Science takes guesswork out of cheese production and reduces waste
2021-03-01
Making cheese leaves a lot to chance as a batch could be ripened for months or even years before a problem is discovered, which could send a prized batch of cheddar to be sold off cheap as an ingredient for processed cheese.
It's part of why cheese is so complex and expensive to make - a factory could invest lots of time and money into what they think will be a top-graded batch, only to discover it's a flop when it's too late to fix.
But new research from RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia allows quality to be checked much earlier and more precisely in the process, giving manufacturers a better chance to react to issues with the ripening process.
Dr ...
The jaws of life - how hypoxia exposure affects jaw cartilage growth
2021-03-01
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) observe underdeveloped jaw cartilage in newborn rats exposed to periods of low oxygen
Tokyo, Japan - Breathing in adequate amounts of oxygen is critical for human life. However, certain disorders can cause individuals to go through periods where they are exposed to periodical low levels of oxygen, called intermittent hypoxia (IH). This is common in people who suffer from some sleep disorders like obstructive sleep apnea. Although we know IH can cause neurological development issues, it is not clear how it affects cartilage. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have shown that IH can result in underdeveloped jaw cartilage in rats.
In an article published in Scientific Reports, researchers ...
Protein kinases significantly contribute to the immunodeficiency in HIV patients
2021-03-01
HIV infections are treated with antiviral drugs which effectively prevent the disease from developing. While pharmacological HIV therapy has advanced considerably, the virus cannot be entirely eliminated from the body with currently available drugs.
However, in roughly one-fifth of HIV patients the immune system does not recover as expected: the quantity of CD4 T cells, reflecting the status of the immune system, remains low even when the quantity of HI viruses in blood is suppressed to very low levels or below the measurement threshold. In such patients, indications of chronic immune activation, which erodes the immune system, can be detected.
In cooperation with the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg in Germany, researchers at the University of Helsinki have ...
Model for wildlife tourism
2021-03-01
Wildlife tourism including white shark cage-diving is growing in popularity, but these industries remain highly contentious amongst tourists, conservationists, and scientists alike.
Many voice concerns about possible negative impacts - especially when it targets potentially dangerous animals - while proponents cite the socio-economic benefits to justify wildlife tourism activities.
In reality, wildlife tourism is complex, requiring managers to balance the benefits and drawbacks to determine what is acceptable for such industries.
To help solve this question of "is wildlife tourism good or bad?", a tool to help managers assess these industries has been created ...
Covid-19: How to do lockdown? Russian scientists may have an answer
2021-03-01
A painful tradeoff between a number of infected and negative economic impact must be considered before deciding on the lockdown strategy within a city. As national economies continue to crumble, citizens wonder whether their governments did a good job at regulating the lockdown measures.
Russian city of St. Petersburg is at the frontlines of this ongoing war with Covid-19. To combat this situation effectively, Russian government allocated significant funds for the research. Results followed. Scientists from Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) modified the existing SIR class pandemic prediction model. Now it is better.
But why? What is the nature ...
Breast cancer screening recalls: simple MRI measurement could avoid 30% of biopsies
2021-03-01
Breast cancer is the commonest fatal cancer in women. Early detection increases a woman's chances of recovery. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an accurate technique for detecting and classifying tumours in breast tissue. However, it sometimes causes "false alarms", thus requiring further investigation (biopsy) and in some cases even resulting in so-called overtreatment, that is to say unnecessary surgery. For the first time, a research team from MedUni Vienna has now confirmed a threshold value for a non-invasive imaging biomarker. This can be incorporated into short standard MRI scans ...
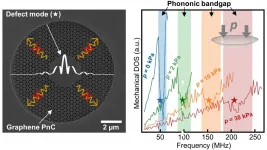
New skills of Graphene: Tunable lattice vibrations
2021-03-01
Without electronics and photonics, there would be no computers, smartphones, sensors, or information and communication technologies. In the coming years, the new field of phononics may further expand these options. That field is concerned with understanding and controlling lattice vibrations (phonons) in solids. In order to realize phononic devices, however, lattice vibrations have to be controlled as precisely as commonly realized in the case of electrons or photons.
Phononic cyrstals
The key building block for such a device is a phononic ...
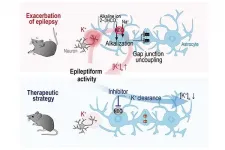
Acute breakdown of the glial network in epilepsy
2021-03-01
Tohoku University scientists and their colleagues in Germany have revealed that a first-time exposure to only a brief period of brain hyperactivity resulted in an acute breakdown of the inter-cellular network of glial cells. Pharmacological intervention of the glial plasticity may provide a new preventative strategy for fighting epilepsy.
The findings were detailed in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Epilepsy is a disorder characterized by neuronal hyper-excitation and a progression of seizures with each episode. Anti-epileptic drugs are mostly aimed at suppressing hyperactivity, ...
