The amazing promise of artificial intelligence in health care
2021-03-08
Artificial intelligence can already scan images of the eye to assess patients for diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of vision loss, and to find evidence of strokes on brain CT scans. But what does the future hold for this emerging technology? How will it change how doctors diagnose disease, and how will it improve the care patients receive?
A team of doctors led by UVA Health's James H. Harrison Jr., MD, PhD, has given us a glimpse of tomorrow in a new article on the current state and future use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the field of pathology. Harrison and other members of the College of American Pathologists' Machine Learning ...
Innovative flat optics will usher the next technological revolution
2021-03-08
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, the group led by Professor Andrea Fratalocchi from Primalight Laboratory of the Computer, Electrical and Mathematical Sciences and Engineering (CEMSE) Division, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia, introduced a new patented, scalable flat-optics technology manufactured with inexpensive semiconductors.
The KAUST-designed technology leverages on a previously unrecognized aspect of optical nanoresonators, which are demonstrated to possess a physical layer that is completely equivalent to a feed-forward deep neural network.
"What we have achieved," explains Fratalocchi, "is a technological process to cover ...
It's time to bolster women in conservation
2021-03-08
Women are largely being excluded from decisions about conservation and natural resources, with potentially detrimental effects on conservation efforts globally, according to research.
A University of Queensland and Nature Conservancy study reviewed a swathe of published conservation science, investigating the cause and impact of gender imbalance in the field.
UQ PhD candidate and Nature Conservancy Director of Conservation in Melanesia Robyn James said it was no secret that females were underrepresented in conservation science.
"In fact, according to a recent analysis of 1051 individual top?publishing authors in ecology, evolution and conservation research, only 11 per cent were women," Ms James said.
"We analysed more than 230 peer-reviewed articles attempting ...
Critically endangered macadamia species becomes a plant supermodel
2021-03-08
One of the world's rarest tree species has been transformed into a sophisticated model that University of Queensland researchers say is the future of plant research.
"Macadamia jansenii is a critically endangered species of macadamia which was only described as a new species in 1991," said Robert Henry, Professor of Innovation at the Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation (QAAFI).
"It grows near Miriam Vale in Queensland and there are only around 100 known trees in existence."
However, with funding from Hort Innovation's Tree Genomics project, and UQ's Genome Innovation Hub Macadamia jansenii has now become the world's most sophisticated plant research model.
Professor Henry said ...
Algorithm helps artificial intelligence systems dodge "adversarial" inputs
2021-03-08
In a perfect world, what you see is what you get. If this were the case, the job of artificial intelligence systems would be refreshingly straightforward.
Take collision avoidance systems in self-driving cars. If visual input to on-board cameras could be trusted entirely, an AI system could directly map that input to an appropriate action -- steer right, steer left, or continue straight -- to avoid hitting a pedestrian that its cameras see in the road.
But what if there's a glitch in the cameras that slightly shifts an image by a few pixels? If the car blindly trusted so-called "adversarial inputs," it might take unnecessary and potentially dangerous action.
A new deep-learning algorithm developed by MIT researchers is designed to help machines ...
Targeted immunotherapy could boost radiotherapy response
2021-03-08
Cancers that are resistant to radiotherapy could be rendered susceptible through treatment with immunotherapy, a new study suggests.
Researchers believe that manipulating bowel cancers based on their 'immune landscape' could unlock new ways to treat resistant tumours.
Cancers can evolve resistance to radiotherapy just as they do with drugs.
The new study found that profiling the immune landscape of cancers before therapy could identify patients who are likely to respond to radiotherapy off the bat, and others who might benefit from priming of their tumour with immunotherapy.
Scientists at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, in collaboration with the University of Leeds and The Francis Crick ...
Someone to watch over AI and keep it honest - and it's not the public!
2021-03-08
The public doesn't need to know how Artificial Intelligence works to trust it. They just need to know that someone with the necessary skillset is examining AI and has the authority to mete out sanctions if it causes or is likely to cause harm.
Dr Bran Knowles, a senior lecturer in data science at Lancaster University, says: "I'm certain that the public are incapable of determining the trustworthiness of individual AIs... but we don't need them to do this. It's not their responsibility to keep AI honest."
Dr Knowles presents (March 8) a research paper 'The Sanction of Authority: Promoting Public Trust in AI' at the ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency (ACM FAccT).
The ...
Pay-off when solar cells can keep their cool
2021-03-08
Lowering the operating temperature of solar panels by just a few degrees can dramatically increase the electricity they generate over their lifetime, KAUST researchers have shown. The hotter a panel gets, the lower its solar power conversion efficiency (PCE) and the faster it will degrade and fail. Finding ways to keep solar panels cool could significantly improve the return on investment of solar-power systems.
The long-standing focus of photovoltaics (PV) research has been to improve solar modules' PCE and make solar power more cost-competitive than nonrenewable power ...
