Is there an association between a pregnant mother's diet and her child's weight?
2021-03-15
Key Points
19.3% of children and adolescents in the United States have obesity and therefore have a higher likelihood of having obesity as adults and developing weight-related diseases.
This AJCN study assessed how strongly mothers' diets during pregnancy were associated with their children's growth rates during specific periods from birth through adolescence.
Study results suggest maternal nutrition during pregnancy may influence her offspring's weight gain during specific periods from birth to adolescence.
A pregnancy diet with higher inflammatory potential was associated with accelerated BMI growth trajectories in children, specifically those between three and ten years of age.
Rockville, ...
European summer droughts since 2015 unprecedented in past two millennia
2021-03-15
Recent summer droughts in Europe are far more severe than anything in the past 2,100 years, according to a new study.
An international team, led by the University of Cambridge, studied the chemical fingerprints in European oak trees to reconstruct summer climate over 2,110 years. They found that after a long-term drying trend, drought conditions since 2015 suddenly intensified, beyond anything in the past two thousand years.
This anomaly is likely the result of human-caused climate change and associated shifts in the jet stream. The results are reported in the journal Nature Geoscience.
Recent summer droughts and heatwaves in Europe have had devastating ecological and economic consequences, which will worsen as the global climate continues to warm.
"We're ...
Saarbrücken based bioinformaticians trace down molecular signals of Parkinson's disease
2021-03-15
In their study, which is now published in the journal Nature Aging, they show that the level of non-coding RNAs in the blood of a Parkinson's patient can be used to track the course of the disease. For their study, the team led by bioinformatics professor Andreas Keller and his doctoral student Fabian Kern created and analyzed the molecular profiles of more than 5,000 blood samples from over 1,600 Parkinson's patients. This resulted in around 320 billion data points, which the researchers analyzed for biomarkers of Parkinson's disease using artificial intelligence methods. ...
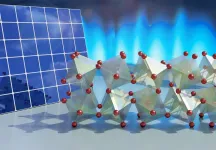
Twisting, flexible crystals key to solar energy production
2021-03-15
DURHAM, N.C. -- Researchers at Duke University have revealed long-hidden molecular dynamics that provide desirable properties for solar energy and heat energy applications to an exciting class of materials called halide perovskites.
A key contributor to how these materials create and transport electricity literally hinges on the way their atomic lattice twists and turns in a hinge-like fashion. The results will help materials scientists in their quest to tailor the chemical recipes of these materials for a wide range of applications in an environmentally friendly way.
The results appear online March 15 in the journal Nature Materials.
"There is a broad ...
Epigenetic mechanism contributing to lifelong stress susceptibility discovered
2021-03-15
An epigenetic modification that occurs in a major cell type in the brain's reward circuitry controls how stress early in life increases susceptibility to additional stress in adulthood, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have learned. In a study in Nature Neuroscience, the team also reported that a small-molecule inhibitor of the enzyme responsible for this modification, currently being developed as an anti-cancer drug, was able to reverse increased vulnerability to lifelong stress in animal models.
"It has long been known that stress exposures throughout life control lifelong susceptibility to subsequent stress. Here ...
Machine learning models for diagnosing COVID-19 are not yet suitable for clinical use
2021-03-15
Researchers have found that out of the more than 300 COVID-19 machine learning models described in scientific papers in 2020, none of them is suitable for detecting or diagnosing COVID-19 from standard medical imaging, due to biases, methodological flaws, lack of reproducibility, and 'Frankenstein datasets.'
The team of researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, carried out a systematic review of scientific manuscripts - published between 1 January and 3 October 2020 - describing machine learning models that claimed to be able to diagnose or prognosticate ...
Could we recycle plastic bags into fabrics of the future?
2021-03-15
In considering materials that could become the fabrics of the future, scientists have largely dismissed one widely available option: polyethylene.
The stuff of plastic wrap and grocery bags, polyethylene is thin and lightweight, and could keep you cooler than most textiles because it lets heat through rather than trapping it in. But polyethylene would also lock in water and sweat, as it's unable to draw away and evaporate moisture. This antiwicking property has been a major deterrent to polyethylene's adoption as a wearable textile.
Now, MIT engineers have spun polyethylene into fibers ...
Melting glaciers could speed up carbon emissions into the atmosphere
2021-03-15
The loss of glaciers worldwide enhances the breakdown of complex carbon molecules in rivers, potentially contributing further to climate change.
An international research team led by the University of Leeds has for the first time linked glacier-fed mountain rivers with higher rates of plant material decomposition, a major process in the global carbon cycle.
As mountain glaciers melt, water is channelled into rivers downstream. But with global warming accelerating the loss of glaciers, rivers have warmer water temperatures and are less prone to variable water flow and sediment movement. These conditions are then much more favourable for fungi to establish and ...
Open door to treatment of renal fibrosis by showing that it is caused by telomere shortening
2021-03-15
Ageing is a common factor in many diseases. So, what if it were possible to treat them by acting on the causes of ageing or, more specifically, by acting on the shortening of telomeres, the structures that protect chromosomes? This strategy is being pursued by the Telomeres and Telomerase Group of the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), which has already succeeded to cure pulmonary fibrosis and infarctions in mice by lengthening telomeres. Now they take a first step towards doing the same with renal fibrosis by demonstrating that short telomeres are at the origin of this disease, ...
