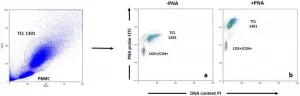
BU researchers identify basic mechanisms that regulate HIV expression
2021-03-08
(Boston)--Despite the positive advances that anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) therapy, commonly called anti-retroviral therapy (ART) or highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), has had on the life expectancy of HIV-positive people, finding a cure for HIV or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) has remained elusive.
"One of the major challenges in curing HIV is that there is a persistent latent reservoir of virus that is not targeted by current antiretroviral treatments and is hidden from immune cells. When treatment is interrupted, this reservoir of the virus allows the HIV ...
Aging-US: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy impact on telomere length & immunosenescence
2021-03-08
Here is a link to a free Altmetric Report on this Research Output
Aging-US published "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases telomere length and decreases immunosenescence in isolated blood cells: a prospective trial" which reported that the aim of the current study was to evaluate whether hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) affects telomere length (TL) and senescent cell concentrations in a normal, non-pathological, aging adult population.
Thirty-five healthy independently living adults, aged 64 and older, were enrolled to receive 60 daily HBOT exposures.
Whole blood samples were collected at baseline, at the 30th and 60th session, and 1-2 weeks following the last HBOT session.
Telomeres length of T helper, T cytotoxic, natural killer and ...
Cheap, nontoxic carbon nanodots poised to be quantum dots of the future
2021-03-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Tiny fluorescent semiconductor dots, called quantum dots, are useful in a variety of health and electronic technologies but are made of toxic, expensive metals. Nontoxic and economic carbon-based dots are easy to produce, but they emit less light. A new study that uses ultrafast nanometric imaging found good and bad emitters among populations of carbon dots. This observation suggests that by selecting only super-emitters, carbon nanodots can be purified to replace toxic metal quantum dots in many applications, the researchers said.
The findings, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, ...
Water temperature key to schistosomiasis risk and prevention strategies
2021-03-08
About one billion people worldwide are at risk for schistosomiasis -- a debilitating disease caused by parasitic worms that live in fresh water and in intermediate snail hosts. A new study finds that the transmission risk for schistosomiasis peaks when water warms to 21.7 degrees centigrade, and that the most effective interventions should include snail removal measures implemented when the temperature is below that risk threshold.
The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences published the results, led by Emory University, the University of South Florida and the ...
Lights on for silicon photonics
2021-03-08
When it comes to microelectronics, there is one chemical element like no other: silicon, the workhorse of the transistor technology that drives our information society. The countless electronic devices we use in everyday life are a testament to how today very high volumes of silicon-based components can be produced at very low cost. It seems natural, then, to use silicon also in other areas where the properties of semiconductors -- as silicon is one -- are exploited technologically, and to explore ways to integrate different functionalities. Of particular interest in this ...
How fast is the universe expanding? Galaxies provide one answer.
2021-03-08
Determining how rapidly the universe is expanding is key to understanding our cosmic fate, but with more precise data has come a conundrum: Estimates based on measurements within our local universe don't agree with extrapolations from the era shortly after the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago.
A new estimate of the local expansion rate -- the Hubble constant, or H0 (H-naught) -- reinforces that discrepancy.
Using a relatively new and potentially more precise technique for measuring cosmic distances, which employs the average stellar brightness within giant elliptical galaxies as a rung on the distance ladder, astronomers calculate a rate -- 73.3 kilometers per second per megaparsec, give or take 2.5 km/sec/Mpc -- that lies in the middle of three ...
Greater tobacco use linked to higher levels of inflammation in HIV-positive people
2021-03-08
Inflammation in the body has been linked to the intensity of tobacco smoking among people with HIV, according to a team of University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers.
Krishna Poudel, associate professor of community health education in the School of Public Health and Health Sciences, and colleagues reported positive linear relationships between intensity, duration and pack-years of smoking and inflammation in HIV-positive people. They believe it to be the first, more thorough examination of specific smoking-related variables with the levels of inflammation in this group, while also taking into account highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) and other important factors.
The study's findings ...
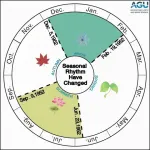
Northern Hemisphere summers may last nearly half the year by 2100
2021-03-08
WASHINGTON--Without efforts to mitigate climate change, summers spanning nearly six months may become the new normal by 2100 in the Northern Hemisphere, according to a new study. The change would likely have far-reaching impacts on agriculture, human health and the environment, according to the study authors.
In the 1950s in the Northern Hemisphere, the four seasons arrived in a predictable and fairly even pattern. But climate change is now driving dramatic and irregular changes to the length and start dates of the seasons, which may become more extreme in the future under a business-as-usual climate scenario.
"Summers are getting longer and hotter while winters shorter and warmer ...