Rocket launches reveal water vapor effect in upper atmosphere
2021-03-01
Results of a 2018 multirocket launch at Poker Flat Research Range north of Fairbanks, Alaska, will help scientists better understand the impact of more water vapor accumulating near the fringe of the Earth's atmosphere.
"This is the first time anyone has experimentally demonstrated that cloud formation in the mesosphere is directly linked to cooling by water vapor itself," said Irfan Azeem, space physicist at Astra LLC in Louisville, Colorado, and principal investigator of the Super Soaker mission.
The NASA-funded project, named Super Soaker, ...
Climate change threatens European forests
2021-03-01
In recent years, European forests have suffered greatly from extreme climate conditions and their impacts. More than half of Europe's forests are potentially at risk from windthrow, forest fire, insect attacks or a combination of these. This is the main result of a study by an international team of scientists with the participation of Henrik Hartmann from the Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry in Jena, Germany. Using satellite data and artificial intelligence, the scientists studied vulnerability to disturbances in the period between 1979 and 2018. In the light of ongoing climate change, their findings are very important for improving mitigation and adaptation strategies ...
Pumping perovskites into a semiconductor platform
2021-03-01
Materials called perovskites can be more readily incorporated into silicon-based semiconducting platforms by using a microfluidic pumping technology developed at KAUST.
The perovskites currently being explored for many applications in new technologies are diverse materials sharing the same crystalline structure as the natural mineral perovskite. These semiconducting materials show great promise in a variety of optoelectronic applications, such as light emitters, sensors and solar cells.
Compared to traditional semiconductors, perovskites are soft and unstable. "This makes it difficult to pattern them using standard lithography methods," says materials scientist Iman Roqan at KAUST.
The challenge tackled by Roqan and her colleagues was to adapt microfluidic technologies to manipulate ...
High school students tend to get more motivated over time
2021-03-01
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Parents may fear that if their high school student isn't motivated to do well in classes, there's nothing that will change that.
But a new study that followed more than 1,600 students over two years found that students' academic motivation often did change - and usually for the better.
Results showed that increasing students' sense of "belongingness" in school was one key way of increasing academic motivation.
"Our results point to a more hopeful picture for students who start out with lower levels of motivation - they tend to shift toward more adaptive ...
Paper addresses research needed to understand smoking and COVID-19
2021-03-01
March 1, 2021 - A new paper published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society discusses how smoking may affect risk for COVID-19 and the types of research that are needed to better understand the link between smoking and COVID-19 risk.
In "Smoking and COVID-19: The Real Deal," Enid Neptune, MD, and Michelle N. Eakin, PhD, of the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, discuss research to date on this topic and propose areas of research that can help clarify this relationship.
Studies have shown that current smokers with COVID-19 have twice the ...
UBCO economist says private security systems bar others from protection
2021-03-01
New research has determined the prevalence of private security systems may be robbing the general public of the police services they need.
Dr. Ross Hickey is an economist in UBC Okanagan's Faculty of Management and the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences. Along with a team of researchers, Hickey examined data from a social survey of Canada victimization, where people answered whether they had added security measures to their homes to protect themselves from crime.
"We are seeing more expenditures on private security systems installed in homes and, as economists, we have to ask why. We know that crime rates are down and expenditure on police is up," says Hickey. "But private security purchases are at an all-time ...
Low-level thinning can help restore redwood forests without affecting stream temperatures
2021-03-01
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Selectively cutting trees in riparian zones to aid forest restoration can be done without adversely affecting streams' water temperature as long as the thinning isn't too intensive, new research by Oregon State University shows.
Published in PLOS One, the study led by OSU College of Agricultural Sciences graduate student David Roon is one of the few to quantify restorative thinning's effects on forest streams.
"We don't know much about what happens with the more subtle changes in shade and light that come with thinning," Roon said. "Most of the research so far has looked at the effects of clearcutting with no stream-side buffer at all, or harvests outside of an untouched buffer area. And regulatory requirements ...
How 'great' was the great oxygenation event?
2021-03-01
Around 2.5 billion years ago, our planet experienced what was possibly the greatest change in its history: According to the geological record, molecular oxygen suddenly went from nonexistent to becoming freely available everywhere. Evidence for the "great oxygenation event" (GOE) is clearly visible, for example, in banded iron formations containing oxidized iron. The GOE, of course, is what allowed oxygen-using organisms - respirators - and ultimately ourselves, to evolve. But was it indeed a "great event" in the sense that the change was radical and sudden, or were the organisms alive at the time already using free oxygen, just at lower levels?
Prof. Dan Tawfik of the Weizmann Institute of Science's Biomolecular Sciences Department explains that the dating of the GOE ...
Bottling the world's coldest plasma
2021-03-01
HOUSTON - (March 1, 2021) - Rice University physicists have discovered a way to trap the world's coldest plasma in a magnetic bottle, a technological achievement that could advance research into clean energy, space weather and astrophysics.
"To understand how the solar wind interacts with the Earth, or to generate clean energy from nuclear fusion, one has to understand how plasma -- a soup of electrons and ions -- behaves in a magnetic field," said Rice Dean of Natural Sciences Tom Killian, the corresponding author of a published study about the work in Physical Review Letters.
