Excessive social media use linked to binge eating in US preteens
2021-03-01
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO
Toronto, ON - Children in the United States who have more screen time at ages 9-10 are more likely to develop binge-eating disorder one year later, according to a new national study.
The study, published in the International Journal of Eating Disorders on March 1, found that each additional hour spent on social media was associated with a 62% higher risk of binge-eating disorder one year later. It also found that each additional hour spent watching or streaming television or movies led to a 39% ...
Cybersecurity researchers build a better 'canary trap'
2021-03-01
HANOVER, N.H. - March 1, 2020 - During World War II, British intelligence agents planted false documents on a corpse to fool Nazi Germany into preparing for an assault on Greece. "Operation Mincemeat" was a success, and covered the actual Allied invasion of Sicily.
The "canary trap" technique in espionage spreads multiple versions of false documents to conceal a secret. Canary traps can be used to sniff out information leaks, or as in WWII, to create distractions that hide valuable information.
WE-FORGE, a new data protection system designed at Dartmouth's Department ...
Assessing a compound's activity, not just its structure, could accelerate drug discovery
2021-03-01
Assessing a drug compound by its activity, not simply its structure, is a new approach that could speed the search for COVID-19 therapies and reveal more potential therapies for other diseases.
This action-based focus -- called biological activity-based modeling (BABM) -- forms the core of a new approach developed by National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) researchers and others. NCATS is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Researchers used BABM to look for potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents whose actions, not their structures, are similar to those of compounds already shown to be effective.
NCATS scientists ...
The missing trillions
2021-03-01
The hidden social, environmental and health costs of the world's energy and transport sectors is equal to more than a quarter of the globe's entire economic output, new research from the University of Sussex Business School and Hanyang University reveals.
According to analysis carried out by Professor Benjamin K. Sovacool and Professor Jinsoo Kim, the combined externalities for the energy and transport sectors worldwide is an estimated average of $24.662 trillion - the equivalent to 28.7% of global Gross Domestic Product.
The study found that the true cost of coal should be more than twice as high as current prices when factoring in the currently unaccounted ...
The selection of leaders of political parties through primary elections penalizes women
2021-03-01
A study by two researchers at the UPF Department of Political and Social Sciences (DCPIS) has examined the effect of selecting party leaders by direct vote by the entire membership (a process known in southern Europe as "primaries" and in English-speaking countries as "one-member-one -vote", OMOV) on the likelihood of a woman winning a leadership competition against male rivals.
Javier Astudillo and Andreu Paneque, a tenured lecturer and PhD with the DCPIS, respectively, and members of the Institutions and Political Actors Research Group, are the authors of the article published recently in the journal ...
In era of online learning, new testing method aims to reduce cheating
2021-03-01
TROY, N.Y. -- The era of widespread remote learning brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic requires online testing methods that effectively prevent cheating, especially in the form of collusion among students. With concerns about cheating on the rise across the country, a solution that also maintains student privacy is particularly valuable.
In research published today in npj Science of Learning, engineers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute demonstrate how a testing strategy they call "distanced online testing" can effectively reduce students' ability to receive help from one another in order to score higher on a test taken at individual homes during social distancing.
"Often in remote online exams, students ...
Behavior of wild capuchin monkeys can be identified by marks left on their tools
2021-03-01
A group of researchers including Tiago Falótico, a Brazilian primatologist at the University of São Paulo's School of Arts, Sciences and Humanities (EACH-USP), archeologists at Spain's Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution (IPHES) and University College London in the UK, and an anthropologist at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Germany, have published an article in the Journal of Archeological Science: Reports describing an analysis of stone tools used by bearded capuchin monkeys (Sapajus libidinosus) that inhabit ...
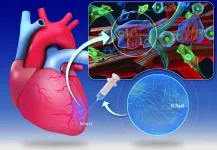
Hydrogel injection may change the way the heart muscle heals after a heart attack
2021-03-01
Researchers at CÚRAM, the SFI Research Centre for Medical Devices based at National University of Ireland Galway, and BIOFORGE Lab, at the University of Valladolid in Spain, have developed an injectable hydrogel that could help repair and prevent further damage to the heart muscle after a heart attack.
The results of their research have just been published in the prestigious journal Science Translational Medicine.
Myocardial infarction or heart disease is a leading cause of death due to the irreversible damage caused to the heart muscle (cardiac tissue) during a heart attack. The regeneration of cardiac tissue is minimal so that the damage caused cannot be repaired by itself. ...
Lake turbidity mitigates impact of warming on walleyes in upper Midwest lakes
2021-03-01
Because walleyes are a cool-water fish species with a limited temperature tolerance, biologists expected them to act like the proverbial "canary in a coal mine" that would begin to suffer and signal when lakes influenced by climate change start to warm. But in a new study, a team of researchers discovered that it is not that simple.
