Worth one's salt
2021-03-22
The first documented record of salt as an ancient Maya commodity at a marketplace is depicted in a mural painted more than 2,500 years ago at Calakmul, a UNESCO World Heritage site in the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico. In the mural that portrays daily life, a salt vendor shows what appears to be a salt cake wrapped in leaves to another person, who holds a large spoon over a basket, presumably of loose, granular salt. This is the earliest known record of salt being sold at a marketplace in the Maya region. Salt is a basic biological necessity and is also useful for preserving food. Salt also was valued ...
Community 'voice' should guide expanding African cities
2021-03-22
Two new environmental policy briefings, aimed at decision makers working on rapidly expanding urban areas in southern Africa, emphasise that local community voices must be included in the early planning stages to minimise ecological impacts.
Urban populations across the African continent and in particular the surrounding areas of urban sprawl, are forecasted to triple by 2050, resulting in higher rates of land conversion that have implications for managing significant environmental changes that lie ahead.
This expansion is happening faster than infrastructure changes can keep-pace, meaning that residents do not have access to important services to reduce the impact of climate-related events such as flooding, droughts, and heat-stress.
A new policy briefing, led by ...
Fourth generation of e-cigarettes is not harmless
2021-03-22
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- A University of California, Riverside, study analyzing fourth-generation electronic cigarette, or EC, pod atomizer design features has found the pod atomizers are similar to those of previous generations and contain elements that may adversely affect health and accumulate in the environment.
EC atomizers are chambers that hold nicotine-containing fluid and upon heating generate an aerosol. The pod-style e-cigarettes have become very popular, especially with young people.
The elements/metals in atomizers are important because chronic exposure could adversely affect human health. Further, EC pod products, which eventually enter the environment, could ...
Don't let the small stuff get you down--your well-being may depend on it
2021-03-22
Suppose you drop your morning coffee and it splatters everywhere. Later a colleague drops by to say hello. Do you grumble a testy acknowledgment, or cheerfully greet her?
In a new study on brain activity led by University of Miami psychologists, researchers found that how a person's brain evaluates fleeting negative stimuli--such as that dropped cup--may influence their long-term psychological well-being.
"One way to think about it is the longer your brain holds on to a negative event, or stimuli, the unhappier you report being," said Nikki Puccetti, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Psychology ...
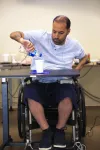
Transcutaneous stimulation improves hand function in people with complete tetraplegia
2021-03-22
East Hanover, NJ. March 22, 2021. Kessler Foundation researchers demonstrated that spinal cord transcutaneous stimulation (scTS) combined with hand training improves upper extremity and hand function in individuals with motor and sensory compete spinal cord injury (SCI). The study results showed immediate and long-lasting gains in strength, sensibility, and voluntary motor function.
The article, "Cervical Spinal Cord Transcutaneous Stimulation Improves Upper Extremity and Hand Function in People with Complete Tetraplegia: A Case Study" (doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3048592), was published January 28, 2021, in IEEE Transactions On Neural Systems And Rehabilitation Engineering. It is available open access at https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9311628.
The authors are Fan Zhang, ...
Reading minds with ultrasound: A less-invasive technique to decode the brain's intentions
2021-03-22
What is happening in your brain as you are scrolling through this page? In other words, which areas of your brain are active, which neurons are talking to which others, and what signals are they sending to your muscles?
Mapping neural activity to corresponding behaviors is a major goal for neuroscientists developing brain-machine interfaces (BMIs): devices that read and interpret brain activity and transmit instructions to a computer or machine. Though this may seem like science fiction, existing BMIs can, for example, connect a paralyzed person with a robotic ...
To live independently longer, look to inexpensive home hacks
2021-03-22
The pandemic has exposed weaknesses in nursing homes, causing many families to rethink whether to keep an aging parent at home instead. Now a new study by UC San Francisco has found that many elderly Americans lack the basic self-care equipment that could enable them to live at home longer, postponing the need to move into residential care facilities.