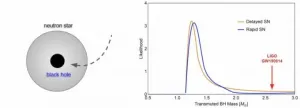
Establishing the origin of solar-mass black holes and the connection to dark matter
2021-03-08
What is the origin of black holes and how is that question connected with another mystery, the nature of dark matter? Dark matter comprises the majority of matter in the Universe, but its nature remains unknown.
Multiple gravitational wave detections of merging black holes have been identified within the last few years by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), commemorated with the 2017 physics Nobel Prize to Kip Thorne, Barry Barish, and Rainer Weiss. A definitive confirmation of the existence of black holes was celebrated with the 2020 physics Nobel Prize awarded to Andrea Ghez, Reinhard Genzel and ...
Strong and balanced T cell response: key to controlling SARS-CoV-2 infection without getting COVID-19
2021-03-08
To effectively fight off SARS-CoV-2, the immune system depends on both antibodies and T cells, a type of white blood cell, which work together to eradicate the virus. However, little was known about virus-specific T cells in asymptomatic patients.
"We now know that many people are getting infected with SARS-CoV-2 without realising it, as they stay healthy and don't develop any symptoms. These asymptomatic infections may provide the key to understanding how the immune system can control the virus without triggering pathological processes," explained Dr Nina Le Bert, Senior Research Fellow ...
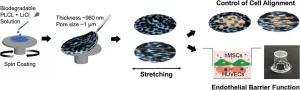
Biological artificial organs like skin, vessels...now produced more easily
2021-03-08
A Korean research group has developed a technology that allows for the differentiation of stem cells into desired cell types, such as vascular mural cells or osteoblasts, without special pretreatment. This technology is expected to facilitate the production of artificial organs for preclinical studies or artificial tissues for transplants such as artificial skin and cardiac patches.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the research group led by Dr. Youngmee Jung of the Center for Biomaterials has developed a new cell co-culture platform ...
Researchers develop improved recycling process for carbon fibres
2021-03-08
In recent years there has been an increased focus on the circular economy and a heightened demand for products made of recyclable materials, however many materials can only be recycled so many times before they begin to wear out.
This is the case with carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites, non-biodegradable materials which, until now, have lacked a viable recycling method.
CRFP composites are present in products such as wind turbines, aeroplane parts, vehicles such as cars and ships, and everyday technology such as laptops and mobile ...
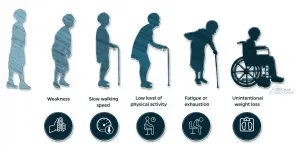
Multisystem failure regarding frailty necessitates multisystem intervention
2021-03-08
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Physicians understand frailty as a dysregulation among multiple systems in the body that make it less resilient and unable to recover completely when faced with a physical challenge such as injury or illness. "Defining frailty on a scientific level, however, has been a challenging task," explains END ...
Research offers insights on how night shift work increases cancer risk
2021-03-08
SPOKANE, Wash. - New clues as to why night shift workers are at increased risk of developing certain types of cancer are presented in a new study conducted at Washington State University Health Sciences Spokane. ...
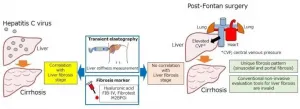
Post-Fontan liver fibrosis goes under the radar
2021-03-08
It is well-known that patients who undergo Fontan surgery slowly develop liver fibrosis for years post-operatively. In the past decade, these incidences have been steadily increasing and this is due partly to the need for an accurate diagnostic method. A research group led by Dr. Daisuke Tokuhara, Associate Professor of Pediatrics, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine and Dr. Yuki Cho have found that the conventional methods of ultrasound elastography and biomarkers via blood tests do not show the actual status of postoperative liver ...
More than 2/3 of Indiana nursing home staff would take COVID-19 vaccine
2021-03-08
INDIANAPOLIS -- In a study conducted shortly before COVID-19 vaccines became available in the U.S., more than two-thirds of nursing home and assisted living staff in Indiana indicated willingness to receive a vaccine immediately or in the future. The study was led by researchers from Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University and the State of Indiana. Vaccine uptake by front-line staff is important because it will help protect against serious illness and death for the high-risk people who receive care in these facilities.
"The vaccines offer the opportunity to return to a more normal life within the nursing ...
Invasive weed may help treat some human diseases, researchers find
2021-03-08
Native to the southeastern United States, a weedy grass has spread northward to Canada and also made its way to Australia and Japan. Andropogon virginicus grows densely packed and up to seven feet tall, disrupting growth patterns of other plants and competing for resources. When burned, it grows back stronger. There is no way to effectively remove the weed once it has invaded. But there might be a way to use it to human advantage.
An international team of researchers has found that A. virginicus extracts appear to be effective against several human diseases, including diabetes and cancer. The results were published on Dec. 31, 2020, in a special issue of Plants, titled ...
