Pediatric emergency visits, hospitalizations down sharply during pandemic: study
2021-03-09
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, children's hospitals across the United States have seen signification reductions in the number of children being treated for common pediatric illnesses like asthma and pneumonia, according to a new multicenter study led by Monroe Carell Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt.
Researchers at Children's Hospital found that 42% fewer children were being seen and hospitalized at 44 children's hospital across the U.S. for both respiratory and non-respiratory illnesses, with the most significant reduction seen in children under age 12. Hospitals saw a decline in the number of children seen or hospitalized for respiratory illness by 62%, while there was 38% reduction for non-respiratory illnesses.
The trend, ...
Engineers propose solar-powered lunar ark as 'modern global insurance policy'
2021-03-09
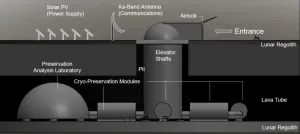
University of Arizona researcher Jekan Thanga is taking scientific inspiration from an unlikely source: the biblical tale of Noah's Ark. Rather than two of every animal, however, his solar-powered ark on the moon would store cryogenically frozen seed, spore, sperm and egg samples from 6.7 million Earth species.
Thanga and a group of his undergraduate and graduate students outline the lunar ark concept, which they call a "modern global insurance policy," in a paper presented over the weekend during the IEEE Aerospace Conference.
"Earth is naturally a volatile environment," said Thanga, a professor of aerospace and mechanical engineering in the UArizona College ...
Lower dose, less toxic radiopharmaceutical produces better outcomes
2021-03-09
Neuroendocrine tumours are cancers that begin in specialised cells called neuroendocrine cells. These cells have traits similar to those of nerve cells and hormone-producing cells. Neuroendocrine tumours, while rare, can occur anywhere in the body. Most affect the cardiothoracic region, eg lungs, appendix, small intestine, pancreas as well as the rectum. There are many types of neuroendocrine tumours: some grow slowly while others develop very rapidly.
Neuroendocrine tumors are characterised by abundant production of somatostatin receptor 2, a naturally circulating hormone that is an important target for scientists studying new treatment approaches.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) is the most commonly used treatment for refractive ...
Study: Increase in taking HIV meds using Amazon Prime model
2021-03-09
Home delivery of HIV medicines in South Africa significantly increased viral suppression compared to those who received clinical care, according to a study by researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The study, conducted with Amazon.com guidance during COVID-19 restrictions in South Africa, showed that among study participants, paying a fee for home delivery and monitoring of antiretroviral therapy (ART) was highly acceptable in the context of low income and high unemployment, and improved health outcomes as a result.
The researching findings were ...
A new predictive model helps identify those at risk for severe COVID-19
2021-03-09
Researchers at the Buck Institute analyzed data from the COVID-19 Symptom Tracker app used by 3 million people in the United Kingdom, adding the use of immunosuppressant medication, use of a mobility aid, shortness of breath, fever, and fatigue to the list of symptoms and comorbidities that increase the risk for severe COVID-19. Results are published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
"Even though there are established risk factors for severe COVID-19 there are no good predictors that enable healthcare providers, or even those who have tested positive, to assess who should seek advanced medical care," says Buck Institute ...
Study reveals process to explain how maternal stress triggers idiopathic preterm birth
2021-03-09
TAMPA, Fla. (March 8, 2021) -- Preterm birth is a END ...
Bridge built between Kähler-Einstein and Chen-Ning Yang's Equations
2021-03-09
Recently, Prof. CHEN Gao from Institute of Geometry and Physics of the University of Science and Technology of China has made breakthrough in the field of complex differential geometry. Using mathematical invention, he buildt a new bridge between the relativity of Einstein and quantum mechanics. This work was published in Inventiones Mathematicae.
In the field of complex differential geometry, there are two crucial physical equations: the Hermitian-Yang-Mills equation, which became the standard model of quantum mechanics, and the Kähler-Einstein equation, which is closely related to relativity. To stably solve these two equations ...
Can chips replace animal testing?
2021-03-09
A team of researchers led by Professor Yaakov Nahmias, director of the Grass Center for Bioengineering at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and founder of Tissue Dynamic, introduced a new technological approach that has the potential to rapidly develop new drugs without the need for animal experiments.
According to Professor Nahmias, "Drug development is a long and expensive endeavor that is defined by multiple failures. The main reason for this failure is that clinical experiments are ultimately based on minimal information gained from animal experiment which often fail to replicate the human response."
The primary animals used in drug development ...
Microchips of the future: Suitable insulators are still missing
2021-03-09
For decades, there has been a trend in microelectronics towards ever smaller and more compact transistors. 2D materials such as graphene are seen as a beacon of hope here: they are the thinnest material layers that can possibly exist, consisting of only one or a few atomic layers. Nevertheless, they can conduct electrical currents - conventional silicon technology, on the other hand, no longer works properly if the layers become too thin.
However, such materials are not used in a vacuum; they have to be combined with suitable insulators - in order to seal them off from unwanted environmental influences, and ...
