Convincing evidence that type 2 diabetes is associated with increased risk of Parkinson's
2021-03-08
Research from Queen Mary University of London has concluded that there is convincing evidence that type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of Parkinson's disease. The same study found that there was also evidence that type 2 diabetes may contribute to faster disease progression in patients who already have Parkinson's.
Treating people with drugs already available for type 2 diabetes may reduce the risk and slow the progression of Parkinson's. Screening for and early treatment of type 2 diabetes in patients with Parkinson's may be advisable.
Previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses have produced conflicting results around ...
Can the digital advertising market achieve privacy without regulation?
2021-03-08
Key Takeaways:
Machine learning offers more accurate targeting in mobile advertising.
Behavioral targeting is more effective than contextual targeting.
There is a possibility for self-regulation because too much behavioral targeting can reduce competition and hurt ad networks' revenues.
CATONSVILLE, MD, March 8, 2021 - It's a common assumption among marketers that if you can customize any form of marketing, particularly mobile advertising, you'll get better results. With this in mind, mobile marketing relies significantly on user tracking data ...
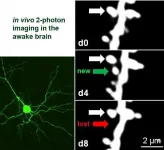
Watching the brain learn
2021-03-08
Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying brain "plasticity"(how the brain can learn, develop and reorganise itself) is crucial for explaining many illnesses and conditions. Neurocientists from the University of Göttingen and University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG) have now managed to repeatedly image synapses, the tiny contact sites between neurons, in awake adult mice. They are the first to discover that adult neurons in the primary visual cortex with an increased number of "silent synapses" (ie newly formed synapses that are inactivated), lacking a certain protein (PSD-95), display structural changes that were previously only reported in young mice. This ...
90% of young women report using a filter or editing their photos before posting
2021-03-08
Professor Rosalind Gill, from City, University of London's Gender and Sexualities Research Centre, has today published a new report to mark International Women's Day.
The report - Changing the Perfect Picture: Smartphones, Social Media and Appearance Pressures - is based on research with 175 young women and nonbinary people in the UK.
Covering a range of issues - experiences of lockdown, feelings about 'body positivity', how to show support for Black Lives Matter - the research documents young people's persistent anger with a mass media that they deem 'too white', 'too heterosexual' and too focused on very narrow definitions ...
Study identifies resilience factors to mitigate burnout in college students
2021-03-08
Mental health issues such as burnout and psychological distress are matters for concern among young adults, and are even more pertinent in today's uncertain global climate. A recent paper by Yale-NUS College alumna Ms Joanna Chue (Class of 2019) and Assistant Professor of Social Sciences (Psychology) Cheung Hoi Shan identified five components of resilience that are applicable in Singapore's cultural context, and demonstrated that college students possessing a higher degree of resilience were less susceptible to burnout and psychological distress. By identifying learnable components ...
Making artificial intelligence understandable -- Constructing explanation processes
2021-03-08
Researchers at Paderborn and Bielefeld University are hoping to change this, and are discussing how the explainability of artificial intelligence can be improved and adapted to the needs of human users. Their work has recently been published in the respected journal IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems. The researchers describe explanation as a social practice, in which both parties co-construct the process of understanding.
Explainability research
"Artificial systems have become complex. This is a serious problem - particularly when humans are held accountable for computer-based decisions," says Professor Philipp Cimiano, a computer scientist at Bielefeld University. Particularly in the ...
Predicting success in therapy with individualized cancer models
2021-03-08
In the EU alone, 78,800 men died of prostate cancer last year. While tumors discovered at an early stage can often be completely removed by surgery and radiation therapy, the prospects of successful treatment are reduced if the cancer has further metastasized. At present, physicians cannot predict drug response or therapy resistance in patients.
Three-dimensional structures
The team led by PD Dr. Marianna Kruithof-de Julio at the Urology Research Laboratory at the Department for BioMedical Research (DBMR) of the University of Bern and Inselspital Bern, has developed a new strategy for the generation of prostate cancer organoids that ...
