Is it worth investing in solar PV with batteries at home?
2021-03-19
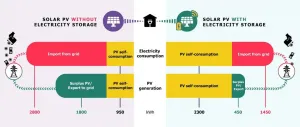
Solar energy is a clean, renewable source of electricity that could potentially play a significant part in fulfilling the world's energy requirements, but there are still some challenges to fully capitalizing on this potential. Researchers looked into some of the issues that hamper the uptake of solar energy and proposed different policies to encourage the use of this technology.
Installing solar panels to offset energy costs and reduce the environmental impact of their homes has been gaining popularity with homeowners in recent years. On a global scale, an increasing number of countries are similarly encouraging the installation of solar photovoltaics ...
Study: Black bears are eating pumas' lunch
2021-03-19
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- A camera-trap study in the Mendocino National Forest in Northern California reveals that black bears are adept at finding and stealing the remains of adult deer killed by pumas. This "kleptoparasitism" by bears, as scientists call it, reduces the calories pumas consume in seasons when the bears are most active. Perhaps in response to this shortage, the pumas hunt more often and eat more small game when the bears are not in hibernation.
The findings are published in the journal Basic and Applied Ecology.
Pumas, also known as mountain lions or cougars, are apex ...
Like an artificial nervous system
2021-03-19
Due to their tissue-like mechanical properties, hydrogels are being increasingly used for biomedical applications; a well-known example are soft contact lenses. These gel-like polymers consist of 90 percent water, are elastic and particularly biocompatible. Hydrogels that are also electrically conductive allow additional fields of application, for example in the transmission of electrical signals in the body or as sensors. An interdisciplinary research team of the Research Training Group (RTG) 2154 "Materials for Brain" at Kiel University (CAU) has now developed a method to produce hydrogels with an excellent level of electrical conductivity. What makes this method special is that the mechanical properties of ...
COVID-19 lockdowns and demographically-relevant Google Trends
2021-03-19
Google Trends reveal how searches related to family and relationship behaviors, such as weddings, contraception, and abortions, changed during lockdowns in the US and Europe.
INFORMATION:
Link to publicly available article: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0248072
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0248072
...
SFU lab one step closer to understanding how life started on Earth
2021-03-19
How did life begin on Earth and could it exist elsewhere? Researchers at Simon Fraser University have isolated a genetic clue--an enzyme known as an RNA polymerase--that provides new insights about the origins of life. The research is published today in the journal Science.
Researchers in SFU molecular biology and biochemistry professor Peter Unrau's laboratory are working to advance the RNA World Hypothesis in answer to fundamental questions on life's beginnings.
The hypothesis suggests that life on our planet began with self-replicating ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules, capable of not only carrying genetic information but also driving chemical reactions essential for life, prior to the evolution ...
Taking a look at the last millennium shows: Droughts in Germany could become more extreme
2021-03-19
In the future, droughts could be even more severe than those that struck parts of Germany in 2018. An analysis of climate data from the last millennium shows that several factors have to coincide to produce a megadrought: not only rising temperatures, but also the amount of solar radiation, as well as certain meteorological and ocean-circulation conditions in the North Atlantic, like those expected to arise in the future. A group of researchers led by the Alfred Wegener Institute have just released their findings in the journal Communications Earth & Environment.
Despite the precipitation this winter, which in ...
Carbon uptake in regrowing Amazon forest threatened by climate and human disturbance
2021-03-19
Large areas of forests regrowing in the Amazon to help reduce carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, are being limited by climate and human activity.
The forests, which naturally regrow on land previously deforested for agriculture and now abandoned, are developing at different speeds. Researchers at the University of Bristol have found a link between slower tree-growth and land previously scorched by fire.
The findings were published today [date] in Nature Communications, and suggest a need for a better protection of these forests if they are to help mitigate the effects of climate change.
Global forests are expected to contribute a quarter of pledged mitigation under the ...
Turns out altruism is for the fish
2021-03-19
OSAKA, Japan. If you were given the option to eat a delicious meal by yourself, or share that meal with your loved ones, you would need as very good excuse ready if you chose the former. Turns out, fish share a similar inclination to look after each other.
For the first time ever, a research group led by researcher Shun Satoh and Masanori Kohda, professor of the Graduate School of Science, Osaka City University, have shown these altruistic tendencies in fish through a series of prosocial choice tasks (PCT) where they gave male convict cichlid fish two choices: the antisocial option of receiving food for themselves alone and the prosocial option of receiving food for themselves and their partner.
"As a result, it can be said that the convict cichlid ...
Bioengineers learn the secrets to precisely turning on and off genes
2021-03-19
In a recent study led by the University of Bristol, scientists have shown how to simultaneously harness multiple forms of regulation in living cells to strictly control gene expression and open new avenues for improved biotechnologies.
Engineered microbes are increasingly being used to enable the sustainable and clean production of chemicals, medicines and much more. To make this possible, bioengineers must control when specific sets of genes are turned on and off to allow for careful regulation of the biochemical processes involved.
