Optimizing disinfection to prevent spread of antibiotic resistance in wastewater
2021-03-02
For nearly a century, improvement in human healthcare has depended heavily on the efficiency with which we can treat bacterial diseases. But today, antibiotic resistance--the ability of certain mutant super-bacteria to block out antibiotics--poses a major threat to healthcare, food security, and overall social development worldwide, threatening to upend much of the progress our civilization has achieved.
Scientists are now urgently attempting to tackle this problem from various angles. Professor Yunho Lee at Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Korea, whose contribution is published in the American Chemical Society's Environmental Science and Technology, is looking at it from the point of view of his field of research--wastewater ...
Indoor air quality study shows aircraft in flight may have lowest particulate levels
2021-03-02
If you're looking for an indoor space with a low level of particulate air pollution, a commercial airliner flying at cruising altitude may be your best option. A newly reported study of air quality in indoor spaces such as stores, restaurants, offices, public transportation -- and commercial jets -- shows aircraft cabins with the lowest levels of tiny aerosol particles.
Conducted in July 2020, the study included monitoring both the number of particles and their total mass across a broad range of indoor locations, including 19 commercial flights in which measurements took place throughout ...
The expanding possibilities of bio-based polymers
2021-03-02
Finding innovative and sustainable solutions to our material needs is one of the core objectives of green chemistry. The myriad plastics that envelop our daily life - from mattresses to food and cars - are mostly made from oil-based monomers which are the building blocks of polymers. Therefore, finding bio-based monomers for polymer synthesis is attractive to achieve more sustainable solutions in materials development.
In a paper published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, researchers from the Kleij group present a new route to prepare biobased polyesters with tuneable properties. The researchers ...
Here's how insects coax plants into making galls
2021-03-02
Insects can reprogram plant growth, transforming ordinary plant parts into intricately patterned shelters that are safe havens for feeding and reproduction.
These structures, called galls, have fascinated biologists for centuries. They're crafted by a variety of insects, including some species of aphids, mites, and wasps. And they take on innumerable forms, each specific in shape and size to the insect species that's created it - from knobs to cone-shaped protrusions to long, thin spikes. Some even resemble flowers.
Insects create galls by manipulating the development of plants, but figuring out exactly how they perform this feat "feels like ...
Mammal ancestors moved in their own unique way
2021-03-02
The backbone is the Swiss Army Knife of mammal locomotion. It can function in all sorts of ways that allows living mammals to have remarkable diversity in their movements. They can run, swim, climb and fly all due, in part, to the extensive reorganization of their vertebral column, which occurred over roughly 320 million years of evolution.
Open any anatomy textbook and you'll find the long-standing hypothesis that the evolution of the mammal backbone, which is uniquely capable of sagittal (up and down) movements, evolved from a backbone that functioned ...
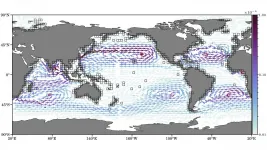
How does plastic debris make its way into ocean garbage patches?
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 2, 2021 -- Tons of plastic debris get released into the ocean every day, and most of it accumulates within the middle of garbage patches, which tend to float on the oceans' surface in the center of each of their regions. The most infamous one, known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, is in the North Pacific Ocean.
Researchers in the U.S. and Germany decided to explore which pathways transport debris from the coasts to the middle of the oceans, as well as the relative strengths of different subtropical gyres in the oceans and how they influence long-term accumulation of debris.
In Chaos, from AIP Publishing, Philippe Miron, Francisco Beron-Vera, Luzie Helfmann, and Peter Koltai report creating a Markov chain ...
Association between COVID-19 lockdown measures, ED visits for violence-related injuries in Wales
2021-03-02
What The Study Did: This study investigates emergency department visits for violence-related injuries occurring at home and outside the home in Cardiff, Wales, before and after COVID-19 lockdown measures were instituted in March 2020.
Authors: Jonathan P. Shepherd, Ph.D., Crime and Security Research Institute at Cardiff University in Wales, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.25511)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Belly fat resistant to every-other-day fasting: study
2021-03-02
In a mouse study, Australian researchers have mapped out what happens behind the scenes in fat tissue during intermittent fasting, showing that it triggers a cascade of dramatic changes, depending on the type of fat deposits and where they are located around the body.
Using state-of-the-art instruments, University of Sydney researchers discovered that fat around the stomach, which can accumulate into a 'protruding tummy' in humans, was found to go into 'preservation mode', adapting over time and becoming more resistant to weight loss.
The findings are published today in Cell Reports.
A research team led by Dr Mark Larance examined fat tissue types from different locations to understand their role during every-other-day fasting, ...
Study reveals impact of lockdown on violence in a UK capital city
2021-03-02
The first UK COVID-19 lockdown saw a "rapid and sustained" fall in violence outside the home in the Welsh capital city, a new study led by Cardiff University has shown.
