Study uncovers safety concerns with some air purifiers
2021-03-16
The market for air purifiers is booming, but a new study has found that some air cleaning technologies marketed for COVID-19 may be ineffective and have unintended health consequences.
The study, authored by researchers at Illinois Tech, Portland State University, and Colorado State University, found that cleaning up one harmful air pollutant can create a suite of others.
Both chamber and field tests found that an ionizing device led to a decrease in some volatile organic compounds (VOCs) including xylenes, but an increase in others, most prominently oxygenated VOCs (e.g., acetone, ethanol) and toluene, substances commonly found in paints, ...
Sleep troubles may complicate the grieving process
2021-03-16
Those who have persistent trouble sleeping may have an especially difficult grieving process after the death of a loved one, a new study co-authored by a University of Arizona researcher finds.
Most people who lose a close friend or family member will experience sleep troubles as part of the grieving process, as the body and mind react to the stress of the event, said study co-author Mary-Frances O'Connor, a professor in the UArizona Department of Psychology.
But O'Connor and her collaborators found that those who had persistent sleep challenges before losing someone were at higher risk for developing complicated grief after a loss. Complicated grief is characterized by a yearning for a lost loved one ...
Easing the burden on transgender and nonbinary graduate students
2021-03-16
It would surprise no one that pursuing a graduate degree can be a stressful endeavor, and for students who are transgender and nonbinary (TNB), the atmosphere can become toxic, according to University of Houston researcher Nathan Grant Smith. In a new paper published in Higher Education, Smith provides an analysis of current literature pertaining to TNB graduate student experiences and suggests interventions in graduate education to create more supportive environments for TNB students.
"Nearly 50% of graduate students report experiencing emotional or psychological distress during their enrollment in graduate school. Levels of distress are particularly high for transgender ...
How sperm remember
2021-03-16
It has long been understood that a parent's DNA is the principal determinant of health and disease in offspring. Yet inheritance via DNA is only part of the story; a father's lifestyle such as diet, being overweight and stress levels have been linked to health consequences for his offspring. This occurs through the epigenome - heritable biochemical marks associated with the DNA and proteins that bind it. But how the information is transmitted at fertilization along with the exact mechanisms and molecules in sperm that are involved in this process has been unclear until now.
A new study from McGill, published recently in Developmental Cell, has made a significant advance in the field by identifying how environmental information is transmitted by ...
What sparked life on Earth? Perhaps bolts from the blue
2021-03-16
Lightning strikes -- perhaps a quintillion of them, occurring over a billion years -- may have provided sparks of life for the early Earth.
A new study by researchers at Yale and the University of Leeds contends that over time, these bolts from the blue unlocked the phosphorus necessary for the creation of biomolecules that would be the basis of life on the planet.
"This work helps us understand how life may have formed on Earth and how it could still be forming on other, Earth-like planets," said lead author Benjamin Hess, a graduate student in Yale's Department of Earth & Planetary ...
Lightning strikes played a vital role in life's origins on Earth
2021-03-16
Lightning strikes were just as important as meteorites in creating the perfect conditions for life to emerge on Earth, geologists say.
Minerals delivered to Earth in meteorites more than 4 billion years ago have long been advocated as key ingredients for the development of life on our planet.
Scientists believed minimal amounts of these minerals were also brought to early Earth through billions of lightning strikes.
But now researchers from the University of Leeds have established that lightning strikes were just as significant as meteorites in performing this essential function and allowing life to manifest.
They say this shows that life could develop on Earth-like planets through the same mechanism at any time if atmospheric conditions are right. The research ...
Project investigates remote control of enzymes using light
2021-03-16
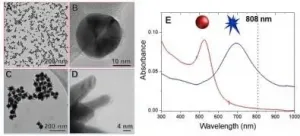
The activity of enzymes in industrial processes, laboratories, and living beings can be remotely controlled using light. This requires their immobilization on the surface of nanoparticles and irradiation with a laser. Near-infrared light can penetrate living tissue without damaging it. The nanoparticles absorb the energy of the radiation and release it back in the form of heat or electronic effects, triggering or intensifying the enzymes' catalytic activity. This configures a new field of study known as plasmonic biocatalysis.