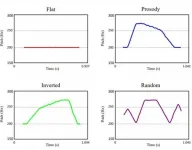
Universal prosodic cues facilitate learning in both animals and humans
2021-03-09
Prosody is a branch of linguistics that analyses and formally represents the elements of oral expression such as pitch, tones and intonation. A study published in Cognition on 5 February shows that there are universal prosodic cues that help with learning in humans and in animals.
This study, published by Juan Manuel Toro, ICREA research professor and Paola Crespo-Bojorque, researchers of the Center for Brain and Cognition (CBC) of the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), is part of the research into language evolution that is being conducted thanks to a European Research Council Starting Grant.
Some of the mechanisms we humans use to learn language are based on general principles ...
Bird parents that receive help live longer
2021-03-09
Long life is common among bird parents that get help with childcare. This finding comes from researchers at the universities of Lund and Oxford who reviewed data from more than 9,000 studies.
Being a parent can be tough. In general, animals that care for many offspring die young, at least in species where parents are not helped by others. However, in some species things are different and parents recruit 'helpers' to assist with childcare. In such group-living species, parents often produce lots of young and also live an exceptionally long time. This new research ...
New therapeutic approach discovered for reducing the risk of thrombosis
2021-03-09
Thrombotic occlusion of blood vessels, which leads to myocardial infarctions, strokes and venous thromboembolisms, is the major cause of death in the western hemisphere. Therefore, it is of critical importance to understand mechanisms preventing thrombus formation. A new study by the research group of Christoph Binder, Principal Investigator at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences and Professor at the Medical University of Vienna, now explains the important role of immunoglobulin-M (IgM) antibodies in preventing thrombosis. The study published in the journal Blood shows that these antibodies recognize microvesicles, which are ...
Two species and a single name: 'Double identity' revealed in a venomous banana spider
2021-03-09
Spiders from the genus Phoneutria - also known as banana spiders - are considered aggressive and among the most venomous spiders in the world, with venom that has a neurotoxic action. These large nocturnal spiders usually inhabit environments disturbed by humans and are often found in banana plantations in the Neotropical region.
One of these spiders, P. boliviensis, is a medically important species widely distributed in Central and South America, whose behaviour, habitat, venom composition, toxicity and bites on humans have already been paid considerable attention in previous research work. Nevertheless, after examining a large pool of museum specimens, biologists from The George Washington University (N. Hazzi and G. Hormiga) began to ...
X marks the spot: How genes on the sex chromosomes are controlled
2021-03-09
Tsukuba, Japan - Because human females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y, somatic cells have special mechanisms that keep expression levels of genes on the X chromosome the same between both sexes. This process is called dosage compensation and has been extensively studied in the fruit fly Drosophila. Now, researchers at the University of Tsukuba (UT) continued work with Drosophila to show that dosage compensation does not occur in the germ cells of male flies.
In an article published in Scientific Reports, the UT researchers investigated this phenomenon in fly primordial germ cells (PGCs), which are present in embryos and are the precursor cells to what ultimately become ...
Earth's deep mantle may have proton rivers made of superionic phases
2021-03-09
Pierfranco Demontis said in 1988, "Ice becomes a fast-ion conductor at high pressure and high temperatures," but his prediction was only hypothetical until recently. After 30 years of study, superionic water ice was verified experimentally in 2018. Superionicity may eventually explain the strong magnetic field in giant planetary interiors.
What about Earth, whose interiors are also under extreme pressure and temperature conditions? Although three-quarters of Earth's surface is covered by water, standalone water or ice rarely exists in Earth's interiors. The most common unit of "water" is hydroxyl, which is associated with host minerals to make ...
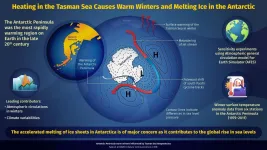
Antarctic Peninsula warming up due to heat in Tasman sea
2021-03-09
The melting of the Earth's ice cover intensified in the 20th century, with glaciers and sea ice in the Arctic and Antarctic regions melting at alarming speeds. In fact, The Antarctic Peninsula (AP), which is the only landmass of Antarctica extending out past the Antarctic Circle, was found to be one of the most rapidly warming regions on the planet during the second half of the 20th century. This rapid change in climate has raised serious concerns of rising sea levels the world over.
Multiple factors have been associated with the melting of the ice cover: the primary factor being the greenhouse gas emissions from human activities that cause ...
A remote, computerized training program eases anxiety in children
2021-03-09
Anxiety levels in the United States are rising sharply and have especially intensified in younger populations. According to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America, anxiety disorders affect 31.9 percent of children ages 13 to 18 years old. Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, children and adolescents have experienced unprecedented interruptions to their daily lives and it is expected that these disruptions may precipitate mental illness, including anxiety, depression, and/or stress related symptoms.
Traditional anxiety and depression treatments include ...
