Rise of marine predators reshaped ocean life as dramatically as sudden mass extinctions
2021-03-08
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Evolutionary arms races between marine animals overhauled ocean ecosystems on scales similar to the mass extinctions triggered by global disasters, a new study shows.
Scientists at Umeå University in Sweden and the Florida Museum of Natural History used paleontological databases to build a multilayered computer model of the history of marine life over the last 500 million years. Their analysis of the fossil record closely echoed a seminal 1981 study by paleontologist J. John Sepkoski - with one key difference.
Sepkoski's ground-breaking statistical work showed abrupt ocean-wide changes in biodiversity about 490 and 250 ...
Oncotarget: Sensitivity testing on ovarian cancer cells isolated from malignant ascites
2021-03-08
Oncotarget published "Chemotherapy sensitivity testing on ovarian cancer cells isolated from malignant ascites" which reported that the authors aim is to determine the feasibility of cell proliferation assays of tumor cells isolated from malignant ascites to predict in vitro chemotherapy sensitivity, and to correlate these results with clinical outcome.
Cell samples were enriched for tumor cells and EOC origin was confirmed by intracellular staining of CK7, surface staining of CA125 and EpCAM, and HE4 gene expression.
In vitro sensitivity to chemotherapy was determined in cell proliferation assays using intracellular ATP content as an indirect measure of cell number.
In twelve of ...
Oncotarget: High-fat ovariectomized mice susceptible to accelerated tumor growth
2021-03-08
Oncotarget published "High-fat diet-fed ovariectomized mice are susceptible to accelerated subcutaneous tumor growth potentially through adipose tissue inflammation, local insulin-like growth factor release, and tumor associated macrophages" which reported that the association between obesity and colorectal cancer (CRC) risk has been well established. This relationship appears to be more significant in men than in women, which may be attributable to sex hormones - controlled animal studies to substantiate these claims and the mechanisms involved are lacking. MC38 murine colon adenocarcinoma ...
Oncotarget: Estrogen receptor α polymorphism is associated with dementia
2021-03-08
Oncotarget recently published "Estrogen receptor α polymorphism is associated with dementia in a Brazilian cohort" which reported that the growth of the elderly population is a worldwide phenomenon and it is associated with chronic diseases, including dementia.
In this scenario, the present study aimed to evaluate a possible association of estrogen receptor α polymorphisms with dementia in a Brazilian cohort.
The genotyping for the ERα PvuII and XbaI polymorphisms were performed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism.
The ERα PvuII pp genotype was associated with a higher odds ratio for dementia (OR = 3.42, 95% CI = 1.33-8.77, p = 0.01, ...
<i>Aging-US</i>: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy impact on telomere length & immunosenescence
2021-03-08
Here is a link to a free Altmetric Report on this Research Output
Aging-US published "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases telomere length and decreases immunosenescence in isolated blood cells: a prospective trial" which reported that the aim of the current study was to evaluate whether hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) affects telomere length (TL) and senescent cell concentrations in a normal, non-pathological, aging adult population.
Thirty-five healthy independently living adults, aged 64 and older, were enrolled to receive 60 daily HBOT exposures.
Whole blood samples were collected at baseline, at the 30th and 60th session, and 1-2 weeks following the last HBOT session.
Telomeres ...
Aging-US: High-CBD Cannabis sativa extracts modulate ACE2 expression in COVID-19
2021-03-08
Aging-US published "In search of preventive strategies: novel high-CBD Cannabis sativa extracts modulate ACE2 expression in COVID-19 gateway tissues" which reported that Cannabis sativa, especially those high in the anti-inflammatory cannabinoid cannabidiol, has been found to alter gene expression and inflammation and harbour anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties.
Working under a Health Canada research license, the Aging-US authors developed over 800 new C. sativa cultivars and hypothesized that high-CBD C. sativa extracts may be used to down-regulate ...
