Immune receptor protein could hold key to treatment of autoimmune diseases
2021-03-17
Autoimmune diseases are typically caused when the immune system, whose purpose is to deal with foreign threats to the body, incorrectly recognizes the body's own proteins and cells as threats and activates immune cells to attack them. In the case of rheumatoid arthritis, a well-known autoimmune disease, immune cells erroneously attack the body's own joint components and proteins, causing painful inflammation and even the destruction of bone! Scientists from Japan have now taken a massive step toward understanding and, potentially, treating rheumatoid arthritis better, with their discovery in a brand-new study. Read on to understand how!
The development of autoimmune diseases is an incredibly complex process, involving several key players ...
Copy invitation
2021-03-17
A sustainable, powerful micro-supercapacitor may be on the horizon, thanks to an international collaboration of researchers from Penn State and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. Until now, the high-capacity, fast-charging energy storage devices have been limited by the composition of their electrodes -- the connections responsible for managing the flow of electrons during charging and dispensing energy. Now, researchers have developed a better material to improve connectivity while maintaining recyclability and low cost.
They published their results on Feb. 8 in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
"The supercapacitor is a very powerful, energy-dense device with a fast-charging rate, in contrast to the typical battery ...
Cellular benefits of gene therapy seen decades after treatment
2021-03-17
An international collaboration between Great Ormond Street Hospital, the UCL GOS Institute for Child Health and Harvard Medical School has shown that the beneficial effects of gene therapy can be seen decades after the transplanted blood stem cells has been cleared by the body.
The research team monitored five patients who were successfully cured of SCID-X1 using gene therapy at GOSH. For 3-18 years patients' blood was regularly analysed to detect which cell types and biomarker chemicals were present in their blood. The results showed that even though the stem cells transplanted as part of gene therapy had been cleared by the patients, the all-important corrected immune cells, called T-cells, were still forming.
Gene therapy works by first removing ...
Identifying cells to better understand healthy and diseased behavior
2021-03-17
In researching the causes and potential treatments for degenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease, neuroscientists frequently struggle to accurately identify cells needed to understand brain activity that gives rise to behavior changes such as declining memory or impaired balance and tremors.
A multidisciplinary team of Georgia Institute of Technology neuroscience researchers, borrowing from existing tools such as graphical models, have uncovered a better way to identify cells and understand the mechanisms of the diseases, potentially leading to better understanding, diagnosis, and treatment.
Their research findings were reported Feb. 24 in the journal eLife. The research was supported by the National Institutes of ...
Double-duty catalyst generates hydrogen fuel while cleaning up wastewater
2021-03-17
Hydrogen is a pollution-free energy source when it's extracted from water using sunlight instead of fossil fuels. But current strategies for "splitting" or breaking apart water molecules with catalysts and light require the introduction of chemical additives to expedite the process. Now, researchers reporting in ACS ES&T Engineering have developed a catalyst that destroys medications and other compounds already present in wastewater to generate hydrogen fuel, getting rid of a contaminant while producing something useful.
Harnessing the sun's energy to split water to make hydrogen fuel is a promising renewable resource, but it is a slow process even when catalysts are used to speed it along. In some cases, alcohols or sugars are added to boost the rate of hydrogen production, ...
High speed air hand dryers spread contamination more than paper towels
2021-03-17
NEW YORK (March 17, 2021) -- High speed air dryers not only leave more contamination on poorly washed hands compared to paper towels, but during hand drying, they can also spread germs onto clothing, ultimately transferring more bacteria to other surfaces, according to a study published today in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
Past research has shown recommended handwashing practices for healthcare workers are often not followed with average adherence of 40%. To better understand the impact of hand drying in hand hygiene, researchers conducted an experiment to learn the role of different hand drying methods in spreading germs from poorly washed hands beyond the restroom.
For ...