Researchers from Cardiff University's Crime and Security Research Institute (CSRI) and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention studied data from Cardiff's sole emergency department (ED) from March to June 2020 and compared it to weekly data from January 2019 onwards.
They found there were almost 60% fewer attendances per week for violent injury outside the home in the first lockdown during ...
Complex fluid dynamics may explain hydroplaning
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 2, 2021 -- When a vehicle travels over a wet or flooded road, water builds up in front of the tire and generates a lift force. In a phenomenon known as hydroplaning, this force can become large enough to lift the vehicle off the ground.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, scientists from the CNRS, the University of Lyon, and The Michelin Group use a laser imaging technique to study water flow in front of and through tire grooves.
To counteract hydroplaning, tread designs are chosen to drain water from the front of the tire without decreasing its ability to adhere to the road. Very few quantitative experimental studies of the movement of water through tire grooves have been done, so little is known about the exact flow patterns in ...
Assessment of hotel-based COVID-19 isolation, quarantine strategy for people experiencing homelessness
2021-03-02
What The Study Did: This study suggests that, during the COVID-19 pandemic, a hotel- based isolation and quarantine strategy that delivers integrated medical and behavioral health support to people experiencing homelessness can be done safely outside the hospital setting.
Authors: Jonathan D. Fuchs, M.D., M.P.H., of the San Francisco Department of Public Health, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0490)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
Assessment of respiratory function in infants, young children wearing face masks during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-03-02
What The Study Did: Wearing surgical face masks for 30 minutes was not associated with changes in respiratory parameters or clinical signs of respiratory distress in this study of 47 infants and young children in Italy.
Authors: Silvia Bloise, M.D., of Sapienza University of Rome in Italy, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0414)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Requests for brand name over generic prescription drugs cost the Medicare program $1.7 billion in a single year, study finds
2021-03-02
The Medicare Part D program would have saved $977 million in a single year if all branded prescription drugs requested by prescribing clinicians had been substituted by a generic option, according to a new study by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. And if Medicare patients had requested generic drugs instead of brand name drugs, the Medicare Part D program would have saved an additional $673 million in one year, for a total savings of $1.7 billion.
Medicare Part D offers supplemental outpatient drug coverage plans for seniors ...
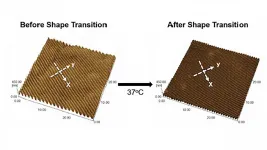
Using stimuli-responsive biomaterials to understand heart development, disease
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 2, 2021 -- Cardiovascular disease remains the number one cause of death globally. Unfortunately, the heart cannot regenerate new tissue, because the cardiomyocytes, or heart muscle cells, do not divide after birth.
In their paper, published in APL Bioengineering by AIP Publishing, Syracuse researchers developed a shape memory polymer to grow cardiomyocytes. Raising the material's temperature from 30 degrees Celsius to 37 degrees Celsius turned the polymer's flat surface into nanowrinkles, which promoted cardiomyocyte alignment.
The research is part of the growing field of mechanobiology, which investigates how physical forces between cells and changes ...
'Fish DJ' tackles fish hearing
2021-03-02
A 'Fish DJ' at The University of Queensland has used her knowledge of cool beats to understand brain networks and hearing in baby fish.
The DJ-turned-researcher used her acoustic experience to design a speaker system for zebrafish larvae and discovered that their hearing is considerably better than originally thought.
PhD candidate Rebecca Poulsen from the Queensland Brain Institute said that combining this new speaker system with whole-brain imaging showed how larvae can hear a range of different sounds they would encounter in the wild.
"For many years ...
AAHA and AAFP release updated feline life stage guidelines to the veterinary community
2021-03-02
[LAKEWOOD, CO; BRIDGEWATER, NJ; March 2, 2021] Two of the world's leading veterinary organizations are proud to announce updated recommendations in the 2021 AAHA/AAFP Feline Life Stage Guidelines. The American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) and the American Association of Feline Practitioners (AAFP) convened a Task Force of experts in feline medicine to define distinct feline life stages and provide a framework for individualized healthcare plans.
Understanding a cat's life stage and lifestyle greatly impacts healthcare strategies. Veterinary professionals have a responsibility to stress ...
Energy switching decisions could widen social inequalities
2021-03-02
New energy tariffs could leave people on bad deals even worse off despite the potential benefits for everyone, research has found.
The study, led by the University of Leeds, found new types of energy contracts designed for a low carbon future could benefit all types of customer, with opportunities to sell excess energy from solar panels or incentives for using energy at off-peak times.
However, many people were unlikely to choose them because they were disengaged from the energy market, didn't trust energy companies, or already feel satisfied with their current tariffs. ...
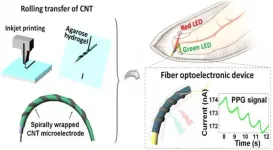
Soft and comfortable e-textiles that can be used to measure photoplenthysmography
2021-03-02
Advances in wearable devices have enabled e-textiles, which fuse lightweight and comfortable textiles with smart electronics, and are garnering attention as the next-generation wearable technology. In particular, fiber electronic devices endowed with electrical properties, while retaining the specific characteristics of textiles, are key elements in manufacturing e-textiles.
