(Press-News.org) Colorectal cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related mortality among men and women in the United States, according to the American Cancer Society. At-home tests, which measure blood in stool as a potential marker for colon cancer, are often used for colorectal cancer screening.
Usage of these tests has increased during the COVID-19 pandemic as people try to avoid clinical visits. However, effectiveness of these screening tools, along with all colon cancer screenings, requires a follow-up colonoscopy if an abnormal test result occurs. The problem is that experts say current follow-up rates are low.
A new study, led by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System (VASDHS), Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and University of California Los Angeles, found delayed time between abnormal stool-based screening and subsequent colonoscopy was associated with an increased risk of a cancer diagnosis and death from colorectal cancer.
The study, published in the February 2, 2021 online edition of Gastroenterology, found those who delayed a colonoscopy by more than twelve months after an abnormal screening test result were at an increased risk of being diagnosed with colorectal cancer. The odds of being diagnosed with late-stage colon cancer increased at 16 months by approximately 33 percent.
"Many colon cancers are asymptomatic and can be growing without the patient even knowing. That is why it is so important to screen. But as our study shows, it is also critical to follow up with a colonoscopy if the screening result is abnormal," said Samir Gupta, MD, corresponding author of the study and professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at UC San Diego School of Medicine and VASDHS.
"Early detection means less invasive treatments and excellent outcomes. When detected early, patients have a 90 percent survival rate with a low risk of recurrence. Late-stage colorectal cancer means more invasive and complex treatment with less than a 15 percent survival rate. As usage of more non-invasive tests for colorectal cancer screening continue to rise during the pandemic, and as more non-invasive screening tests come onto the market in the future, it is critical to ensure all patients with abnormal colorectal cancer screening tests get a timely colonoscopy."
The national study involved 204,733 veterans ages 50 to 75 with an abnormal screening test. A limitation of the study was a high proportion of men; 5,453 women were included.
"There are no national standards or mandates to guide patients, providers or health care systems on the clinically acceptable period of time between abnormal screening and colonoscopy," said Folasade May MD, PhD, senior author of the study and assistant professor of medicine at UCLA. "We hope our findings will inform national standards for appropriate time intervals and interventions to improve timely colonoscopies and colorectal cancer outcomes."
A family history, smoking and poor diet are significant risk factors of colon cancer. Symptoms include rectal bleeding, low-iron anemia, a change in bowel habits and unexplained weight loss.
In 2018, the American Cancer Society updated guidelines for colorectal cancer screening. It is now recommended that those age 45 with an average risk of colon cancer begin regular screenings. Previously, the guideline recommended screening begin at age 50 for people at average risk.
"In general, prevention and early detection efforts have substantially dropped death rates in the United States. However, the pandemic has resulted in many people missing cancer screenings or not doing follow-up colonoscopies after abnormal at-home screenings," said Gupta. "We strongly encourage patients to schedule an appointment if they receive an abnormal screening test. Our hospital and clinical settings are following all COVID-19 safety guidelines. Hesitancy to follow up on your health care could have fatal consequences."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of the study include: Yazmin San Miguel, Joshua Demb and Maria Elena Martinez, all with UC San Diego.
Researchers at the George Washington University and University of California, Los Angeles, have developed and demonstrated for the first time a photonic digital to analog converter without leaving the optical domain. Such novel converters can advance next-generation data processing hardware with high relevance for data centers, 6G networks, artificial intelligence and more.
Current optical networks, through which most of the world's data is transmitted, as well as many sensors, require a digital-to-analog conversion, which links digital systems synergistically to analog components.
Using a silicon photonic chip platform, Volker J. Sorger, an associate professor of electrical and computer ...
DeKalb, Ill. -- If you build it, they might not come. That's the key finding of a END ...
DENVER (Feb. 2, 2021) - Jongeun You, a researcher at the University of Colorado Denver, recently END ...
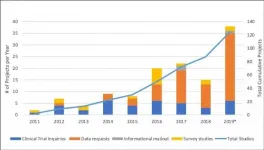
Amsterdam, February 2, 2021 - The Canadian Neuromuscular Disease Registry (CNDR) was launched in 2010 to increase efficient patient access to cutting-edge research and clinical trials, to increase understanding of the natural history and epidemiology of neuromuscular disease across Canada, and to facilitate research collaboration. An assessment of CNDR's accomplishments, published in the Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, found that it has been successful in securing funding and engaging the community over the past 10 years. With more than 4,000 enrolled patients, data from the registry have been used in over 125 research projects as of 2019, including clinical trial and research notifications, patient questionnaires, and data analyses around ...
The mesmerizing flow of a sidewinder moving obliquely across desert sands has captivated biologists for centuries and has been variously studied over the years, but questions remained about how the snakes produce their unique motion. Sidewinders are pit vipers, specifically rattlesnakes, native to the deserts of the southwestern United State and adjacent Mexico.
Scientists had already described the microstructure of the skin on the ventral, or belly, surface of snakes. Many of the snakes studied, including all viper species, had distinctive rearward facing "microspicules" (micron-sized protrusions on scales) that had been interpreted in the context of reducing ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Studies have shown that nearly half of all medical students in the U.S. report symptoms of burnout, a long-term reaction to stress characterized by emotional exhaustion, cynicism and feelings of decreased personal accomplishment. Beyond the personal toll, the implications for aspiring and practicing physicians can be severe, from reduced quality of care to increased risk of patient safety incidents.
According to a new study published on Tuesday, Feb. 2, in JAMA Network Open, students who identify as lesbian, gay or bisexual ...
Period poverty, a lack of access to menstrual hygiene products, and other unmet menstrual health needs can have far-reaching consequences for women and girls in the United States and globally.
New research led by George Mason University's College of Health and Human Services found that more than 14% of college women experienced period poverty in the past year, and 10% experienced period poverty every month. Women who experienced period poverty every month (68%) or in the past year (61.2%) were more likely to experience moderate or severe depression than those who did not experience period poverty (43%).
Dr. Jhumka Gupta, an associate professor at George Mason University was senior author of the study published in BMC Women's Health. ...
MINNEAPOLIS- February 2, 2021 - In Minnesota, there are currently about END ...
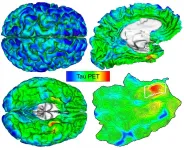
BOSTON - Amyloid-beta and tau are the two key abnormal protein deposits that accumulate in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease, and detecting their buildup at an early stage may allow clinicians to intervene before the condition has a chance to take hold. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has now developed an automated method that can identify and track the development of harmful tau deposits in a patient's brain. The research, which is published in END ...
Nearly 11 percent of people admitted to an intensive care unit in Sweden between 2010 and 2018 received opioid prescriptions on a regular basis for at least six months and up to two years after discharge. That is according to a study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet published in Critical Care Medicine. The findings suggest some may become chronic opioid users despite a lack of evidence of the drugs' long-term effectiveness and risks linked to increased mortality.
"We know that the sharp rise in opioid prescriptions in the U.S. has contributed to a deadly opioid crisis there," says first author Erik von Oelreich, PhD student in the Department of Physiology and ...