Ultrafast intra-atom motion tracked using synchrotron radiation
2021-03-17
Scientists in Japan have observed, and interfered with, the ultrafast motion of electron movement inside of a Xenon atom using the coherent pairs of short light waves in synchrotron radiation. Xenon, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by five nested shells containing a total of 54 electrons, is used in flash lamps, and it burns bright and fast. The luminescent electrons move there on a time scale of one billionth of a second. The fast electron movement is however six orders of magnitude slower than that the scientists observed. Using the synchrotron facility at Institute for Molecular Science, they tracked the electron movement in relaxation to shed energy by dropping from an outer shell to an inner shell. The process happens at a timescale of femtoseconds, ...
New bioink brings 3D-printing of human organs closer to reality
2021-03-17
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have designed a new bioink which allows small human-sized airways to be 3D-bioprinted with the help of patient cells for the first time. The 3D-printed constructs are biocompatible and support new blood vessel growth into the transplanted material. This is an important first step towards 3D-printing organs. The new study has been published in Advanced Materials.
Chronic lung diseases are the third leading cause of death worldwide with an EU cost of more than €380 billion annually. For many chronic diseases ...
Health promotion, prevention, and psychosocial health
2021-03-17
The promotion of psychosocial health among individuals, groups, and society is an increasingly important subject in the field of public health. Psychosocial health is a complex interaction between the psyche of an individual and the social environment in which that individual lives. Promoting psychosocial health is often challenging and complex for health care professionals. Therefore, an important question of public health significance is: "how can we address and improve the psychosocial health of individuals, groups, as well as society in general?"
An interdisciplinary team of specialists ...
Artificial light affects plant pollination even during the daytime
2021-03-17
The use of artificial light at night around the world has increased enormously in recent years, causing adverse effects on the survival and reproduction of nocturnal organisms. Artificial light at night interferes with vital ecological processes such as the nighttime pollination of plants by nocturnal insects, which could have consequences for agricultural crop yields and reproduction of wild plants.
Scientists from the University of Zurich and Agroscope have now demonstrated for the first time that artificial light at night also adversely affects insects' pollination behavior during the daytime. In an experiment, they used commercial ...
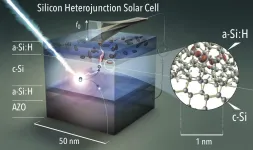
Solar cells: Losses made visible on the nanoscale
2021-03-17
Silicon solar cells are now so cheap and efficient that they can generate electricity at prices of less than 2 cent/kWh. The most efficient silicon solar cells today are made with less than 10 nanometres thin selective amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) contact layers, which are responsible for separating the light-generated charges . Efficiencies of over 24% are achieved at HZB with such silicon heterojunction solar cells and are also part of a tandem solar cell that lead to a recently reported efficiency record of 29.15 % (A. Al-Ashouri, et al. Science 370, (2020)). The current world record from Japan for a ...
Looking for new explanations of TC genesis from the vertical coupling of Durian's embryo
2021-03-17
Tropical Cyclone (TC) is an intense atmospheric vortex with a warm core and low pressure structure, and generates over the tropical or subtropical warm ocean. The problem of TC genesis has been paid great attention by scientists since the 1950s, but due to the lack of the observation data over sea, this problem has become the most difficult and challenging topic in the researches of TC.
Cumulus convections are considered to be the most basic element in the TC generation process. The formation of TC in the Northwest Pacific is often associated with the mesoscale convective system (MCS) or mesoscale convective complex (MCC). Meanwhile, in the stratiform ...
Conspiracy theories influence our behavior -- even if we do not believe in them
2021-03-17
Not least because of the COVID-19 pandemic, conspiracy theories are more topical than ever. They are reported and discussed in almost all media and communication channels. But what influence do they have on our behavior? Scientists led by behavioral economist Loukas Balafoutas investigated this question in a recently published study. The result: We don't need to believe in conspiracy theories for them to have an impact on us. Merely being confronted with them suffices.