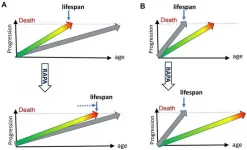
Aging-US: DNA- and telomere-damage does not limit lifespan: evidence from rapamycin
2021-03-08
Aging-US published "DNA- and telomere-damage does not limit lifespan: evidence from rapamycin" which reported that failure of rapamycin to extend lifespan in DNA repair mutant and telomerase-knockout mice, while extending lifespan in normal mice, indicates that neither DNA damage nor telomere shortening limits normal lifespan or causes normal aging.
Dr. Mikhail V. Blagosklonny said, "As a provocative title has recently announced, 'rapamycin fails to extend lifespan in DNA repair -deficient mice' [1]. The word 'fails' implies bad news. Rapamycin tried but failed. Yet, it is expected that the anti-aging ...
Cognitive fatigue changes functional connectivity in brain's fatigue network
2021-03-08
East Hanover, NJ. March 8, 2021. Kessler Foundation researchers have demonstrated changes in the functional connectivity within the 'fatigue network' in response to cognitive fatigue. This finding, the first of its kind, was reported in Scientific Reports on December 14, 2020 in the open access article, "Using functional connectivity changes associated with cognitive fatigue to delineate a fatigue network" (doi: 10.1038//s41598-020-78768-3).
The authors are Glenn Wylie, DPhil, Brian Yao, PhD, Helen M. Genova, PhD, Michele H. Chen, PhD, and John DeLuca, PhD, of Kessler Foundation. All have faculty appointments at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School. Dr. Wylie is also a research scientist at The Department of Veterans' Affairs War-related Injury and Illness ...
Study of coronavirus variants predicts virus evolving to escape current vaccines
2021-03-08
A new study of the U.K. and South Africa variants of SARS-CoV-2 predicts that current vaccines and certain monoclonal antibodies may be less effective at neutralizing these variants and that the new variants raise the specter that reinfections could be more likely.
The study was published in Nature on March 8, 2021. A preprint of the study was first posted to BioRxiv on January 26, 2021.
David Ho (Credit: Columbia University Irving Medical Center)
The study's predictions are now being borne out with the first reported results of the Novavax vaccine, says the study's lead author David ...
Study finds two servings of fish per week can help prevent recurrent heart disease
2021-03-08
Hamilton, ON (March 8, 2021) - An analysis of several large studies involving participants from more than 60 countries, spearheaded by researchers from McMaster University, has found that eating oily fish regularly can help prevent cardiovascular disease (CVD) in high-risk individuals, such as those who already have heart disease or stroke.
The critical ingredient is omega-3 fatty acids, which researchers found was associated with a lower risk of major CVD events such as heart attacks and strokes by about a sixth in high-risk people who ate two servings of fish rich in omega-3 each week.
"There is a significant protective benefit of fish consumption in people with cardiovascular disease," said lead co-author Andrew Mente, associate ...
3D printing materials for printing aorta model to study optimal CT scanning protocols
2021-03-08
Personalised 3D printed models created from cardiac imaging data, mainly from cardiac CT images have been increasingly used in cardiovascular disease, primarily in the preoperative planning and simulation of complex surgical procedures, as well as medical education. 3D printed models are proved to be highly accurate in replicating normal anatomy and cardiac pathology with reported differences less than 0.5 mm between 3D printed models and original sources images. Further to these applications, a new research direction of utilising 3D printed models is to study the optimal CT scanning protocols in cardiovascular disease with the aim of reducing radiation dose while preserving diagnostic image quality. To achieve ...
Finding key to low-cost, fast production of solid-state batteries for EVs
2021-03-08
A new fabrication technique could allow solid-state automotive lithium-ion batteries to adopt nonflammable ceramic electrolytes using the same production processes as in batteries made with conventional liquid electrolytes.
The melt-infiltration technology developed by materials science researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology uses electrolyte materials that can be infiltrated into porous yet densely packed, thermally stable electrodes.
The one-step process produces high-density composites based on pressure-less, capillary-driven infiltration of a molten solid electrolyte into porous bodies, including multilayered electrode-separator stacks.
