Dogs infected with Leishmania parasites smell more attractive to female sand flies
2021-03-18
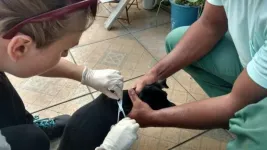
Dogs infected with the Leishmania parasite smell more attractive to female sand flies than males, say researchers.
The study published in PLOS Pathogens is led by Professor Gordon Hamilton of Lancaster University.
In Brazil, the parasite Leishmania infantum is transmitted by the bite of infected female Lutzomyia longipalpis sand flies.
Globally over 350 million people are at risk of leishmaniasis, with up to 300,000 new cases annually. In Brazil alone there are approximately 4,500 deaths each year from the visceral form of the disease and children under 15 years old are more likely to be affected.
Leishmania parasites ...
Vaccines alone may not be enough to end pandemic
2021-03-18
WASHINGTON -- Even as vaccines are becoming more readily available in the U.S., protecting against the asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic spread of the virus (SARS-CoV-2) that causes COVID-19 is key to ending the pandemic, say two Georgetown infectious disease experts.
In their Perspective, " END ...
Found in space: Complex carbon-based molecules
2021-03-18
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Much of the carbon in space is believed to exist in the form of large molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Since the 1980s, circumstantial evidence has indicated that these molecules are abundant in space, but they have not been directly observed.
Now, a team of researchers led by MIT Assistant Professor Brett McGuire has identified two distinctive PAHs in a patch of space called the Taurus Molecular Cloud (TMC-1). PAHs were believed to form efficiently only at high temperatures -- on Earth, they occur as byproducts of burning fossil fuels, and they're also found in char marks on grilled ...
Yale researchers create 'Ancestry.com' for cells
2021-03-18
One of great mysteries of human biology is how a single cell can give rise to the 37 trillion cells contained in the average body, each with its own specialized role. Researchers at Yale University and the Mayo Clinic have devised a way to recreate the earliest stages of cellular development that gives rise to such an amazing diversity of cell types.
Using skin cells harvested from two living humans, researchers in the lab of Yale's Flora Vaccarino were able to track their cellular lineage by identifying tiny variations or mutations contained within the genomes of those cells.
These "somatic" or non-inherited mutations are generated at each cell division during a human's development. The percentage of cells bearing the traces of any ...
Double duty: Gut's immune system helps regulate food processing, too
2021-03-18
The small intestine is ground zero for survival of animals. It is responsible for absorbing the nutrients crucial to life and it wards off toxic chemicals and life-threatening bacteria.
In a new study published March 18 in the journal Science, Yale researchers report the critical role played by the gut's immune system in these key processes. The immune system, they found, not only defends against pathogens but regulates which nutrients are taken in.
The findings may provide insights into origins of metabolic disease and malnutrition that is common in ...
Discovery of a 'winged' shark in the Cretaceous seas
2021-03-18
93 million years ago, bizarre, winged sharks swam in the waters of the Gulf of Mexico. This newly described fossil species, called Aquilolamna milarcae, has allowed its discoverers to erect a new family. Like manta rays, these 'eagle sharks' are characterised by extremely long and thin pectoral fins reminiscent of wings. The specimen studied was 1.65 metres long and had a span of 1.90 metres.
Aquilolamna milarcae had a caudal fin with a well-developed superior lobe, typical of most pelagic sharks, such as whale sharks and tiger sharks. Thus, its anatomical features thus ...
How bushfire smoke traveled around the world
2021-03-18
It's not just how hot the fires burn - it's also where they burn that matters. During the recent extreme fire season in Australia, which began in 2019 and burned into 2020, millions of tons of smoke particles were released into the atmosphere. Most of those particles followed a typical pattern, settling to the ground after a day or week; yet the ones created in fires burning in one corner of the country managed to blanket the entire Southern hemisphere for months. A pair of Israeli scientists managed to track puzzling January and February 2020 spikes in a measure of particle-laden haze to those fires, and then, in a paper recently published in Science, they ...
Self-compassion can lessen feelings of work-from-home loneliness, finds study
2021-03-18
INDIANAPOLIS -- The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is keeping millions of Americans from their usual offices, as they find themselves still working at home. Even with the vaccine now being distributed, working from home may still be the future for some, and new research suggests the resulting work loneliness negatively impacts employee well-being. ...
Estimating the timing of the earliest SARS-CoV-2 case in Hubei Province, China
2021-03-18
Researchers who simulated early stages of the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in Wuhan, China, conclude that the virus was likely circulating earlier than has been described, possibly even in mid-October 2019. The findings do not reveal whether the virus that first emerged was less "fit" than the virus that spread throughout China, say the authors, but the estimates do further distance the first ("index") case from the outbreak at the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, which has received much attention. A concerted effort has been made to determine when the SARS-CoV-2 virus ...
Could leak in blood-brain barrier be cause of poor memory?
