Inexpensive tin packs a big punch for the future of supercapacitors
2021-03-17
A sustainable, powerful micro-supercapacitor may be on the horizon, thanks to an international collaboration of researchers from Penn State and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. Until now, the high-capacity, fast-charging energy storage devices have been limited by the composition of their electrodes -- the connections responsible for managing the flow of electrons during charging and dispensing energy. Now, researchers have developed a better material to improve connectivity while maintaining recyclability and low cost. ...
A deep dive into cells' RNA reality
2021-03-17
(BOSTON) ¬-- Human cells typically transcribe half of their roughly 20,000 genes into RNA molecules at any given time. Just like with proteins, the function of those RNA species not only relies on their abundance but also their precise localization within the 3D space of each cell. Many RNA molecules convey gene information from the cell's nucleus to the protein-synthesizing machinery distributed throughout the cytoplasm (messenger RNAs or mRNAs), others are components of that machinery itself, while still different ones regulate genes and their expression, or have functions that remain to be discovered. Importantly, many diseases including cancer and neurological diseases have signatures that appear as changes in the abundance and distribution of RNAs.
To enable the analysis ...
The a7 protein is ready for its close-up
2021-03-17
DALLAS - March 17, 2021 - UT Southwestern researchers have identified the structure of a key member of a family of proteins called nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in three different shapes. The work, published online today in Cell, could eventually lead to new pharmaceutical treatments for a large range of diseases or infections including schizophrenia, lung cancer, and even COVID-19.
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are members of a broader super-family of proteins called Cys-loop receptors that function as ion channels on cell surfaces and are found in the membranes of many cell types. When the right molecule settles ...
Three times the gains
2021-03-17
From climate change and carbon emissions to biodiversity and global hunger, humanity faces so many challenges that tackling them quickly is a daunting task. One solution that potentially addresses multiple issues could provide the impetus society needs to make significant progress.
An international team of 26 authors, including six at UC Santa Barbara, has just published a study in the prestigious journal Nature offering a combined solution to several of humanity's most pressing challenges. It is the most comprehensive assessment to date of where strict ocean protection can contribute ...
Suicide risk prediction models could be cost-effective in clinical practice
2021-03-17
BOSTON - There are several effective interventions to reduce the risk of suicide, the tenth-leading cause of death in the United States, but difficulties in identifying people at risk for suicide and concerns about the potentially high costs of suicide-prevention strategies have hampered their wider use.
But as researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) demonstrate, statistical suicide risk prevention models could be implemented cost-effectively in U.S. health care systems and might help save many lives each year.
By evaluating data on the incidence of suicide and suicide attempts, the costs to society and the health care system of suicide, and the cost and effectiveness of suicide risk-reduction interventions, Eric ...
Global warming helps invasive species flourish - study models likely combined effects on ecosystems
2021-03-17
Increased global temperatures help invasive species establish themselves in ecosystems, new research led by a Swansea University bioscientist has shown.
The study, published by the Royal Society, gives an insight into the probable combined effects of species invasions, which are becoming more common, and global warming.
Climate warming and biological invasions result in the loss of species. They also alter the structure of ecosystems and the ways in which species interact.
While there is already extensive research on how climate change and invasions affect ...
Protecting the ocean delivers a comprehensive solution for climate, fishing and biodiversity
2021-03-17
London, UK (17 March 2021)--A new study published in the prestigious peer-reviewed scientific journal Nature today offers a combined solution to several of humanity's most pressing challenges. It is the most comprehensive assessment to date of where strict ocean protection can contribute to a more abundant supply of healthy seafood and provide a cheap, natural solution to address climate change--in addition to protecting embattled species and habitats.
An international team of 26 authors identified specific areas that, if protected, would safeguard over 80% of the habitats for endangered marine species, and increase fishing catches by more than eight million metric tons. The study is also the first to quantify the potential release of carbon dioxide into the ocean ...
New technique reveals genes underlying human evolution
2021-03-17
One of the best ways to study human evolution is by comparing us with nonhuman species that, evolutionarily speaking, are closely related to us. That closeness can help scientists narrow down precisely what makes us human, but that scope is so narrow it can also be extremely hard to define. To address this complication, researchers from Stanford University have developed a new technique for comparing genetic differences.
Through two separate sets of experiments with this technique, the researchers discovered new genetic differences between humans and chimpanzees. They found a significant ...
A remedy for the spread of false news?
2021-03-17
Stopping the spread of political misinformation on social media may seem like an impossible task. But a new study co-authored by MIT scholars finds that most people who share false news stories online do so unintentionally, and that their sharing habits can be modified through reminders about accuracy.
When such reminders are displayed, it can increase the gap between the percentage of true news stories and false news stories that people share online, as shown in online experiments that the researchers developed.