The aurora's very high altitude booster
2021-03-09
A critical ingredient for auroras exists much higher in space than previously thought, according to new research in the journal Scientific Reports. The dazzling light displays in the polar night skies require an electric accelerator to propel charged particles down through the atmosphere. Scientists at Nagoya University and colleagues in Japan, Taiwan and the US have found that it exists beyond 30,000 kilometres above the Earth's surface - offering insight not just about Earth, but other planets as well.
The story of aurora formation begins with supersonic plasma propelled from the Sun into space as high-speed, charged particles. When these charged particles get close to Earth, they are ...
New brain sensor offers Alzheimer's answers
2021-03-09
Scientists at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have developed a tool to monitor communications within the brain in a way never before possible, and it has already offered an explanation for why Alzheimer's drugs have limited effectiveness and why patients get much worse after going off of them.
The researchers expect their new method will have tremendous impact on our understanding of depression, sleep disorders, autism, neurological diseases and major psychiatric conditions. It will speed scientific research into the workings of the brain, they say, and facilitate the development of new treatments.
"We can now 'see' how brain cells communicate in sharp detail in both the healthy and diseased brains," said lead researcher J. Julius Zhu, PhD, of UVA's Department ...
Low-voltage, low-power pressure sensors for monitoring health
2021-03-09
(LOS ANGELES) - Recent advances in technology have opened many possibilities for using wearable and implantable sensors to monitor various indicators of patient health. Wearable pressure sensors are designed to respond to very small changes in bodily pressure, so that physical functions such as pulse rate, blood pressure, breathing rates and even subtle changes in vocal cord vibrations can be monitored in real time with a high degree of sensitivity.
Such responses occur when a substance in the sensor "gates," or allows selected pressure signals to pass to a transistor, which then conducts and amplifies these signals for detection. A recent type of transistor, organic electrochemical transistors ...
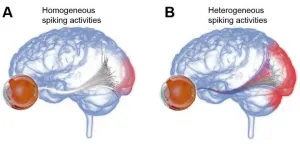
Diverse neural signals are key to rich visual information!
2021-03-09
Visual sensation begins at the retina, which is the neural tissue located at the back of eyeballs. It has been known that the retina detects light using photoreceptors which are light-sensitive nerve cells.In case of retinal degenerative diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration, those light sensing neurons are gradually damaged, leading to a profound vision loss. At this moment, no cure is available for the abovementioned ailments. But, microelectronic retinal prostheses can create artificial vision by electrically stimulating remaining retinal neurons although the prosthetic vision is still far removed from normal vision.
To further improve the quality of prosthetic artificial vision, Dr. Maesoon ...
Wild relatives offer a solution to devastating chickpea disease Ascochyta blight
2021-03-09
A staple for many, chickpeas are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber and offer many health benefits, such as improving digestion and reducing the risk of ailments including heart disease and cancer. However, chickpeas possess a rather narrow genetic diversity and are susceptible to Ascochyta blight, a devastating disease that can cause a yield loss of up to 100 percent. In Australia alone, this disease costs an average of $4.8 million annually.
To help curtail the impact of Ascochyta blight, plant pathologists in Western Australia have turned to wild relatives of the ...
Covid-19 risk increases with airborne pollen
2021-03-09
In the spring of 2020, the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic appeared to coincide with the tree pollen season in the northern hemisphere. These observations prompted an international team of researchers to conduct an extensive investigation: The scientists wanted to know whether there is a demonstrable link between airborne pollen concentrations and SARS-CoV-2 infection rates.
Pollen is a significant environmental factor influencing infection rates
Under the leadership of first author Athanasios Damialis, the team at the Chair of Environmental Medicine at TUM collected data on airborne pollen concentrations, weather conditions and SARS-CoV-2 infections - taking into consideration the variation of infection rates from ...
Opinions and attitudes can last when they are based on emotion
2021-03-09
Depending on the topic, people's attitudes can change from moment to moment or last a lifetime. The factors that make one opinion long-lasting and another ephemeral, however, are not always clear.
Past studies have demonstrated that opinions based on hard facts and data can remain constant over time, but new research published in the journal Psychological Science reveals that attitudes based on feelings and emotions can also stand the test of time. This research has implications for both predicting whose attitudes are fixed versus fleeting and how to nudge people to form more long-lasting opinions.
"We have ...
Digital books harm young children's learning--unless the books have the right enhancements
2021-03-09
Washington, March 9, 2021--A comprehensive meta-analysis of prior research has found, overall, that children ages 1 to 8 were less likely to understand picture books when they read the digital, versus print, version. However, when digital picture books contain the right enhancements that reinforce the story content, they outperform their print counterparts. The results were published today in Review of Educational Research, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
Authors Natalia Kucirkova at the University of Stavanger in Norway and The Open University in the United Kingdom, and May Irene Furenes and Adriana G. Bus at the University of Stavanger, analyzed the results of 39 studies that included a total 1,812 children between the ages of 1 and 8. For their ...
[1] ... [2559]
[2560]
[2561]
[2562]
[2563]
[2564]
[2565]
[2566]
2567
[2568]
[2569]
[2570]
[2571]
[2572]
[2573]
[2574]
[2575]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.