'Island of Rats' recovers
2021-03-08
Along the western edge of Alaska's Aleutian archipelago, a group of islands that were inadvertently populated with rodents came to earn the ignominious label of the "Rat Islands." The non-native invaders were accidentally introduced to these islands, and others throughout the Aleutian chain, through shipwrecks dating back to the 1700s and World War II occupation. The resilient rodents, which are known to be among the most damaging invasive animals, adapted and thrived in the new setting and eventually overwhelmed the island ecosystems, disrupting the natural ecological order and driving out native species.
A coordinated conservation effort that removed the rats from one of the islands formerly known as Rat Island has become a new example of how ecosystems can ...
Tocilizumab cuts mortality risk in severely ill COVID-19 patients finds new trial conducted in India
2021-03-08
Tocilizumab, an anti-inflammatory drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, improves outcomes in severely ill COVID-19 patients, finds the results of a new trial conducted in hospitals across India -- one of the world's most ethnically diverse countries. Researchers from the University of Bristol and Medanta Institute of Education and Research in India who led the study, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, say it adds to existing evidence supporting the drug's use in critically ill patients.
Conducted in 12 public and private hospitals across India, the COVID ...
Retreat to win -- How to sustain an online campaign and survive trolling and abuse
2021-03-08
Trolling and extreme levels of abuse can kill an online campaign but momentum can be maintained, and the energy and morale of exhausted activists effectively restored, by tactical retreat and taking time out, new research into the landmark 'No More Page 3' campaign in the United Kingdom shows.
Dr. Sarah Glozer of the University of Bath School of Management and Dr. Lauren McCarthy of the Royal Holloway University of London School of Business and Management studied the 'No More Page 3' campaign, which from 2012 lobbied The Sun mass-circulation newspaper to stop publishing a photo of a topless woman on page 3, a daily feature launched in 1970. Page 3, the No More Page 3 campaign argued, was a symbol of institutionalised sexism. The Sun removed the Page 3 feature ...
Research shows we're surprisingly similar to Earth's first animals
2021-03-08
The earliest multicellular organisms may have lacked heads, legs, or arms, but pieces of them remain inside of us today, new research shows.
According to a UC Riverside study, 555-million-year-old oceanic creatures from the Ediacaran period share genes with today's animals, including humans.
"None of them had heads or skeletons. Many of them probably looked like three-dimensional bathmats on the sea floor, round discs that stuck up," said Mary Droser, a geology professor at UCR. "These animals are so weird and so different, it's difficult to assign them to modern categories of living organisms just by looking at them, and it's not like we can extract their DNA -- we can't."
However, well-preserved fossil records ...
Paw hygiene no reason to ban assistance dogs from hospitals
2021-03-08
Over 10,000 people in Europe use an assistance dog; think of guide dogs for people with a visual impairment, hearing dogs for people with a hearing impairment, medical response service dogs and psychiatric service dogs.
According to a UN-agreement and the Dutch law, these dogs are welcome in stores, hospitals and other public places. However, in practice, many assistance dog users and their dogs are regularly refused entry. In the Netherlands, four out of five assistance dog users indicate that they regularly experience problems with this.
Often, hygiene reasons are ...
Nanoenzymes designed with a unique combination of structure and functions
2021-03-08
Researchers at the UAB have designed minimalist biostructures that imitate natural enzymes, capable of carrying out two differentiated and reversibly regulated activities thanks to a unique combination of structural and functional properties. The strategy used opens the door to the creation of "intelligent" nanomaterials with tailor-made combinations of catalytic functions.
There is an increasing interest in synthetic systems that can execute bioinspired chemical reactions without requiring the complex structures that characterise enzymes in their components. One of the most explored approaches is the self-assembly of peptides - molecules smaller than proteins - due to their biocompatibility and how their structural and functional properties can be controlled.
Researchers from the ...