"Getting people to think about accuracy makes them more discerning in their sharing, regardless of ideology," says MIT professor David Rand, co-author of a newly published paper detailing the results. "And it translates ...
Recreational cannabis use among adults in the home is on the rise, but what about the children?
2021-03-17
Among adults with children living in the home, cannabis use was more common in states with legalized cannabis use, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia Irving Medical Center and the City University of New York. Legalization for recreational and medical use were both linked with significantly higher prevalence of past-month and daily cannabis use. Until now, most tobacco control and harm reduction efforts protecting youth from exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke focused on parental cigarette smoking, ensuring smoke-free homes, and not smoking in the presence of children. The findings are published ...
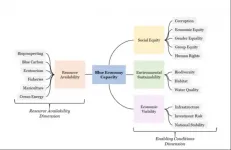
The Blue Economy is more than resources: It has to focus on social equity and governance
2021-03-17
The future of an equitable and sustainable global ocean, or "Blue Economy," depends on more than the resources available for technological advancement and industry expansion. A recent UBC-led study found that socioeconomic and governance conditions such as national stability, corruption and human rights greatly affect the ability to achieve a Blue Economy.
The study, published today in Nature, scored criteria across five global regions: Africa, Americas, Asia, Europe and Oceania, to identify the areas of investment and research necessary to develop ocean resources in a manner that is consistent with a Blue Economy ethos (socially ...
Advanced mouse embryos grown outside the uterus
2021-03-17
To observe how a tiny ball of identical cells on its way to becoming a mammalian embryo first attaches to an awaiting uterine wall and then develops into nervous system, heart, stomach and limbs: This has been a highly-sought grail in the field of embryonic development for nearly 100 years. Prof. Jacob Hanna of the Weizmann Institute of Science and his group have now accomplished this feat. The method they created for growing mouse embryos outside the womb during the initial stages after embryo implantation will give researchers an unprecedented tool for understanding the development program encoded in the genes, and it may provide detailed insight into birth and developmental defects as well as those involved ...
A new view on plate tectonics
2021-03-17
Forces acting inside the Earth have been constantly reshaping the continents and ocean basins over millions of years. What Alfred Wegener published as an idea in 1915 has finally been accepted since the 1960s, providing a unifying view about our planet. The fact that the theory of plate tectonics took so long to gain acceptance had two simple reasons. First, the geological formations that are most important for its understanding lie at the bottom of the oceans. Secondly, forces controlling the processes act below the seafloor and are hence hidden from our view. Many details of plate tectonics are therefore still unclear today.
Today, ...
New study reveals habitat that could increase jaguar numbers
2021-03-17
Tucson, Ariz. (March 16, 2021) - This week, a new, peer-reviewed scientific study finds that there is far more potential jaguar habitat in the U.S. than was previously thought. Scientists identified an area of more than 20 million acres that could support jaguars in the U.S., 27 times the size of designated critical habitat.
The results, published in the journal Oryx, are based on a review of 12 habitat models for jaguars within Arizona and New Mexico, conclusively identifying areas suitable for the recovery of these wild cats. Based on the expanded habitat area, the authors conclude that findings uncover new opportunities for jaguar conservation in North America that ...
Missing baryons found in far-out reaches of galactic halos
2021-03-17
Researchers have channeled the universe's earliest light - a relic of the universe's formation known as the cosmic microwave background (CMB) - to solve a missing-matter mystery and learn new things about galaxy formation. Their work could also help us to better understand dark energy and test Einstein's theory of general relativity by providing new details about the rate at which galaxies are moving toward us or away from us.
Invisible dark matter and dark energy account for about 95% of the universe's total mass and energy, and the majority of the 5% that is considered ordinary matter is also largely unseen, such as the gases at the outskirts of galaxies that comprise their so-called halos.
Most ...
Arctic was once lush and green, could be again, new research shows
2021-03-17
Imagine not a white, but a green Arctic, with woody shrubs as far north as the Canadian coast of the Arctic Ocean. This is what the northernmost region of North America looked like about 125,000 years ago, during the last interglacial period, finds new research from the University of Colorado Boulder.
Researchers analyzed plant DNA more than 100,000 years old retrieved from lake sediment in the Arctic (the oldest DNA in lake sediment analyzed in a publication to date) and found evidence of a shrub native to northern Canadian ecosystems 250 miles (400 km) farther north than its current range.
As the Arctic warms much ...
Text me about cervical cancer
2021-03-17
An estimated 14,480 new cases of invasive cervical cancer will be diagnosed in the United States this year, according to the American Cancer Society. Cases that could be prevented or cured with better education from screening to treatment based on improved provider-patient communication, says a Michigan State University researcher.
The issue is particularly acute for Black women, said Sabrina Ford, an associate professor in the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Biology within MSU's College of Human Medicine. Ford's research was published ...