2021-03-18
Have you forgotten where you laid your keys? Ever wondered where you had parked your car? Or having trouble remembering the name of the new neighbor? Unfortunately, these things seem to get worse as one gets older. A big question for researchers is where does benign forgetfulness end and true disease begin?
One of the keys to having a healthy brain at any age is having a healthy blood-brain barrier, a complex interface of blood vessels that run through the brain. Researchers reviewed more than 150 articles to look at what happens to the blood-brain barrier as we age. Their findings were published March 15 in Nature ...
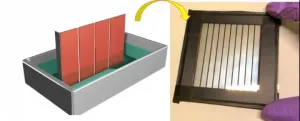
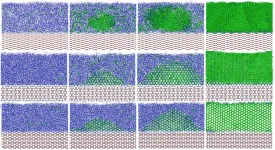
New perovskite fabrication method for solar cells paves way to large-scale production
2021-03-18
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 18, 2021--A new, simpler solution process for fabricating stable perovskite solar cells overcomes the key bottleneck to large-scale production and commercialization of this promising renewable-energy technology, which has remained tantalizingly out of reach for more than a decade.
"Our work paves the way for low-cost, high-throughput commercial-scale production of large-scale solar modules in the near future," said Wanyi Nie, a research scientist fellow in the Center of Integrated Nanotechnologies at Los Alamos National Laboratory and corresponding ...
'Vulnerable' countries experience lower COVID-19 infection and death rates than the norm
2021-03-18
During a pandemic like COVID-19, vulnerable countries are traditionally the focus of global attention and concern. However, new research suggests that we need to rebuild our understanding. A study published in KeAi's Global Health Journal, examined the relationship between state vulnerabilities (measured using the Fragile States Index (FSI) from Fund for Peace) and COVID-19 incidence and death rates in 146 countries. The FSI consists of 12 specific indicators covering cohesion, economy, politics and society. "When using the total FSI score for statistical analysis, we were surprised to find that, overall, the more fragile countries had lower cumulative incidence and fatality rates for COVID-19," explains one of the study's authors, Yangmu ...
Reversing cancer's gluttony
2021-03-18
In new findings published online March 18, 2021 in the journal Cancer Cell, an international team of researchers, led by scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Moores Cancer Center, describe how pancreatic cancer cells use an alternative method to find necessary nutrients, defying current therapies, to help them grow and spread.
Pancreatic cancer accounts for roughly 3 percent of all cancers in the United States, but it is among the most aggressive and deadly, resulting in 7 percent of all cancer deaths annually. Pancreatic cancer is especially deadly once it metastasizes, with the number of people who are alive five years later declining from 37 percent to just 3 percent.
All cancer cells require a constant supply of nutrients. Some types ...
New material: Rapid color change
2021-03-18
Smart glass can change its color quickly through electricity. A new material developed by chemists of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität (LMU) in Munich has now set a speed record for such a change.
On the highway at night. It rains, the bright headlights of the car behind you are blinding. How convenient to have an automatically dimming rearview mirror in such a case. Technically, this helpful extra is based on electrochromic materials. When a voltage is applied, their light absorption and color change. Controlled by a light sensor, the rearview mirror can thus filter out strongly dazzling light.
Recently, experts discovered that, in addition to established inorganic electrochromic materials, a new generation of highly ordered lattice structures can also be equipped ...
Using conservation criminology to understand restaurant's role in urban wild meat trade
2021-03-18
KINSHASA, DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO (March 18, 2021) - A new study in the journal Conservation Science and Practice finds that restaurants in urban areas in Central Africa play a key role in whether protected wildlife winds up on the menu.
The study, by a team of scientists from Michigan State University, Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), and University of Maryland, used a crime science "hot product" approach, which looks at frequently stolen items coveted by thieves. The approach offered new insights into wildlife targeted by the urban wild meat trade and can inform urban wildlife policies.
The study engaged lower, middle, and upper-level tiered restaurants to understand which species were traded. ...
Study reveals significant concerns over growing scale of sex selective abortions in Nepal
2021-03-18
Detailed, new analysis published this week in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) Open highlights significant concerns about a growing issue of sex selective abortion of girls in Nepal.
Drawing on census data from 2011 and follow-on survey data from 2016, the social scientists estimate that roughly one in 50 girl births were 'missing' from records (i.e. had been aborted) between 2006-11 (22,540 girl births in total). In the year before the census (June 2010 - June 2011) this had risen to one in 38.
For certain areas of the country, the practice was more widespread. In Arghakhanchi, the most affected district, one in every six girl births were 'missing' in census data. In the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal's main urban centre, around 115 boys are born for ...
Babies pay attention with down payment from immature brain region
2021-03-18
Anyone who has watched an infant's eyes follow a dangling trinket dancing in front of them knows that babies are capable of paying attention with laser focus.
But with large areas of their young brains still underdeveloped, how do they manage to do so?
Using an approach pioneered at Yale that uses fMRI (or functional magnetic resonance imaging) to scan the brains of awake babies, a team of university psychologists show that when focusing their attention infants under a year of age recruit areas of their frontal cortex, a section of the brain involved in more advanced functions that was previously thought to be immature in babies. The findings were ...