Research conducted at the University of São Paulo's Chemistry Institute (IQ-USP) in Brazil investigated the activity of enzymes immobilized on gold ...
New study predicts changing Lyme disease habitat across the West Coast
2021-03-16
FLAGSTAFF, Ariz. -- March 16, 2021 -- The findings of a recent analysis conducted by the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope, suggest that ecosystems suitable for harboring ticks that carry debilitating Lyme disease could be more widespread than previously thought in California, Oregon and Washington.
Bolstering the research were the efforts of an army of "citizen scientists" who collected and submitted 18,881 ticks over nearly three years through the Free Tick Testing Program created by the Bay Area Lyme Foundation, which funded the research, producing a wealth of data for scientists to analyze.
This new study builds on initial research led by the ...
Is there life on mars today and where?
2021-03-16
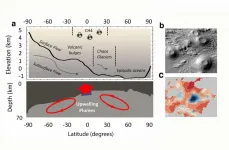
March 16, 2021, Mountain View, CA - In a comment published today in Nature Astronomy, Dr. Nathalie Cabrol, Director of the Carl Sagan Center for Research at the SETI Institute, challenges assumptions about the possibility of modern life on Mars held by many in the scientific community.
As the Perseverance rover embarks on a journey to seek signs of ancient life in the 3.7 billion years old Jezero crater, Cabrol theorizes that not only life could still be present on Mars today, but it could also be much more widespread and accessible than previously believed. Her conclusions are based on years of exploration of early Mars analogs in extreme environments in the Chilean altiplano and the Andes funded ...
What happened to mars's water? It is still trapped there
2021-03-16
Billions of years ago, the Red Planet was far more blue; according to evidence still found on the surface, abundant water flowed across Mars and forming pools, lakes, and deep oceans. The question, then, is where did all that water go?
The answer: nowhere. According to new research from Caltech and JPL, a significant portion of Mars's water--between 30 and 99 percent--is trapped within minerals in the planet's crust. The research challenges the current theory that the Red Planet's water escaped into space.
The Caltech/JPL team found that around four billion years ago, Mars was home to enough water to have covered the whole planet in an ocean about 100 to 1,500 meters deep; a volume roughly ...
Going back in time restores decades of quiet corn drama
2021-03-16
URBANA, Ill. - Corn didn't start out as the powerhouse crop it is today. No, for most of the thousands of years it was undergoing domestication and improvement, corn grew humbly within the limits of what the environment and smallholder farmers could provide.
For its fertilizer needs, early corn made friends with nitrogen-fixing soil microbes by leaking an enticing sugary cocktail from its roots. The genetic recipe for this cocktail was handed down from parent to offspring to ensure just the right microbes came out to play.
But then the Green Revolution changed everything. Breeding tools improved dramatically, leading to faster-growing, higher-yielding hybrids than the world had ...
Image release: Cosmic lens reveals faint radio galaxy
2021-03-16
Radio telescopes are the world's most sensitive radio receivers, capable of finding extremely faint wisps of radio emission coming from objects at the farthest reaches of the universe. Recently, a team of astronomers used the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) to take advantage of a helping hand from nature to detect a distant galaxy that likely is the faintest radio-emitting object yet found.
The discovery was part of the VLA Frontier Fields Legacy Survey, led by NRAO Astronomer Eric Murphy, which used distant clusters of galaxies as natural lenses ...
Tired at the office? Take a quick break; your work will benefit
2021-03-16
Recent research shows that people are more likely to take "microbreaks" at work on days when they're tired - but that's not a bad thing. The researchers found microbreaks seem to help tired employees bounce back from their morning fatigue and engage with their work better over the course of the day.
At issue are microbreaks, which are short, voluntary and impromptu respites in the workday. Microbreaks include discretionary activities such as having a snack, chatting with a colleague, stretching or working on a crossword puzzle.
"A microbreak is, by definition, short," says Sophia Cho, co-author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor ...
