Majority of cancer patients with COVID-19 have similar immune response to people without cancer
2021-03-22
March 22, 2021 (BRONX, NY)-- Most people with cancer who are infected by the novel coronavirus produce antibodies at a rate comparable to the rest of the population--but their ability to do so depends on their type of cancer and the treatments they've received, according to a new study by researchers at Montefiore Health System and Albert Einstein College of Medicine. The findings, published online today in Nature Cancer, may lead to better care for cancer patients, who face a heightened risk of dying from COVID-19, and suggests that cancer patients should ...
Hormone drugs may disarm COVID-19 spike protein and stop disease progression
2021-03-22
PHILADELPHIA--Hormone drugs that reduce androgen levels may help disarm the coronavirus spike protein used to infect cells and stop the progression of severe COVID-19 disease, suggests a new preclinical study from researchers in the Abramson Cancer Center at the University of Pennsylvania and published online in Cell Press's iScience.
Researchers show how two receptors--known as ACE2 and TMPRSS2--are regulated by the androgen hormone and used by SARS-CoV-2 to gain entry into host cells. Blocking the receptors with the clinically proven inhibitor Camostat and other anti-androgen therapies prevented viral entry and replication, they also showed in lab studies.
The findings provide more insight into the molecular mechanisms of the virus but also support ...
Researchers' algorithm designs soft robots that sense
2021-03-22
There are some tasks that traditional robots -- the rigid and metallic kind -- simply aren't cut out for. Soft-bodied robots, on the other hand, may be able to interact with people more safely or slip into tight spaces with ease. But for robots to reliably complete their programmed duties, they need to know the whereabouts of all their body parts. That's a tall task for a soft robot that can deform in a virtually infinite number of ways.
MIT researchers have developed an algorithm to help engineers design soft robots that collect more useful information about their surroundings. The deep-learning algorithm suggests an optimized placement of sensors within the robot's body, allowing it to better interact with ...
Diamond color centers for nonlinear photonics
2021-03-22
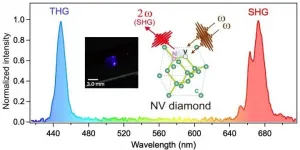
Tsukuba, Japan - Researchers from the Department of Applied Physics at the University of Tsukuba demonstrated second-order nonlinear optical effects in diamonds by taking advantage of internal color center defects that break inversion symmetry of diamond crystal. This research may lead to faster internet communications, all-optical computers, and even open a route to next generation quantum sensing technologies.
Current fiber optical technology uses light pulses to transfer broad-bandwidth data that let you check your email, watch videos, and everything else on the Internet. The main drawback is that light pulses hardly interact with each other, so the information must be converted into electrical signals to allow your computer ...
Cells burn more calories after just one bout of moderate aerobic exercise, OSU study finds
2021-03-22
In a recent study testing the effects of exercise on overall metabolism, researchers at Oregon State University found that even a single session of moderate aerobic exercise makes a difference in the cells of otherwise sedentary people.
Mitochondria are the part of the cell responsible for the biological process of respiration, which turns fuels such as sugars and fats into energy, so the researchers focused only on mitochondria function.
"What we found is that, regardless of what fuel the mitochondria were using, there were mild increases in the ability to burn off the fuels," said Matt Robinson, lead author on the study and an assistant professor ...
Deluge of DNA changes drives progression of fatal melanomas
2021-03-22
Melbourne researchers have revealed how melanoma cells are flooded with DNA changes as this skin cancer progresses from early, treatable stages through to fatal end-stage disease.
Using genomics, the team tracked DNA changes occurring in melanoma samples donated by patients as their disease progressed, right through to the time the patient died. This revealed dramatic and chaotic genetic changes that accumulated in the melanoma cells as the cancers progressed, providing clues to potential new approaches to treating this disease.
The research, published in Nature Communications, was led by Professor Mark Shackleton, Professor Director of Oncology at Alfred Health and Monash University; Professor ...
Pain differs: Researchers unveil distinct neural circuits
2021-03-22
Clinically, multiple lines of evidence show that chronic pain and depressive symptoms are frequently encountered. Patients suffered from both pain and depression are likely to become insensitive to drug treatment, indicating a refractory disease. The neural mechanism under this comorbidity remains unclear.
In a study published in Nature Neuroscience, the research team led by Prof. ZHANG Zhi and Dr. LI Juan from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), reported the discrete thalamocortical circuits underlying the pain symptom caused by tissue injury and depression-like states.
Being the gateway towards cerebral cortex and considered as the major source of 'nociceptive ...
Researchers use AI to estimate focal mechanism parameters of earthquake
2021-03-22
The research team led by Prof. ZHANG Jie from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences made progress on real-time determination of earthquake focal mechanism through deep learning. The work was published in Nature Communications.
Since there are connections between characteristics of the rupture surface of the source fault and seismic wave radiated by the source, it's vital to monitor the earthquake by immediate determination of the source focal mechanism which inferred from multiple ground seismic records.
However, it's hard to calculate the mechanism from the simple ...