"While the melting point of traditional ...
These sea slugs sever their own heads and regenerate brand-new bodies
2021-03-08
You've heard of animals that can lose and then regenerate a tail or limb. But scientists reporting in the journal Current Biology on March 8 have now discovered two species of sacoglossan sea slug that can do even better, shedding and then regenerating a whole new body complete with the heart and other internal organs. The researchers also suggest that the slugs may use the photosynthetic ability of chloroplasts they incorporate from the algae in their diet to survive long enough for regeneration.
"We were surprised to see the head moving just after autotomy," said Sayaka Mitoh of Nara ...
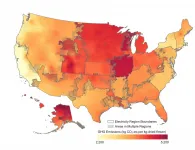
Insatiable demand for cannabis has created a giant carbon footprint
2021-03-08
It's no secret that the United States' $13 billion cannabis industry is big business. Less obvious to many is the environmental toll this booming business is taking, in the form of greenhouse gas emissions from commercial, mostly indoor production.
A new study by Colorado State University researchers provides the most detailed accounting to date of the industry's carbon footprint, a sum around which there is only limited understanding. What is clear, though, is that consumer demand for cannabis is insatiable and shows no signs of stopping as more states sign on to legalization.
The study, ...
Economic benefits of protecting nature now outweigh those of exploiting it, global data reveal
2021-03-08
The economic benefits of conserving or restoring natural sites "outweigh" the profit potential of converting them for intensive human use, according to the largest-ever study comparing the value of protecting nature at particular locations with that of exploiting it.
A research team led by the University of Cambridge and the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) analysed dozens of sites - from Kenya to Fiji and China to the UK - across six continents. A previous breakthrough study in 2002 only had information for five sites.
The findings, published in the journal Nature Sustainability, come just weeks after a landmark report by Cambridge Professor Partha Dasgupta called for the value of biodiversity to be placed at the heart of global economics.
For the latest ...
Sea level rise up to four times global average for coastal communities
2021-03-08
Coastal populations are experiencing relative sea-level rise up to four times faster than the global average - according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today in Nature Climate Change is the first to analyse global sea-level rise combined with measurements of sinking land.
The impact of subsidence combined with sea-level rise has until now been considered a local issue rather than a global one.
But the new study shows that coastal inhabitants are living with an average sea level rise of 7.8 mm - 9.9 mm per year over the past twenty years, compared with a global average rise of 2.6mm a year.
And the impacts are far larger than the global numbers reported ...
New method could democratize deep learning-enhanced microscopy
2021-03-08
LA JOLLA--(March 8, 2021) Deep learning is a potential tool for scientists to glean more detail from low-resolution images in microscopy, but it's often difficult to gather enough baseline data to train computers in the process. Now, a new method developed by scientists at the Salk Institute could make the technology more accessible--by taking high-resolution images, and artificially degrading them.
The new tool, which the researchers call a "crappifier," could make it significantly easier for scientists to get detailed images of cells or cellular structures that have previously been difficult to observe because they require low-light conditions, such as mitochondria, which can ...
Hospital admissions associated with noncommunicable diseases during COVID-19 outbreak in Brazil
2021-03-08
What The Study Did: Researchers assessed the number of hospital admissions for noncommunicable diseases (abnormal tissue growths, metabolic diseases, cardiovascular diseases and musculoskeletal diseases) in São Paulo, Brazil, between January and June last year compared with the corresponding periods in the previous three years.
Authors: Fernando Adami, Ph.D., of the Laboratório de Epidemiologia e Análise de Dados, Centro Universitário Saúde ABC in São Paulo, Brazil, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0799)
Editor's Note: Please ...
In a leap for battery research, machine learning gets scientific smarts
2021-03-08
Menlo Park, Calif. -- Scientists have taken a major step forward in harnessing machine learning to accelerate the design for better batteries: Instead of using it just to speed up scientific analysis by looking for patterns in data, as researchers generally do, they combined it with knowledge gained from experiments and equations guided by physics to discover and explain a process that shortens the lifetimes of fast-charging lithium-ion batteries.