Their findings are reported today in the journal Nature Communications.
Veronica Greco, lead author ...
New findings about immune system reaction to malaria and sickle cell disease
2021-03-19
Scientists have discovered in more detail than ever before how the human body's immune system reacts to malaria and sickle cell disease.
The researchers from the universities of Aberdeen, Edinburgh, Exeter and Imperial College, London have published their findings in Nature Communications.
Every year there are ~200 million cases of malaria, which causes ~400,000 deaths.
As it causes resistance against malaria, the sickle cell disease mutation has spread widely, especially in people from Africa.
But if a child inherits a double dose of the gene - from both mother and father - they will develop ...
Particulates are more dangerous than previously thought
2021-03-19
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have for the first time observed photochemical processes inside the smallest particles in the air. In doing so, they discovered that additional oxygen radicals that can be harmful to human health are formed in these aerosols under everyday conditions. They report on their results today in the journal Nature Communications.
It is well known that airborne particulate matter can pose a danger to human health. The particles, with a maximum diameter of ten micrometres, can penetrate deep into lung tissue and settle ...
CU cancer researcher wins two awards to study drug-resistant cancer cells
2021-03-19
Sabrina L. Spencer, PhD, is a CU Boulder researcher and a CU Cancer Center member. Spencer recently won two awards: the Damon Runyon-Rachleff Innovation Award (from the Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation) and the Emerging Leader Award (from The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research). The preliminary research she used to apply for the grants, "Melanoma subpopulations that rapidly escape MAPK pathway inhibition incur DNA damage and rely on stress signalling," was published in Nature Communications on March 19, 2021. We spoke to Spencer about the awards and how she plans to use them to ...
New plutonium research helps distinguish nuclear power pollution from global fall out
2021-03-19
Researchers looking at miniscule levels of plutonium pollution in our soils have made a breakthrough which could help inform future 'clean up' operations on land around nuclear power plants, saving time and money.
Publishing in the journal Nature Communications, researchers show how they have measured the previously 'unmeasurable' and taken a step forward in differentiating between local and global sources of plutonium pollution in the soil.
By identifying the isotopic 'fingerprint' of trace-level quantities of plutonium in the soil which matched the ...
Study shows stronger brain activity after writing on paper than on tablet or smartphone
2021-03-19
A study of Japanese university students and recent graduates has revealed that writing on physical paper can lead to more brain activity when remembering the information an hour later. Researchers say that the unique, complex, spatial and tactile information associated with writing by hand on physical paper is likely what leads to improved memory.
"Actually, paper is more advanced and useful compared to electronic documents because paper contains more one-of-a-kind information for stronger memory recall," said Professor Kuniyoshi L. Sakai, a neuroscientist at the University of Tokyo and corresponding author of the research recently published in Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. The research was completed with collaborators from the NTT Data Institute of Management Consulting.
Contrary ...
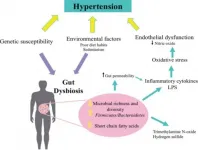
Study examines fermented milks' potential benefits for decreasing high blood pressure through modulation of gut microbiota
2021-03-19
Philadelphia, March 19, 2021 - In recent years, fermented dairy foods have been gaining attention for their health benefits, and a new review published in the Journal of Dairy Science indicates these foods could help reduce conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure). A team of investigators from the Center for Food Research and Development in Sonora, Mexico, and the National Technological Institute of Mexico in Veracruz reports on numerous studies of fermented milks as antihypertensive treatments and in relation to gut microbiota modulation. They also examine the potential mechanistic pathways of gut modulation through antihypertensive fermented milks.
In addition to the impact of genetics and the environment, there is growing ...
In pandemic, potentially avoidable hospitalizations for non-COVID conditions fell more among whites
2021-03-19
During the first six months of the pandemic, as people attempted to stay away from hospitals caring for those sick with COVID-19, potentially avoidable hospitalizations for non-COVID-19-related conditions fell far more among white patients than Black patients, according to a new study that looked at admissions to UCLA Health hospitals.
The findings indicate that the COVID-19 crisis has exacerbated existing racial health care disparities and suggest that during the pandemic, African Americans may have had worse access than whites to outpatient care that could have helped prevent deterioration of their non-COVID-19 health conditions, said Dr. ...
Starving tumors by blocking glutamine uptake
2021-03-19
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - March 19, 2021 - Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute have identified a drug candidate that blocks the uptake of glutamine, a key food source for many tumors, and slows the growth of melanoma. The drug is a small molecule that targets a glutamine transporter, SLC1A5, which pumps the nutrient into cancer cells--offering a promising new approach for treating melanoma and other cancers. The study was published in the journal Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.
"While great strides have been made recently in the treatment of melanoma, many patients' tumors become resistant to therapy, and this has become a major obstacle in the successful treatment of the disease," says Ze'ev ...