Atomic techniques reveal the evolution of a bacterial protein
2021-03-22
A combination of an array of atomic-level techniques has allowed researchers to show how changes in an environment-sensing protein enable bacteria to survive in different habitats, from the human gut to deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
"The study gives us unprecedented atomic-level insight into how bacteria adapt to changing conditions," says Stefan Arold, professor of bioscience at KAUST. "To obtain these insights, we pushed the limits of three different methods of investigation and combined their results into a unified picture."
The histone-like nucleoid-structuring (H-NS) protein allows bacteria to sense changes in their environment, such as changes in temperature and salinity. Previously, the team had shown how the intestinal pathogen Salmonella typhimurium ...
Human fondness, faith in machines grows during pandemic
2021-03-22
People are not very nice to machines. The disdain goes beyond the slot machine that emptied your wallet, a dispenser that failed to deliver a Coke or a navigation system that took you on an unwanted detour.
Yet USC researchers report that people affected by COVID-19 are showing more goodwill -- to humans and to human-like autonomous machines.
"The new discovery here is that when people are distracted by something distressing, they treat machines socially like they would treat other people. We found greater faith in technology due to the pandemic and a closing of the gap between humans and machines," said Jonathan Gratch, senior author of the study and director for virtual humans research at the USC Institute for Creative Technologies.
The findings, which appeared recently ...
Bacteria may aid anti-cancer immune response
2021-03-22
Cancer immunotherapy may get a boost from an unexpected direction: bacteria residing within tumor cells. In a new study published in Nature, researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science and their collaborators have discovered that the immune system "sees" these bacteria and shown they can be harnessed to provoke an immune reaction against the tumor. The study may also help clarify the connection between immunotherapy and the gut microbiome, explaining the findings of previous research that the microbiome affects the success of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy treatments of the past decade or so have dramatically improved recovery rates from certain ...
United States ranks lowest in overall policies to help parents support children
2021-03-22
National work-family policies that give lower-income families more time together while allowing them paid time off are more effective for children's psychological health than cash transfers, according to a study of developed nations led by Baylor University.
In a study of about 200,000 children in 20 developed nations, the United States ranked lowest in overall policies aimed at helping parents support children.
The study, published in the journal Social Forces, supports the view of critics who say that the United States government does not do enough to mandate ...
Does 'harsh parenting' lead to smaller brains?
2021-03-22
Repeatedly getting angry, hitting, shaking or yelling at children is linked with smaller brain structures in adolescence, according to a new study published in Development and Psychology. It was conducted by Sabrina Suffren, PhD, at Université de Montréal and the CHU Sainte?Justine Research Centre in partnership with researchers from Stanford University.
The harsh parenting practices covered by the study are common and even considered socially acceptable by most people in Canada and around the world.
"The implications go beyond changes in the brain. I think what's ...
Lung cancer resistance: the key is glucose
2021-03-22
Cancers are not only made of tumor cells. In fact, as they grow, they develop an entire cellular ecosystem within and around them. This "tumor microenvironment" is made up of multiple cell types, including cells of the immune system, like T lymphocytes and neutrophils.
The tumor microenvironment has predictably drawn a lot of interest from cancer researchers, who are constantly searching for potential therapeutic targets. When it comes to the immune cells, most research focuses on T lymphocytes, which have become primary targets of cancer immunotherapy ...
Global biodiversity awareness tracked with Wikipedia page views
2021-03-22
Wikipedia page views could be used to monitor global awareness of biodiversity, proposes a research team from UCL, ZSL, and the RSPB.
Using their new metric, the research team found that awareness of biodiversity is marginally increasing, but the rate of change varies greatly between different groups of animals, as they report in a paper included in an upcoming special section of Conversation Biology.
Lead author, PhD student Joe Millard (UCL Centre for Biodiversity & Environment Research, UCL Biosciences and Institute of Zoology, ZSL) said: "As extinctions and biodiversity losses ramp up worldwide, largely due to climate change and other human actions, it's vital that ...
Motherless gorillas beat the odds
2021-03-22
A study by the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund shows that gorilla families come together to support young gorillas that lose their mothers.
The findings, published in the journal eLife, use the Fossey Fund's more than 50-year dataset to discover how maternal loss influences young gorillas' social relationships, survival and future reproduction. The study shows when young mountain gorillas lose their mothers, the rest of the group helps buffer the loss by strengthening their relationships with the orphans.
"Mothers are incredibly important for survival early in life--this is something that is shared across all mammals," said lead author Dr. Robin Morrison. "But in social mammals, like ourselves, mothers often continue to provide vital support up to adulthood and even beyond."
"In ...
Expressing some doubts about android faces
2021-03-22
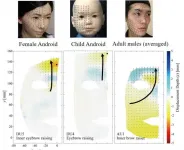
Osaka, Japan - Researchers from the Graduate School of Engineering and Symbiotic Intelligent Systems Research Center at Osaka University used motion capture cameras to compare the expressions of android and human faces. They found that the mechanical facial movements of the robots, especially in the upper regions, did not fully reproduce the curved flow lines seen in the faces of actual people. This research may lead to more lifelike and expressive artificial faces.