It was the first time this approach, known as "scientific machine learning," has been applied to battery cycling, said Will Chueh, an associate ...
Five days of antibiotics fine for children with pneumonia
2021-03-08
Hamilton, ON (March 8, 2021) - Many parents know the struggle of having to make children with pneumonia finish the usual 10-day course in antibiotics despite the child feeling better after a few days of medication.
New research from McMaster University has proven that a five-day course of high-dose amoxicillin will do just as well for children six months to 10 years old with common pneumonia.
"Several studies have proven that adults with pneumonia do fine with short courses of antibiotics, and now we have proved a short course of antibiotics also works for children," said Dr. Jeffrey ...
For teens, outdoor recreation during the pandemic linked to improved well-being
2021-03-08
A study from North Carolina State University found outdoor play and nature-based activities helped buffer some of the negative mental health impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic for adolescents.
Researchers said the findings, published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, point to outdoor play and nature-based activities as a tool to help teenagers cope with major stressors like the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as future natural disasters and other global stressors. Researchers also underscore the mental health implications of restricting outdoor recreation opportunities for adolescents, and the need to increase ...
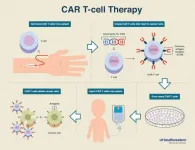
New CAR T-Cell therapy extends remission in heavily relapsed multiple myeloma patients
2021-03-08
DALLAS - March 8, 2021 - A new type of CAR T-cell therapy more than triples the expected length of remission for multiple myeloma patients who have relapsed several times, according to an international clinical trial with UT Southwestern as the lead enrolling site.
Results of the trial, published recently in the New England Journal of Medicine, were significantly better than those seen with other therapies available to heavily relapsed and refractory myeloma patients who had already received the three main classes of treatment. Nearly three-quarters of the patients had at least a partial response to the therapy. About a third achieved a complete remission, with the disappearance of all traces of cancer.
Median time without the disease worsening was 8.8 months with this new ...
UCLA-led study reveals 'hidden costs' of being Black in the US
2021-03-08
A woman grips her purse tightly as you approach. A store manager follows you because you look "suspicious." You enter a high-end restaurant, and the staff assume you're applying for a job. You're called on in work meetings only when they're talking about diversity.
The indignities and humiliations Black men -- even those who have "made it" -- regularly endure have long been seen as part and parcel of life in the United States among the Black community, a sort of "Black tax" that takes a heavy toll on physical and mental health.
Now, a new UCLA-led study reveals these "hidden costs" of being Black in America. ...
Study: Moral outrage is attractive among long-term relationship seekers
2021-03-08
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - Moral outrage is an attractive behavior, particularly to people seeking long-term relationships, according to a new paper by researchers including a University of Arkansas psychologist.
The work indicates that people who displayed moral outrage were considered more benevolent and trustworthy than a control person not displaying outrage, and therefore more likely to possess other prosocial behaviors that would benefit a long-term relationship. There was a catch, however: Researchers found that people had to take action to address the moral wrong in question and not just talk about ...
New research shows marijuana THC stays in breast milk for six weeks
2021-03-08
Aurora, Colo. (March 8, 2021) - In a new study published in JAMA Pediatrics, researchers at Children's Hospital Colorado (Children's Colorado) have found that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive component of marijuana, stays in breast milk for up to six weeks, further supporting the recommendations of the American Academy of Pediatrics, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine to abstain from marijuana use during pregnancy and while a mother is breastfeeding. This is the first study examining THC in breastmilk and plasma among women with known marijuana use in pregnancy since a 1982 study in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"With the increasing utilization of marijuana in society as a ...
[1] ... [2562]
[2563]
[2564]
[2565]
[2566]
[2567]
[2568]
[2569]
2570
[2571]
[2572]
[2573]
[2574]
[2575]
[2576]
[2577]
[2578]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.