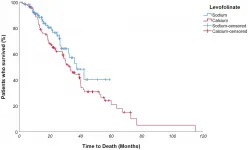
Oncotarget: Folinic acid in colorectal cancer: Esquire or fellow knight?
2021-03-15
Oncotarget published "Folinic acid in colorectal cancer: esquire or fellow knight? Real-world results from a mono institutional, retrospective study" which reported that the stock of therapeutic weapons available in metastatic colorectal cancer has been progressively grown over the years, with improving both survival and patients' clinical outcome: notwithstanding advances in the knowledge of mCRC biology, as well as advances in treatment, fluoropyrimidine antimetabolite drugs have been for 30 years the mainstay of chemotherapy protocols for this malignancy.
5-Fluorouracil seems to act differently depending on administration method: elastomer-mediated continuous infusion better inhibits Thymidylate ...
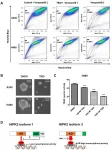
Oncotarget: A novel isoform of Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2
2021-03-15
Oncotarget published "A novel isoform of Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 promotes YAP/TEAD transcriptional activity in NSCLC cells" which reported that In this study, the authors show that a new HIPK2 isoform increases TEAD reporter activity in NSCLC cells.
They detected and cloned a novel HIPK2 isoform 3 and found that its forced overexpression promotes TEAD reporter activity in NSCLC cells.
Expressing HIPK2 isoform 3_K228A kinase-dead plasmid failed to increase TEAD reporter activity in NSCLC cells.
Next, they showed that two siRNAs targeting HIPK2 decreased HIPK2 isoform 3 and YAP protein levels in NSCLC cells.
In summary, this Oncotarget study indicates that HIPK2 isoform 3, the main HIPK2 isoform ...
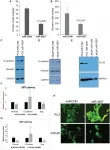
Oncotarget: MicroRNA-4287 is controlling epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer
2021-03-15
The cover for issue 51 of Oncotarget features Figure 5, "miR-4287 overexpression regulates EMT in prostate cancer cell lines," published in "MicroRNA-4287 is a novel tumor suppressor microRNA controlling epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer" by Bhagirath, et al. which reported that the authors analyzed the role of miR-4287 in PCa using clinical tissues and cell lines.
Receiver operating curve analysis showed that miR-4287 distinguishes prostate cancer from normal with a specificity of 88.24% and with an Area under the curve of 0.66. Further, these authors found that miR-4287 ...
In severe COVID, cytokine "hurricane" in lung attracts damaging inflammatory cells
2021-03-15
NEW YORK, NY (March 15, 2021)--A cytokine "hurricane" centered in the lungs drives respiratory symptoms in patients with severe COVID-19, a new study by immunologists at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons suggests.
Two cytokines, CCL2 and CCL3, appear critical in luring immune cells, called monocytes, from the bloodstream into the lungs, where the cells launch an overaggressive attempt to clear the virus.
Targeting these specific cytokines with inhibitors may calm the immune reaction and prevent lung tissue damage. Currently, one drug that blocks immune responses to CCL2 is being studied in clinical trials of patients with severe COVID-19.
Survivors of severe COVID-19, the study also found, had a greater abundance of antiviral T cells in their lungs ...
Significant variation found in timing andselection of genetic tests for non--small-cell lung cancer
2021-03-15
Philadelphia, March 15, 2021 - Biomarker testing surveys specific disease-associated molecules to predict treatment response and disease progression; however its use has complicated the diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In a new study in The Journal of Molecular Diagnosis, published by Elsevier, investigators provide for the first time a complete overview of biomarker testing, spanning multiple treatment lines, in a single cohort of patients.
Using exploratory data analysis and process-mining techniques in a real-world setting, investigators identified significant variation in test utilization and treatment. They also found that while ...
Study reveals new clues about the architecture of X chromosomes
2021-03-15
BOSTON - Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have uncovered new clues that add to the growing understanding of how female mammals, including humans, "silence" one X chromosome. Their new study, published in Molecular Cell, demonstrates how certain proteins alter the "architecture" of the X chromosome, which contributes to its inactivation. Better understanding of X chromosome inactivation could help scientists figure out how to reverse the process, potentially leading to cures for devastating genetic disorders.
Female mammals have two copies of the X chromosome in all of their cells. Each X chromosome contains many genes, but only one of the pair ...
Voltage from the parquet
2021-03-15
Ingo Burgert and his team at Empa and ETH Zurich has proven it time and again: Wood is so much more than "just" a building material. Their research aims at extending the existing characteristics of wood in such a way that it is suitable for completely new ranges of application. For instance, they have already developed high-strength, water-repellent and magnetizable wood. Now, together with the Empa research group of Francis Schwarze and Javier Ribera, the team has developed a simple, environmentally friendly process for generating electricity from a type of wood sponge, as they reported last week in the journal Science Advances.
Voltage through deformation
If you want to generate electricity ...