Previous studies have shown that beliefs in conspiracy theories have an influence on the behavior of their adherents. For example, they lead to lower voter turnout or a lower willingness to get vaccinated. For years now, conspiracy theories have been ...
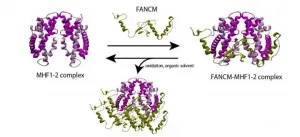
Elusive protein complex could hold the key to treating chromosomal disorders
2021-03-17
One of the most vital functions performed by the cells in our body is DNA repair, a task so crucial to our well-being that failing to execute it can lead to consequences as dreadful as cancer. The process of DNA repair involves a complex interplay between several gene pathways and proteins. One such pathway is the "Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway," whose genes participate in DNA repair. FANCM, a component of this pathway, is tasked with the elimination of harmful DNA "inter-strand cross-links," and interacts with another component called MHF in order to function. The importance of the FANCM-MHF complex is well-documented: its loss can result in chromosomal ...
Hepatitis B: What people can learn from donkeys
2021-03-17
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are among the major global health problems. Particularly problematic is the high number of chronic courses of the disease, causing the deaths of more than 800.000 people globally every year. So far, there is no therapy to cure the condition. "With the discovery of a new hepatitis B virus in donkeys and zebras capable of causing prolonged infections, we now have the opportunity for a better understanding of the chronic course of the disease and thus also for mitigation or prevention of severe clinical consequences," explains Prof. Dr. Jan Felix Drexler, DZIF ...
SARS-CoV-2 infects cells via specific viral entry factors
2021-03-17
A new study uncovers which cell types can be infected by SARS-CoV-2 due to their viral entry factors. The study also suggests that increased gene expression of these viral entry factors in some individuals partially explains the differences of COVID-19 severity reported in relation to age, gender and smoking status. The study evolved from the Human Cell Atlas Lung Biological Network with main contributions from Helmholtz Zentrum München, the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, the Wellcome Sanger Institute and University Medical Center Groningen.
COVID-19 does not affect everyone in the same way. While the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 primarily ...
The health of older women is determined by the characteristics of their partner
2021-03-17
The health of women aged 65 and over appears to be related, in addition to their own socioeconomic characteristics, with that of their partners, as a result of traditional gender norms. This is one of the main conclusions of research led by Jordi Gumà, a researcher at the UPF Department of Political and Social Sciences, conducted in conjunction with Jeroen Spijker, a Ramon y Cajal I3 researcher at the Centre for Demographic Studies of the Autonomous University of Barcelona (CED-UAB), focusing on the case of Spain.
The study, published in Gaceta Sanitaria, analyses the health differences among the Spanish ...
Solving ancient problem of nucleic acid synthesis helps to design new antiviral drugs
2021-03-17
An international team of scientists from the University of Turku, Finland and PennState University, USA have solved a long-standing mystery of how living organisms distinguish RNA and DNA building blocks during gene expression paving the way for the design of new antiviral drugs. The new insights were published in the journal Nature Communications.
All cellular organisms use two types of nucleic acids, RNA and DNA to store, propagate and utilize their genetic information. The synthesis of DNA is carried out by enzymes called DNA polymerases and is needed to accurately transfer the genetic information from generation to generation. ...
Stimulating the immune system to fight cancer
2021-03-17
Our immune system is very successful when it comes to warding off viruses and bacteria. It also recognizes cancer cells as potential enemies and fights them. However, cancer cells have developed strategies to evade surveillance by the immune system and to prevent immune response.
In recent years, fighting cancer with the help of the immune system has entered into clinical practice and gained increasing importance as a therapeutical approach. Current therapies apply so-called immune checkpoint inhibitors. Immune checkpoints are located on the surface ...
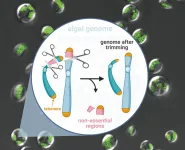
Genome scalpel invented for industrial microalgae to efficiently turn CO<sub>2</sub> into biofuel
2021-03-17
A single-celled alga undergoes genome surgery to remove non-essential parts. This can lead to a most efficient cellular factory for producing sustainable biofuels from sunlight and carbon dioxide.
