 in American Educational Research Journal, Alvarado reports that having college-bound friends increases the likelihood that a student will enroll in college. However, the effect of having college-bound friends is diminished for Black and Latino students compared with white and Asian students, especially for males and especially for selective and highly selective colleges, due to structural ...
Can't solve a riddle? The answer might lie in knowing what doesn't work
2021-03-04
Ever get stuck trying to solve a puzzle?
You look for a pattern, or a rule, and you just can't spot it. So you back up and start over.
That's your brain recognizing that your current strategy isn't working, and that you need a new way to solve the problem, according to new research from the University of Washington. With the help of about 200 puzzle-takers, a computer model and functional MRI (fMRI) images, researchers have learned more about the processes of reasoning and decision-making, pinpointing the brain pathway that springs into action when problem-solving ...
Earth has a hot new neighbour -- and it's an astronomer's dream
2021-03-04
A newly discovered planet could be our best chance yet of studying rocky planet atmospheres outside the solar system, a new international study involving UNSW Sydney shows.
The planet, called Gliese 486b (pronounced Glee-seh), is a 'super-Earth': that is, a rocky planet bigger than Earth but smaller than ice giants like Neptune and Uranus. It orbits a red dwarf star around 26 light-years away, making it a close neighbour - galactically speaking.
With a piping-hot surface temperature of 430 degrees Celsius, Gliese 486b is too hot to support ...
A parental paradox for Black girls in the justice system
2021-03-04
COLUMBUS, Ohio - For Black girls in the juvenile justice system, attention from a caregiver might amount to too much of a bad thing, a recent study suggests.
Though parental attentiveness would generally be considered beneficial to troubled youths, the finding hints at the possibility that a history of trauma in a household's adults may filter down to younger generations, researchers say.
The study, examining how family and peer social support influenced post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms in Black girls who were in detention, found that lower self-esteem, less optimism about the future and higher negative behaviors by peers were associated with greater PTSD symptoms in these girls. But one more factor also correlated with those symptoms: a higher level of caregiver support.
"This ...
Moms need guidance on what to eat when their breastfeeding infant has a food allergy
2021-03-04
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, IL (March 4, 2021) - Many new mothers with infants want very much to breastfeed as it is the gold standard for early nutrition. What to do when you find out your young child has a food allergy, and you are breastfeeding? A new study in Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific journal of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), found that more than 28% of the women were given no guidance on whether they could eat the same food their breastfeeding child was allergic to.
"We found that guidance from healthcare practitioners for breastfeeding mothers in this situation ...
Field study shows icing can cost wind turbines up to 80% of power production
2021-03-04
AMES, Iowa - Wind turbine blades spinning through cold, wet conditions can collect ice nearly a foot thick on the yard-wide tips of their blades.
That disrupts blade aerodynamics. That disrupts the balance of the entire turbine. And that can disrupt energy production by up to 80 percent, according to a recently published field study led by Hui Hu, Iowa State University's Martin C. Jischke Professor in Aerospace Engineering and director of the university's Aircraft Icing Physics and Anti-/De-icing Technology Laboratory.
Hu has been doing laboratory studies of turbine-blade icing for about 10 years, including performing experiments ...
[1] ... [2569]
[2570]
[2571]
[2572]
[2573]
[2574]
[2575]
[2576]
2577
[2578]
[2579]
[2580]
[2581]
[2582]
[2583]
[2584]
[2585]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.