Lung cancer resistance: the key is glucose
2021-03-22
Cancers are not only made of tumor cells. In fact, as they grow, they develop an entire cellular ecosystem within and around them. This "tumor microenvironment" is made up of multiple cell types, including cells of the immune system, like T lymphocytes and neutrophils.
The tumor microenvironment has predictably drawn a lot of interest from cancer researchers, who are constantly searching for potential therapeutic targets. When it comes to the immune cells, most research focuses on T lymphocytes, which have become primary targets of cancer immunotherapy ...
Global biodiversity awareness tracked with Wikipedia page views
2021-03-22
Wikipedia page views could be used to monitor global awareness of biodiversity, proposes a research team from UCL, ZSL, and the RSPB.
Using their new metric, the research team found that awareness of biodiversity is marginally increasing, but the rate of change varies greatly between different groups of animals, as they report in a paper included in an upcoming special section of Conversation Biology.
Lead author, PhD student Joe Millard (UCL Centre for Biodiversity & Environment Research, UCL Biosciences and Institute of Zoology, ZSL) said: "As extinctions and biodiversity losses ramp up worldwide, largely due to climate change and other human actions, it's vital that ...
Motherless gorillas beat the odds
2021-03-22
A study by the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund shows that gorilla families come together to support young gorillas that lose their mothers.
The findings, published in the journal eLife, use the Fossey Fund's more than 50-year dataset to discover how maternal loss influences young gorillas' social relationships, survival and future reproduction. The study shows when young mountain gorillas lose their mothers, the rest of the group helps buffer the loss by strengthening their relationships with the orphans.
"Mothers are incredibly important for survival early in life--this is something that is shared across all mammals," said lead author Dr. Robin Morrison. "But in social mammals, like ourselves, mothers often continue to provide vital support up to adulthood and even beyond."
"In ...
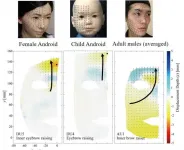
Expressing some doubts about android faces
2021-03-22
Osaka, Japan - Researchers from the Graduate School of Engineering and Symbiotic Intelligent Systems Research Center at Osaka University used motion capture cameras to compare the expressions of android and human faces. They found that the mechanical facial movements of the robots, especially in the upper regions, did not fully reproduce the curved flow lines seen in the faces of actual people. This research may lead to more lifelike and expressive artificial faces.
The field of robotics has advanced a great deal over the past decades. However, while current androids can appear very humanlike at first, their active facial expressions may still be unnatural and slightly unsettling to us. The exact reasons ...
Study estimates rising global burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer
2021-03-22
Although cancers that occur in the gallbladder or bile ducts are rare, their rates are increasing. A recent study provides details on the burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer (GBTC) across 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017. The findings are published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Determining GBTC estimates and trends in different global regions can help to guide research priorities and policies for prevention and treatment. With this in mind, a team of scientists examined publicly available information ...
Having a single personal doctor may sometimes lead to unnecessary tests
2021-03-22
Patient care by a single primary care physician is associated with many health benefits, including increased treatment adherence and decreased hospital admissions and mortality risk. But can the relationship built between doctor and patient also lead to unnecessary care?
A new University of Florida study finds that male patients who have a single general physician were more likely to receive a prostate cancer screening test during a period when the test was not recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force. The study, which appears in END ...
Toxic PAH air pollutants from fossil fuels 'multiply' in sunlight
2021-03-22
When power stations burn coal, a class of compounds called Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, or PAHs, form part of the resulting air pollution. Researchers have found that PAHs toxins degrade in sunlight into 'children' compounds and by-products.
Some 'children' compounds can be more toxic than the 'parent' PAHs. Rivers and dams affected by PAHs are likely contaminated by a much larger number of toxins than are emitted by major polluters, researchers show in Chemosphere.
A coal-fired power station and a cigarette have more in common than one might think. So do the exhaust pipes from cars and burning crop residues. The same is true for an aeroplane passing high over a wildfire ...
Major 'State of the Planet' report out in advance of first Nobel Prize Summit
2021-03-22
Human actions are threatening the resilience and stability of Earth's biosphere - the wafer-thin veil around Earth where life thrives. This has profound implications for the development of civilizations, say an international group of researchers in a report published for the first Nobel Prize Summit, a digital gathering to be held in April to discuss the state of the planet in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Humanity is now the dominant force of change on planet Earth," according to the analysis published in Ambio, a journal of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
"The risks we are taking are astounding," says co-author Johan Rockström, director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and co-author of the analysis. "We are at the dawn of what must be a transformative ...