Researchers from the Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have stripped hundred-kilobase genome from a type of oil-producing microalgae, knocking out genes non-essential for it to function. By doing so, they have created a "genome scalpel" that can trim microalgal genomes rapidly and creatively.
The 'minimal genome' microalgae produced is potentially useful as a model organism for further study of the molecular and biological function of every gene, or as a 'chassis' strain for synthetic biologists to augment for customized ...
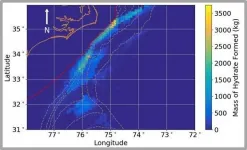
Modeling the probability of methane hydrate deposits on the seafloor
2021-03-17
RALEIGH, N.C. -- Methane hydrate, an ice-like material made of compressed natural gas, burns when lit and can be found in some regions of the seafloor and in Arctic permafrost.
Thought to be the world's largest source of natural gas, methane hydrate is a potential fuel source, and if it "melts" and methane gas is released into the atmosphere, it is a potent greenhouse gas. For these reasons, knowing where methane hydrate might be located, and how much is likely there, is important.
A team of researchers from Sandia National Laboratories and the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory have developed a new system to model the likelihood of finding methane ...
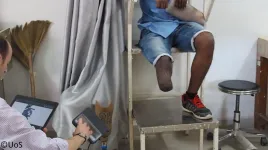
Cambodian study assesses 3D scanning technologies for prosthetic limb design
2021-03-17
Cutting-edge 3D scanners have been put to the test by researchers from the University of Southampton and partners Exceed Worldwide to help increase the quality and quantity of prosthetics services around the world.
The study, carried out within the END ...
What brings olfactory receptors to the cell surface
2021-03-17
A team of scientists led by Dietmar Krautwurst from the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich has now identified address codes in odorant receptor proteins for the first time. Similar to zip codes, the codes ensure that the sensor proteins are targeted from inside the cell to the cell surface, where they begin their work as odorant detectors. The new findings could contribute to the development of novel test systems with which the odorant profiles of foods can be analyzed in a high-throughput process and thus could be better controlled.
The ...
Crystal structure prediction of multi-elements random alloy
2021-03-17
Alchemy, which attempted to turn cheap metals such as lead and copper into gold, has not yet succeeded. However, with the development of alloys in which two or three auxiliary elements are mixed with the best elements of the times, modern alchemy can produce high-tech metal materials with high strength, such as high entropy alloys. Now, together with artificial intelligence, the era of predicting the crystal structure of high-tech materials has arrived without requiring repetitive experiments.
A joint research team of Professor Ji Hoon Shim and Dr. Taewon Jin (first author, currently at KAIST) of POSTECH's Department of Chemistry, and Professor Jaesik Park of POSTECH Graduate School of Artificial Intelligence have together developed a system that predicts ...
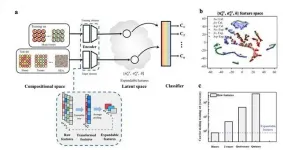
Not just for numbers: Anchoring biases decisions involving sight, sound, and touch
2021-03-17
TROY, N.Y. -- Numeric anchoring is a long-established technique of marketing communication. Once a price is mentioned, that number serves as the basis for -- or "anchors" -- all future discussions and decisions. But new research shows that this phenomenon is not limited to decisions that involve numbers, the use and understanding of which require high-level cognitive thinking. Anchoring also biases judgments at relatively low levels of cognition when no numbers are involved.
In research recently published in the Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, Gaurav Jain, an assistant professor in the Lally School of Management at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, demonstrated that anchoring even occurs in perceptual domains, ...
[1] ... [2535]
[2536]
[2537]
[2538]
[2539]
[2540]
[2541]
[2542]
2543
[2544]
[2545]
[2546]
[2547]
[2548]
[2549]
[2550]
[2551]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.