"After analyzing walleye early-life growth rates in many lakes in the upper Midwest over the last three decades, we determined that water clarity affects how growth rates of walleyes change as lakes start to warm," said Tyler Wagner, Penn State adjunct professor of fisheries ecology. ...
Understanding the spatial and temporal dimensions of landscape dynamics
2021-03-01
The Earth's surface is subject to continual changes that dynamically shape natural landscapes. Global phenomena like climate change play a role, as do short-term, local events of natural or human origin. The 3D Geospatial Data Processing (3DGeo) research group of Heidelberg University has developed a new analysis method to help improve our understanding of processes shaping the Earth's surface like those observed in coastal or high-mountain landscapes. Unlike conventional methods that usually compare two snapshots of the topography, the Heidelberg approach can determine - fully automatically and over long periods - when and where surface alterations occur and which type of associated changes they represent.
The method, known ...
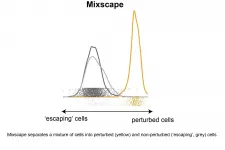
New algorithm identifies 'escaping' cells in single-cell CRISPR screens
2021-03-01
A team of researchers from New York University and the New York Genome Center has developed a new computational tool to help understand the function and regulation of human genes. The results, published today in the journal Nature Genetics, demonstrate how to interpret experiments that combine the use of CRISPR to perturb genes along with multimodal single-cell sequencing technologies.
The article describes how the new approach, called mixscape, helped to identify a new molecular mechanism for the regulation of immune checkpoint proteins that govern the immune system's ability to identify and destroy cancer cells.
"Our approach will help scientists to connect ...
Second order optical merons, or light pretending to be a ferromagnet
2021-03-01
The scientists have demonstrated how to structure light such that its polarization behaves like a collective of spins in a ferromagnet forming half-skyrmion (also known as merons). To achieve this the light was trapped in a thin liquid crystal layer between two nearly perfect mirrors. Skyrmions in general are found, e.g., as elementary excitations of magnetization in a two-dimensional ferromagnet but do not naturally appear in electromagnetic (light) fields.
One of the key concepts in physics, and science overall is the notion of a "field" which can describe the spatial distribution ...
Novel soft tactile sensor with skin-comparable characteristics for robots
2021-03-01
A joint research team co-led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has developed a new soft tactile sensor with skin-comparable characteristics. A robotic gripper with the sensor mounted at the fingertip could accomplish challenging tasks such as stably grasping fragile objects and threading a needle. Their research provided new insight into tactile sensor design and could contribute to various applications in the robotics field, such as smart prosthetics and human-robot interaction.
Dr Shen Yajing, Associate Professor at CityU's Department of Biomedical Engineering ...
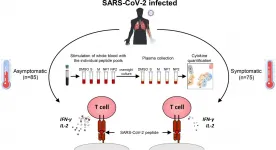
Balanced T cell response key to avoiding COVID-19 symptoms, study suggests
2021-03-01
By analyzing blood samples from individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2, researchers in Singapore have begun to unpack the different responses by the body's T cells that determine whether or not an individual develops COVID-19. The study, published today in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that clearing the virus without developing symptoms requires T cells to mount an efficient immune response that produces a careful balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory molecules.
Many people infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus do not develop any symptoms, and the infection ...
Adverse childhood and combat experiences may drive veterans' suicidal thoughts
2021-03-01
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- The rate of suicide among post-9/11 military veterans has been rising for nearly a decade. While there are a number of factors associated with suicide, veterans have unique experiences that may contribute to them thinking about killing themselves.
"Compared to their civilian peers, veterans are more likely to report having experienced traumatic adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) such as physical and emotional abuse," stated Keith Aronson, associate director of the Clearinghouse for Military Family Readiness at Penn State and the Social Science Research Institute ...
Study examines what makes people susceptible to fake health news
2021-03-01
LAWRENCE -- A new study from University of Kansas journalism & mass communication researchers examines what influences people to be susceptible to false information about health and argues big tech companies have a responsibility to help prevent the spread of misleading and dangerous information.
Researchers shared a fake news story with more than 750 participants that claimed a deficiency of vitamin B17 could cause cancer. Researchers then measured if how the article was presented -- including author credentials, writing style and whether the article was labeled as "suspicious" or "unverified" -- affected how participants perceived its credibility and whether they would adhere to the article's recommendations or share it on social media. The findings showed that ...
Metal whispering: Finding a better way to recover precious metals from electronic waste
2021-03-01
AMES, Iowa - Inspired by nature's work to build spiky structures in caves, engineers at Iowa State University have developed technology capable of recovering pure and precious metals from the alloys in our old phones and other electrical waste.
Using controlled applications of oxygen and relatively low temperatures, the engineers say they can dealloy a metal by slowly moving the most reactive components to the surface where they form stalagmite-like spikes of metal oxides.