Organic crystals' ice-forming superpowers
2021-03-18
At the heart of clouds are ice crystals. And at the heart of ice crystals, often, are aerosol particles - dust in the atmosphere onto which ice can form more easily than in the open air.
It's a bit mysterious how this happens, though, because ice crystals are orderly structures of molecules, while aerosols are often disorganized chunks. New research by Valeria Molinero, distinguished professor of chemistry, and Atanu K. Metya, now at the Indian Institute of Technology Patna, shows how crystals of organic molecules, a common component of aerosols, can get the ...
Animal behaviour: Female wild bonobos provide care for infants outside their social group
2021-03-18
Observations of groups of wild bonobos, reported in Scientific Reports, suggest that two infants may have been adopted by adult females belonging to different social groups. The findings may represent the first report of cross-group adoption in wild bonobos, and potentially also the first cases of cross-group adoption in wild apes.
Bonobos form social groups of multiple males and females that sometimes temporarily associate with one another. Nahoko Tokuyama and colleagues observed four groups of wild bonobos between April 2019 and March 2020 in the Luo Scientific Reserve in Wamba, Democratic Republic of the Congo. The authors identified two infants whom ...
Palaeontology: Prehistoric armoured dinosaur may have been able to dig
2021-03-18
Newly excavated skeletal remains of an ankylosaurid -- a large armoured herbivore that lived during the Cretaceous Period -- may indicate that members of this family of dinosaurs were able to dig, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. The specimen, known as MPC-D 100/1359, may further our understanding of ankylosaurid behaviour during the Late Cretaceous (84-72 million years ago).
Yuong-Nam Lee and colleagues excavated the skeletal elements of MPC-D 100/1359 from a deposit of the Baruungoyot Formation in the southern Gobi Desert, Mongolia, ...
New analysis shows potential for 'solar canals' in California
2021-03-18
UC Santa Cruz researchers published a new study--in collaboration with UC Water and the Sierra Nevada Research Institute at UC Merced--that suggests covering California's 6,350 km network of public water delivery canals with solar panels could be an economically feasible means of advancing both renewable energy and water conservation.
The concept of "solar canals" has been gaining momentum around the world as climate change increases the risk of drought in many regions. Solar panels can shade canals to help prevent water loss through evaporation, and some types of solar panels also work better over canals, because the cooler environment keeps them from overheating. ...
Artificial neuron device could shrink energy use and size of neural network hardware
2021-03-18
Training neural networks to perform tasks, such as recognizing images or navigating self-driving cars, could one day require less computing power and hardware thanks to a new artificial neuron device developed by researchers at the University of California San Diego. The device can run neural network computations using 100 to 1000 times less energy and area than existing CMOS-based hardware.
Researchers report their work in a paper published Mar. 18 in Nature Nanotechnology.
Neural networks are a series of connected layers of artificial neurons, where the output of one layer provides the ...
System detects errors when medication is self-administered
2021-03-18
From swallowing pills to injecting insulin, patients frequently administer their own medication. But they don't always get it right. Improper adherence to doctors' orders is commonplace, accounting for thousands of deaths and billions of dollars in medical costs annually. MIT researchers have developed a system to reduce those numbers for some types of medications.
The new technology pairs wireless sensing with artificial intelligence to determine when a patient is using an insulin pen or inhaler, and flags potential errors in the patient's administration method. "Some past work reports that up to 70% of patients do not ...
Researchers identify a way to reverse high blood sugar and muscle loss
2021-03-18
A study by Monash University has uncovered that liver metabolism is disrupted in people with obesity-related type 2 diabetes, which contributes to high blood sugar and muscle loss - also known as skeletal muscle atrophy.
Using human trials as well as mouse models, collaborative research led by Dr Adam Rose at Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute has found the liver metabolism of the amino acid alanine is altered in people with obesity-related type 2 diabetes. By selectively silencing enzymes that break down alanine in liver cells, high blood sugar and muscle loss can be reversed by the restoration of skeletal muscle protein synthesis, a critical determinant of muscle size and strength.
The research, published today in Nature Metabolism, has shown the altered liver metabolism ...
Scientists see cross-group adoption of young bonobo apes in the wild for the first time
2021-03-18
Scientists have witnessed bonobo apes adopting infants who were born outside of their social group for the first time in the wild.
Researchers, including psychologists at Durham University, UK, twice saw the unusual occurrence among bonobos in the Democratic Republic of Congo, in central Africa.
They say their findings give us greater insight into the parental instincts of one of humans' closest relatives and could help to explain the emotional reason behind why people readily adopt children who they have had no previous connection with.
The research, led by Kyoto University, in Japan, is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Researchers observed a number of bonobo groups over several years in the Wamba area of ...
[1] ... [2516]
[2517]
[2518]
[2519]
[2520]
[2521]
[2522]
[2523]
2524
[2525]
[2526]
[2527]
[2528]
[2529]
[2530]
[2531]
[2532]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.