In the study, researchers focused on three inexpensive, low-tech assistive devices: grab bars around the toilet and in the shower or tub area; a shower or tub seat; and a raised toilet or toilet seat. They identified approximately 2,600 seniors who were representative of Medicare recipients nationwide and were drawn from the National Health and Aging ...
University of Ottawa researchers close in on root of slow motor learning in autism
2021-03-22
Social deficits attract so much attention in the study of autism spectrum disorder, it's easy to forget there are motor learning deficits during early childhood as well. For autistic kids hoping to throw a ball around the schoolyard and connect with classmates, these physical skill differences can isolate a child further.
In a new study published in Nature Neuroscience, researchers from the University of Ottawa's Faculty of Medicine have closed in on the neurological underpinnings of the motor learning delay.
Dr. Simon Chen's lab in the Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine of the Faculty of Medicine used a mouse model of autism to demonstrate a shortage ...
Focusing on the unhealthy brain to speed drug discovery
2021-03-22
Though 40 million concussions are recorded annually, no effective treatment exists for them or for many other brain-related illnesses. In collaboration with Dragan Maric of the National Institutes of Health, Badri Roysam, Hugh Roy and Lillie Cranz Cullen University Professor and Chair of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and his team are working to speed up drug development to treat brain diseases and injuries like concussion by developing new tools.
"We are interested in mapping and profiling unhealthy and drug-treated brain tissue in unprecedented detail to reveal multiple biological processes at once - in context," said Roysam about his latest paper published ...
Long-haul COVID: Columbia physicians review what's known
2021-03-22
NEW YORK, NY (March 22, 2021)--The first year of the COVID-19 pandemic has taken the lives of millions of people around the world but has also left hundreds with lingering symptoms or completely new symptoms weeks after recovery.
Much is unknown about what causes these symptoms and how long they last. But with nearly 740,000 cases of COVID reported in New York City since last March--and 28 million in the United States--physicians are increasingly seeing these "long-haulers" in their practices.
"Over the course of the summer, we started getting a sense of what issues these people were having," ...
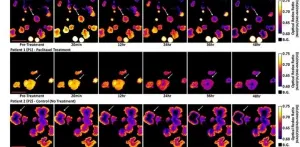
Redox imaging allows measurement of drug responses in lab-grown cancer samples
2021-03-22
Organoids are tiny three-dimensional cellular assemblies that are grown in a laboratory from tissue-specific cells. They are particularly interesting to biologists because of their ability to mimic the characteristics of the original tissues. If scientists extract cells from a tumor, then they can grow cancer organoids that mimic the characteristics of the source tumor.
This possibility for individual-level studies of tumor properties makes cancer organoids an exciting tool from the perspective of an emerging field called precision cancer medicine. Daniel Gil of the University of Wisconsin ...
New Barrett's esophagus monitoring method could aid in easier and more precise prognoses
2021-03-22
CLEVELAND--A new technique for sampling and testing cells from Barrett's esophagus (BE) patients could result in earlier and easier identification of patients whose disease has progressed toward cancer or whose disease is at high risk of progressing toward cancer, according to a collaborative study by investigators at Case Western Reserve University and Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center (JHKCC).
Published in the journal Gastroenterology, the findings show the combination of esophageal "brushing" with a massively parallel sequencing method can provide an accurate assessment of the ...
Healthy sleep may rely on long-overlooked brain cells
2021-03-22
For something we spend one-third of our lives doing, we still understand remarkably little about how sleep works -- for example, why can some people sleep deeply through any disturbance, while others regularly toss and turn for hours each night? And why do we all seem to need a different amount of sleep to feel rested?
For decades, scientists have looked to the behavior of the brain's neurons to understand the nature of slumber. Now, though, researchers at UC San Francisco have confirmed that a different type of brain cell that has received far less study -- astrocytes, named for their star-like shape -- can influence how long and how deeply animals sleep. The findings could open new avenues for exploring sleep disorder therapies and help scientists better understand brain diseases linked ...