'Opposite action' could improve industrial gas separation
2021-03-19
A more energy-efficient method improves how an industrial gas is purified by reversing the traditional process. The concept was developed and successfully tested by scientists at Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) in Japan and colleagues. The findings were reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Acetylene is a gas used in many industries, including as a fuel in welding and a chemical building block for materials like plastics, paints, glass and resins. To produce acetylene, it first needs to be purified from carbon dioxide. Traditionally, this is done by passing the acetylene/carbon ...
Maintaining body weight won't save colorectal cancer survivors
2021-03-19
Colorectal cancer survivors who maintained a stable body weight but lost muscle and developed fatty deposits in their muscles faced a 40 percent higher risk of premature death than patients who avoided both health issues.
"The conventional wisdom has been that colorectal cancer patients should avoid losing or gaining weight during treatment," said Dr. Justin C. Brown, Assistant Professor and Director of the Cancer Metabolism Program at Pennington Biomedical Research Center. "But maintaining your weight does not mean your body composition remains the same. Muscle can ...
The Lancet Inf. Dis.: Vaccination alone is unlikely to contain COVID-19 infections in UK
2021-03-19
COVID-19 vaccines being rolled out in the UK are effective in preventing severe disease, but the extent to which they prevent against infection is still unclear.
First modelling study looking at relaxing control measures (eg, mask wearing, physical distancing, and lockdown measures) and planned vaccination rollout in the UK suggests that vaccination alone may not be enough to prevent the spread of infection - with the R number estimated to be 1.58 even if the vaccine prevents 85% of new infections occurring, after vaccine rollout is complete and all other control measures are removed.
Relaxing control measures is highly likely to lead to another wave of infection, ...
Psychologists report an error in the NICE guidelines for autism
2021-03-19
Reporting in the Lancet Psychiatry today, psychologists at the University of Bath highlight that a widely used technique for autism screening is being misused, which may have prevented many people from receiving an autism diagnosis over the past decade.
When individuals with suspected autism are assessed by a GP, a decision to refer them to a specialist for diagnosis is informed by using the Autism Spectrum Quotient. This ten-point scale, known as the 'AQ-10', is an internationally used technique, whereby individuals agree or disagree with statements such as 'I find it difficult to work out people's intentions'. ...
Illinois youth opioid use linked with other substance misuse, mental health issues
2021-03-18
URBANA, Ill. - Opioid use has dramatically increased in the 21st century, especially among young adults. A new study from the University of Illinois provides insights on usage patterns among Illinois high school students to help inform prevention and treatment strategies.
"The societal and personal costs of opioid misuse are massive. There's been a lot of focus on trying to understand how to combat the current epidemic. But we also need to make sure we have good data in order to know how we should apply our efforts," says Allen Barton, assistant professor in the Department of Human Development and Family Studies at U of I and lead author on the study.
The researchers based their study ...
Novel coronavirus circulated undetected months before first COVID-19 cases in Wuhan, China
2021-03-18
Using molecular dating tools and epidemiological simulations, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues at the University of Arizona and Illumina, Inc., estimate that the SARS-CoV-2 virus was likely circulating undetected for at most two months before the first human cases of COVID-19 were described in Wuhan, China in late-December 2019.
Writing in the March 18, 2021 online issue of Science, they also note that their simulations suggest that the mutating virus dies out naturally more than three-quarters of the time without causing an epidemic.
"Our study was designed to answer the question of how long could SARS-CoV-2 have circulated in China before it was discovered," said senior author Joel O. Wertheim, PhD, associate professor in the ...
Research finds surprising electron interaction in 'magic-angle' graphene
2021-03-18
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- In 2018, physicists showed that something interesting happens when two sheets of the nanomaterial graphene are placed on top of each other. When one layer is rotated to a "magic angle" of around 1.1 degrees with respect to the other, the system becomes a superconductor -- meaning it conducts electricity with zero resistance. Even more exciting, there was evidence that it was an unconventional form of superconductivity -- a type that can happen at temperatures well above absolute zero, where most superconducting materials function.
Since the initial discovery, researchers have been working to understand this exotic state of matter. Now, a research ...
Researchers identify DNA elements that affect MECP2 expression
2021-03-18
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital (NRI) have identified and characterized two regions of DNA required for the proper expression of Mecp2/MECP2 in mice and humans.
These findings, published in Genes & Development, are helping to shed light on the function of these DNA regions and how they could be potential targets for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions for intellectual disabilities such as Rett Syndrome and MECP2 Duplication Syndrome.
Both of these intellectual disabilities are examples of the importance of precise MeCP2 protein levels for proper brain function. A decrease in this protein leads to Rett Syndrome, while an increase in this protein ...
[1] ... [2514]
[2515]
[2516]
[2517]
[2518]
[2519]
[2520]
[2521]
2522
[2523]
[2524]
[2525]
[2526]
[2527]
[2528]
[2529]
[2530]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.