Study finds racial disparities in COVID-19 deaths in nursing homes
2021-03-08
Nursing homes with the largest proportions of non-White residents experience 3.3 times more COVID-19 deaths than do nursing homes with the largest proportions of White residents, according to a new study from the University of Chicago. The paper, published in JAMA Network Open, suggests that these differences are likely due to nursing home size and the level of coronavirus spread in the local community, reinforcing the inseparability of long-term care facilities from society at large when it comes to bringing the COVID-19 pandemic to heel.
Since the start of the ...
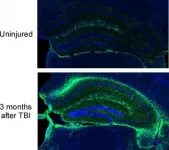
Complement inhibition reverses mental losses in preclinical traumatic brain injury models
2021-03-08
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of disability and a risk factor for early-onset dementia. The injury is characterized by a physical insult followed acutely by complement driven neuroinflammation. Complement, a part of the innate immune system that functions both in the brain and throughout the body, enhances the body's ability to fight pathogens, promote inflammation and clear damaged cells. Complement plays a role in the brain, regardless of infection or injury, as it influences brain development and synapse formation. In TBI, complement- induced inflammation partially determines the outcome in the weeks immediately following injury. However, more research is needed to define a role for the complement system in neurodegeneration ...
Membrane around tumors may be key to preventing metastasis
2021-03-08
For cancer cells to metastasize, they must first break free of a tumor's own defenses. Most tumors are sheathed in a protective "basement" membrane -- a thin, pliable film that holds cancer cells in place as they grow and divide. Before spreading to other parts of the body, the cells must breach the basement membrane, a material that itself has been tricky for scientists to characterize.
Now MIT engineers have probed the basement membrane of breast cancer tumors and found that the seemingly delicate coating is as tough as plastic wrap, yet surprisingly elastic like a party balloon, able to inflate to twice its original size.
But while a balloon becomes much easier to blow up after some initial effort, the team found that a basement membrane becomes stiffer as it expands. ...
A plant's place in history can predict susceptibility to pathogens
2021-03-08
Found around the world, powdery mildew is a fungal disease especially harmful to plants within the sunflower family. Like most invasive pathogens, powdery mildew is understudied and learning how it affects hosts can help growers make more informed decisions and protect their crops.
Scientists at the University of Washington and the University of Central Florida inoculated 126 species of plants in the sunflower family with powdery mildew, growing 500 plants from seeds that were collected from the wild and provided from the USDA germplasm network. Through this ...
Are higher obesity rates in minority groups a product of systemic racism?
2021-03-08
BOSTON - The higher rates of obesity in Black, Indigenous and People of Color (BIPOC) compared with other groups in the United States can be attributed in large part to systemic racism, according to a new perspective article published in the Journal of Internal Medicine. The authors offer a 10-point strategy to study and solve the public health issues responsible for this disparity.
"First, it is important to recognize that the interplay of obesity and racism is real. Once persons recognize this, they can begin to appropriately address and treat obesity in BIPOC communities," says co-author Fatima Cody ...
Hypertension disorders of pregnancy increase risk of premature maternal mortality
2021-03-08
Women who experienced hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDPs) but did not develop chronic hypertension have a greater risk of premature mortality, specifically cardiovascular disease (CVD)-related deaths, according to a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC). A separate JACC study examined the cardiovascular health risks associated with pregnancy in obese women with heart disease.
HDPs, which occur in approximately 10% of all pregnancies worldwide, are among the most common health issues during pregnancy. There are four types of HDPs: chronic hypertension, gestational hypertension (GHTN), preeclampsia and ...
Why odors trigger powerful memories
2021-03-08
Other senses re-routed during evolution, but not sense of smell
Loss of smell linked to depression and poor quality of life
Smell research can help treatments for loss in COVID-19
CHICAGO ---Odors evoke powerful memories, an experience enshrined in literature by Marcel Proust and his beloved madeleine.
A new Northwestern Medicine paper is the first to identify a neural basis for how the brain enables odors to so powerfully elicit those memories. The paper shows unique connectivity between the hippocampus--the seat of memory in the brain--and olfactory areas in humans.
This new research suggests a neurobiological basis for privileged access by olfaction to memory areas in the brain. The study compares connections between primary sensory areas--including ...
New technique brings the study of molecular configuration into the microscopic domain
2021-03-08
Researchers have developed a spectroscopic microscope to enable optical measurements of molecular conformations and orientations in biological samples. The novel measurement technique allows researchers to image biological samples at the microscopic level more quickly and accurately.
The new instrument is based on the discrete frequency infrared spectroscopic imaging technique developed by researchers at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
"This project is about bringing the study ...
Speeding treatment for urinary tract infections in children
2021-03-08
DALLAS - March 8, 2021 - A study led by UT Southwestern and Children's Health researchers defines parameters for the number of white blood cells that must be present in children's urine at different concentrations to suggest a urinary tract infection (UTI). The findings, published recently in Pediatrics, could help speed treatment of this common condition and prevent potentially lifelong complications.