Novel hydrogen fuel purification membrane paves the way for greener future
2021-03-08
Hydrogen has been hailed as the 'fuel of the future' owing to several reasons. First, compared to the conventionally used hydrocarbons, hydrogen exhibits higher energy yield. Second, the commercial use of hydrogen fuel, which yields only water as a byproduct product, would help mitigate the imminent global warming crisis by reducing the use of exhaustible and polluting fossil fuels. Thus, ongoing research has been focusing on efficient and environment-friendly ways to produce of hydrogen fuel.
Solar hydrogen production through photoelectrochemical (PEC) water-splitting reaction is an attractive "green" method of ...
Research foresees an end to deregulated competitive public transport
2021-03-08
Research from the University of Kent predicts an end to deregulated competitive pubic transport in the UK as a consequence of Covid-19 social distancing measures leading to drastically reduced ridership, requiring a major rethinking of the provision of public transport.
This paper, published in Transport Policy, argues that the situation will require a fundamental approach to long-term policy for transport as a whole. This is an opportunity to reconstruct the system whilst addressing such problems as the environmental impact of transport, congestion and questions of transport justice such as accessibility ...
New inhibitor found to combat drug-resistant cancer cells
2021-03-08
A new substance could improve the treatment of persistent cancers. Researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the University of Greifswald have developed a new inhibitor that makes drug-resistant tumour cells respond again to chemotherapy. The new substance blocks a protein in the cancer cells that normally transports the cancer drugs back out of the cells. The results were published in the scientific journal Molecules.
In addition to radiation therapy, cytotoxic agents, also known as chemotherapy, are frequently used to treat cancer. They prevent cells from dividing and thus cancer cells are unable to multiply unchecked. "Cytotoxic agents remain a very important form ...
Meet Turing structures in manmade interface
2021-03-08
In 1952, Alan Turing, the father of computer science and artificial intelligence, proposed that certain repetitive natural patterns may be produced by the interaction of two specific substances through the "reaction-diffusion" process. In this system, activator promotes the reaction and inhibitor inhibits the reaction. When the two meet, the reaction diffuses. When the difference in diffusion coefficient between the two reaches a certain level, the high diffusion ratio between them will cause the system imbalance and induce the formation of periodic complex patterns.
"Turing structure" exists widely in nature, such as the body patterns of zebras, the phyllotaxis of sunflowers, the follicle spacing of ...
Breast cancer: Mathematics for precision medicine
2021-03-08
The precise choice of treatment for breast cancer depends upon the status of the hormone receptors (for oestrogen and progesterone). Their conventional determination by means of immunohistochemistry (IHC) is associated with a certain error rate, which can be reduced by adding genomic data. Even conventional statistics can bring about a notable improvement but now it is possible to use decision theory to optimally combine diagnostic findings, particularly where they are contradictory. This is the finding of a recent study conducted by MedUni Vienna under the leadership of Wolfgang Schreiner from the Center for Medical Statistics, Informatics and Intelligent Systems (CeMSIIS). The methodology has applications way beyond breast cancer and can be deployed ...
Chiral amines synthesized by nickel-catalysed asymmetric reductive hydroalkylation
2021-03-08
Recently, research group, led by Prof. FU Yao and associate research fellow LU Xi From Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and School of Chemistry and Materials Science of the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), has made significant achievements in the field of synthesis of chiral amines. They developed a mild and general nickel-catalysed asymmetric reductive hydroalkylation and realized the modular synthesis of chiral aliphatic amines.
Results were published in Nature Communications on Feb. 26, 2021.
Chiral amines are important chiral auxiliaries and key synthetic intermediates of pharmaceuticals and natural products. ...
Most distant quasar with powerful radio jets discovered
2021-03-08
With the help of the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (ESO's VLT), astronomers have discovered and studied in detail the most distant source of radio emission known to date. The source is a "radio-loud" quasar -- a bright object with powerful jets emitting at radio wavelengths -- that is so far away its light has taken 13 billion years to reach us. The discovery could provide important clues to help astronomers understand the early Universe.
Quasars are very bright objects that lie at the centre of some galaxies and are powered by supermassive black holes. As the black hole consumes the surrounding gas, energy is released, allowing astronomers to ...
Most distant cosmic jet providing clues about early universe
2021-03-08
Astronomers using the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) and Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) have found and studied the most distant cosmic jet discovered so far -- a jet of material propelled to nearly the speed of light by the supermassive black hole in a quasar some 13 billion light-years from Earth. The quasar is seen as it was when the universe was only 780 million years old, and is providing scientists with valuable information about how galaxies evolved and supermassive black holes grew when the universe was that young.
The studies indicate that the quasar -- a galaxy harboring a black hole 300 million times more massive than the Sun -- has a jet of fast-moving particles only about 1,000 years ...
[1] ... [2564]
[2565]
[2566]
[2567]
[2568]
[2569]
[2570]
[2571]
2572
[2573]
[2574]
[2575]
[2576]
[2577]
[2578]
[2579]
[2580]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.