Optoelectronic devices are generally constructed using layers of semiconductors, electrodes, and insulators; their performance is greatly affected by the size and structure of the electrodes. Fiber electronic components for e-textiles need to be fabricated on thin, pliable threads; since these ...
Rice plant resists arsenic
2021-03-02
The agricultural cultivation of the staple food of rice harbours the risk of possible contamination with arsenic that can reach the grains following uptake by the roots. In their investigation of over 4,000 variants of rice, a Chinese-German research team under the direction of Prof. Dr Rüdiger Hell from the Centre for Organismal Studies (COS) of Heidelberg University and Prof. Dr Fang-Jie Zhao of Nanjing Agricultural University (China) discovered a plant variant that resists the toxin. Although the plants thrive in arsenic-contaminated fields, the grains contain far less arsenic than other ...
Astrophysicist's 2004 theory confirmed: Why the Sun's composition varies
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON -- About 17 years ago, J. Martin Laming, an astrophysicist at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory, theorized why the chemical composition of the Sun's tenuous outermost layer differs from that lower down. His theory has recently been validated by combined observations of the Sun's magnetic waves from the Earth and from space.
His most recent scientific journal article describes how these magnetic waves modify chemical composition in a process completely new to solar physics or astrophysics, but already known in optical sciences, having been the subject of Nobel Prizes awarded to Steven Chu in 1997 and Arthur Ashkin in 2018.
Laming ...
Human instinct can be as useful as algorithms in detecting online 'deception'
2021-03-02
Travellers looking to book a hotel should trust their gut instinct when it comes to online reviews rather than relying on computer algorithms to weed out the fake ones, a new study suggests.
Research, led by the University of York in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, shows the challenges of online 'fake' reviews for both users and computer algorithms. It suggests that a greater awareness of the linguistic characteristics of 'fake' reviews can allow online users to spot the 'real' from the 'fake' for themselves.
Dr Snehasish Banerjee, Lecturer in Marketing from the University of York's Management School, said: "Reading and writing online reviews ...
Under 55's found lockdown most challenging, finds survey
2021-03-02
A UK wide survey of 2252 adults, carried out five weeks into the first lockdown revealed 95% of those who took part were following lockdown restrictions. Of that 95% more than 80% reported finding it challenging. Adjusting to changes in daily routines, and mental and physical health struggles were the most common challenges faced by participants. Women and adults under the age of 55 were most likely to report experiencing challenges.
The research, 'What challenges do UK adults face when adhering to COVID-19-related instructions? Cross-sectional survey in a representative sample'*, was published in the journal, Preventive ...
Sequential treatment with immunotherapy and checkpoint inhibitors prolongs anti-tumor activity
2021-03-02
TAMPA, Fla. - Advanced melanoma is one of the deadliest types of cancer, with a 5-year survival rate of only 27% for patients with distant metastases. Recent advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have greatly improved patient prognosis; however, many patients eventually develop resistance and disease recurrence. Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center are investigating how to combine and sequence new therapies to improve survival. In a new article published in Cancer Immunology Research, the Moffitt team shows that sequential administration of immunotherapy followed by targeted therapy prolongs anti-tumor responses in preclinical models and may be a potential ...
Groundbreaking research into white-rot fungi proves its value in carbon sequestration
2021-03-02
A foundational study conducted by scientists at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) shows for the first time that white-rot fungi are able to use carbon captured from lignin as a carbon source.
The research confirms a hypothesis from Davinia Salvachúa Rodriguez, the senior author of a newly published paper. Until now, scientists were unsure whether white-rot fungi--the most efficient lignin-degrading organisms in nature--actually consume the products generated from breaking down lignin.
"What we have demonstrated here is that white-rot fungi can actually utilize lignin-derived aromatic compounds as a carbon source, which means they can eat them and utilize them to grow," Salvachúa said. "That is another strategy for carbon sequestration in ...
A new blindness gene uncovered in a canine study
2021-03-02
Inherited retinal dystrophy is a common cause of blindness, with as many as two million people suffering from the disorder globally. No effective treatment is available for retinal dystrophies. Gene therapy is expected to offer a solution, but developing such therapies is possible only when the genetic cause of the disease is known. Related mutations have been identified in more than 70 genes so far, but the genetic background of the disease remains unknown in as many as half of the patients.
"Retinal dystrophy has been described in over 100 dog breeds, with related investigations helping to identify new genes associated and pathogenic mechanisms with blindness across different ...
[1] ... [2545]
[2546]
[2547]
[2548]
[2549]
[2550]
[2551]
[2552]
2553
[2554]
[2555]
[2556]
[2557]
[2558]
[2559]
[2560]
[2561]
... [8791]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.