Large new study reveals rates of brain abnormalities in healthy children
2021-03-22
A large study of brain MRI scans from 11,679 nine- and ten-year-old children reviewed by UC San Francisco neuroradiologists identified potentially life-threatening conditions in 1 in 500 children, and more minor but possibly clinically significant brain abnormalities in 1 out of 25 children.
The results provide the best estimates to date of the true incidence of various structural abnormalities in the developing brain, and raise the question of whether all MRI brain imaging obtained during research studies should be reviewed by board-certified radiologists, as was done in this study, in the hopes of saving lives and alerting participants to incidental findings that ought to be medically evaluated.
One ...
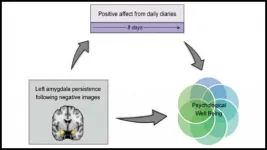
Negative mood linked to prolonged amygdala activity
2021-03-22
How the amygdala responds to viewing negative and subsequent neutral stimuli may impact our daily mood, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
The amygdala evaluates the environment to find potential threats. If a threat does appear, the amygdala can stay active and respond to new stimuli like they are threatening too. This is helpful when you are in a dangerous situation, but less so when spilling your coffee in the morning keeps you on edge for the rest of the day.
In a recent study, Puccetti et al. examined data collected from the "Midlife ...
New study implicates disease-driving B cells in fatty liver disease development
2021-03-22
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (03/22/2021) -- New research from the University of Minnesota Medical School suggests that disease-driving B cells, a white blood cell, play a role in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) - the most common chronic liver condition in the U.S. Their findings could lead to targeted therapies for NAFLD, which currently affects a quarter of the nation and has no FDA-approved treatments.
After noticing that patients with the disease showed a large number of inflammatory B cells in their livers, Xavier Revelo, PhD, an assistant professor in the Department of Integrative Biology and Physiology and senior author, began studying B cells in NAFLD.
"This disease is increasing in prevalence ...
Trinity scientists find that binding iron improves the effect of anti-TB drug Bedaquiline
2021-03-22
Although Tuberculosis, or TB, killed nearly as many people as COVID-19 (approx. 1.8 million) in 2020, it did not receive as much media and public attention. The pandemic has proven that transmissible infection is indeed a global issue. TB remains a serious public health concern in Ireland, particularly with the presence of multi-drug resistant types and the numbers of complex cases here continuing to rise, with cases numbering over 300 annually.
Science tells us that iron is crucial for daily human function, but it is also an essential element for the survival of ...
Electrode interphase formation
2021-03-22
Batteries charge and recharge--apparently all thanks to a perfect interplay of electrode material and electrolyte. However, for ideal battery function, the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) plays a crucial role. Materials scientists have now studied nucleation and growth of this layer in atomic detail. According to the study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, the properties of anions and solvent molecules need to be well balanced.
In lithium-ion batteries, the SEI forms at the beginning of the first charging process, when a potential is applied. Elements from the electrolyte deposit on the graphite electrode and form a coating that soon ...
A sense for the unseen: Novel DNA sensor can rapidly detect antibiotic-resistant pathogens
2021-03-22
Antibiotics have revolutionized the field of medicine by making it possible to treat most known microbial diseases today. However, their uncontrolled usage has led to the major global problem of antibiotic resistance. As we continue to exploit antibiotics, sometimes at doses much higher than needed, disease-causing bacteria are rapidly evolving defense strategies to evade them. These drug-resistant bacteria, also known as "superbugs," cause severe infections that are difficult to treat and can eventually be fatal.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a particularly vicious group of superbugs that have developed resistance to the antibiotic methicillin, is a major cause of hospital-acquired infections. Accurate and timely diagnosis ...
Arctic methane release due to melting ice is likely to happen again
2021-03-22
Boulder, Colo., USA: Beneath the cold, dark depths of the Arctic ocean sit vast reserves of methane. These stores rest in a delicate balance, stable as a solid called methane hydrates, at very specific pressures and temperatures. If that balance gets tipped, the methane can get released into the water above and eventually make its way to the atmosphere. In its gaseous form, methane is one of the most potent greenhouse gases, warming the Earth about 30 times more efficiently than carbon dioxide. Understanding possible sources of atmospheric methane is critical for accurately predicting future climate change.
