Association of vitamin D levels, race/ethnicity, clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results
2021-03-19
What The Study Did: Researchers examined if differences in vitamin D levels greater than levels traditionally considered sufficient (30 ng/mL) are associated with having test results positive for COVID-19 in White and in Black individuals.
Authors: David O. Meltzer, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4117)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article ...
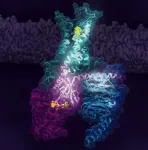
Conformational equilibria in GPCRs provides critical clues about activation mechanisms
2021-03-19
A multinational research team led by Dr. Adnan Sljoka (RIKEN), Prof. R. Scott Prosser (Univ. of Toronto) with collaborations with Dr. Duy Phuoc Tran and Prof. Akio Kitao (Tokyo Tech) and Prof. Roger K. Sunahara (Univ. of California San Diego) has carried out experimental and computational studies, revealing key steps associated with the activation of the human adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR). A2AR is a member of superfamily of receptors called G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) (major drug targets) which engage the G protein and initiates cell signaling. The research team discovered that A2AR is represented by at least two inactive conformations and three active conformations whose populations are dependent on ligands and activation ...
Cancer immunotherapy may also treat certain autoimmune diseases
2021-03-19
A team of researchers has found disrupting the interaction between cancer cells and certain immune cells is more effective at killing cancer cells than current immunotherapy treatments.
The findings, which include studies in cell lines and animal models, appeared in JCI Insight and focus on END ...
Large-scale study finds AI-powered COVID-19 solution by RADlogics reduces turnaround time
2021-03-19
MOSCOW, RUSSIA -
Moscow Center for Diagnostics & Telemedicine and RADLogics shared the results of a large-scale study (Moscow Experiment on the Computer Vision for the Analysis of Medical Images - mosmed.ai, NCT04489992) conducted by the Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies of the Moscow Health Care Department. The clinical research found that the introduction of RADLogics' AI-Powered solution into radiology workflow to analyze Chest-CT scans during the COVID-19 pandemic reduced report turnaround ...
Polymerized estrogen provides neuroprotection in preclinical testing
2021-03-19
TROY, N.Y. -- A novel form of polymerized estrogen developed at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute can provide neuroprotection when implanted at the site of a spinal cord injury -- preventing further damage. This promising result, found in a preclinical model, was recently published in ACS Chemical Neuroscience, and it lays the groundwork for further advancement of this new biomaterial.
"What we saw that gives us hope is more neuroprotection, meaning we saw more spared neurons and more spared axons in the tissue," said Ryan Gilbert, a professor of biomedical engineering at Rensselaer, and co-author on this paper. "We believe that the estrogen released from our biomaterial design is providing a neuroprotective response."
After a spinal cord injury, the body's inflammatory ...
Happiness can be learned
2021-03-19
The results showed that several psychological well-being measures gradually increased within participants from the beginning to the end of the course. That was especially true for life satisfaction, perceived well-being, self-awareness and emotional self-regulation. The participants in the study also reported a significant decrease in anxiety, perceived stress, negative thoughts, rumination and anger tendencies. The researchers observed, simultaneously, improvements in the positive aspects and a reduction of negative emotions, both in the short term and longitudinally ...
Living a stress-free life may have benefits, but also a downside
2021-03-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Stress is a universal human experience that almost everyone deals with from time to time. But a new study found that not only do some people report feeling no stress at all, but that there may be downsides to not experiencing stress.
The researchers found that people who reported experiencing no stressors were more likely to experience better daily well-being and fewer chronic health conditions. However, they were also more likely to have lower cognitive function, as well.
David M. Almeida, professor of human development and family studies at Penn State, said the study suggests that small, daily stressors could potentially benefit the brain, despite being an inconvenience.
"It's possible that experiencing stressors creates opportunities for you ...
How RNA editing affects the immune system
2021-03-19
Three University of Colorado Cancer Center researchers are part of a team that recently published a paper offering new insight into how the immune system relates to cancer. Quentin Vicens, PhD, Jeffrey Kieft, PhD, and Beat Vögeli, PhD, are authors on the paper, which looks at how an enzyme called ADAR1 operates in pathways associated with cancer.
"In a cell, ADAR1 edits native RNA -- or self-RNA -- so that the cell recognizes it as its own. It's a key protection against autoimmune disorders," Kieft says. "But if a virus infects, viral RNA isn't edited by ADAR1, so the cell can recognize that and react. The cell knows it has foreign RNA, and it activates immune responses to fight off that infection."
For their paper published last month in the ...
Adults in Canada report adverse childhood experiences
2021-03-19
Nearly two-thirds of middle-aged and older adults in Canada report adverse childhood experiences
Hamilton, ON (Mar. 19, 20121) - New research from McMaster University has found that roughly three in every five Canadian adults aged 45 to 85 have been exposed to childhood abuse, neglect, intimate partner violence or other household adversity.
The research, which estimates the prevalence of a broad range of adverse childhood experiences, was published in CMAJ Open.