The field of robotics has advanced a great deal over the past decades. However, while current androids can appear very humanlike at first, their active facial expressions may still be unnatural and slightly unsettling to us. The exact reasons ...
Study estimates rising global burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer
2021-03-22
Although cancers that occur in the gallbladder or bile ducts are rare, their rates are increasing. A recent study provides details on the burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer (GBTC) across 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017. The findings are published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Determining GBTC estimates and trends in different global regions can help to guide research priorities and policies for prevention and treatment. With this in mind, a team of scientists examined publicly available information ...
Having a single personal doctor may sometimes lead to unnecessary tests
2021-03-22
Patient care by a single primary care physician is associated with many health benefits, including increased treatment adherence and decreased hospital admissions and mortality risk. But can the relationship built between doctor and patient also lead to unnecessary care?
A new University of Florida study finds that male patients who have a single general physician were more likely to receive a prostate cancer screening test during a period when the test was not recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force. The study, which appears in END ...
Toxic PAH air pollutants from fossil fuels 'multiply' in sunlight
2021-03-22
When power stations burn coal, a class of compounds called Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, or PAHs, form part of the resulting air pollution. Researchers have found that PAHs toxins degrade in sunlight into 'children' compounds and by-products.
Some 'children' compounds can be more toxic than the 'parent' PAHs. Rivers and dams affected by PAHs are likely contaminated by a much larger number of toxins than are emitted by major polluters, researchers show in Chemosphere.
A coal-fired power station and a cigarette have more in common than one might think. So do the exhaust pipes from cars and burning crop residues. The same is true for an aeroplane passing high over a wildfire ...
Major 'State of the Planet' report out in advance of first Nobel Prize Summit
2021-03-22
Human actions are threatening the resilience and stability of Earth's biosphere - the wafer-thin veil around Earth where life thrives. This has profound implications for the development of civilizations, say an international group of researchers in a report published for the first Nobel Prize Summit, a digital gathering to be held in April to discuss the state of the planet in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Humanity is now the dominant force of change on planet Earth," according to the analysis published in Ambio, a journal of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
"The risks we are taking are astounding," says co-author Johan Rockström, director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and co-author of the analysis. "We are at the dawn of what must be a transformative ...
Personal values & political worldviews shape perception of COVID-19 risk more than its severity
2021-03-22
Study taken throughout the pandemic shows those who feel government should be less controlling believe COVID-19 poses less risk, which in turn was associated with the adoption of fewer protective behaviours
"A fearful population is not necessarily desirable... people may be underestimating or overestimating the actual risk at different times."
People's politics and values are exerting a bigger influence on how much of a threat they feel from COVID-19 compared to objective indicators such as the number of confirmed cases.
That's the finding of a new University of Cambridge survey which measured how attitudes to the coronavirus have varied over the course of 10 months of the pandemic for more ...
Evidence supports Covid hearing loss link, say scientists
2021-03-22
Hearing loss and other auditory problems are strongly associated with Covid-19 according to a systematic review of research evidence led by University of Manchester and NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) scientists.
Professor Kevin Munro and PhD researcher Ibrahim Almufarrij found 56 studies that identified an association between COVID-19 and auditory and vestibular problems.
They pooled data from 24 of the studies to estimate that the prevalence of hearing loss was 7.6%, tinnitus was 14.8% and vertigo was 7.2%.
They publish their findings in the International Journal of Audiology.
However, the team - who followed up their review carried out a year ago - ...
Eating processed meat could increase dementia?risk?
2021-03-22
Scientists from the University of Leeds's Nutritional Epidemiology Group used data from 500,000 people, discovering that consuming a 25g serving of processed meat a day, the equivalent to one rasher of bacon, is associated with a 44% increased risk of developing the disease.
But their findings also show eating some unprocessed red meat, such as beef, pork or veal, could be protective, as people who consumed 50g a day were 19% less likely to develop dementia.?
The researchers were exploring a potential link between consumption of meat and the development of dementia, a health condition that affects 5%-8% of over 60s worldwide.
Their results, titled Meat consumption and risk of incident dementia: cohort study of 493888 UK Biobank participants, are published today in the American ...
Readmission rate high for adults hospitalized for diabetic ketoacidosis
2021-03-21
WASHINGTON--One in five adults with type 1 diabetes who require in-hospital treatment of the life-threatening condition diabetic ketoacidosis has an unplanned repeat hospital visit within a month and is twice as likely to die during the second hospitalization, a new study finds. The results, which will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, also identified several factors that increased the readmission risk for these patients.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, which can occur from insufficient insulin medicine or from an infection, is a dangerous accumulation of acid in the blood due to ...
[1] ... [2509]
[2510]
[2511]
[2512]
[2513]
[2514]
[2515]
[2516]
2517
[2518]
[2519]
[2520]
[2521]
[2522]
[2523]
[2524]
[2525]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.