A modified protein appears to trigger lung fibrosis after environmental exposure
2021-03-18
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - The triggers and causes of a severe scarring disease of the lungs -- idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, or IPF -- remain unclear.
Now research published in Science Translational Medicine shows how cadmium and carbon black can trigger lung macrophages to produce a modified protein, citrullinated vimentin, or cit vim, which leads to lung fibrosis. Researchers from the University of Alabama at Birmingham and three other American universities also describe a sequence of mechanistic steps in lung macrophages and lung fibroblasts that leads to the lung scarring.
One of the enzymes involved in these steps -- peptidylarginine deiminase 2, or PAD2 -- may be a promising target to attenuate cadmium/carbon black-induced ...
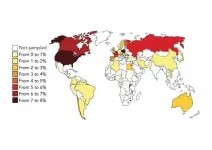
COVID-19 pandemic impacts mental health worldwide
2021-03-18
March 18, 2021 -- A study conducted at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health reports a high global prevalence of both depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic and shows how implementation of mitigation strategies including public transportation and school closures, and stay-at-home orders impacted such disorders. The results are published in Psychological Medicine.
"Our research found an elevated global prevalence of these mental health issues during COVID-19 and also revealed there was a wide variance in each at the region- and country-level," said, João Castaldelli-Maia, MD, PhD, NIDA-INVEST Postdoctoral Fellow in the Department of Epidemiology, and ...
Animal model opens way to test Alzheimer's disease therapies
2021-03-18
Our knowledge of Alzheimer's disease has grown rapidly in the past few decades but it has proven difficult to translate fundamental discoveries about the disease into new treatments. Now researchers at the California National Primate Research Center at the University of California, Davis, have developed a model of the early stages of Alzheimer's disease in rhesus macaques. The macaque model, published March 18 in the journal Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association could allow better testing of new treatments.
The model was developed by Professor John Morrison's laboratory ...
Parental burnout hits individualist Western countries hardest
2021-03-18
IN BRIEF:
It's a first: approximately 100 scientists in 42 countries joined forces to learn about the incidence of parental burnout.
They found that Western countries are the most affected by parental burnout.
The cause? The often individualistic culture of Western countries. This international study, published in Affective Science, shows how culture, rather than socio-economic factors, plays a predominant role in parental burnout.
The individualism is more pronounced during health crises.
Does the incidence of parental burnout depend on a country's culture? This question was at the heart of the first international study on the subject for which hundreds of scientists in 42 countries mobilised. In other words, the global scientific ...
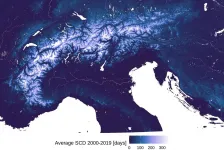
For the first time, an Alpine-wide study shows that snow cover has been declinin
2021-03-18
The results, published in the renowned scientific journal The Cryosphere, have made it possible to reliably describe snow trends at up to 2000 metres above sea level. Higher than that, there are too few measuring stations to be able to extract reliable information for the entire Alpine region. This consistent data set spans five decades and was created through the collaboration of more than 30 scientists from each of the Alpine states. The results and data collected represent a valuable aid for future studies, especially those which centre on climate change.
"This ...
Dolphins adapt to survive invasive coastal constructions
2021-03-18
Bottlenose dolphins learn to cope with coastal construction activities. That is the conclusion of a study published in END ...
Harbour porpoises attracted to oil platforms when searching for food
2021-03-18
A large gathering of fish tempts harbour porpoises to search for food around oil and gas platforms, even though the noise from these industrial plants normally to scare the whales away. Decommissioned platforms may therefore serve as artificial reefs in the North Sea.
Harbour porpoises are one of the smallest of all whales and the only whale that with certainty breeds in Danish waters. The harbour porpoise was protected in 1967 in Danish Waters, and researchers from Aarhus University, Denmark, have previously shown that underwater noise from ships, and seismic surveys of the seabed scare the porpoises away.
A brand new study now shows that in some parts of the year there are ...
Women in cities less likely to have children
2021-03-18
A new study in Behavioral Ecology, published by Oxford University Press, finds that women are less likely to procreate in urban areas that have a higher percentage of females than males in the population.
Although the majority modern cities have more women than men and thus suffer from lower fertility rates, the effects of female-biased sex ratios - having more women than men in a population - is less studied than male-biased ratios. Researchers here analyzed how female-biased sex ratios are linked to marriages, reproductive histories, dispersal, and the effects of urbanization on society.
The research team from University of Turku, University of Helsinki and Pennsylvania ...
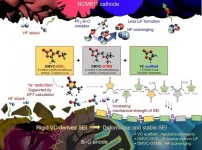
UNIST to develop new electrolyte additives for high-energy-density LIBs
2021-03-18
A joint research team, affiliated with UNIST has unveiled a novel electrolyte additive that could enable a long lifespan and fast chargeability of high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries (LIBs).
Published in the February 2021 issue of Nature Communications, this research has been carried out by Professor Nam-Soon Choi and Professor Sang Kyu Kwak in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Sung You Hong in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST. It has also been participated by Professor Jaephil Cho in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST.