Using laser-cooled strontium, ...
Visiting water bodies worth £700bn to economies, study finds
2021-03-01
Europeans spend more than £700 billion (€800bn) a year on recreational visits to water bodies - but perceived poor water quality costs almost £90 billion (€100bn) in lost visits, a new study has found.
The new research - led by a European collaboration involving the University of Exeter and the University of Stirling - used data from 11,000 visits in 14 different countries to analyse the economic value of water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, waterfalls, beaches and seaside promenades.
The research team estimated that people spend an average of £35 (€40) travelling to and from these sites, with a typical family making 45 such trips each year.
The team also found ...
Microplastic sizes in Hudson-Raritan Estuary and coastal ocean revealed
2021-03-01
Rutgers scientists for the first time have pinpointed the sizes of microplastics from a highly urbanized estuarine and coastal system with numerous sources of fresh water, including the Hudson River and Raritan River.
Their study of tiny pieces of plastic in the Hudson-Raritan Estuary in New Jersey and New York indicates that stormwater could be an important source of the plastic pollution that plagues oceans, bays, rivers and other waters and threatens aquatic and other life.
"Stormwater, an understudied pathway for microplastics to enter waterways, had similar or higher concentrations of ...
The right '5-a-day' mix is 2 fruit and 3 vegetable servings for longer life
2021-03-01
DALLAS, March 1, 2021 — Studies representing nearly 2 million adults worldwide show that eating about five daily servings of fruits and vegetables, in which 2 are fruits and 3 are vegetables, is likely the optimal amount for a longer life, according to new research published today in the American Heart Association’s flagship journal Circulation.
Diets rich in fruits and vegetables help reduce risk for numerous chronic health conditions that are leading causes of death, including cardiovascular disease and cancer. Yet, only about one in 10 adults eat enough fruits or vegetables, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“While groups like the ...
Single cell sequencing opens new avenues for eradicating leukemia at its source
2021-03-01
A new method, described in a study published today in the journal Nature Communications, has the potential to boost international research efforts to find drugs that eradicate cancer at its source.
Most cancerous tissue consists of rapidly dividing cells with a limited capacity for self-renewal, meaning that the bulk of cells stop reproducing after a certain number of divisions. However, cancer stem cells can replicate indefinitely, fuelling long-term cancer growth and driving relapse.
Cancer stem cells that elude conventional treatments like chemotherapy are one of the reasons ...
'Overwhelming' international support for more government action on environment, message-testing experiment finds
2021-03-01
With eight months to go before the UN Climate Change Conference (COP26), an international survey experiment has found evidence of "overwhelming" support across seven major countries for governments to "do more" to protect the environment.
The survey directly asks the public about policies they want to see backed by governments at COP26, when the UK and Italy will gather world leaders in Glasgow from 1 November to commit to urgent global climate action.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge worked with polling agency YouGov on a message-testing experiment involving 14,627 adults, with ...
Top diversity and equity leaders in psychiatry offer guidelines for academic medicine
2021-03-01
Diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) leaders in academic medicine are subject to increasing expectations with limited resources and there is an urgent need for psychiatry departments to commit to fully supporting their efforts, according to an article now available in the American Journal of Psychiatry written by top DEI leaders in academic psychiatry from across the country.
The authors, representing prominent public and private institutions, include Ayana Jordan, M.D., Ph.D., Yale University, and current APA ECP Trustee-at-Large; Ruth S. Shim, M.D., M.P.H. University ...
Why COVID-19 vaccine distribution methods fall short and 3 ways to improve them
2021-03-01
BINGHAMTON, NY - Several proposals have emerged on how to distribute the COVID-19 vaccine, but they fall short in ensuring that the vaccine is distributed fairly. A team including Binghamton University professor Nicole Hassoun suggests three ways to more fairly and effectively distribute the vaccine so that people in poor countries get the vaccine as soon as possible.
"Although many people in rich countries will receive a vaccine for COVID-19 this year, many people in poor countries will likely have to wait years to get one," said Hassoun. "Ethical vaccine allocation requires closing this gap and ensuring that everyone can access a vaccine ...
Financial incentives for hospitals boost rapid changes to opioid use disorder treatment
2021-03-01
PHILADELPHIA-- Hospital emergency departments (EDs) not only care for patients with overdose and other complications from opioid use, but they also serve as vital touch points to engage patients into longer-term treatment. After an overdose, patients are at risk for repeat overdose and death. Pennsylvania is unique in establishing a voluntary incentive program to improve the rate at which patients with opioid use disorder receive follow-up treatment after emergency department care. Evaluations of the program show that financial incentives are effective in producing rapid treatment innovations for opioid use disorder.
In a study, researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at ...
[1] ... [2553]
[2554]
[2555]
[2556]
[2557]
[2558]
[2559]
[2560]
2561
[2562]
[2563]
[2564]
[2565]
[2566]
[2567]
[2568]
[2569]
... [8791]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.