Army, Air Force fund research to pursue quantum computing
2021-03-16
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- Joint Army- and Air Force-funded researchers have taken a step toward building a fault-tolerant quantum computer, which could provide enhanced data processing capabilities.
Quantum computing has the potential to deliver new computing capabilities for how the Army plans to fight and win in what it calls multi-domain operations. It may also advance materials discovery, artificial intelligence, biochemical engineering and many other disciplines needed for the future military; however, because qubits, the fundamental building blocks of quantum computers, are intrinsically fragile, a longstanding barrier to quantum computing has been effective implementation of quantum error correction.
Researchers at University of Massachusetts Amherst, ...
Standing out from the crowd
2021-03-16
Corporate strategies should be as unique as possible, in fact highly specific to each individual company. This enables companies to compete successfully in the long term. However, the capital market and others, including analysts, often react negatively to the idea of unique strategies. The reason is that deviating from typical industry standards makes them more complex to evaluate. This regularly discourages companies from focusing on unique strategies, even though they would be beneficial for the company in the long term. This contradiction is known as the "uniqueness paradox". A research team from the Universities of Göttingen and Groningen has investigated the influence of different types of investors on the extent of the paradox and thus on the choice of unique strategies. The results ...
Could birth control pills ease concussion symptoms in female athletes?
2021-03-16
Higher progesterone level is protective in mild traumatic brain injury
Blood flow in brain is linked to progesterone and stress symptom levels
Most concussion research has been focused on male athletes
CHICAGO --- Could birth control pills help young female athletes recover faster from concussions and reduce their symptoms?
A new Northwestern Medicine pilot study has shown when a female athlete has a concussion injury during the phase of her menstrual cycle when progesterone is highest, she feels less stress. Feeling stressed is one symptom of a concussion. Feeling less stressed is a marker of recovery.
The study also revealed for the first time the physiological reason for the neural protection is increased ...
Leaders take note: Feeling powerful can have a hidden toll
2021-03-16
New research from the University of Florida Warrington College of Business finds that feeling psychologically powerful makes leaders' jobs seem more demanding. And perceptions of heightened job demands both help and hurt powerful leaders.
Trevor Foulk of the University of Maryland Robert H. Smith School of Business and Klodiana Lanaj, Martin L. Schaffel Professor at UF, note that while power-induced job demands are key to helping leaders more effectively pursue their goals and feel that their jobs are meaningful each day at work, these demands can also cause pain and discomfort, felt in the evening at home.
"Power is generally considered a desirable thing, as leaders often seek power, and it's very rare for leaders to turn powerful roles down," Foulk said. "However, this view is qualified ...
Controlling sloshing motions in sea-based fish farming cages improves fish welfare
2021-03-16
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Sea-based fish farming systems using net pens are hard on the environment and the fish. A closed cage can improve fish welfare, but fresh seawater must be continuously circulated through the cage. However, ocean waves can cause this circulating water to slosh inside the cage, creating violent motions and endangering the cage and the fish.
A study using a scale-model fish containment system is reported in Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing. The study shows why violent sloshing motions arise and how to minimize them.
Gentle currents can be artificially maintained inside cylindrical closed cages developed for salmon farming. The current is produced by injecting seawater through ...
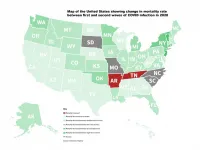
Second COVID-19 wave in Europe less lethal than first wave
2021-03-16
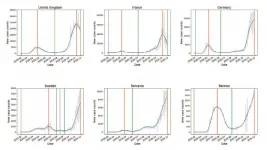
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- As Europe experienced its enormous second wave of the COVID-19 disease, researchers noticed the mortality rate -- progression from cases to deaths -- was much lower than during the first wave.
This inspired researchers from the University of Sydney and Tsinghua University to study and quantify the mortality rate on a country-by-country basis to determine how much the mortality rate from the second wave decreased from the first.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, Nick James, Max Menzies, and Peter Radchenko introduce methods to study the progression of COVID-19 cases to deaths during the pandemic's different waves. Their methods involve applied mathematics, specifically nonlinear dynamics, and time series analysis.