As the demand for large-capacity batteries (i.e., EV batteries) increases, efforts are actively underway to replace the conventional lithium-ion ...
Four lichen species new to science discovered in Kenyan cloud forests
2021-03-18
Researchers from the University of Helsinki's Finnish Museum of Natural History Luomus and the National Museums of Kenya have discovered four lichen species new to science in the rainforests of the Taita Hills in southeast Kenya.
Micarea pumila, M. stellaris, M. taitensis and M. versicolor are small lichens that grow on bark of trees and on decaying wood. The species were described based on morphological features and DNA-characters.
"Species that belong to the Micarea genus are known all over the world, including Finland. However, the Micarea species recently described from the Taita ...
How to get customers to talk about you
2021-03-18
Researchers from Arizona State University, New York University, and Northwestern University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how marketers can fuel positive WOM without using explicit incentives.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "How Marketing Perks Influence Word of Mouth" and is authored by Monika Lisjak, Andrea Bonezzi, and Derek Rucker.
Word-of-mouth (WOM) is arguably the most influential means of persuasion and can be a critical driver of a company's growth. For this reason, many companies offer consumers incentives to encourage them to generate WOM. Classic examples of this practice are referral and seeding programs, whereby a company literally "pays" ...
Size matters when it comes to atomic properties
2021-03-18
A study from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, has yielded new answers to fundamental questions about the relationship between the size of an atom and its other properties, such as electronegativity and energy. The results pave the way for advances in future material development. For the first time, it is now possible under certain conditions to devise exact equations for such relationships.
"Knowledge of the size of atoms and their properties is vital for explaining chemical reactivity, structure and the properties of molecules and materials of all kinds. This is fundamental research that is necessary for us to make important advances," explains Martin Rahm, the main author of the study and research leader from ...
UTSA researcher studies key predictors for college retention
2021-03-18
(MARCH 17, 2021) - The current outbreak of COVID-19 has raised many questions about the value of consideration of standardized testing through the admissions process. One of the many Coronavirus cancellations included a growing number of universities to waive SAT and ACT scores as an admissions requirement for 2022 applicants.
With schools shifting their policy to making standardized "test-optional" and possibly permanently phasing out testing scores in the future as some college experts argue that standardized tests create barriers to students which could reduce their likelihood of acceptance.
A new study led by senior research scientist Paul Westrick from the College Board (ACT, Inc.), along with UTSA professor of management, ...
TU Graz researchers identify chemical processes as key to understanding landslides
2021-03-18
Mass movements such as landslides and hill-slope debris flows cause billions of euros in economic damage around the world every year. Between 20 and 80 million euros are spent annually from the disaster fund to repair disaster damage in Austria, 15 to 50 percent of which is attributable to mud flows and landslides. Now, a team of geologists from Graz University of Technology (TU Graz), in cooperation with the Burgenland state road administration, identified for the first time the chemical influencing factors and triggers for recurrent mass movements in fine-grained sediments. From results published in the journal Science of the Total Environment, preventive measures and strategies ...
2021 INS Standards highlight anti-reflux technology for needleless connectors
2021-03-18
Lenexa, Kan. -- The Infusion Nurses Society has expanded its guidance on the use of needleless connectors to include anti-reflux technology in its recently published 2021 Infusion Therapy Standards of Practice, according to Nexus Medical, makers of the Nexus TKO®-6P Anti-Reflux connector.
As INS' most recognized publication, the updated Standards outline specific categories of needleless connector technology based on the device's internal mechanism for fluid displacement -- negative displacement, positive displacement, neutral and anti-reflux. Of all the categories, the authors note that anti-reflux needleless connectors cause the least amount of blood reflux, which can ...
Lab-created heart valves can grow with the recipient
2021-03-17
A groundbreaking new study led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers from both the College of Science and Engineering and the Medical School shows for the first time that lab-created heart valves implanted in young lambs for a year were capable of growth within the recipient. The valves also showed reduced calcification and improved blood flow function compared to animal-derived valves currently used when tested in the same growing lamb model.
If confirmed in humans, these new heart valves could prevent the need for repeated valve replacement surgeries in thousands of children born each year with congenital heart defects. The valves can also be stored for at least six months, which means they could provide surgeons with an "off the shelf" option for treatment.
The ...
A new, vital player in graft-versus-host disease and organ transplant rejection
2021-03-17
A long noncoding RNA whose function was previously unknown turns out to play a vital role in mobilizing the immune response following a bone marrow transplant or solid organ transplantation.
This RNA molecule, cataloged in scientific databases simply as Linc00402, helps activate immune defenders known as T cells in response to the presence of foreign human cells, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center and Michigan Medicine.
The investigation, which included samples from more than 50 patients who underwent a bone marrow or heart transplant, suggests inhibiting ...
Health disparities in type 1 diabetes and COVID-19 infection with Dr. Kathryn Sumpter
2021-03-17
MEMPHIS, Tenn. - Non-Hispanic black patients with Type 1 diabetes and COVID-19 were almost four times as likely to present to the hospital with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) compared to non-Hispanic whites, according to an article published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism by Le Bonheur Pediatric Endocrinologist Kathryn Sumpter, MD.