Mitigating impact of artificial light at night in tropical forests
2021-03-17
Artificial light at night (ALAN) is a major factor in global insect decline. In a paper published today in Insect Conservation and Diversity, Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute (SCBI) scientists and partners found that using amber-colored filters to remove the blue spectra of light from "warm white" LED (light-emitting diode) lamps drastically reduces insect attraction to nocturnal lighting in a tropical forest. This is the first study to validate quantitative predictions of how lamp color affects insect attraction and provide clear recommendations to mitigate the negative impacts of ALAN on wildlife in rainforest ecosystems.
"While ...
Modelling speed-ups in nutrient-seeking bacteria
2021-03-17
Many bacteria swim towards nutrients by rotating the helix-shaped flagella attached to their bodies. As they move, the cells can either 'run' in a straight line, or 'tumble' by varying the rotational directions of their flagella, causing their paths to randomly change course. Through a process named 'chemotaxis,' bacteria can decrease their rate of tumbling at higher concentrations of nutrients, while maintaining their swimming speeds. In more hospitable environments like the gut, this helps them to seek out nutrients more easily. However, in more nutrient-sparse ...
'Time lost is brain lost'
2021-03-17
A new study involving UCLA researchers finds that mobile stroke units (MSUs) - state-of-the-art ambulances built to provide stroke patients with emergency neurological diagnosis and treatment prior to hospital arrival -- improve patient outcomes and lessen the chance for disability by delivering care faster than standard stroke care.
The UCLA Mobile Stroke Unit serves as a shared regional resource of LA County EMS Provider Agencies, taking patients to 15 different stroke center hospitals within 3 regions in Los Angeles County. The MSU carries a CT scanner that can directly image the brain and blood vessels in the field. UCLA was one of seven national mobile stroke unit programs to participate in the clinical trial, which was presented March 17 at the ...
Losing rivers
2021-03-17
Water is an ephemeral thing. It can emerge from an isolated spring, as if by magic, to birth a babbling brook. It can also course through a mighty river, seeping into the soil until all that remains downstream is a shady arroyo, the nearby trees offering the only hint of where the water has gone.
The interplay between surface water and groundwater is often overlooked by those who use this vital resource due to the difficulty of studying it. Assistant professors Scott Jasechko and Debra Perrone, of UC Santa Barbara, and their colleagues leveraged their enormous ...
Aspirin use may decrease ventilation, ICU admission and death in COVID-19 patients
2021-03-17
George Washington University researchers found low dose aspirin may reduce the need for mechanical ventilation, ICU admission and in-hospital mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Final results indicating the lung protective effects of aspirin were published today in Anesthesia & Analgesia.
"As we learned about the connection between blood clots and COVID-19, we knew that aspirin - used to prevent stroke and heart attack - could be important for COVID-19 patients," Jonathan Chow, MD, assistant professor of anesthesiology and critical care medicine and director of the Critical Care Anesthesiology ...
Study finds plants would grow well in solar cell greenhouses
2021-03-17
A recent study shows that lettuce can be grown in greenhouses that filter out wavelengths of light used to generate solar power, demonstrating the feasibility of using see-through solar panels in greenhouses to generate electricity.
"We were a little surprised - there was no real reduction in plant growth or health," says Heike Sederoff, co-corresponding author of the study and a professor of plant biology at North Carolina State University. "It means the idea of integrating transparent solar cells into greenhouses can be done."
Because plants do not use all of the wavelengths of light for photosynthesis, researchers have explored the idea of creating semi-transparent organic solar ...
Scientists create model of an early human embryo from skin cells
2021-03-17
AUSTRALIAN - LED INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH TEAM GENERATES THE FIRST MODEL OF EARLY HUMAN EMBRYOS FROM SKIN CELLS
In a discovery that will revolutionize research into the causes of early miscarriage, infertility and the study of early human development - an international team of scientists led by Monash University in Melbourne, Australia has generated a model of a human embryo from skin cells.
The team, led by Professor Jose Polo, has successfully reprogrammed these fibroblasts or skin cells into a 3-dimensional cellular structure that is morphologically and molecularly similar to human blastocysts. Called iBlastoids, these can be used to model the biology of ...
Racial/ethnic disparities in very preterm, preterm birth before, during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-03-17
What The Study Did: Racial and ethnic disparities in very preterm birth and preterm birth among 8,026 women were similar during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in New York City compared with the same period the year prior in this observational study.
Authors: Teresa Janevic, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1816)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article ...
[1] ... [2521]
[2522]
[2523]
[2524]
[2525]
[2526]
[2527]
[2528]
2529
[2530]
[2531]
[2532]
[2533]
[2534]
[2535]
[2536]
[2537]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.