NASA images reveal important forests and wetlands are disappearing in Belize
2021-03-15
AUSTIN, Texas -- Using NASA satellite images and machine learning, researchers with The University of Texas at Austin have mapped changes in the landscape of northwestern Belize over a span of four decades, finding significant losses of forest and wetlands, but also successful regrowth of forest in established conservation zones that protect surviving structures of the ancient Maya.
The research serves as a case study for other rapidly developing and tropical regions of the globe, especially in places struggling to balance forest and wetland conservation with agricultural needs and food security.
"Broad-scale global studies show that tropical deforestation and wetland destruction is occurring ...
Story tips: Urban climate impacts, materials' dual approach and healing power
2021-03-15
Modeling - Urban climate impacts
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have identified a statistical relationship between the growth of cities and the spread of paved surfaces like roads and sidewalks. These impervious surfaces impede the flow of water into the ground, affecting the water cycle and, by extension, the climate.
"We've shown that there is a specific mathematical shape to the relationship between a city's population and the total paved area," ORNL's Christa Brelsford said. "Using that, we examined climate model predictions and determined they correctly represent some important attributes ...
Three bacterial strains discovered on space station may help grow plants on Mars
2021-03-15
In order to withstand the rigors of space on deep-space missions, food grown outside of Earth needs a little extra help from bacteria. Now, a recent discovery aboard the International Space Station (ISS) has researchers may help create the 'fuel' to help plants withstand such stressful situations.
Publishing their findings to END ...
Women veterinarians earn $100K less than men annually
2021-03-15
ITHACA, N.Y. - Women veterinarians make less than their male counterparts, new research from Cornell University's College of Veterinary Medicine has found ¬- with an annual difference of around $100,000 among the top quarter of earners.
The disparity predominantly affects recent graduates and the top half of earners, according to the research, the first overarching study of the wage gap in the veterinary industry.
"Veterinarians can take many paths in their careers, all of which affect earning potential," said the paper's senior author, Dr. Clinton Neill, assistant professor in the Department of Population Medicine and Diagnostic Sciences.
"Similar to what's been found in the human medicine world, we found the wage gap was more prominent ...
When English and French mix in literature
2021-03-15
Do children learning French as a second language see benefits from reading bilingual French-English children's books?
A study recently published in the journal Language and Literacy found that bilingual books, which are not often used in French immersion classrooms, are seen by students as an effective tool for second language learning.
To find out more on this topic, we spoke with the co-author of the paper, Joël Thibeault, Assistant Professor of French education at uOttawa's Faculty of Education.
What is the topic of your research?
"My research focuses on the educational value of bilingual children's books in the teaching of French as a second language. To highlight this value, I zeroed in on elementary students in French immersion ...
Faster drug discovery through machine learning
2021-03-15
Drugs can only work if they stick to their target proteins in the body. Assessing that stickiness is a key hurdle in the drug discovery and screening process. New research combining chemistry and machine learning could lower that hurdle.
The new technique, dubbed DeepBAR, quickly calculates the binding affinities between drug candidates and their targets. The approach yields precise calculations in a fraction of the time compared to previous state-of-the-art methods. The researchers say DeepBAR could one day quicken the pace of drug discovery and protein engineering.
"Our method is orders of magnitude faster than before, meaning we can have drug discovery that is both efficient and reliable," ...
What happens in your brain when you 'lose yourself' in fiction
2021-03-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio - If you count yourself among those who lose themselves in the lives of fictional characters, scientists now have a better idea of how that happens.
Researchers found that the more immersed people tend to get into "becoming" a fictional character, the more they use the same part of the brain to think about the character as they do to think about themselves.
"When they think about a favorite fictional character, it appears similar in one part of the brain as when they are thinking about themselves," said Timothy Broom, lead author of the study and doctoral student in psychology at The Ohio State University.
The study was published ...
Pre-term births in Tennessee decreased during pandemic
2021-03-15
Statewide stay-at-home orders put in place as Tennessee fought to control the spread of coronavirus last March were associated with a 14% lower rate of preterm birth, according to a research letter published today in JAMA Pediatrics.
Preterm infants have higher morbidity and mortality risks than babies born at term.
Senior author Stephen Patrick, MD, director of the Vanderbilt Center for Child Health Policy and a neonatologist at the Monroe Carell Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt and his colleagues had observed in March that there appeared to be fewer infants than usual in the NICU at ...
Video-led feedback programme reduces behaviour problems in children as young as 12 months
2021-03-15
A home-based parenting programme to prevent childhood behaviour problems, which very unusually focuses on children when they are still toddlers and, in some cases, just 12 months old, has proven highly successful during its first public health trial.
The six-session programme involves providing carefully-prepared feedback to parents about how they can build on positive moments when playing and engaging with their child using video clips of everyday interactions, which are filmed by a health professional while visiting their home.
It was trialled with 300 families of children who had shown early signs of behaviour problems. Half of the families received the programme alongside routine ...
[1] ... [2527]
[2528]
[2529]
[2530]
[2531]
[2532]
[2533]
[2534]
2535
[2536]
[2537]
[2538]
[2539]
[2540]
[2541]
[2542]
[2543]
... [8819]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.