The study examined 180 patients with Type 1 diabetes and laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 from 52 clinical sites, including Le Bonheur Children's. The objective of the study was to evaluate instances of DKA, a serious complication of Type 1 diabetes, in patients with Type 1 diabetes and COVID-19 and determine if minorities had increased ...
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird
2021-03-17
ITHACA, N.Y. - If you want to build a fully functional nanosized robot, you need to incorporate a host of capabilities, from complicated electronic circuits and photovoltaics to sensors and antennas.
But just as importantly, if you want your robot to move, you need it to be able to bend.
Cornell researchers have created micron-sized shape memory actuators that enable atomically thin two-dimensional materials to fold themselves into 3D configurations. All they require is a quick jolt of voltage. And once the material is bent, it holds its shape - even after the voltage is removed.
As a demonstration, the team created what ...
Ultrasound has potential to damage coronaviruses, study finds
2021-03-17
The coronavirus' structure is an all-too-familiar image, with its densely packed surface receptors resembling a thorny crown. These spike-like proteins latch onto healthy cells and trigger the invasion of viral RNA. While the virus' geometry and infection strategy is generally understood, little is known about its physical integrity.
A new study by researchers in MIT's Department of Mechanical Engineering suggests that coronaviruses may be vulnerable to ultrasound vibrations, within the frequencies used in medical diagnostic imaging.
Through computer simulations, the team has modeled the virus' mechanical response to vibrations across a range of ultrasound ...
Cancer survivors face elevated heart disease risk, study finds
2021-03-17
A new study has found that about 35% of Americans with a cancer history had an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease in the next decade, compared with about 23% of those who didn't have cancer.
Based on a risk calculator that estimates a person's 10-year chances of developing heart disease or stroke, researchers from The Ohio State University found that the average estimated 10-year risk for a cancer survivor was about 8%, compared to 5% for those who didn't have a history of cancer.
The new study appears in the journal PLOS ONE.
"We know that obesity, cancer and cardiovascular disease share some common risk factors, and in addition to those shared risk factors, cancer patients also receive treatments including radiation and chemotherapy that can affect their cardiovascular ...
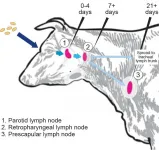
MSU scientists one million 'hops' closer to ending a disease endemic in cattle
2021-03-17
Many people have never heard of Brucellosis, but farmers and ranchers in the United States forced to cull animals that test positive for the disease and people infected by the animal-transmitted Brucella abortus (B. abortus) pathogen that suffer chronic, Malaria-type symptoms, certainly have.
Brucellosis is an agricultural and human health concern on a global scale. It was introduced over 100 years ago to Bison and elk in Yellowstone National Park by cattle and has been circulating among the wild herds ever since, leading to periodic outbreaks and reinfection. There is no vaccine for humans, and experimental studies ...
Study explores how environmental exposures before conception may impact fetal development
2021-03-17
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (March 16, 2021) -- Older age at the time of conception and alcohol consumption during pregnancy have long been known to impact fetal development.
Now, a new report published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences suggests older age and alcohol consumption in the year leading up to conception also may have an impact by epigenetically altering a specific gene during development of human eggs, or oocytes.
Although the study did not determine the ultimate physical effects of this change, it provides important insights into the intricate relationship between environmental exposures, genetic regulation and human development.
"While the outcome of the change isn't clear, our findings give us a valuable look into ...
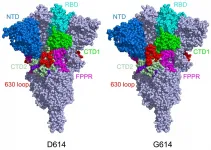
A sturdier spike protein explains the faster spread of coronavirus variants
2021-03-17
BOSTON - March 16, 2021 - The fast-spreading UK, South Africa, and Brazil coronavirus variants are raising both concerns and questions about whether COVID-19 vaccines will protect against them. New work led by Bing Chen, PhD, at Boston Children's Hospital analyzed how the structure of the coronavirus spike proteins changes with the D614G mutation -- carried by all three variants -- and showed why these variants are able to spread more quickly. The team reports its findings in Science (March 16, 2020).
Chen's team imaged the spikes with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), ...
Polystyrene waste is everywhere
2021-03-17
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory and their partners from Clemson University have discovered a green, low-energy process to break down polystyrene, a type of plastic that is widely used in foam packaging materials, disposable food containers, cutlery, and many other applications.
Polystyrene is part of a much larger global plastic waste problem. Hundreds of millions metric tons of polymers are produced each year, a large majority of which is discarded after use. Due to the chemical stability and durability of industrial polymers, plastic waste does not easily degrade in landfills and is often burned, which produces carbon dioxide and other hazardous gases. ...
[1] ... [2520]
[2521]
[2522]
[2523]
[2524]
[2525]
[2526]
[2527]
2528
[2529]
[2530]
[2531]
[2532]
[2533]
[2534]
[2535]
[2536]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.