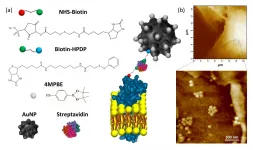
A biosensor for measuring extracellular hydrogen peroxide concentrations
2021-03-08
Several processes in the human body are regulated by biochemical reactions involving hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Although it can act as a 'secondary messenger', relaying or amplifying certain signals between cells, H2O2 is generally toxic because of its oxidant character. The latter means that it converts (oxidizes) biochemical molecules like proteins and DNA. The oxidizing property of H2O2 is of potential therapeutic relevance for cancer, though: deliberately causing tumor cells to increase their H2O2 concentration would be a way to destroy them. In light of this, but also for monitoring pathologies associated with H2O2 overproduction, it is crucial to have a means to reliably quantify hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the extracellular environment. Now, Leonardo Puppulin ...
COVID-19: Biomarkers linked to severe forms of the disease
2021-03-08
A team of researchers from the CHUM Research Centre has identified new biomarkers associated with the severity of COVID-19 in infected patients.
Recent scientific literature has shown that the immune response plays a central part in the severity of COVID-19 disease. Understanding the immune responses generated during the course of the disease is therefore essential to determine which patients are at highest risk for serious complications and death from the disease.
In a new study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, scientists and clinicians led by Dr.?Catherine Larochelle, researcher at the CHUM Research Centre, have ...
Hybrid microbes: Genome transfer between different bacteria strains explored
2021-03-08
Bacteria integrate genetic material from other bacterial strains more easily than previously thought, which can lead to improved fitness and accelerated evolution. This is shown in a recent study by biophysicists at the University of Cologne. The team analysed genome transfer between bacteria of different lineages. The study was published in the journal PNAS.
In the experiment, the team brought one strain of bacteria into contact with DNA fragments from another strain. The uptake of foreign genetic material is known as horizontal gene transfer -- in contrast to vertical gene transfer, by which genes are inherited from a parent cell of the same lineage. The results show that ...
Hospital-based violence intervention program engages vulnerable populations
2021-03-08
DES PLAINES, IL - A Boston violence intervention advocacy program is effectively engaging the client population that hospital-based violence intervention programs (HVIPs) have been designed to support. This is the conclusion of a study titled Boston Violence Intervention Advocacy Program: Challenges and Opportunities for Client Engagement and Goal Achievement, to be published in the March 2021 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
According to the study, HVIPs should consider which types of client needs prove most challenging to address and which novel strategies will engage vulnerable populations not typically targeted by intervention programs. ...
Unique sensor network for measuring greenhouse gases
2021-03-08
The sensor network MUCCnet (Munich Urban Carbon Column network) consists of five high-precision optical instruments that analyze the sun's light spectra. They measure the concentration of the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and carbon monoxide (CO). Since each gas has its own unique spectral "fingerprint", concentrations of these gases can be determined in the columns of air between the instruments and the sun.
"By measuring a vertical column of the atmosphere, local disturbances, such as the disproportionate influence of neighboring stacks, can be removed. Therefore, this type of greenhouse gas balancing is considered particularly robust and accurate," says Prof. Jia Chen.
Measurements at five locations in and around Munich
One of MUCCnet's measurement devices is ...
Study highlights barriers for women and marginalized groups in supramolecular chemistry
2021-03-08
A new study by the international network Women In Supramolecular Chemistry (WISC) has highlighted the equality, diversity and inclusion (EDI) issues faced by women and marginalised groups working within that field.
The network has also set out a 'calling in' approach to address these issues.
The study, led by Dr Jennifer Leigh and Dr Jennifer Hiscock (both University of Kent) alongside WISC's wider team of international researchers, found that both men and women in the supramolecular community wanted to see more mentoring opportunities and more visibility for women and marginalised groups. There is a desire for more guidance during the transition from postdoctoral researcher to independent Principal Investigator, to ensure women can be retained ...
No more sitting in the dark?