In the Arctic Ocean today, ice sheets exert pressure on the ground below them. That pressure diffuses ...
Cancer screenings rebounded quickly after drop at start of pandemic
2021-03-22
Screenings for breast cancer and colon cancer dropped dramatically during the early months of the coronavirus pandemic, but use of the procedures returned to near-normal levels by the end of July 2020, according to a new study.
Analyzing insurance claims from more than 6 million Americans with private health coverage, researchers found that mammography rates among women aged 45 to 64 declined by 96% during March and April 2020 as compared to January and February.
Similarly, the weekly rate of colorectal cancer screenings among adults aged 45 to 64 and older declined by 95% during the period.
By the end of July 2020, however, the rate of mammograms among women had rebounded and was slightly higher than it had been before the pandemic was declared. The rate of colonoscopies also rebounded, ...
Trinity researchers tackle the spiders from Mars
2021-03-22
Researchers at Trinity College Dublin have been shedding light on the enigmatic "spiders from Mars", providing the first physical evidence that these unique features on the planet's surface can be formed by the sublimation of CO2 ice.
Spiders, more formally referred to as araneiforms, are strange-looking negative topography radial systems of dendritic troughs; patterns that resemble branches of a tree or fork lightning. These features, which are not found on Earth, are believed to be carved into the Martian surface by dry ice changing directly from solid to gas (sublimating) in the spring. Unlike Earth, Mars' atmosphere comprises mainly of CO2 and as temperatures decrease in winter, this deposits onto the surface as CO2 ...
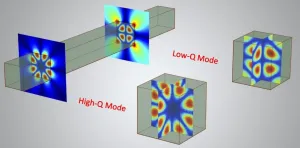
Finding high-Q resonant modes in a dielectric nanocavity
2021-03-22
Optical resonators provide the foundation of modern photonics and optics. Thanks to its extreme energy confinement, the high-Q-factor optical resonator optimizes light-matter interaction and photonic device performance by enabling low-threshold laser and enhanced nonlinear harmonic generation.
Two typical structures, the photonic crystal cavity and the whispering gallery cavity, are frequently used to obtain extremely high-Q factors. However, these structures may require dimensions that are comparable to--or several times larger than--the operating wavelength. Whether there is a general way to find out all high-Q modes in a dielectric ...
Ending tuberculosis is a race against time and drug resistance
2021-03-22
The tuberculosis (TB) burden in the WHO European Region as a whole is decreasing, and is down 19% overall for 2015-2019, according to the latest WHO/European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) report Tuberculosis surveillance and monitoring in Europe 2021 (2019 data).
Regional TB mortality has gone down, declining by 9.4% between 2018 and 2019. This is notably higher than the average global decline in TB mortality (3.7%) and enough to have reached the End TB Strategy milestone of a 35% reduction by 2020 compared to 2015.
However, TB is second only to COVID-19 as an infectious disease that kills, and drug resistance is a major concern. There are also worrying indications that the COVID-19 pandemic may stall progress or cause significant setbacks in the fight against TB.
The ...
Uniform drying time for goldenseal to enhance medicinal qualities of forest herb
2021-03-22
Developing a standardized drying protocol for goldenseal could lead to more predictable health applications and outcomes by preserving the alkaloids found in the plant, which is native to Appalachia, according to Penn State researchers, who conducted a new study of the medicinal forest herb.
The roots and rhizomes of goldenseal -- Hydrastis canadensis -- have been used for hundreds of years as a source of antimicrobials and compounds to treat intestinal ailments, noted study co-author Eric Burkhart, associate teaching professor, ecosystem science ...
[1] ... [2505]
[2506]
[2507]
[2508]
[2509]
[2510]
[2511]
[2512]
2513
[2514]
[2515]
[2516]
[2517]
[2518]
[2519]
[2520]
[2521]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.