Personal values & political worldviews shape perception of COVID-19 risk more than its severity
2021-03-22
Study taken throughout the pandemic shows those who feel government should be less controlling believe COVID-19 poses less risk, which in turn was associated with the adoption of fewer protective behaviours
"A fearful population is not necessarily desirable... people may be underestimating or overestimating the actual risk at different times."
People's politics and values are exerting a bigger influence on how much of a threat they feel from COVID-19 compared to objective indicators such as the number of confirmed cases.
That's the finding of a new University of Cambridge survey which measured how attitudes to the coronavirus have varied over the course of 10 months of the pandemic for more ...
Evidence supports Covid hearing loss link, say scientists
2021-03-22
Hearing loss and other auditory problems are strongly associated with Covid-19 according to a systematic review of research evidence led by University of Manchester and NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) scientists.
Professor Kevin Munro and PhD researcher Ibrahim Almufarrij found 56 studies that identified an association between COVID-19 and auditory and vestibular problems.
They pooled data from 24 of the studies to estimate that the prevalence of hearing loss was 7.6%, tinnitus was 14.8% and vertigo was 7.2%.
They publish their findings in the International Journal of Audiology.
However, the team - who followed up their review carried out a year ago - ...
Eating processed meat could increase dementia?risk?
2021-03-22
Scientists from the University of Leeds's Nutritional Epidemiology Group used data from 500,000 people, discovering that consuming a 25g serving of processed meat a day, the equivalent to one rasher of bacon, is associated with a 44% increased risk of developing the disease.
But their findings also show eating some unprocessed red meat, such as beef, pork or veal, could be protective, as people who consumed 50g a day were 19% less likely to develop dementia.?
The researchers were exploring a potential link between consumption of meat and the development of dementia, a health condition that affects 5%-8% of over 60s worldwide.
Their results, titled Meat consumption and risk of incident dementia: cohort study of 493888 UK Biobank participants, are published today in the American ...
Readmission rate high for adults hospitalized for diabetic ketoacidosis
2021-03-21
WASHINGTON--One in five adults with type 1 diabetes who require in-hospital treatment of the life-threatening condition diabetic ketoacidosis has an unplanned repeat hospital visit within a month and is twice as likely to die during the second hospitalization, a new study finds. The results, which will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, also identified several factors that increased the readmission risk for these patients.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, which can occur from insufficient insulin medicine or from an infection, is a dangerous accumulation of acid in the blood due to ...
Weekly insulin helps patients with type 2 diabetes achieve similar blood sugar control to daily insulin
2021-03-21
WASHINGTON--A new once-weekly basal insulin injection demonstrated similar efficacy and safety and a lower rate of low blood sugar episodes compared with a daily basal insulin, according to a phase 2 clinical trial. The study results, which will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, compared an investigational drug called basal insulin Fc (BIF) with insulin degludec, a commercially available long-lasting daily insulin, in patients with type 2 diabetes.
"These study results demonstrate that BIF has promise as a once-weekly basal insulin and could be an advancement in insulin therapy," ...
COVID-19 can cause atypical thyroid inflammation
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Some patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 disease seem to experience inflammation of the thyroid gland that is different from thyroid inflammation caused by other viruses, according to a study presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
One-third of the study participants still had signs of thyroid inflammation after three months, even though their thyroid function had normalized. The study is following patients to determine whether this inflammation will trigger permanent thyroid dysfunction.
In spring 2020, 15 percent of the COVID-19 patients hospitalized in acute medicine units ...
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients with obesity are significantly more likely to need ICU care
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--People with obesity who are hospitalized with COVID-19 have a significantly higher rate of ICU admissions and longer duration of ICU stay compared to people with a normal body mass index (BMI), according to a study presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
"The association between obesity and a more severe clinical course of COVID-19 highlights the vulnerability of this population during the current pandemic and the need for public health efforts to prevent and treat obesity, in the current pandemic and beyond," said lead researcher Yu Mi Kang, M.D., Ph.D., of Yale New Haven ...
Poor diabetes control in children tied to high risk for COVID-19 complications, death
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Children with poorly controlled type 1 diabetes have a 10 times higher risk of COVID-19-related complications and death compared to those with well-controlled diabetes, according to a study presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
"This study shows keeping diabetic children's blood sugar under control is more important than ever during the pandemic," said lead author Manish Raisingani, M.D., of the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences and Arkansas Children's in Little Rock, Ark. "The findings will help children with type 1 diabetes and their families make better choices about the safety of attending school in person and engaging ...