"Our research showed that adverse childhood experiences are highly prevalent in the Canadian population, with 62% of Canadian adults aged 45 to 85 reporting at least one exposure," said Divya Joshi, the study's lead author and a postdoctoral fellow in the Department ...
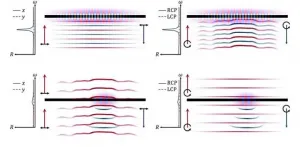
Looking at optical Fano resonances under a new light
2021-03-19
In 1961, physicist Ugo Fano provided the first theoretical explanation to an anomalous asymmetry observed in the spectral profiles of noble gases. He put forth an impactful interpretation of this phenomenon, now called "Fano resonance," stating that if a discrete excited state of a system falls within the energy range of a continuum of other possible states, these two can interfere with each other and give rise to abnormal peaks and dips in the system's frequency response.
Though Fano resonance can occur in various physical systems, recent progress in metasurfaces and nanotechnology has drawn attention to this phenomenon as a potentially powerful tool in optics. ...
Researchers design a biological device capable of computing by printing cells on paper
2021-03-19
The Research Group on Synthetic Biology for Biomedical Applications at Pompeu Fabra University in Barcelona, Spain, has designed a cellular device capable of computing by printing cells on paper. For the first time, they have developed a living device that could be used outside the laboratory without a specialist, and it could be produced on an industrial scale at low cost. The study is published in Nature Communications and was carried out by Sira Mogas-Díez, Eva Gonzalez-Flo and Javier Macía.
We currently have many electronic devices available to us such as computers and tablets whose computing power is highly efficient. But, despite their ...
More stroke patients receiving mechanical clot removal, yet racial disparities persist
2021-03-19
DALLAS, March 19, 2021 -- Mechanical removal of blood clots causing a stroke is increasing, yet racial differences in treatment persist, according to late-breaking science presented today at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
Mechanical clot-removal or endovascular therapy is a non-surgical treatment that uses tiny tubes, or catheters, to remove a blood clot. In 2015, several major clinical trials confirmed that endovascular therapy ...
Technique based on artificial intelligence permits automation of crop seed analysis
2021-03-19
In Brazil, researchers affiliated with the Center for Nuclear Energy in Agriculture (CENA) and the Luiz de Queiroz College of Agriculture (ESALQ), both part of the University of São Paulo (USP), have developed a methodology based on artificial intelligence to automate and streamline seed quality analysis, a process required by law and currently done manually by analysts accredited with the Ministry of Agriculture.
The group used light-based technology like that deployed in plant and cosmetics analysis to acquire images of the seeds. They then turned to machine learning to automate the image interpretation ...
Stroke risk higher than expected among COVID-19 patients
2021-03-19
DALLAS, March 19, 2021 -- New research found patients hospitalized with COVID-19 had a higher risk of stroke, compared with patients who had similar infectious conditions such as influenza and sepsis in prior studies. Those who had an ischemic stroke were more likely to be older, male, Black race, or have high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes or an irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation) compared with other COVID-19 patients, according to late-breaking science presented today at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2021. The meeting is being held virtually, March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated ...
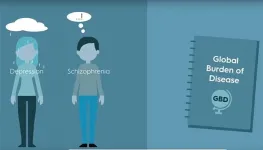
Disability highest for schizophrenia and personality disorders
2021-03-19
Schizophrenia and personality disorders are the most disabling mental health conditions to live with, according to scientists from The University of Queensland.
A Danish-Australian research team studied a cohort of 6.9 million Danish residents in the Danish Psychiatric Central Research Register to understand the burden of disability associated with 18 mental and substance use disorders.
Professor John McGrath from UQ Queensland Brain Institute's and the Queensland Centre for Mental Health Research said the data was used to develop a new method for measuring disability that took comorbidities into account.
"Traditionally the impact of mental disorders has been presented for an entire nation, ...
More is better, when it comes to case volume for complex gastrointestinal cancer surgery
2021-03-19
Key takeaways
Nearly half of gastrointestinal cancer operations in this study were performed at 42 U.S. News & World Report "Best Hospitals."
These top-ranked hospitals performed more than four times the annual case volume of unranked hospitals.
Higher hospital case volume was associated with better outcomes, even after accounting for patient characteristics and complicating factors.
Patients with complex gastrointestinal (GI) cancers may fare better by seeking surgical care at high-volume, top-ranked hospitals.
CHICAGO (March 19, 2021, 9 a.m. CDT): A new study reinforces the principle that "practice makes perfect" ...
Study: Older multiple myeloma patients can be spared of long-term steroids
2021-03-19
The combination of cancer therapy lenalidomide plus the steroid dexamethasone (together called Rd) is considered standard treatment for elderly patients with multiple myeloma. However, prolonged steroid use can be harmful for some older adults.
A new study published in Blood found that switching select older patients to a lower dose of lenalidomide and discontinuing dexamethasone after nine months was not only safe, but it also yielded similar outcomes as compared with patients who received continuous Rd.