That leaves the least-reactive components in a purified, liquid core surrounded by brittle metal-oxide spikes "to create a so-called 'ship-in-a-bottle structure,'" said Martin Thuo, the leader of the research project and an associate professor of materials science and ...
New cancer scan could guide brain surgery
2021-03-01
A type of ultrasound scan can detect cancer tissue left behind after a brain tumour is removed more sensitively than surgeons, and could improve the outcome from operations, a new study suggests.
The new ultrasound technique, called shear wave elastography, could be used during brain surgery to detect residual cancerous tissue, allowing surgeons to remove as much as possible.
Researchers believe that the new type of scan, which is much faster to carry out and more affordable than 'gold standard' MRI scans, has the potential to reduce a patient's risk of relapse by cutting the chances that a tumour will grow ...
The risk of ADHD may be lower if children grow up in green environments
2021-03-01
The amount of green space surrounding children's homes could be important for their risk of developing ADHD. This is shown by new research results from iPSYCH.
A team of researchers from Aarhus University has studied how green space around the residence affects the risk of children and adolescents being diagnosed with ADHD. And the researchers find an association.
"Our findings show that children who have been exposed to less green surroundings in their residential area in early childhood, which we define as lasting up until age five, have an increased risk of receiving an ADHD diagnosis when compared to children who have been surrounded by the highest level of green space," says ...
Deciphering the genetics behind eating disorders
2021-03-01
Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa and binge-eating disorder are the three main eating disorders that 4 out of in 10 individuals living in Western Europe will experience at some point in their lives. In recent years, studies on the genetic basis of anorexia nervosa have highlighted the existence of predisposing genetic markers, which are shared with other psychiatric disorders. By analysing the genome of tens of thousands of British people, a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), King's College London, the University College London, the University of North Carolina (UNC) and The Icahn ...
A new theory for how memories are stored in the brain
2021-03-01
Research from the University of Kent has led to the development of the MeshCODE theory, a revolutionary new theory for understanding brain and memory function. This discovery may be the beginning of a new understanding of brain function and in treating brain diseases such as Alzheimer's.
In a paper published by Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, Dr Ben Goult from Kent's School of Biosciences describes how his new theory views the brain as an organic supercomputer running a complex binary code with neuronal cells working as a mechanical computer. He explains ...
Hotter, drier, CRISPR: editing for climate change
2021-03-01
Gene editing technology will play a vital role in climate-proofing future crops to protect global food supplies, according to scientists at The University of Queensland.
Biotechnologist Dr Karen Massel from UQ's Centre for Crop Science has published a review of gene editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 to safeguard food security in farming systems under stress from extreme and variable climate conditions.
"Farmers have been manipulating the DNA of plants using conventional breeding technologies for millennia, and now with new gene-editing technologies, we can do this with unprecedented safety, precision and speed," Dr Massel said.
"This type of gene editing mimics the way cells repair in nature."
Her review recommended ...
Childhood exposure to diversity is best chance for community cohesion in immigration
2021-03-01
New research from the University of Kent reveals social cohesion with immigration is best ensured through childhood exposure to diversity in local neighbourhoods, leading to acceptance of other groups.
The research, which is published in Oxford Economic Papers, builds on the Nobel Laureate economist Thomas Schelling's Model of Segregation, which showed that a slight preference by individuals and families towards their own groups can eventually result in complete segregation of communities.
Shedding new light on this issue, researchers from Kent's School of Economics have introduced the theory ...
Will we enjoy work more once routine tasks are automated? - Not necessarily, a study shows
2021-03-01
Will we enjoy our work more once routine tasks are automated? - Not necessarily, suggests a recent study
Research conducted at Åbo Akademi University suggests that when routine work tasks are being replaced with intelligent technologies, the result may be that employees no longer experience their work as meaningful.
Advances in new technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics and digital applications have recently resurrected discussions and speculations about the future of working life. Researchers predict that new technologies will affect, in particular, routine and structured work tasks. According to estimations, 7-35 percent ...
Walking away from the beat - why police officers are voluntarily leaving in large numbers
2021-03-01
Home Office data shows the number of police officers voluntarily resigning from the force in England and Wales has more than doubled in the last eight years.
Scant attention has been paid to the reason for this mass exodus. Until now. Researchers from the University of Portsmouth studied government statistics, and discovered the numbers of officers voluntarily resigning from the police service is rising - from 1,158 in the year ending March 2012 to 2,363 in the year ending March 2020. The figure amounts to 1.83 per cent of the total police officer population in England and Wales up from 0.86 per cent eight years ago.
Dr Sarah Charman, from the Institute of Criminal Justice Studies at the University of Portsmouth, led the study. ...
[1] ... [2551]
[2552]
[2553]
[2554]
[2555]
[2556]
[2557]
[2558]
2559
[2560]
[2561]
[2562]
[2563]
[2564]
[2565]
[2566]
[2567]
... [8791]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.