Common drugs for type 2 diabetes and obesity do not increase breast cancer risk
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Commonly used medications for type 2 diabetes and obesity called glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), are not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, despite previous studies that suggested a possible link, according to a study presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
"GLP-1RAs can be used as adjunct to diet and exercise in subjects with type 2 diabetes and those without type 2 diabetes and excess weight, without an increased risk of breast cancer or noncancerous masses in the breast," said lead researcher Giovana Fagundes Piccoli, M.D., of the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil.
GLP-1 RAs have been shown to be effective in treating obesity and type 2 diabetes ...
Genetic evidence suggests men can develop PCOS-like condition
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--New genetic research suggests men can develop characteristics of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)--a common metabolic and reproductive disorder that affects women. The study was presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
PCOS is a common disorder characterized by irregular menstrual periods, disruption of normal metabolism and elevated testosterone levels. PCOS affects up to 10% of all women of reproductive age. The disorder can lead to obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease, which are often life-long conditions.
Men who have genetic risk factors ...
Sleep disturbances may contribute to weight gain in menopause
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Addressing sleep symptoms during menopause may reduce susceptibility to weight gain, according to a small study presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
"Our findings suggest that not only estrogen withdrawal but also sleep disturbances during menopause may contribute to changes in a woman's body that could predispose midlife women to weight gain," said lead researcher Leilah Grant, Ph.D., of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston, Mass. "Helping women sleep better during menopause may therefore reduce the chances ...
Largest-ever analysis of its kind finds Cushing's syndrome triples risk of death
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Endogenous Cushing's syndrome, a rare hormonal disorder, is associated with a threefold increase in death, primarily due to cardiovascular disease and infection, according to a study whose results will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
The research, according to the study authors, is the largest systematic review and meta-analysis to date of studies of endogenous (meaning "inside your body") Cushing's syndrome. Whereas Cushing's syndrome most often results from external factors--taking cortisol-like medications such as prednisone--the endogenous type occurs when the body overproduces the hormone cortisol, affecting multiple bodily ...
Many endocrine patients, providers want to continue telehealth after pandemic
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Two-thirds of patients with chronic endocrine health problems who need close monitoring say they would like to continue with telemedicine follow-up visits after the COVID-19 pandemic ends, according to a survey that will be presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting. Three-quarters of providers also said they want to continue with telehealth after the pandemic.
"Endocrinology clinics have significant number of patients who need long-term close follow-up for medication adjustments, symptom checks and counseling," said lead researcher Maryam Nemati, M.D., of San Joaquin General Hospital in French Camp, Calif. "Our ...
Combination thyroid hormone therapies treat hypothyroidism as well as levothyroxine
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Treatment of hypothyroidism, which results from an underactive thyroid gland, should be individualized and consideration should be given to alternatives to the first-line therapy, including desiccated thyroid extract and combination therapy to replace the body's two main thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Results of their new randomized clinical study are being presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
Combination therapy has been shown to be equally as effective as the standard treatment with levothyroxine alone, researchers say.
"There are now proven good treatment options for the more than one in 10 patients with hypothyroidism who continue to experience symptoms of fatigue, mental fogginess, weight ...
Study finds oral testosterone therapy undecanoate is effective, with no liver toxicity
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--An industry-supported study of an oral testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), testosterone undecanoate (TU, brand name Jatenzo) finds it is an effective, long-term treatment for men with low testosterone levels, with no evidence of liver toxicity. The findings are being presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
TST is currently available in multiple modes of administration, including implantable pellets, transdermal gels and intramuscular injections.
"For many men with low testosterone levels, an oral option is preferred to avoid issues associated with other ...
Night owls with gestational diabetes may face higher risk of pregnancy complications
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Among women who develop diabetes during pregnancy, night owls have a higher risk of complications for mother and baby than early birds do, according to a study whose results will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
Compared with other pregnant women with gestational diabetes, those with a preference for evening activity had three times higher the chance of having preeclampsia, which is pregnancy-induced high blood pressure, and four times the rate of their newborns being treated in a neonatal intensive care unit, the study investigators reported.
These findings suggest a ...
First targeted therapy for children with achondroplasia shows persistent height gain
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Children with achondroplasia, the most common form of disproportionate short stature, grow taller with trends in improved body proportions after two years of daily vosoritide treatment, a new study analysis finds. Results of the industry-sponsored study will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
"This is the first robust evidence of a precision therapy for achondroplasia," said the lead investigator, Ravi Savarirayan, M.D., Ph.D., a professor at Murdoch Children's Research Institute at Royal Children's Hospital in Parkville, Australia.
Achondroplasia is a genetic bone growth ...
[1] ... [2522]
[2523]
[2524]
[2525]
[2526]
[2527]
[2528]
[2529]
2530
[2531]
[2532]
[2533]
[2534]
[2535]
[2536]
[2537]
[2538]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.