Multiple myeloma, a cancer affecting the blood plasma cells (a type of white blood cell in the bone marrow), most commonly ...
Intelligent insect counter opens new opportunities for nature monitoring
2021-03-19
3,938 moths are part of a major insect study based on artificial intelligence, and researchers from Aarhus University have just published their results in the scientific journal Sensors.
They have developed a counting machine that uses ultraviolet light to attract insects and register them with image recognition. The invention may have a decisive impact on research into climate change and biodiversity.
"If we can monitor the development of moth populations, we can gain new knowledge about how climate change affects our nature. Our technology takes an important step towards automating the very extensive work entailed in counting insects," ...
Virtual reality could help to reduce pain for people with nerve injuries
2021-03-19
We all feel physical pain in different ways, but people with nerve injuries often have a dysfunctional pain suppression system, making them particularly prone to discomfort.
Now researchers have uncovered that virtual reality (VR) can reduce types of pain typically seen in patients with nerve injuries - and that VR can boost the dysfunctional pain suppression system, giving people with chronic pain a possible game-changing hope.
Dr Sam Hughes, Lecturer in Psychology at the University of Plymouth, led the study focusing on conditioned pain modulation ...
A new dye shakes up solar cells
2021-03-19
In 1991, scientists Brian O'Regan and Michael Grätzel at EPFL published a seminal paper describing a new type of solar cell: the dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC), also known as "Grätzel cell". Simple and cheap to build while being flexible and versatile, DSSCs are already manufactured on a multi-megawatt scale, cutting a significant slice of the photovoltaic market, which currently supplies almost 3% of all the world's electricity, well in the race to reduce carbon emissions.
Now, Dan Zhang and Marko Stojanovic, two PhD students in Grätzel's lab at EPFL's School of Basic Sciences, have led the development of a simple dye for DSSCs, called MS5. In devices, this new sensitizer can either be used as single dye, ...
TPU scientists offer new plasmon energy-based method to remove CO2 from atmosphere
2021-03-19
Researchers from Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with their colleagues from the Czech Republic have found a method to synthesize cyclic carbonates from atmospheric CO2. Cyclic carbonates are organic compounds, used as electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries, green solvents as well as in pharmaceutical drugs manufacturing. The scientists managed to synthetize carbonates under sunlight and at room temperature, while conventional methods require synthesis under high pressure and temperatures. The research findings are published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A (IF:11,301; Q1).
"The increase in CO2 levels in the atmosphere is a global environmental problem. The solutions of the problem are usually focused on measures to reduce CO2 emissions. An alternative method is to use the CO2 already ...
How flashlight fish communicate with light signals in the school
2021-03-19
Flashlight fish have the ability to generate situation-specific blink patterns resembling a visual Morse code. Researchers at Ruhr-Universität Bochum have shown in laboratory and field experiments that the animals use these light signals to coordinate their behaviour in the school when visibility is limited. Both the light intensity and the blinking frequency affected the animals' behaviour. The team headed by Peter Jägers and Professor Stefan Herlitze from the Department of General Zoology and Neurobiology has shared their findings in the journal Scientific Reports, published online on 19 ...
Health declining in Gen X and Gen Y, national study shows
2021-03-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Recent generations show a worrying decline in health compared to their parents and grandparents when they were the same age, a new national study reveals.
Researchers found that, compared to previous generations, members of Generation X and Generation Y showed poorer physical health, higher levels of unhealthy behaviors such as alcohol use and smoking, and more depression and anxiety.
The results suggest the likelihood of higher levels of diseases and more deaths in younger generations than we have seen in the past, said Hui Zheng, ...
Important advance in research on future drugs
2021-03-19
Most drugs operate via the membranes that surround the body's cells. A study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden has now mapped the structure and mechanism of MGST2, a membrane enzyme that, amongst other things, plays a part in chronic inflammation and cancer. The study, which is published in the journal Nature Communications, can make a significant contribution to the development of future drugs.
All our cells are enclosed in a fat-rich membrane. The cells' equivalent to organs, the organelles, are also enclosed by membranes. Embedded in the cell's internal and external membranes are proteins that regulate a large number of vital functions. ...
Parkinson's disease: When molecular guardians need to be protected
2021-03-19
Parkinson's disease is the second most common, age-related, neurodegenerative disease: In Germany alone, about 300,000 people are affected and experience sometimes major limitations to their quality of life. Although Parkinson's is so widespread, there is still no treatment that targets the cause of the disease and can stop it in its tracks.
However, current research provides new hope: A research team at the University of Konstanz led by Professor Marcus Groettrup describes a new approach for developing future treatments for Parkinson's. The biologists demonstrated that the ubiquitin-like ...
[1] ... [2512]
[2513]
[2514]
[2515]
[2516]
[2517]
[2518]
[2519]
2520
[2521]
[2522]
[2523]
[2524]
[2525]
[2526]
[2527]
[2528]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.