2021-03-08
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) - Concussion, a form of traumatic brain injury, is a common injury among children and teens. Concussions can have adverse effects on physical, cognitive, emotional and sleep health. Clinical guidelines for managing concussion in children and teens traditionally recommend complete physical and cognitive rest until symptom resolution, followed by a gradual return to activities like school and sports. These guidelines are often disputed and based on expert consensus as opposed to strong evidence. The challenge has been how to quantify the amount of physical and cognitive activity that children and teens should engage in during recovery. A new study by researchers at the Center for ...
Latest research delineates the effectiveness of "quitlines" for smoking cessation
2021-03-08
While cigarette smoking continues to be the leading cause of preventable disease, disability and death in the U.S., the evidence base for cessation support has revealed that telephone call centers, or "quitlines," have been a particularly successful intervention, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which recently published a compilation of scientific research in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Titled "The Role of Quitlines in Tobacco Cessation," the supplement is composed of nine peer-reviewed articles and three commentaries presenting the latest science on quitlines' effectiveness for smoking termination. The compilation demonstrates the relevance and importance of call ...
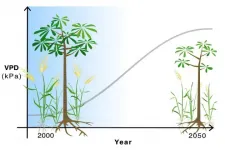
Atmospheric drying will lead to lower crop yields, shorter trees across the globe
2021-03-08
A global observation of an ongoing atmospheric drying -- known by scientists as a rise in vapor pressure deficit -- has been observed worldwide since the early 2000s. In recent years, this concerning phenomenon has been on the rise, and is predicted to amplify even more in the coming decades as climate change intensifies.
In a new paper published in the journal Global Change Biology, research from the University of Minnesota and Western University in Ontario, Canada, outlines global atmospheric drying significantly reduces productivity of both crops and non-crop plants, even under well-watered conditions. The new findings were established on a large-scale analysis covering 50 years of research and 112 plant species.
"When there ...
The impact of lockdown drives us to make poorer choices
2021-03-08
Lockdown and other restrictions imposed to control the COVID-19 pandemic have had unseen negative effects on the cognitive capacity and mental health of the population. A study led by the UOC's research group Open Evidence, in collaboration with international universities and BDI Schlseinger Group Market Research, has gauged the impact of the measures taken during the first and second waves of the virus on citizens of three European Union countries. The study concludes that the shock produced by the situation has reduced people's cognitive capacity, leading them to take more risks, ...
A giant, sizzling planet may be orbiting the star Vega
2021-03-08
Astronomers have discovered new hints of a giant, scorching-hot planet orbiting Vega, one of the brightest stars in the night sky.
The research, published this month in The Astrophysical Journal, was led by University of Colorado Boulder student Spencer Hurt, an undergraduate in the Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences.
It focuses on an iconic and relatively young star, Vega, which is part of the constellation Lyra and has a mass twice that of our own sun. This celestial body sits just 25 light-years, or about 150 trillion miles, from Earth--pretty close, astronomically speaking.
Scientists can also see Vega with telescopes even when it's light out, which makes ...
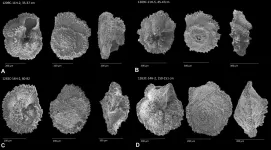
Oceans were stressed preceding abrupt, prehistoric global warming
2021-03-08
Microscopic fossilized shells are helping geologists reconstruct Earth's climate during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), a period of abrupt global warming and ocean acidification that occurred 56 million years ago. Clues from these ancient shells can help scientists better predict future warming and ocean acidification driven by human-caused carbon dioxide emissions.
Led by Northwestern University, the researchers analyzed shells from foraminifera, an ocean-dwelling unicellular organism with an external shell made of calcium carbonate. After analyzing the calcium isotope composition of the fossils, the researchers concluded that massive volcanic activity injected large amounts of carbon dioxide into the Earth system, causing global warming and ocean acidification.
They ...
[1] ... [2563]
[2564]
[2565]
[2566]
[2567]
[2568]
[2569]
[2570]
2571
[2572]
[2573]
[2574]
[2575]
[2576]
[2577]
[2578]
[2579]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.