"We take a time series, ...
Crying human tear glands grown in the lab
2021-03-16
Researchers from the lab of Hans Clevers (Hubrecht Institute) and the UMC Utrecht used organoid technology to grow miniature human tear glands that actually cry. The organoids serve as a model to study how certain cells in the human tear gland produce tears or fail to do so. Scientists everywhere can use the model to identify new treatment options for patients with tear gland disorders, such as dry eye disease. Hopefully in the future, the organoids can even be transplanted into patients with non-functioning tear glands. The results will be published in Cell Stem Cell on the 16th of March.
The tear gland is located in the upper part of the eye socket. It secretes tear fluid, which is essential for lubrication and nutrition of the cornea and has antibacterial components. Rachel Kalmann ...
Squishy white blood cells quickly become highly stiff and viscous in response to a threat
2021-03-16
Like a well-trained soldier, a white blood cell uses specialized abilities to identify and ultimately destroy dangerous intruders, including creating a protrusion to effectively reach out, lock-on, probe, and possibly attack its prey. Researchers reporting March 16 in Biophysical Journal show in detail that these cells take seconds to morph into these highly rigid and viscous defensive units.
Senior author Julien Husson (@_julienhusson), a biophysicist at École Polytechnique near Paris, and collaborators showed previously that certain white blood cells, called T cells, ...
Brain disease research reveals differences between sexes
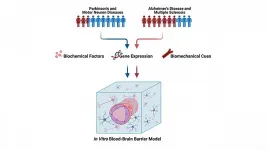
2021-03-16
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Men and women are impacted differently by brain diseases, like Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Researchers are urging their colleagues to remember those differences when researching treatments and cures.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, University of Maryland scientists highlight a growing body of research suggesting sex differences play roles in how patients respond to brain diseases, as well as multiple sclerosis, motor neuron disease, and other brain ailments.
That is progress from just a few years ago, said Alisa Morss ...
Tear glands in a dish can cry
2021-03-16
Stem-cell-derived organoids that swell up with tears could shed light on the biology of crying and dry-eye disease, suggests a study publishing March 16 in the journal Cell Stem Cell. Although regenerative therapies using human tear-gland organoids will not be possible anytime soon, these researchers have demonstrated that the organoids can engraft, integrate, and produce mature tear products upon transplantation into mouse tear glands.
"We hope that scientists will use our model to identify new treatment options for patients with tear-gland disorders by either testing new drugs on a patient's organoids or expanding healthy cells and, one day, using them for transplantation," says senior study author Hans Clevers (@HansClevers) of the Hubrecht Institute.
The ...
Second-wave COVID mortality dropped markedly in (most) wealthier zones
2021-03-16
Wealthier northeastern US states and Western European countries tended to have significantly lower mortality rates during second-wave COVID-19 infections, new research from the University of Sydney and Tsinghua University has shown. However, the pattern was not as general as expected, with notable exceptions to this trend in Sweden and Germany.
Researchers say mortality change could have several explanations:
European first-wave case counts were underestimated;
First-wave deaths disproportionately affected the elderly;
Second-wave infections tended to affect younger people;
With some ...
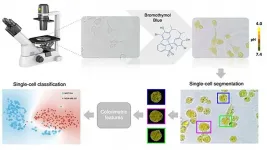
Machine learning can identify cancerous cells by their acidity
2021-03-16
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Cancerous cells exhibit several key differences from healthy cells that help identify them as dangerous. For instance, the pH -- the level of acidity -- within a cancerous cell is not the same as the pH within a healthy cell.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore developed a method of using machine learning to determine whether a single cell is cancerous by detecting its pH. They describe their work in the journal APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing.
"The ability to identify single cells has acquired a paramount importance in the field of precision and personalized medicine," ...
[1] ... [2539]
[2540]
[2541]
[2542]
[2543]
[2544]
[2545]
[2546]
2547
[2548]
[2549]
[2550]
[2551]
[2552]
[2553]
[2554]
[2555]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.