UTIs account for up to 7 percent of fevers in children up to 24 months old and are a common driver of hospital emergency room visits. However, says study leader Shahid Nadeem, M.D., assistant professor of pediatrics at UTSW as well as an emergency department physician and pediatric nephrologist at Children's Medical Center Dallas, these bacterial infections ...
Financial pollution in the US health system
2021-03-08
Boston, MA - Financial pollution arises when exorbitant or unnecessary healthcare spending depletes resources needed for the wellbeing of the population. This is the subject of a JAMA Health Forum Insight co-authored by researchers in the Department of Population Medicine at Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute and Harvard Medical School. The Insight was published in the March 8, 2021 issue of JAMA Health Forum.
The authors lay out the rationale for "financial pollution" as a metaphor to express the urgency of addressing wasteful health care spending and to guide innovative policymaking. Akin to environmental pollution, financial ...
Understanding the resilience of barrier islands and coastal dunes after storms
2021-03-08
When a coastline undergoes massive erosion, like a hurricane flattening a beach and its nearby environments, it has to rebuild itself - relying on the resilience of its natural coastal structures to begin piecing itself back together in a way that will allow it to survive the next large phenomena that comes its way.
Drs. Orencio Duran Vinent, assistant professor, and Ignacio Rodriguez-Iturbe, Distinguished University Professor and Wofford Cain Chair I Professor, in the Department of Ocean Engineering at Texas A&M University, are investigating the resilience of barrier ...
A better way to measure acceleration
2021-03-08
You're going at the speed limit down a two-lane road when a car barrels out of a driveway on your right. You slam on the brakes, and within a fraction of a second of the impact an airbag inflates, saving you from serious injury or even death.
The airbag deploys thanks to an accelerometer -- a sensor that detects sudden changes in velocity. Accelerometers keep rockets and airplanes on the correct flight path, provide navigation for self-driving cars, and rotate images so that they stay right-side up on cellphones and tablets, among other essential tasks.
Addressing the increasing ...
Brain activity foreshadows changes in stock prices
2021-03-08
Forecasting changes in stock prices may be possible with the help of brain activity in regions associated with how people feel before making investment choices. Scientists could accurately forecast market price changes based on the average brain activity among a group but failed when using only prior stock trends or people's investment choices, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Scientists have used the average brain activity among a group to predict which videos will go viral and which crowdfunding campaigns will receive funding. In a new study, Stallen et al. investigated if this relationship extends to a more ...
New discovery explains antihypertensive properties of green and black tea
2021-03-08
Irvine, CA - March 8, 2021 - A new study from the University of California, Irvine shows that compounds in both green and black tea relax blood vessels by activating ion channel proteins in the blood vessel wall. The discovery helps explain the antihypertensive properties of tea and could lead to the design of new blood pressure-lowering medications.
Published in Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, the discovery was made by the laboratory of Geoffrey Abbott, PhD, a professor in the Department of Physiology and Biophysics at the UCI School of Medicine. Kaitlyn Redford, a graduate student in the Abbott Lab, was first author of the study titled, "KCNQ5 potassium channel activation underlies vasodilation by tea."
Results from the research revealed that two catechin-type ...
New teamwork model could improve patient health care
2021-03-08
HOUSTON - (March 8, 2021) - Health care teams must prepare for anything, including the unconventional work environments brought about by a global pandemic and social unrest.
Multiracial medical team having a discussion as they stand grouped together around a tablet computer on a stair well, overhead view
Open communication and trust are essential for successful teamwork in challenging health care situations, as detailed in "Building effective healthcare team development interventions in uncertain times: Tips for success." The paper was authored by researchers at Rice University, the University of Texas MD Anderson ...
Sophisticated skin
2021-03-08
Squids have long been a source of fascination for humans, providing the stuff of legend, superstition and myth. And it's no wonder -- their odd appearances and strange intelligence, their mastery of the open ocean can inspire awe in those who see them.
Legends aside, squids continue to intrigue people today -- people like UC Santa Barbara professor Daniel Morse -- for much the same, albeit more scientific, reasons. Having evolved for hundreds of millions of years to hunt, communicate, evade predators and mate in the vast, often featureless expanses of open water, squids have developed some of the most sophisticated skin in the animal kingdom.
"For centuries, people have been amazed at the ability of squids to change the color and patterns of their skin -- which they ...
Assessing regulatory fairness through machine learning
2021-03-08
The perils of machine learning - using computers to identify and analyze data patterns, such as in facial recognition software - have made headlines lately. Yet the technology also holds promise to help enforce federal regulations, including those related to the environment, in a fair, transparent way, according to a new study by Stanford researchers.
The analysis, published this week in the proceedings of the Association of Computing Machinery Conference on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency(link is external), evaluates machine learning techniques designed to support a U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) initiative to reduce ...
[1] ... [2561]
[2562]
[2563]
[2564]
[2565]
[2566]
[2567]
[2568]
2569
[2570]
[2571]
[2572]
[2573]
[2574]
[2575]
[2576]
[2577]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.